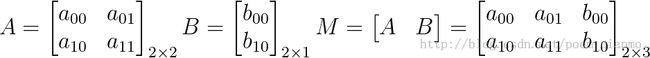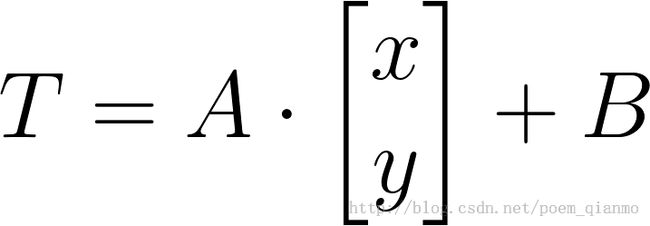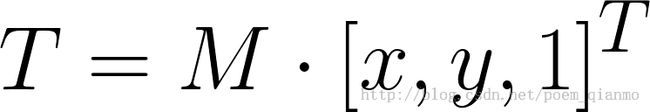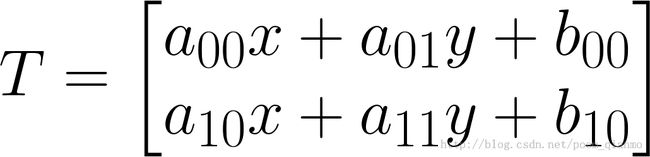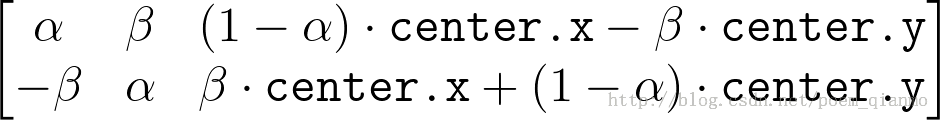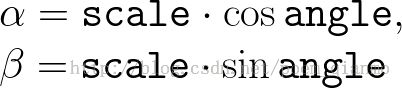【OpenCV入门教程之十八】OpenCV仿射变换 & SURF特征点描述合辑
本系列文章由@浅墨_毛星云 出品,转载请注明出处。
文章链接: http://blog.csdn.net/poem_qianmo/article/details/33320997
作者:毛星云(浅墨) 微博:http://weibo.com/u/1723155442
知乎:http://www.zhihu.com/people/mao-xing-yun
写作当前博文时配套使用的OpenCV版本: 2.4.9
本篇文章中,我们一起探讨了OpenCV中仿射变换和SURF特征点描述相关的知识点,主要一起了解OpenCV中仿射变换相关的函数warpAffine和getRotationMatrix2D,SURF算法在OpenCV中进一步的体现与应用。此博文一共有两个配套的麻雀虽小但五脏俱全的示例程序,其经过浅墨详细注释过的代码都在文中贴出,且文章最后提供了综合示例程序的下载。
依然是先看看示例程序截图:
一、仿射变换
1.1 初识仿射变换
仿射变换(Affine Transformation或 Affine Map),又称仿射映射,是指在几何中,一个向量空间进行一次线性变换并接上一个平移,变换为另一个向量空间的过程。它保持了二维图形的“平直性”(即:直线经过变换之后依然是直线)和“平行性”(即:二维图形之间的相对位置关系保持不变,平行线依然是平行线,且直线上点的位置顺序不变)。
一个任意的仿射变换都能表示为乘以一个矩阵(线性变换)接着再加上一个向量(平移)的形式。
那么, 我们能够用仿射变换来表示如下三种常见的变换形式:
- 旋转,rotation (线性变换)
- 平移,translation(向量加)
- 缩放,scale(线性变换)
如果进行更深层次的理解,仿射变换代表的是两幅图之间的一种映射关系。
而我们通常使用2 x 3的矩阵来表示仿射变换。
考虑到我们要使用矩阵 A 和 B 对二维向量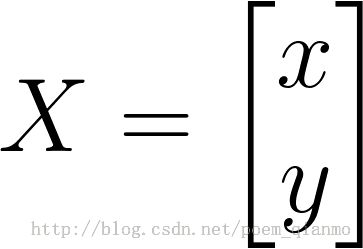 做变换, 所以也能表示为下列形式:
做变换, 所以也能表示为下列形式:
1. 2 仿射变换的求法
我们知道,仿射变换表示的就是两幅图片之间的一种联系 . 关于这种联系的信息大致可从以下两种场景获得:
本系列文章由@浅墨_毛星云 出品,转载请注明出处。
文章链接: http://blog.csdn.net/poem_qianmo/article/details/33320997
作者:毛星云(浅墨) 微博:http://weibo.com/u/1723155442
知乎:http://www.zhihu.com/people/mao-xing-yun
写作当前博文时配套使用的OpenCV版本: 2.4.9一、仿射变换
1.1 初识仿射变换
仿射变换(Affine Transformation或 Affine Map),又称仿射映射,是指在几何中,一个向量空间进行一次线性变换并接上一个平移,变换为另一个向量空间的过程。它保持了二维图形的“平直性”(即:直线经过变换之后依然是直线)和“平行性”(即:二维图形之间的相对位置关系保持不变,平行线依然是平行线,且直线上点的位置顺序不变)。
一个任意的仿射变换都能表示为乘以一个矩阵(线性变换)接着再加上一个向量(平移)的形式。
那么, 我们能够用仿射变换来表示如下三种常见的变换形式:
- 旋转,rotation (线性变换)
- 平移,translation(向量加)
- 缩放,scale(线性变换)
如果进行更深层次的理解,仿射变换代表的是两幅图之间的一种映射关系。
而我们通常使用2 x 3的矩阵来表示仿射变换。
考虑到我们要使用矩阵 A 和 B 对二维向量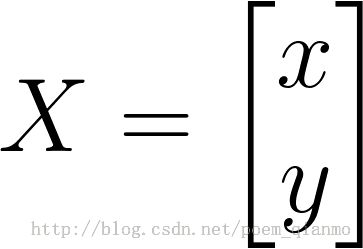 做变换, 所以也能表示为下列形式:
做变换, 所以也能表示为下列形式:
1. 2 仿射变换的求法
我们知道,仿射变换表示的就是两幅图片之间的一种联系 . 关于这种联系的信息大致可从以下两种场景获得:
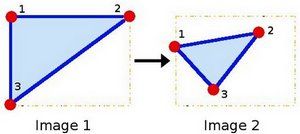
见下图:
其中,点1, 2 和 3 (在图一中形成一个三角形) 与图二中三个点是一一映射的关系, 且他们仍然形成三角形, 但形状已经和之前不一样了。我们能通过这样两组三点求出仿射变换 (可以选择自己喜欢的点), 接着就可以把仿射变换应用到图像中去。
1.3 仿射变换相关的函数使用
OpenCV仿射变换相关的函数一般涉及到warpAffine和getRotationMatrix2D这两个:
- 使用OpenCV函数warpAffine 来实现一些简单的重映射.
- 使用OpenCV函数getRotationMatrix2D 来获得旋转矩阵。
下面分别对其进行讲解。
1.3.1 warpAffine函数详解
warpAffine函数的作用是依据如下式子,对图像做仿射变换。
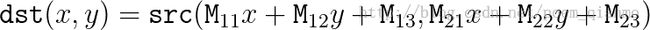
函数原型如下:
C++: void warpAffine(InputArray src,OutputArray dst, InputArray M, Size dsize, int flags=INTER_LINEAR, intborderMode=BORDER_CONSTANT, const Scalar& borderValue=Scalar())
- 第一个参数,InputArray类型的src,输入图像,即源图像,填Mat类的对象即可。
- 第二个参数,OutputArray类型的dst,函数调用后的运算结果存在这里,需和源图片有一样的尺寸和类型。
- 第三个参数,InputArray类型的M,2×3的变换矩阵。
- 第四个参数,Size类型的dsize,表示输出图像的尺寸。
- 第五个参数,int类型的flags,插值方法的标识符。此参数有默认值INTER_LINEAR(线性插值),可选的插值方式如下:
- INTER_NEAREST - 最近邻插值
- INTER_LINEAR - 线性插值(默认值)
- INTER_AREA - 区域插值
- INTER_CUBIC –三次样条插值
- INTER_LANCZOS4 -Lanczos插值
- CV_WARP_FILL_OUTLIERS - 填充所有输出图像的象素。如果部分象素落在输入图像的边界外,那么它们的值设定为 fillval.
- CV_WARP_INVERSE_MAP –表示M为输出图像到输入图像的反变换,即 。因此可以直接用来做象素插值。否则, warpAffine函数从M矩阵得到反变换。
- 第六个参数,int类型的borderMode,边界像素模式,默认值为BORDER_CONSTANT。
- 第七个参数,const Scalar&类型的borderValue,在恒定的边界情况下取的值,默认值为Scalar(),即0。
见下图:
其中,点1, 2 和 3 (在图一中形成一个三角形) 与图二中三个点是一一映射的关系, 且他们仍然形成三角形, 但形状已经和之前不一样了。我们能通过这样两组三点求出仿射变换 (可以选择自己喜欢的点), 接着就可以把仿射变换应用到图像中去。
1.3 仿射变换相关的函数使用
OpenCV仿射变换相关的函数一般涉及到warpAffine和getRotationMatrix2D这两个:
- 使用OpenCV函数warpAffine 来实现一些简单的重映射.
- 使用OpenCV函数getRotationMatrix2D 来获得旋转矩阵。
1.3.1 warpAffine函数详解
warpAffine函数的作用是依据如下式子,对图像做仿射变换。
![]()
函数原型如下:
C++: void warpAffine(InputArray src,OutputArray dst, InputArray M, Size dsize, int flags=INTER_LINEAR, intborderMode=BORDER_CONSTANT, const Scalar& borderValue=Scalar())
- 第一个参数,InputArray类型的src,输入图像,即源图像,填Mat类的对象即可。
- 第二个参数,OutputArray类型的dst,函数调用后的运算结果存在这里,需和源图片有一样的尺寸和类型。
- 第三个参数,InputArray类型的M,2×3的变换矩阵。
- 第四个参数,Size类型的dsize,表示输出图像的尺寸。
- 第五个参数,int类型的flags,插值方法的标识符。此参数有默认值INTER_LINEAR(线性插值),可选的插值方式如下:
- INTER_NEAREST - 最近邻插值
- INTER_LINEAR - 线性插值(默认值)
- INTER_AREA - 区域插值
- INTER_CUBIC –三次样条插值
- INTER_LANCZOS4 -Lanczos插值
- CV_WARP_FILL_OUTLIERS - 填充所有输出图像的象素。如果部分象素落在输入图像的边界外,那么它们的值设定为 fillval.
- CV_WARP_INVERSE_MAP –表示M为输出图像到输入图像的反变换,即 。因此可以直接用来做象素插值。否则, warpAffine函数从M矩阵得到反变换。
- 第六个参数,int类型的borderMode,边界像素模式,默认值为BORDER_CONSTANT。
- 第七个参数,const Scalar&类型的borderValue,在恒定的边界情况下取的值,默认值为Scalar(),即0。
另外提一点,我们的WarpAffine函数与一个叫做cvGetQuadrangleSubPix( )的函数类似,但是不完全相同。 WarpAffine要求输入和输出图像具有同样的数据类型,有更大的资源开销(因此对小图像不太合适)而且输出图像的部分可以保留不变。而 cvGetQuadrangleSubPix 可以精确地从8位图像中提取四边形到浮点数缓存区中,具有比较小的系统开销,而且总是全部改变输出图像的内容。
1.3.2 getRotationMatrix2D
计算二维旋转变换矩阵。变换会将旋转中心映射到它自身。
C++: Mat getRotationMatrix2D(Point2fcenter, double angle, double scale)
- 第一个参数,Point2f类型的center,表示源图像的旋转中心。
- 第二个参数,double类型的angle,旋转角度。角度为正值表示向逆时针旋转(坐标原点是左上角)。
- 第三个参数,double类型的scale,缩放系数。
此函数计算以下矩阵:
其中:
1.4 仿射变换相关核心函数在OpenCV中的实现源代码
这个部分贴出OpenCV中本节相关函数的源码实现细节,来给想了解实现细节的小伙伴们参考。浅墨暂时不在源码的细节上挖深作详细注释。
1.4.1 OpenCV2.X中warpAffine函数源代码
首先,是warpAffine函数的实现源码。
void cv::warpAffine( InputArray _src,OutputArray _dst,
InputArray _M0, Sizedsize,
int flags, int borderType,const Scalar& borderValue )
{
Mat src = _src.getMat(), M0 = _M0.getMat();
_dst.create( dsize.area() == 0 ? src.size() : dsize, src.type() );
Mat dst = _dst.getMat();
CV_Assert( src.cols > 0 && src.rows > 0 );
if( dst.data == src.data )
src = src.clone();
double M[6];
Mat matM(2, 3, CV_64F, M);
int interpolation = flags & INTER_MAX;
if( interpolation == INTER_AREA )
interpolation = INTER_LINEAR;
CV_Assert( (M0.type() == CV_32F || M0.type() == CV_64F) &&M0.rows == 2 && M0.cols == 3 );
M0.convertTo(matM, matM.type());
#ifdef HAVE_TEGRA_OPTIMIZATION
if( tegra::warpAffine(src, dst, M, flags, borderType, borderValue) )
return;
#endif
if( !(flags & WARP_INVERSE_MAP) )
{
double D = M[0]*M[4] - M[1]*M[3];
D = D != 0 ? 1./D : 0;
double A11 = M[4]*D, A22=M[0]*D;
M[0] = A11; M[1] *= -D;
M[3] *= -D; M[4] = A22;
double b1 = -M[0]*M[2] - M[1]*M[5];
double b2 = -M[3]*M[2] - M[4]*M[5];
M[2] = b1; M[5] = b2;
}
int x;
AutoBuffer<int> _abdelta(dst.cols*2);
int* adelta = &_abdelta[0], *bdelta = adelta + dst.cols;
const int AB_BITS = MAX(10, (int)INTER_BITS);
const int AB_SCALE = 1 << AB_BITS;
/*
#if defined (HAVE_IPP) &&(IPP_VERSION_MAJOR >= 7)
int depth = src.depth();
int channels = src.channels();
if( ( depth == CV_8U || depth == CV_16U ||depth == CV_32F ) &&
( channels == 1 || channels == 3 || channels == 4 ) &&
( borderType == cv::BORDER_TRANSPARENT || ( borderType ==cv::BORDER_CONSTANT ) ) )
{
int type = src.type();
ippiWarpAffineBackFunc ippFunc =
type == CV_8UC1 ? (ippiWarpAffineBackFunc)ippiWarpAffineBack_8u_C1R :
type == CV_8UC3 ? (ippiWarpAffineBackFunc)ippiWarpAffineBack_8u_C3R :
type == CV_8UC4 ? (ippiWarpAffineBackFunc)ippiWarpAffineBack_8u_C4R :
type == CV_16UC1 ? (ippiWarpAffineBackFunc)ippiWarpAffineBack_16u_C1R :
type == CV_16UC3 ? (ippiWarpAffineBackFunc)ippiWarpAffineBack_16u_C3R :
type == CV_16UC4 ? (ippiWarpAffineBackFunc)ippiWarpAffineBack_16u_C4R :
type == CV_32FC1 ? (ippiWarpAffineBackFunc)ippiWarpAffineBack_32f_C1R :
type == CV_32FC3 ? (ippiWarpAffineBackFunc)ippiWarpAffineBack_32f_C3R :
type == CV_32FC4 ? (ippiWarpAffineBackFunc)ippiWarpAffineBack_32f_C4R :
0;
int mode =
flags == INTER_LINEAR ? IPPI_INTER_LINEAR :
flags == INTER_NEAREST ? IPPI_INTER_NN :
flags == INTER_CUBIC ? IPPI_INTER_CUBIC :
0;
if( mode && ippFunc )
{
double coeffs[2][3];
for( int i = 0; i < 2; i++ )
{
for( int j = 0; j < 3; j++ )
{
coeffs[i][j] =matM.at<double>(i, j);
}
}
bool ok;
Range range(0, dst.rows);
IPPwarpAffineInvoker invoker(src, dst, coeffs, mode, borderType,borderValue, ippFunc, &ok);
parallel_for_(range, invoker, dst.total()/(double)(1<<16));
if( ok )
return;
}
}
#endif
*/
for( x = 0; x < dst.cols; x++ )
{
adelta[x] = saturate_cast<int>(M[0]*x*AB_SCALE);
bdelta[x] = saturate_cast<int>(M[3]*x*AB_SCALE);
}
Range range(0, dst.rows);
warpAffineInvokerinvoker(src, dst, interpolation, borderType,
borderValue,adelta, bdelta, M);
parallel_for_(range, invoker, dst.total()/(double)(1<<16));
}
1.4.2 OpenCV2.X中getRotationMatrix2D函数源代码
cv::Mat cv::getRotationMatrix2D( Point2f center,double angle, double scale )
{
angle *= CV_PI/180;
double alpha = cos(angle)*scale;
double beta = sin(angle)*scale;
Mat M(2, 3, CV_64F);
double* m = (double*)M.data;
m[0] = alpha;
m[1] = beta;
m[2] = (1-alpha)*center.x - beta*center.y;
m[3] = -beta;
m[4] = alpha;
m[5] = beta*center.x + (1-alpha)*center.y;
return M;
}
1.5 OpenCV仿射变换示例程序
看完上面的讲解和函数线吗实现,下面是一个以warpAffine和getRotationMatrix2D函数为核心的对图像进行仿射变换的示例程序。
//-----------------------------------【程序说明】----------------------------------------------
// 程序名称::《【OpenCV入门教程之十八】OpenCV仿射变换 & SURF特征点描述合辑》 博文配套源码 之 仿射变换
// 开发所用IDE版本:Visual Studio 2010
// 开发所用OpenCV版本: 2.4.9
// 2014年6月 Created by 浅墨
// 浅墨的微博:@浅墨_毛星云 http://weibo.com/1723155442
// 浅墨的知乎:http://www.zhihu.com/people/mao-xing-yun
// 浅墨的豆瓣:http://www.douban.com/people/53426472/
//----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
//-----------------------------------【头文件包含部分】---------------------------------------
// 描述:包含程序所依赖的头文件
//----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
#include "opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp"
#include "opencv2/imgproc/imgproc.hpp"
#include <iostream>
//-----------------------------------【命名空间声明部分】--------------------------------------
// 描述:包含程序所使用的命名空间
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
using namespace cv;
using namespace std;
//-----------------------------------【宏定义部分】--------------------------------------------
// 描述:定义一些辅助宏
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
#define WINDOW_NAME1 "【原始图窗口】" //为窗口标题定义的宏
#define WINDOW_NAME2 "【经过Warp后的图像】" //为窗口标题定义的宏
#define WINDOW_NAME3 "【经过Warp和Rotate后的图像】" //为窗口标题定义的宏
//-----------------------------------【全局函数声明部分】--------------------------------------
// 描述:全局函数的声明
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
static void ShowHelpText( );
//-----------------------------------【main( )函数】--------------------------------------------
// 描述:控制台应用程序的入口函数,我们的程序从这里开始执行
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
int main( )
{
//【0】改变console字体颜色
system("color 1A");
//【0】显示欢迎和帮助文字
ShowHelpText( );
//【1】参数准备
//定义两组点,代表两个三角形
Point2f srcTriangle[3];
Point2f dstTriangle[3];
//定义一些Mat变量
Mat rotMat( 2, 3, CV_32FC1 );
Mat warpMat( 2, 3, CV_32FC1 );
Mat srcImage, dstImage_warp, dstImage_warp_rotate;
//【2】加载源图像并作一些初始化
srcImage = imread( "1.jpg", 1 );
if(!srcImage.data ) { printf("读取图片错误,请确定目录下是否有imread函数指定的图片存在~! \n"); return false; }
// 设置目标图像的大小和类型与源图像一致
dstImage_warp = Mat::zeros( srcImage.rows, srcImage.cols, srcImage.type() );
//【3】设置源图像和目标图像上的三组点以计算仿射变换
srcTriangle[0] = Point2f( 0,0 );
srcTriangle[1] = Point2f( static_cast<float>(srcImage.cols - 1), 0 );
srcTriangle[2] = Point2f( 0, static_cast<float>(srcImage.rows - 1 ));
dstTriangle[0] = Point2f( static_cast<float>(srcImage.cols*0.0), static_cast<float>(srcImage.rows*0.33));
dstTriangle[1] = Point2f( static_cast<float>(srcImage.cols*0.65), static_cast<float>(srcImage.rows*0.35));
dstTriangle[2] = Point2f( static_cast<float>(srcImage.cols*0.15), static_cast<float>(srcImage.rows*0.6));
//【4】求得仿射变换
warpMat = getAffineTransform( srcTriangle, dstTriangle );
//【5】对源图像应用刚刚求得的仿射变换
warpAffine( srcImage, dstImage_warp, warpMat, dstImage_warp.size() );
//【6】对图像进行缩放后再旋转
// 计算绕图像中点顺时针旋转50度缩放因子为0.6的旋转矩阵
Point center = Point( dstImage_warp.cols/2, dstImage_warp.rows/2 );
double angle = -30.0;
double scale = 0.8;
// 通过上面的旋转细节信息求得旋转矩阵
rotMat = getRotationMatrix2D( center, angle, scale );
// 旋转已缩放后的图像
warpAffine( dstImage_warp, dstImage_warp_rotate, rotMat, dstImage_warp.size() );
//【7】显示结果
imshow( WINDOW_NAME1, srcImage );
imshow( WINDOW_NAME2, dstImage_warp );
imshow( WINDOW_NAME3, dstImage_warp_rotate );
// 等待用户按任意按键退出程序
waitKey(0);
return 0;
}
//-----------------------------------【ShowHelpText( )函数】----------------------------------
// 描述:输出一些帮助信息
//----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
static void ShowHelpText()
{
//输出一些帮助信息
printf( "\n\n\n\t欢迎来到【仿射变换】示例程序~\n\n");
printf("\t当前使用的OpenCV版本为 OpenCV "CV_VERSION);
printf( "\n\n\t\t\t\t\t\t\t\t by浅墨\n\n\n"
);
}
效果图:
二、SURF特征点描述
通过上一篇文章SURF相关内容的讲解,我们已经对SURF算法有了一定的理解。SURF算法为每个检测到的特征定义了位置和尺度,尺度值可用于定义围绕特征点的窗口大小,不论物体的尺度在窗口是什么样的,都将包含相同的视觉信息,这些信息用于表示特征点以使得他们与众不同。
在特征匹配中,特征描述子通常是用于N维向量,在光照不变以及少许透视变形的情况下很理想。另外,优质的描述子可以通过简单的距离测量进行比较,比如欧氏距离。因此,他们在特征匹配算法中,用处是很大的。
在OpenCV中,使用SURF进行特征点描述主要是drawMatches方法和BruteForceMatcher类的运用,让我们一起来认识他们。
2.1 drawMatches函数详解
drawMatches用于绘制出相匹配的两个图像的关键点,它有如下两个版本的C++函数原型:
C++: void drawMatches(const Mat& img1,
constvector<KeyPoint>& keypoints1,
const Mat& img2,
constvector<KeyPoint>& keypoints2,
constvector<DMatch>& matches1to2,
Mat& outImg,
const Scalar&matchColor=Scalar::all(-1),
const Scalar&singlePointColor=Scalar::all(-1),
const vector<char>&matchesMask=vector<char>(),
intflags=DrawMatchesFlags::DEFAULT )
C++: void drawMatches(const Mat& img1,
constvector<KeyPoint>& keypoints1,
const Mat& img2,
constvector<KeyPoint>& keypoints2,
const vector<vector<DMatch>>&matches1to2,
Mat& outImg,
const Scalar&matchColor=Scalar::all(-1),
const Scalar&singlePointColor=Scalar::all(-1),
constvector<vector<char>>& matchesMask=vector<vector<char>>(),
intflags=DrawMatchesFlags::DEFAULT )
除了第五个参数matches1to2和第九个参数matchesMask有细微的差别以外,两个版本的基本上相同。
- 第一个参数,const Mat&类型的img1,第一幅源图像。
- 第二个参数,const vector<KeyPoint>&类型的keypoints1,根据第一幅源图像得到的特征点,它是一个输出参数。
- 第三个参数,const Mat&类型的img2,第二幅源图像。
- 第四个参数,const vector<KeyPoint>&类型的keypoints2,根据第二幅源图像得到的特征点,它是一个输出参数。
- 第五个参数,matches1to2,第一幅图像到第二幅图像的匹配点,即表示每一个图1中的特征点都在图2中有一一对应的点、
- 第六个参数,Mat&类型的outImg,输出图像,其内容取决于第五个参数标识符falgs。
- 第七个参数,const Scalar&类型的matchColor,匹配的输出颜色,即线和关键点的颜色。它有默认值Scalar::all(-1),表示颜色是随机生成的。
- 第八个参数,const Scalar&类型的singlePointColor,单一特征点的颜色,它也有表示随机生成颜色的默认值Scalar::all(-1)。
- 第九个参数,matchesMask,确定哪些匹配是会绘制出来的掩膜,如果掩膜为空,表示所有匹配都进行绘制。
- 第十个参数,int类型的flags,特征绘制的标识符,有默认值DrawMatchesFlags::DEFAULT。可以在如下这个DrawMatchesFlags结构体中选取值:
struct DrawMatchesFlags
{
enum
{
DEFAULT = 0, // Output image matrix will be created (Mat::create),
// i.e. existing memory ofoutput image may be reused.
// Two source images,matches, and single keypoints
// will be drawn.
// For each keypoint, only the center pointwill be
// drawn (without a circlearound the keypoint with the
// keypoint size andorientation).
DRAW_OVER_OUTIMG = 1, // Output image matrix will not be
// created (usingMat::create). Matches will be drawn
// on existing contentof output image.
NOT_DRAW_SINGLE_POINTS = 2, // Single keypoints will not be drawn.
DRAW_RICH_KEYPOINTS = 4 // For each keypoint, the circle around
// keypoint withkeypoint size and orientation will
// be drawn.
};
};
2.2 OpenCV2.X中drawMatches函数源代码
在D:\Program Files(x86)\opencv\sources\modules\features2d\src\draw.cpp路径下,有drawMatches函数两个版本的源码。在这里贴出OpenCV中本其源码实现细节,来给想了解实现细节的小伙伴们参考。
void drawMatches( const Mat& img1,const vector<KeyPoint>& keypoints1,
const Mat& img2, constvector<KeyPoint>& keypoints2,
constvector<DMatch>& matches1to2, Mat& outImg,
const Scalar& matchColor,const Scalar& singlePointColor,
const vector<char>&matchesMask, int flags )
{
if( !matchesMask.empty() && matchesMask.size() !=matches1to2.size() )
CV_Error( CV_StsBadSize, "matchesMask must have the same size asmatches1to2" );
Mat outImg1, outImg2;
_prepareImgAndDrawKeypoints( img1, keypoints1, img2, keypoints2,
outImg, outImg1,outImg2, singlePointColor, flags );
// draw matches
for( size_t m = 0; m < matches1to2.size(); m++ )
{
if( matchesMask.empty() || matchesMask[m] )
{
int i1 = matches1to2[m].queryIdx;
int i2 = matches1to2[m].trainIdx;
CV_Assert(i1 >= 0 && i1 <static_cast<int>(keypoints1.size()));
CV_Assert(i2 >= 0 && i2 <static_cast<int>(keypoints2.size()));
const KeyPoint &kp1 = keypoints1[i1], &kp2 = keypoints2[i2];
_drawMatch( outImg, outImg1, outImg2, kp1, kp2, matchColor, flags );
}
}
}
void drawMatches( const Mat& img1,const vector<KeyPoint>& keypoints1,
const Mat& img2, constvector<KeyPoint>& keypoints2,
constvector<vector<DMatch> >& matches1to2, Mat& outImg,
const Scalar& matchColor,const Scalar& singlePointColor,
constvector<vector<char> >& matchesMask, int flags )
{
if( !matchesMask.empty() && matchesMask.size() !=matches1to2.size() )
CV_Error( CV_StsBadSize, "matchesMask must have the same size asmatches1to2" );
Mat outImg1, outImg2;
_prepareImgAndDrawKeypoints( img1, keypoints1, img2, keypoints2,
outImg, outImg1, outImg2,singlePointColor, flags );
// draw matches
for( size_t i = 0; i < matches1to2.size(); i++ )
{
for( size_t j = 0; j < matches1to2[i].size(); j++ )
{
int i1 = matches1to2[i][j].queryIdx;
int i2 = matches1to2[i][j].trainIdx;
if( matchesMask.empty() || matchesMask[i][j] )
{
const KeyPoint &kp1 =keypoints1[i1], &kp2 = keypoints2[i2];
_drawMatch( outImg,outImg1, outImg2, kp1, kp2, matchColor, flags );
}
}
}
}
}
BruteForceMatcher类源码分析
接下来,我们看看本文示例程序中会用到的BruteForceMatcher类的源码分析。在D:\Program Files(x86)\opencv\sources\modules\legacy\include\opencv2\legacy\legacy.hpp路径下,可以找到BruteForceMatcher类的定义。
template<class Distance>
class CV_EXPORTS BruteForceMatcher : publicBFMatcher
{
public:
BruteForceMatcher( Distance d = Distance() ) : BFMatcher(Distance::normType,false) {(void)d;}
virtual ~BruteForceMatcher() {}
};
其公共继承自BFMatcher类。而BFMatcher类位于D:\Program Files(x86)\opencv\sources\modules\features2d\include\opencv2\features2d\features2d.hpp
路径之下,我们一起看看其代码:
/*
*Brute-force descriptor matcher.
*
*For each descriptor in the first set, this matcher finds the closest
*descriptor in the second set by trying each one.
*
*For efficiency, BruteForceMatcher is templated on the distance metric.
*For float descriptors, a common choice would be cv::L2<float>.
*/
class CV_EXPORTS_W BFMatcher : publicDescriptorMatcher
{
public:
CV_WRAP BFMatcher( int normType=NORM_L2, bool crossCheck=false );
virtual ~BFMatcher() {}
virtual bool isMaskSupported() const { return true; }
virtual Ptr<DescriptorMatcher> clone(bool emptyTrainData=false ) const;
AlgorithmInfo* info() const;
protected:
virtual void knnMatchImpl( const Mat& queryDescriptors,vector<vector<DMatch> >& matches, int k,
const vector<Mat>& masks=vector<Mat>(), boolcompactResult=false );
virtual void radiusMatchImpl( const Mat& queryDescriptors,vector<vector<DMatch> >& matches, float maxDistance,
const vector<Mat>& masks=vector<Mat>(), boolcompactResult=false );
int normType;
bool crossCheck;
};
发现公共其继承自DescriptorMatcher类,再次进行溯源,在D:\Program Files(x86)\opencv\sources\modules\features2d\include\opencv2\features2d\features2d.hpp路径下找到DescriptorMatcher类的定义。
/****************************************************************************************\
* DescriptorMatcher *
\****************************************************************************************/
/*
*Abstract base class for matching two sets of descriptors.
*/
class CV_EXPORTS_W DescriptorMatcher :public Algorithm
{
public:
virtual ~DescriptorMatcher();
/*
* Add descriptors to train descriptor collection.
* descriptors Descriptors toadd. Each descriptors[i] is a descriptors set from one image.
*/
CV_WRAP virtual void add( const vector<Mat>& descriptors );
/*
* Get train descriptors collection.
*/
CV_WRAP const vector<Mat>& getTrainDescriptors() const;
/*
* Clear train descriptors collection.
*/
CV_WRAP virtual void clear();
/*
* Return true if there are not train descriptors in collection.
*/
CV_WRAP virtual bool empty() const;
/*
* Return true if the matcher supports mask in match methods.
*/
CV_WRAP virtual bool isMaskSupported() const = 0;
/*
* Train matcher (e.g. train flann index).
* In all methods to match the method train() is run every time beforematching.
* Some descriptor matchers (e.g. BruteForceMatcher) have emptyimplementation
* of this method, other matchers really train their inner structures
* (e.g. FlannBasedMatcher trains flann::Index). So nonemptyimplementation
* of train() should check the class object state and dotraing/retraining
* only if the state requires that (e.g. FlannBasedMatcher trainsflann::Index
* if it has not trained yet or if new descriptors have been added to thetrain
* collection).
*/
CV_WRAP virtual void train();
/*
* Group of methods to match descriptors from image pair.
* Method train() is run in this methods.
*/
// Find one best match for each query descriptor (if mask is empty).
CV_WRAP void match( const Mat& queryDescriptors, const Mat&trainDescriptors,
CV_OUT vector<DMatch>&matches, const Mat& mask=Mat() ) const;
// Find k best matches for each query descriptor (in increasing order ofdistances).
// compactResult is used when mask is not empty. If compactResult isfalse matches
// vector will have the same size as queryDescriptors rows. IfcompactResult is true
// matches vector will not contain matches for fully masked out querydescriptors.
CV_WRAP void knnMatch( const Mat& queryDescriptors, const Mat&trainDescriptors,
CV_OUTvector<vector<DMatch> >& matches, int k,
const Mat& mask=Mat(),bool compactResult=false ) const;
// Find best matches for each query descriptor which have distance lessthan
// maxDistance (in increasing order of distances).
void radiusMatch( const Mat& queryDescriptors, const Mat&trainDescriptors,
vector<vector<DMatch> >& matches, float maxDistance,
const Mat&mask=Mat(), bool compactResult=false ) const;
/*
* Group of methods to match descriptors from one image to image set.
* See description of similar methods for matching image pair above.
*/
CV_WRAP void match( const Mat& queryDescriptors, CV_OUTvector<DMatch>& matches,
constvector<Mat>& masks=vector<Mat>() );
CV_WRAP void knnMatch( const Mat& queryDescriptors, CV_OUTvector<vector<DMatch> >& matches, int k,
const vector<Mat>& masks=vector<Mat>(), boolcompactResult=false );
void radiusMatch( const Mat& queryDescriptors,vector<vector<DMatch> >& matches, float maxDistance,
const vector<Mat>&masks=vector<Mat>(), bool compactResult=false );
// Reads matcher object from a file node
virtual void read( const FileNode& );
// Writes matcher object to a file storage
virtual void write( FileStorage& ) const;
// Clone the matcher. If emptyTrainData is false the method create deepcopy of the object, i.e. copies
// both parameters and train data. If emptyTrainData is true the methodcreate object copy with current parameters
// but with empty train data.
virtual Ptr<DescriptorMatcher> clone( bool emptyTrainData=false )const = 0;
CV_WRAP static Ptr<DescriptorMatcher> create( const string&descriptorMatcherType );
protected:
/*
* Class to work with descriptors from several images as with one mergedmatrix.
* It is used e.g. in FlannBasedMatcher.
*/
class CV_EXPORTS DescriptorCollection
{
public:
DescriptorCollection();
DescriptorCollection( const DescriptorCollection& collection );
virtual ~DescriptorCollection();
// Vector of matrices "descriptors" will be merged to onematrix "mergedDescriptors" here.
void set( const vector<Mat>& descriptors );
virtual void clear();
const Mat& getDescriptors() const;
const Mat getDescriptor( int imgIdx, int localDescIdx ) const;
const Mat getDescriptor( int globalDescIdx ) const;
void getLocalIdx( int globalDescIdx, int& imgIdx, int&localDescIdx ) const;
int size() const;
protected:
Mat mergedDescriptors;
vector<int> startIdxs;
};
// In fact the matching is implemented only by the following two methods.These methods suppose
// that the class object has been trained already. Public match methodscall these methods
// after calling train().
virtual void knnMatchImpl( const Mat& queryDescriptors,vector<vector<DMatch> >& matches, int k,
const vector<Mat>&masks=vector<Mat>(), bool compactResult=false ) = 0;
virtual void radiusMatchImpl( const Mat& queryDescriptors,vector<vector<DMatch> >& matches, float maxDistance,
const vector<Mat>& masks=vector<Mat>(), bool compactResult=false) = 0;
static bool isPossibleMatch( const Mat& mask, int queryIdx, inttrainIdx );
static bool isMaskedOut( const vector<Mat>& masks, intqueryIdx );
static Mat clone_op( Mat m ) { return m.clone(); }
void checkMasks( const vector<Mat>& masks, intqueryDescriptorsCount ) const;
// Collection of descriptors from train images.
vector<Mat> trainDescCollection;
};
可以发现,DescriptorMatcher类和之前我们讲到FeatureDetector 类和DescriptorExtractor类一样,都是继承自他们“德高望重的祖先”Algorithm基类的。
而我们用BruteForceMatcher类时用到最多的match方法,是它从DescriptorMatcher类那里的“拿来主义”。定义如下:
//为各种描述符找到一个最佳的匹配(若掩膜为空)
CV_WRAP void match( const Mat& queryDescriptors, const Mat&trainDescriptors,
CV_OUTvector<DMatch>& matches, const Mat& mask=Mat() ) const;
2.3 SURF特征匹配示例程序
这个示例程序中,我们利用SurfDescriptorExtractor类进行特征向量的相关计算。
程序利用了SURF特征的特征描述办法,其操作封装在类SurfFeatureDetector中,利用类内的detect函数可以检测出SURF特征的关键点,保存在vector容器中。第二步利用SurfDescriptorExtractor类进行特征向量的相关计算。将之前的vector变量变成向量矩阵形式保存在Mat中。最后强行匹配两幅图像的特征向量,利用了类BruteForceMatcher中的函数match。
程序的核心思想是:
- 使用 DescriptorExtractor 接口来寻找关键点对应的特征向量。
- 使用 SurfDescriptorExtractor 以及它的函数 compute 来完成特定的计算。
- 使用 BruteForceMatcher 来匹配特征向量。
- 使用函数 drawMatches 来绘制检测到的匹配点。
关键点讲解:OpenCV2引入了一个通用类,用于提取不同的特征点描述子,计算如下:
//【4】计算描述子(特征向量)
SurfDescriptorExtractorextractor;
Matdescriptors1, descriptors2;
extractor.compute(srcImage1, keyPoint1, descriptors1 );
extractor.compute(srcImage2, keyPoints2, descriptors2 );
这里的结果为一个Mat矩阵,它的行数与特征点向量中元素个数是一致的。每行都是一个N维描述子的向量,比如SURF算法默认的描述子维度为64,该向量描绘了特征点周围的强度样式。两个特征点越相似,他们的特征向量也越靠近。这些描述子在图像匹配中尤其有用,如我们想匹配同一个场景中的两幅图像。首先,我们检测每幅图像中的特征,然后提取他们的描述子。第一幅图像中的每一个特征描述子向量都会与第二幅图中的描述子进行比较,得分最高的一对描述子,也就是两个向量的距离最近)将被视为那个特征的最佳匹配。该过程对于第一幅图像中的所有特征进行重复,这便是BruteForceMatcher中实行的最基本的策略。相关代码如下:
//【5】使用BruteForce进行匹配
//实例化一个匹配器
BruteForceMatcher<L2<float> > matcher;
std::vector<DMatch > matches;
//匹配两幅图中的描述子(descriptors)
matcher.match(descriptors1, descriptors2, matches );
BruteForceMatcher是由DescriptorMatcher派生出来的一个类,而DescriptorMatcher定义了不同的匹配策略的共同接口。调用match方法后,在其第三个参数输出一个cv::DMatch向量。于是我们定义一个std::vector<DMatch>类型的matches。
调用match方法之后,我们便可以使用drawMatches方法对匹配到的点进行绘制,并最终显示出来。相关代码如下:
//【6】绘制从两个图像中匹配出的关键点
MatimgMatches;
drawMatches(srcImage1, keyPoint1, srcImage2, keyPoints2, matches, imgMatches );//进行绘制
//【7】显示效果图
imshow("匹配图", imgMatches );
核心部分讲解完毕,下面我们一起来看看详细注释的示例程序的完全体。
//-----------------------------------【程序说明】----------------------------------------------
// 程序名称::《【OpenCV入门教程之十八】OpenCV仿射变换 & SURF特征点描述合辑》 博文配套源码 之 仿射变换
// 开发所用IDE版本:Visual Studio 2010
// 开发所用OpenCV版本: 2.4.9
// 2014年6月 Created by 浅墨
// 浅墨的微博:@浅墨_毛星云 http://weibo.com/1723155442
// 浅墨的知乎:http://www.zhihu.com/people/mao-xing-yun
// 浅墨的豆瓣:http://www.douban.com/people/53426472/
//----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
//-----------------------------------【头文件包含部分】---------------------------------------
// 描述:包含程序所依赖的头文件
//----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
#include "opencv2/core/core.hpp"
#include "opencv2/features2d/features2d.hpp"
#include "opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp"
#include <opencv2/nonfree/nonfree.hpp>
#include<opencv2/legacy/legacy.hpp>
#include <iostream>
//-----------------------------------【命名空间声明部分】--------------------------------------
// 描述:包含程序所使用的命名空间
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
using namespace cv;
using namespace std;
//-----------------------------------【全局函数声明部分】--------------------------------------
// 描述:全局函数的声明
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
static void ShowHelpText( );//输出帮助文字
//-----------------------------------【main( )函数】--------------------------------------------
// 描述:控制台应用程序的入口函数,我们的程序从这里开始执行
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
int main( )
{
//【0】改变console字体颜色
system("color 1A");
//【0】显示欢迎和帮助文字
ShowHelpText( );
//【1】载入素材图
Mat srcImage1 = imread("1.jpg",1);
Mat srcImage2 = imread("2.jpg",1);
if( !srcImage1.data || !srcImage2.data )
{ printf("读取图片错误,请确定目录下是否有imread函数指定的图片存在~! \n"); return false; }
//【2】使用SURF算子检测关键点
int minHessian = 700;//SURF算法中的hessian阈值
SurfFeatureDetector detector( minHessian );//定义一个SurfFeatureDetector(SURF) 特征检测类对象
std::vector<KeyPoint> keyPoint1, keyPoints2;//vector模板类,存放任意类型的动态数组
//【3】调用detect函数检测出SURF特征关键点,保存在vector容器中
detector.detect( srcImage1, keyPoint1 );
detector.detect( srcImage2, keyPoints2 );
//【4】计算描述符(特征向量)
SurfDescriptorExtractor extractor;
Mat descriptors1, descriptors2;
extractor.compute( srcImage1, keyPoint1, descriptors1 );
extractor.compute( srcImage2, keyPoints2, descriptors2 );
//【5】使用BruteForce进行匹配
// 实例化一个匹配器
BruteForceMatcher< L2<float> > matcher;
std::vector< DMatch > matches;
//匹配两幅图中的描述子(descriptors)
matcher.match( descriptors1, descriptors2, matches );
//【6】绘制从两个图像中匹配出的关键点
Mat imgMatches;
drawMatches( srcImage1, keyPoint1, srcImage2, keyPoints2, matches, imgMatches );//进行绘制
//【7】显示效果图
imshow("匹配图", imgMatches );
waitKey(0);
return 0;
}
//-----------------------------------【ShowHelpText( )函数】----------------------------------
// 描述:输出一些帮助信息
//----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
static void ShowHelpText()
{
//输出一些帮助信息
printf( "\n\n\n\t欢迎来到【SURF特征描述】示例程序~\n\n");
printf("\t当前使用的OpenCV版本为 OpenCV "CV_VERSION
"\n\n\t\t\t\t\t\t\t\t by浅墨\n\n\n" );
}
看看运行效果图。
两幅原始图:
效果图:
本篇文章的配套源代码请点击这里下载:
【浅墨OpenCV入门教程之十八】配套源代码之【仿射变换】 下载
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
【浅墨OpenCV入门教程之十八】配套源代码之【SURF特征点描述】 下载
OK,今天的内容大概就是这些,我们下篇文章见:)
另外提一点,我们的WarpAffine函数与一个叫做cvGetQuadrangleSubPix( )的函数类似,但是不完全相同。 WarpAffine要求输入和输出图像具有同样的数据类型,有更大的资源开销(因此对小图像不太合适)而且输出图像的部分可以保留不变。而 cvGetQuadrangleSubPix 可以精确地从8位图像中提取四边形到浮点数缓存区中,具有比较小的系统开销,而且总是全部改变输出图像的内容。
1.3.2 getRotationMatrix2D
计算二维旋转变换矩阵。变换会将旋转中心映射到它自身。
C++: Mat getRotationMatrix2D(Point2fcenter, double angle, double scale)
- 第一个参数,Point2f类型的center,表示源图像的旋转中心。
- 第二个参数,double类型的angle,旋转角度。角度为正值表示向逆时针旋转(坐标原点是左上角)。
- 第三个参数,double类型的scale,缩放系数。
此函数计算以下矩阵:
其中:
1.4 仿射变换相关核心函数在OpenCV中的实现源代码
这个部分贴出OpenCV中本节相关函数的源码实现细节,来给想了解实现细节的小伙伴们参考。浅墨暂时不在源码的细节上挖深作详细注释。
1.4.1 OpenCV2.X中warpAffine函数源代码
void cv::warpAffine( InputArray _src,OutputArray _dst,
InputArray _M0, Sizedsize,
int flags, int borderType,const Scalar& borderValue )
{
Mat src = _src.getMat(), M0 = _M0.getMat();
_dst.create( dsize.area() == 0 ? src.size() : dsize, src.type() );
Mat dst = _dst.getMat();
CV_Assert( src.cols > 0 && src.rows > 0 );
if( dst.data == src.data )
src = src.clone();
double M[6];
Mat matM(2, 3, CV_64F, M);
int interpolation = flags & INTER_MAX;
if( interpolation == INTER_AREA )
interpolation = INTER_LINEAR;
CV_Assert( (M0.type() == CV_32F || M0.type() == CV_64F) &&M0.rows == 2 && M0.cols == 3 );
M0.convertTo(matM, matM.type());
#ifdef HAVE_TEGRA_OPTIMIZATION
if( tegra::warpAffine(src, dst, M, flags, borderType, borderValue) )
return;
#endif
if( !(flags & WARP_INVERSE_MAP) )
{
double D = M[0]*M[4] - M[1]*M[3];
D = D != 0 ? 1./D : 0;
double A11 = M[4]*D, A22=M[0]*D;
M[0] = A11; M[1] *= -D;
M[3] *= -D; M[4] = A22;
double b1 = -M[0]*M[2] - M[1]*M[5];
double b2 = -M[3]*M[2] - M[4]*M[5];
M[2] = b1; M[5] = b2;
}
int x;
AutoBuffer<int> _abdelta(dst.cols*2);
int* adelta = &_abdelta[0], *bdelta = adelta + dst.cols;
const int AB_BITS = MAX(10, (int)INTER_BITS);
const int AB_SCALE = 1 << AB_BITS;
/*
#if defined (HAVE_IPP) &&(IPP_VERSION_MAJOR >= 7)
int depth = src.depth();
int channels = src.channels();
if( ( depth == CV_8U || depth == CV_16U ||depth == CV_32F ) &&
( channels == 1 || channels == 3 || channels == 4 ) &&
( borderType == cv::BORDER_TRANSPARENT || ( borderType ==cv::BORDER_CONSTANT ) ) )
{
int type = src.type();
ippiWarpAffineBackFunc ippFunc =
type == CV_8UC1 ? (ippiWarpAffineBackFunc)ippiWarpAffineBack_8u_C1R :
type == CV_8UC3 ? (ippiWarpAffineBackFunc)ippiWarpAffineBack_8u_C3R :
type == CV_8UC4 ? (ippiWarpAffineBackFunc)ippiWarpAffineBack_8u_C4R :
type == CV_16UC1 ? (ippiWarpAffineBackFunc)ippiWarpAffineBack_16u_C1R :
type == CV_16UC3 ? (ippiWarpAffineBackFunc)ippiWarpAffineBack_16u_C3R :
type == CV_16UC4 ? (ippiWarpAffineBackFunc)ippiWarpAffineBack_16u_C4R :
type == CV_32FC1 ? (ippiWarpAffineBackFunc)ippiWarpAffineBack_32f_C1R :
type == CV_32FC3 ? (ippiWarpAffineBackFunc)ippiWarpAffineBack_32f_C3R :
type == CV_32FC4 ? (ippiWarpAffineBackFunc)ippiWarpAffineBack_32f_C4R :
0;
int mode =
flags == INTER_LINEAR ? IPPI_INTER_LINEAR :
flags == INTER_NEAREST ? IPPI_INTER_NN :
flags == INTER_CUBIC ? IPPI_INTER_CUBIC :
0;
if( mode && ippFunc )
{
double coeffs[2][3];
for( int i = 0; i < 2; i++ )
{
for( int j = 0; j < 3; j++ )
{
coeffs[i][j] =matM.at<double>(i, j);
}
}
bool ok;
Range range(0, dst.rows);
IPPwarpAffineInvoker invoker(src, dst, coeffs, mode, borderType,borderValue, ippFunc, &ok);
parallel_for_(range, invoker, dst.total()/(double)(1<<16));
if( ok )
return;
}
}
#endif
*/
for( x = 0; x < dst.cols; x++ )
{
adelta[x] = saturate_cast<int>(M[0]*x*AB_SCALE);
bdelta[x] = saturate_cast<int>(M[3]*x*AB_SCALE);
}
Range range(0, dst.rows);
warpAffineInvokerinvoker(src, dst, interpolation, borderType,
borderValue,adelta, bdelta, M);
parallel_for_(range, invoker, dst.total()/(double)(1<<16));
}
1.4.2 OpenCV2.X中getRotationMatrix2D函数源代码
cv::Mat cv::getRotationMatrix2D( Point2f center,double angle, double scale )
{
angle *= CV_PI/180;
double alpha = cos(angle)*scale;
double beta = sin(angle)*scale;
Mat M(2, 3, CV_64F);
double* m = (double*)M.data;
m[0] = alpha;
m[1] = beta;
m[2] = (1-alpha)*center.x - beta*center.y;
m[3] = -beta;
m[4] = alpha;
m[5] = beta*center.x + (1-alpha)*center.y;
return M;
}
1.5 OpenCV仿射变换示例程序
看完上面的讲解和函数线吗实现,下面是一个以warpAffine和getRotationMatrix2D函数为核心的对图像进行仿射变换的示例程序。
//-----------------------------------【程序说明】----------------------------------------------
// 程序名称::《【OpenCV入门教程之十八】OpenCV仿射变换 & SURF特征点描述合辑》 博文配套源码 之 仿射变换
// 开发所用IDE版本:Visual Studio 2010
// 开发所用OpenCV版本: 2.4.9
// 2014年6月 Created by 浅墨
// 浅墨的微博:@浅墨_毛星云 http://weibo.com/1723155442
// 浅墨的知乎:http://www.zhihu.com/people/mao-xing-yun
// 浅墨的豆瓣:http://www.douban.com/people/53426472/
//----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
//-----------------------------------【头文件包含部分】---------------------------------------
// 描述:包含程序所依赖的头文件
//----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
#include "opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp"
#include "opencv2/imgproc/imgproc.hpp"
#include <iostream>
//-----------------------------------【命名空间声明部分】--------------------------------------
// 描述:包含程序所使用的命名空间
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
using namespace cv;
using namespace std;
//-----------------------------------【宏定义部分】--------------------------------------------
// 描述:定义一些辅助宏
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
#define WINDOW_NAME1 "【原始图窗口】" //为窗口标题定义的宏
#define WINDOW_NAME2 "【经过Warp后的图像】" //为窗口标题定义的宏
#define WINDOW_NAME3 "【经过Warp和Rotate后的图像】" //为窗口标题定义的宏
//-----------------------------------【全局函数声明部分】--------------------------------------
// 描述:全局函数的声明
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
static void ShowHelpText( );
//-----------------------------------【main( )函数】--------------------------------------------
// 描述:控制台应用程序的入口函数,我们的程序从这里开始执行
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
int main( )
{
//【0】改变console字体颜色
system("color 1A");
//【0】显示欢迎和帮助文字
ShowHelpText( );
//【1】参数准备
//定义两组点,代表两个三角形
Point2f srcTriangle[3];
Point2f dstTriangle[3];
//定义一些Mat变量
Mat rotMat( 2, 3, CV_32FC1 );
Mat warpMat( 2, 3, CV_32FC1 );
Mat srcImage, dstImage_warp, dstImage_warp_rotate;
//【2】加载源图像并作一些初始化
srcImage = imread( "1.jpg", 1 );
if(!srcImage.data ) { printf("读取图片错误,请确定目录下是否有imread函数指定的图片存在~! \n"); return false; }
// 设置目标图像的大小和类型与源图像一致
dstImage_warp = Mat::zeros( srcImage.rows, srcImage.cols, srcImage.type() );
//【3】设置源图像和目标图像上的三组点以计算仿射变换
srcTriangle[0] = Point2f( 0,0 );
srcTriangle[1] = Point2f( static_cast<float>(srcImage.cols - 1), 0 );
srcTriangle[2] = Point2f( 0, static_cast<float>(srcImage.rows - 1 ));
dstTriangle[0] = Point2f( static_cast<float>(srcImage.cols*0.0), static_cast<float>(srcImage.rows*0.33));
dstTriangle[1] = Point2f( static_cast<float>(srcImage.cols*0.65), static_cast<float>(srcImage.rows*0.35));
dstTriangle[2] = Point2f( static_cast<float>(srcImage.cols*0.15), static_cast<float>(srcImage.rows*0.6));
//【4】求得仿射变换
warpMat = getAffineTransform( srcTriangle, dstTriangle );
//【5】对源图像应用刚刚求得的仿射变换
warpAffine( srcImage, dstImage_warp, warpMat, dstImage_warp.size() );
//【6】对图像进行缩放后再旋转
// 计算绕图像中点顺时针旋转50度缩放因子为0.6的旋转矩阵
Point center = Point( dstImage_warp.cols/2, dstImage_warp.rows/2 );
double angle = -30.0;
double scale = 0.8;
// 通过上面的旋转细节信息求得旋转矩阵
rotMat = getRotationMatrix2D( center, angle, scale );
// 旋转已缩放后的图像
warpAffine( dstImage_warp, dstImage_warp_rotate, rotMat, dstImage_warp.size() );
//【7】显示结果
imshow( WINDOW_NAME1, srcImage );
imshow( WINDOW_NAME2, dstImage_warp );
imshow( WINDOW_NAME3, dstImage_warp_rotate );
// 等待用户按任意按键退出程序
waitKey(0);
return 0;
}
//-----------------------------------【ShowHelpText( )函数】----------------------------------
// 描述:输出一些帮助信息
//----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
static void ShowHelpText()
{
//输出一些帮助信息
printf( "\n\n\n\t欢迎来到【仿射变换】示例程序~\n\n");
printf("\t当前使用的OpenCV版本为 OpenCV "CV_VERSION);
printf( "\n\n\t\t\t\t\t\t\t\t by浅墨\n\n\n"
);
}
效果图:
二、SURF特征点描述
通过上一篇文章SURF相关内容的讲解,我们已经对SURF算法有了一定的理解。SURF算法为每个检测到的特征定义了位置和尺度,尺度值可用于定义围绕特征点的窗口大小,不论物体的尺度在窗口是什么样的,都将包含相同的视觉信息,这些信息用于表示特征点以使得他们与众不同。
在特征匹配中,特征描述子通常是用于N维向量,在光照不变以及少许透视变形的情况下很理想。另外,优质的描述子可以通过简单的距离测量进行比较,比如欧氏距离。因此,他们在特征匹配算法中,用处是很大的。
在OpenCV中,使用SURF进行特征点描述主要是drawMatches方法和BruteForceMatcher类的运用,让我们一起来认识他们。
2.1 drawMatches函数详解
drawMatches用于绘制出相匹配的两个图像的关键点,它有如下两个版本的C++函数原型:
C++: void drawMatches(const Mat& img1, constvector<KeyPoint>& keypoints1, const Mat& img2, constvector<KeyPoint>& keypoints2, constvector<DMatch>& matches1to2, Mat& outImg, const Scalar&matchColor=Scalar::all(-1), const Scalar&singlePointColor=Scalar::all(-1), const vector<char>&matchesMask=vector<char>(), intflags=DrawMatchesFlags::DEFAULT )
C++: void drawMatches(const Mat& img1, constvector<KeyPoint>& keypoints1, const Mat& img2, constvector<KeyPoint>& keypoints2, const vector<vector<DMatch>>&matches1to2, Mat& outImg, const Scalar&matchColor=Scalar::all(-1), const Scalar&singlePointColor=Scalar::all(-1), constvector<vector<char>>& matchesMask=vector<vector<char>>(), intflags=DrawMatchesFlags::DEFAULT )
除了第五个参数matches1to2和第九个参数matchesMask有细微的差别以外,两个版本的基本上相同。
- 第一个参数,const Mat&类型的img1,第一幅源图像。
- 第二个参数,const vector<KeyPoint>&类型的keypoints1,根据第一幅源图像得到的特征点,它是一个输出参数。
- 第三个参数,const Mat&类型的img2,第二幅源图像。
- 第四个参数,const vector<KeyPoint>&类型的keypoints2,根据第二幅源图像得到的特征点,它是一个输出参数。
- 第五个参数,matches1to2,第一幅图像到第二幅图像的匹配点,即表示每一个图1中的特征点都在图2中有一一对应的点、
- 第六个参数,Mat&类型的outImg,输出图像,其内容取决于第五个参数标识符falgs。
- 第七个参数,const Scalar&类型的matchColor,匹配的输出颜色,即线和关键点的颜色。它有默认值Scalar::all(-1),表示颜色是随机生成的。
- 第八个参数,const Scalar&类型的singlePointColor,单一特征点的颜色,它也有表示随机生成颜色的默认值Scalar::all(-1)。
- 第九个参数,matchesMask,确定哪些匹配是会绘制出来的掩膜,如果掩膜为空,表示所有匹配都进行绘制。
- 第十个参数,int类型的flags,特征绘制的标识符,有默认值DrawMatchesFlags::DEFAULT。可以在如下这个DrawMatchesFlags结构体中选取值:
struct DrawMatchesFlags
{
enum
{
DEFAULT = 0, // Output image matrix will be created (Mat::create),
// i.e. existing memory ofoutput image may be reused.
// Two source images,matches, and single keypoints
// will be drawn.
// For each keypoint, only the center pointwill be
// drawn (without a circlearound the keypoint with the
// keypoint size andorientation).
DRAW_OVER_OUTIMG = 1, // Output image matrix will not be
// created (usingMat::create). Matches will be drawn
// on existing contentof output image.
NOT_DRAW_SINGLE_POINTS = 2, // Single keypoints will not be drawn.
DRAW_RICH_KEYPOINTS = 4 // For each keypoint, the circle around
// keypoint withkeypoint size and orientation will
// be drawn.
};
};
2.2 OpenCV2.X中drawMatches函数源代码
在D:\Program Files(x86)\opencv\sources\modules\features2d\src\draw.cpp路径下,有drawMatches函数两个版本的源码。在这里贴出OpenCV中本其源码实现细节,来给想了解实现细节的小伙伴们参考。
void drawMatches( const Mat& img1,const vector<KeyPoint>& keypoints1,
const Mat& img2, constvector<KeyPoint>& keypoints2,
constvector<DMatch>& matches1to2, Mat& outImg,
const Scalar& matchColor,const Scalar& singlePointColor,
const vector<char>&matchesMask, int flags )
{
if( !matchesMask.empty() && matchesMask.size() !=matches1to2.size() )
CV_Error( CV_StsBadSize, "matchesMask must have the same size asmatches1to2" );
Mat outImg1, outImg2;
_prepareImgAndDrawKeypoints( img1, keypoints1, img2, keypoints2,
outImg, outImg1,outImg2, singlePointColor, flags );
// draw matches
for( size_t m = 0; m < matches1to2.size(); m++ )
{
if( matchesMask.empty() || matchesMask[m] )
{
int i1 = matches1to2[m].queryIdx;
int i2 = matches1to2[m].trainIdx;
CV_Assert(i1 >= 0 && i1 <static_cast<int>(keypoints1.size()));
CV_Assert(i2 >= 0 && i2 <static_cast<int>(keypoints2.size()));
const KeyPoint &kp1 = keypoints1[i1], &kp2 = keypoints2[i2];
_drawMatch( outImg, outImg1, outImg2, kp1, kp2, matchColor, flags );
}
}
}
void drawMatches( const Mat& img1,const vector<KeyPoint>& keypoints1,
const Mat& img2, constvector<KeyPoint>& keypoints2,
constvector<vector<DMatch> >& matches1to2, Mat& outImg,
const Scalar& matchColor,const Scalar& singlePointColor,
constvector<vector<char> >& matchesMask, int flags )
{
if( !matchesMask.empty() && matchesMask.size() !=matches1to2.size() )
CV_Error( CV_StsBadSize, "matchesMask must have the same size asmatches1to2" );
Mat outImg1, outImg2;
_prepareImgAndDrawKeypoints( img1, keypoints1, img2, keypoints2,
outImg, outImg1, outImg2,singlePointColor, flags );
// draw matches
for( size_t i = 0; i < matches1to2.size(); i++ )
{
for( size_t j = 0; j < matches1to2[i].size(); j++ )
{
int i1 = matches1to2[i][j].queryIdx;
int i2 = matches1to2[i][j].trainIdx;
if( matchesMask.empty() || matchesMask[i][j] )
{
const KeyPoint &kp1 =keypoints1[i1], &kp2 = keypoints2[i2];
_drawMatch( outImg,outImg1, outImg2, kp1, kp2, matchColor, flags );
}
}
}
}
}
BruteForceMatcher类源码分析
接下来,我们看看本文示例程序中会用到的BruteForceMatcher类的源码分析。在D:\Program Files(x86)\opencv\sources\modules\legacy\include\opencv2\legacy\legacy.hpp路径下,可以找到BruteForceMatcher类的定义。
template<class Distance>
class CV_EXPORTS BruteForceMatcher : publicBFMatcher
{
public:
BruteForceMatcher( Distance d = Distance() ) : BFMatcher(Distance::normType,false) {(void)d;}
virtual ~BruteForceMatcher() {}
};
其公共继承自BFMatcher类。而BFMatcher类位于D:\Program Files(x86)\opencv\sources\modules\features2d\include\opencv2\features2d\features2d.hpp
路径之下,我们一起看看其代码:
/*
*Brute-force descriptor matcher.
*
*For each descriptor in the first set, this matcher finds the closest
*descriptor in the second set by trying each one.
*
*For efficiency, BruteForceMatcher is templated on the distance metric.
*For float descriptors, a common choice would be cv::L2<float>.
*/
class CV_EXPORTS_W BFMatcher : publicDescriptorMatcher
{
public:
CV_WRAP BFMatcher( int normType=NORM_L2, bool crossCheck=false );
virtual ~BFMatcher() {}
virtual bool isMaskSupported() const { return true; }
virtual Ptr<DescriptorMatcher> clone(bool emptyTrainData=false ) const;
AlgorithmInfo* info() const;
protected:
virtual void knnMatchImpl( const Mat& queryDescriptors,vector<vector<DMatch> >& matches, int k,
const vector<Mat>& masks=vector<Mat>(), boolcompactResult=false );
virtual void radiusMatchImpl( const Mat& queryDescriptors,vector<vector<DMatch> >& matches, float maxDistance,
const vector<Mat>& masks=vector<Mat>(), boolcompactResult=false );
int normType;
bool crossCheck;
};
发现公共其继承自DescriptorMatcher类,再次进行溯源,在D:\Program Files(x86)\opencv\sources\modules\features2d\include\opencv2\features2d\features2d.hpp路径下找到DescriptorMatcher类的定义。
/****************************************************************************************\
* DescriptorMatcher *
\****************************************************************************************/
/*
*Abstract base class for matching two sets of descriptors.
*/
class CV_EXPORTS_W DescriptorMatcher :public Algorithm
{
public:
virtual ~DescriptorMatcher();
/*
* Add descriptors to train descriptor collection.
* descriptors Descriptors toadd. Each descriptors[i] is a descriptors set from one image.
*/
CV_WRAP virtual void add( const vector<Mat>& descriptors );
/*
* Get train descriptors collection.
*/
CV_WRAP const vector<Mat>& getTrainDescriptors() const;
/*
* Clear train descriptors collection.
*/
CV_WRAP virtual void clear();
/*
* Return true if there are not train descriptors in collection.
*/
CV_WRAP virtual bool empty() const;
/*
* Return true if the matcher supports mask in match methods.
*/
CV_WRAP virtual bool isMaskSupported() const = 0;
/*
* Train matcher (e.g. train flann index).
* In all methods to match the method train() is run every time beforematching.
* Some descriptor matchers (e.g. BruteForceMatcher) have emptyimplementation
* of this method, other matchers really train their inner structures
* (e.g. FlannBasedMatcher trains flann::Index). So nonemptyimplementation
* of train() should check the class object state and dotraing/retraining
* only if the state requires that (e.g. FlannBasedMatcher trainsflann::Index
* if it has not trained yet or if new descriptors have been added to thetrain
* collection).
*/
CV_WRAP virtual void train();
/*
* Group of methods to match descriptors from image pair.
* Method train() is run in this methods.
*/
// Find one best match for each query descriptor (if mask is empty).
CV_WRAP void match( const Mat& queryDescriptors, const Mat&trainDescriptors,
CV_OUT vector<DMatch>&matches, const Mat& mask=Mat() ) const;
// Find k best matches for each query descriptor (in increasing order ofdistances).
// compactResult is used when mask is not empty. If compactResult isfalse matches
// vector will have the same size as queryDescriptors rows. IfcompactResult is true
// matches vector will not contain matches for fully masked out querydescriptors.
CV_WRAP void knnMatch( const Mat& queryDescriptors, const Mat&trainDescriptors,
CV_OUTvector<vector<DMatch> >& matches, int k,
const Mat& mask=Mat(),bool compactResult=false ) const;
// Find best matches for each query descriptor which have distance lessthan
// maxDistance (in increasing order of distances).
void radiusMatch( const Mat& queryDescriptors, const Mat&trainDescriptors,
vector<vector<DMatch> >& matches, float maxDistance,
const Mat&mask=Mat(), bool compactResult=false ) const;
/*
* Group of methods to match descriptors from one image to image set.
* See description of similar methods for matching image pair above.
*/
CV_WRAP void match( const Mat& queryDescriptors, CV_OUTvector<DMatch>& matches,
constvector<Mat>& masks=vector<Mat>() );
CV_WRAP void knnMatch( const Mat& queryDescriptors, CV_OUTvector<vector<DMatch> >& matches, int k,
const vector<Mat>& masks=vector<Mat>(), boolcompactResult=false );
void radiusMatch( const Mat& queryDescriptors,vector<vector<DMatch> >& matches, float maxDistance,
const vector<Mat>&masks=vector<Mat>(), bool compactResult=false );
// Reads matcher object from a file node
virtual void read( const FileNode& );
// Writes matcher object to a file storage
virtual void write( FileStorage& ) const;
// Clone the matcher. If emptyTrainData is false the method create deepcopy of the object, i.e. copies
// both parameters and train data. If emptyTrainData is true the methodcreate object copy with current parameters
// but with empty train data.
virtual Ptr<DescriptorMatcher> clone( bool emptyTrainData=false )const = 0;
CV_WRAP static Ptr<DescriptorMatcher> create( const string&descriptorMatcherType );
protected:
/*
* Class to work with descriptors from several images as with one mergedmatrix.
* It is used e.g. in FlannBasedMatcher.
*/
class CV_EXPORTS DescriptorCollection
{
public:
DescriptorCollection();
DescriptorCollection( const DescriptorCollection& collection );
virtual ~DescriptorCollection();
// Vector of matrices "descriptors" will be merged to onematrix "mergedDescriptors" here.
void set( const vector<Mat>& descriptors );
virtual void clear();
const Mat& getDescriptors() const;
const Mat getDescriptor( int imgIdx, int localDescIdx ) const;
const Mat getDescriptor( int globalDescIdx ) const;
void getLocalIdx( int globalDescIdx, int& imgIdx, int&localDescIdx ) const;
int size() const;
protected:
Mat mergedDescriptors;
vector<int> startIdxs;
};
// In fact the matching is implemented only by the following two methods.These methods suppose
// that the class object has been trained already. Public match methodscall these methods
// after calling train().
virtual void knnMatchImpl( const Mat& queryDescriptors,vector<vector<DMatch> >& matches, int k,
const vector<Mat>&masks=vector<Mat>(), bool compactResult=false ) = 0;
virtual void radiusMatchImpl( const Mat& queryDescriptors,vector<vector<DMatch> >& matches, float maxDistance,
const vector<Mat>& masks=vector<Mat>(), bool compactResult=false) = 0;
static bool isPossibleMatch( const Mat& mask, int queryIdx, inttrainIdx );
static bool isMaskedOut( const vector<Mat>& masks, intqueryIdx );
static Mat clone_op( Mat m ) { return m.clone(); }
void checkMasks( const vector<Mat>& masks, intqueryDescriptorsCount ) const;
// Collection of descriptors from train images.
vector<Mat> trainDescCollection;
};
可以发现,DescriptorMatcher类和之前我们讲到FeatureDetector 类和DescriptorExtractor类一样,都是继承自他们“德高望重的祖先”Algorithm基类的。
而我们用BruteForceMatcher类时用到最多的match方法,是它从DescriptorMatcher类那里的“拿来主义”。定义如下:
//为各种描述符找到一个最佳的匹配(若掩膜为空)
CV_WRAP void match( const Mat& queryDescriptors, const Mat&trainDescriptors,
CV_OUTvector<DMatch>& matches, const Mat& mask=Mat() ) const;
2.3 SURF特征匹配示例程序
这个示例程序中,我们利用SurfDescriptorExtractor类进行特征向量的相关计算。
程序利用了SURF特征的特征描述办法,其操作封装在类SurfFeatureDetector中,利用类内的detect函数可以检测出SURF特征的关键点,保存在vector容器中。第二步利用SurfDescriptorExtractor类进行特征向量的相关计算。将之前的vector变量变成向量矩阵形式保存在Mat中。最后强行匹配两幅图像的特征向量,利用了类BruteForceMatcher中的函数match。
程序的核心思想是:
- 使用 DescriptorExtractor 接口来寻找关键点对应的特征向量。
- 使用 SurfDescriptorExtractor 以及它的函数 compute 来完成特定的计算。
- 使用 BruteForceMatcher 来匹配特征向量。
- 使用函数 drawMatches 来绘制检测到的匹配点。
关键点讲解:OpenCV2引入了一个通用类,用于提取不同的特征点描述子,计算如下:
//【4】计算描述子(特征向量)
SurfDescriptorExtractorextractor;
Matdescriptors1, descriptors2;
extractor.compute(srcImage1, keyPoint1, descriptors1 );
extractor.compute(srcImage2, keyPoints2, descriptors2 );
这里的结果为一个Mat矩阵,它的行数与特征点向量中元素个数是一致的。每行都是一个N维描述子的向量,比如SURF算法默认的描述子维度为64,该向量描绘了特征点周围的强度样式。两个特征点越相似,他们的特征向量也越靠近。这些描述子在图像匹配中尤其有用,如我们想匹配同一个场景中的两幅图像。首先,我们检测每幅图像中的特征,然后提取他们的描述子。第一幅图像中的每一个特征描述子向量都会与第二幅图中的描述子进行比较,得分最高的一对描述子,也就是两个向量的距离最近)将被视为那个特征的最佳匹配。该过程对于第一幅图像中的所有特征进行重复,这便是BruteForceMatcher中实行的最基本的策略。相关代码如下:
//【5】使用BruteForce进行匹配
//实例化一个匹配器
BruteForceMatcher<L2<float> > matcher;
std::vector<DMatch > matches;
//匹配两幅图中的描述子(descriptors)
matcher.match(descriptors1, descriptors2, matches );
BruteForceMatcher是由DescriptorMatcher派生出来的一个类,而DescriptorMatcher定义了不同的匹配策略的共同接口。调用match方法后,在其第三个参数输出一个cv::DMatch向量。于是我们定义一个std::vector<DMatch>类型的matches。
调用match方法之后,我们便可以使用drawMatches方法对匹配到的点进行绘制,并最终显示出来。相关代码如下:
//【6】绘制从两个图像中匹配出的关键点
MatimgMatches;
drawMatches(srcImage1, keyPoint1, srcImage2, keyPoints2, matches, imgMatches );//进行绘制
//【7】显示效果图
imshow("匹配图", imgMatches );
核心部分讲解完毕,下面我们一起来看看详细注释的示例程序的完全体。
//-----------------------------------【程序说明】----------------------------------------------
// 程序名称::《【OpenCV入门教程之十八】OpenCV仿射变换 & SURF特征点描述合辑》 博文配套源码 之 仿射变换
// 开发所用IDE版本:Visual Studio 2010
// 开发所用OpenCV版本: 2.4.9
// 2014年6月 Created by 浅墨
// 浅墨的微博:@浅墨_毛星云 http://weibo.com/1723155442
// 浅墨的知乎:http://www.zhihu.com/people/mao-xing-yun
// 浅墨的豆瓣:http://www.douban.com/people/53426472/
//----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
//-----------------------------------【头文件包含部分】---------------------------------------
// 描述:包含程序所依赖的头文件
//----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
#include "opencv2/core/core.hpp"
#include "opencv2/features2d/features2d.hpp"
#include "opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp"
#include <opencv2/nonfree/nonfree.hpp>
#include<opencv2/legacy/legacy.hpp>
#include <iostream>
//-----------------------------------【命名空间声明部分】--------------------------------------
// 描述:包含程序所使用的命名空间
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
using namespace cv;
using namespace std;
//-----------------------------------【全局函数声明部分】--------------------------------------
// 描述:全局函数的声明
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
static void ShowHelpText( );//输出帮助文字
//-----------------------------------【main( )函数】--------------------------------------------
// 描述:控制台应用程序的入口函数,我们的程序从这里开始执行
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
int main( )
{
//【0】改变console字体颜色
system("color 1A");
//【0】显示欢迎和帮助文字
ShowHelpText( );
//【1】载入素材图
Mat srcImage1 = imread("1.jpg",1);
Mat srcImage2 = imread("2.jpg",1);
if( !srcImage1.data || !srcImage2.data )
{ printf("读取图片错误,请确定目录下是否有imread函数指定的图片存在~! \n"); return false; }
//【2】使用SURF算子检测关键点
int minHessian = 700;//SURF算法中的hessian阈值
SurfFeatureDetector detector( minHessian );//定义一个SurfFeatureDetector(SURF) 特征检测类对象
std::vector<KeyPoint> keyPoint1, keyPoints2;//vector模板类,存放任意类型的动态数组
//【3】调用detect函数检测出SURF特征关键点,保存在vector容器中
detector.detect( srcImage1, keyPoint1 );
detector.detect( srcImage2, keyPoints2 );
//【4】计算描述符(特征向量)
SurfDescriptorExtractor extractor;
Mat descriptors1, descriptors2;
extractor.compute( srcImage1, keyPoint1, descriptors1 );
extractor.compute( srcImage2, keyPoints2, descriptors2 );
//【5】使用BruteForce进行匹配
// 实例化一个匹配器
BruteForceMatcher< L2<float> > matcher;
std::vector< DMatch > matches;
//匹配两幅图中的描述子(descriptors)
matcher.match( descriptors1, descriptors2, matches );
//【6】绘制从两个图像中匹配出的关键点
Mat imgMatches;
drawMatches( srcImage1, keyPoint1, srcImage2, keyPoints2, matches, imgMatches );//进行绘制
//【7】显示效果图
imshow("匹配图", imgMatches );
waitKey(0);
return 0;
}
//-----------------------------------【ShowHelpText( )函数】----------------------------------
// 描述:输出一些帮助信息
//----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
static void ShowHelpText()
{
//输出一些帮助信息
printf( "\n\n\n\t欢迎来到【SURF特征描述】示例程序~\n\n");
printf("\t当前使用的OpenCV版本为 OpenCV "CV_VERSION
"\n\n\t\t\t\t\t\t\t\t by浅墨\n\n\n" );
}
看看运行效果图。
两幅原始图:
效果图:
本篇文章的配套源代码请点击这里下载:
【浅墨OpenCV入门教程之十八】配套源代码之【仿射变换】 下载
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
【浅墨OpenCV入门教程之十八】配套源代码之【SURF特征点描述】 下载
OK,今天的内容大概就是这些,我们下篇文章见:)