数字信号处理Day1自制电子音乐
第一天的课程感觉比较简单,主要介绍Karplus-Strong Algorithm
给出方程 y[n]=αy[n−M]+x[n],
x[n]是输入,M是延迟,α是衰弱系数
我们要衰减D次,总的采样数就是D*M
下面是最直接的实现
关于x = x(:).';的语法是这样的,这是一个转置,但是是非共轭转置,如果是x',那么1+i就成了1-i
function y = ks_loop(x, alpha, D)
% Length of the output signal must be larger than the length of the input signal,
% that is, D must be larger than 1
if D < 1
error('Duration D must be greater than 1');
end
% Make sure the input is a row-vector
x = x(:).';
% Number of input samples
M = length(x);
% Number of output samples
size_y = D * M;
% Initialize with random input x
y = zeros(1, size_y);
y(1:M) = x;
for index = (M+1):size_y
y(index) = alpha * y(index - M);
end
y = y(:);
return
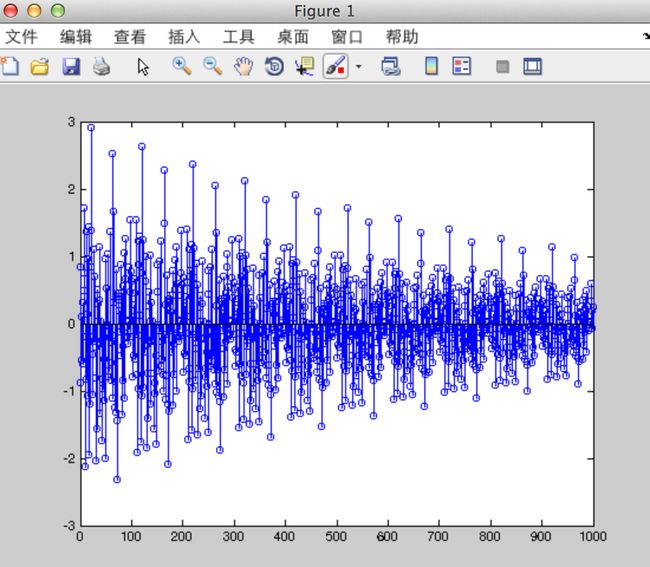
下面来测试一下
x = randn(100, 1);
stem(x);
y = ks_loop(x, 0.9, 10);
stem(y);
其实,你已经完成了KS算法
要知道,在matlab和octave这样的软件中,矩阵运算比单个运算速度要快很多,于是就有了优化的版本
function y = ks(x, alpha, D)
% Length of the output signal must be larger than the length of the input signal,
% that is, D must be larger than 1
if D < 1
error('Duration D must be greater than 1.');
end
% Make sure the input is a row-vector
x = x(:).';
% Number of input samples
M = length(x);
% number of output samples
size_y = D * M;
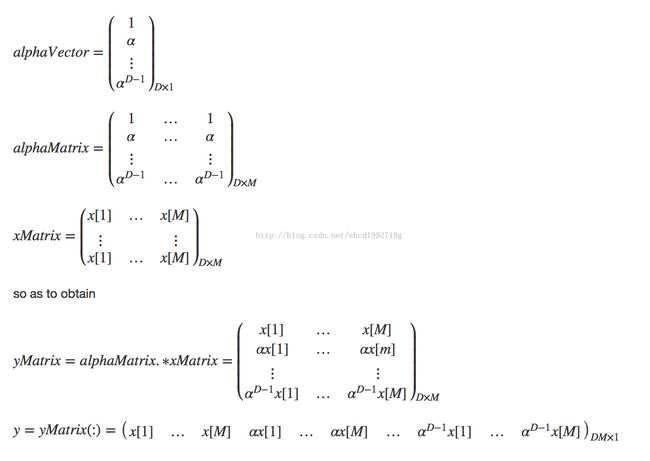
% Create a vector of the powers of alpha, [alpha^0 alpha^1 ....]
size_alphaVector = D;
alphaVector = (alpha*ones(size_alphaVector,1)).^((0:(size_alphaVector-1))');
% Create a matrix with M columns, each being the vector of the powers of alpha
alphaMatrix = repmat(alphaVector, 1, M);
% Create a matrix with D rows filled by the input signal x
xMatrix = repmat(x, D, 1);
% Multipliy the two, and take the transpose so we can read it out
% column-by-column
yMatrix = (alphaMatrix .* xMatrix).';
% Read out the output column by columnn
y = yMatrix(:);
return
在matlab中,你可以用 soundsc(y, FS)来播放音乐
y是我们的采样数据,FS是频率
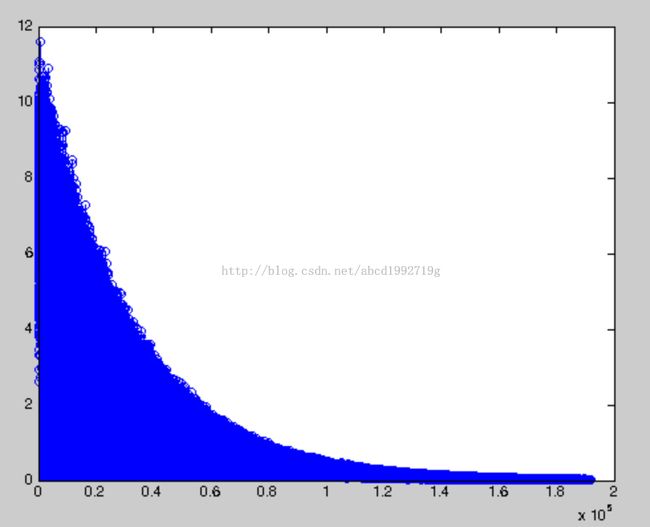
下面这个例子可以播放opening chord of Hard day's night 开头的音乐,太神奇了
因为牵扯到音乐的相关知识,一些参数就不大懂,只画出了最后的采样图看看
clear all
close all
clc
% Parameters:
%
% - Fs : sampling frequency
% - F0 : frequency of the notes forming chord
% - gain : gains of individual notes in the chord
% - duration : duration of the chord in second
% - alpha : attenuation in KS algorithm
Fs = 48000;
% D2, D3, F3, G3, F4, A4, C5, G5
F0 = 440*[2^-(31/12); 2^-(19/12); 2^-(16/12); 2^(-14/12); 2^-(4/12); 1; 2^(3/12); 2^(10/12)];
gain = [1.2 3.0 1.0 2.2 1.0 1.0 1.0 3.5];
duration = 4;
alpha = 0.9785;
% Number of samples in the chord
nbsample_chord = Fs*duration;
% This is used to correct alpha later, so that all the notes decay together
% (with the same decay rate)
first_duration = ceil(nbsample_chord / round(Fs/F0(1)));
% Initialization
chord = zeros(nbsample_chord, 1);
for i = 1:length(F0)
% Get M and duration parameter
current_M = round(Fs/F0(i));
current_duration = ceil(nbsample_chord/current_M);
% Correct current alpha so that all the notes decay together (with the
% same decay rate)
current_alpha = alpha^(first_duration/current_duration);
% Let Paul's high D on the bass ring a bit longer
if i == 2
current_alpha = current_alpha^.8;
end
% Generate input and output of KS algorithm
x = rand(current_M, 1);
y = ks(x, current_alpha, current_duration);
y = y(1:nbsample_chord);
% Construct the chord by adding the generated note (with the
% appropriate gain)
chord = chord + gain(i) * y;
end
% Play output
soundsc(chord, Fs);