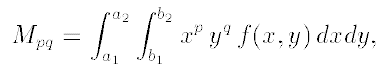图像处理之计算二值连通区域的质心
图像处理之计算二值连通区域的质心
一:几何距(Geometric Moments)知识与质心寻找原理
1. Image Moments是图像处理中非常有用的算法,可以用来计算区域图像
的质心,方向等几何特性,同时Mpq的高阶具有旋转不变性,可以用来
实现图像比较分类,正是因为Moments有这些特性,很多手绘油画效果
也会基于该算法来模拟实现。它的数学表达为:
它的低阶M00,M01, M10可以用来计算质心,中心化以后M11,M02,M20
可以用来计算区域的方向/角度
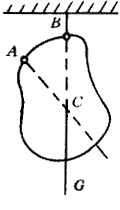
2. 什么是质心
就是通过该点,区域达到一种质量上的平衡状态,可能物理学上讲的比较多,简单点的
说就是规则几何物体的中心,不规则的可以通过挂绳子的方法来寻找。
二:算法流程
1. 输入图像转换为二值图像
2. 通过连通组件标记算法找到所有的连通区域,并分别标记
3. 对每个连通区域运用计算几何距算法得到质心
4. 用不同颜色绘制连通区域与质心,输出处理后图像
三:算法效果
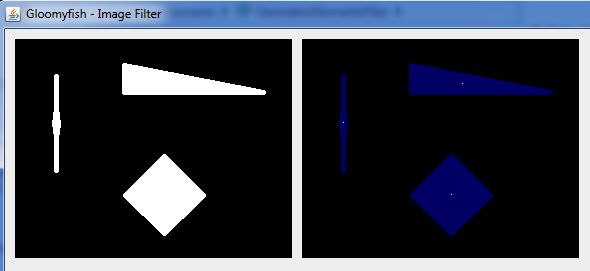
左边为原图, 右边蓝色为连通组件标记算法处理以后结果,白色点为质心
四:关键代码解析
1. 计算几何距算法代码
doublem00 = moments(pixels, width, height, 0, 0);
doublexCr = moments(pixels, width, height, 1, 0) / m00;// row
doubleyCr = moments(pixels, width, height, 0, 1) / m00;// column
return new double[]{xCr, yCr};
2. 连通组件标记算法代码参见这里:
http://blog.csdn.net/jia20003/article/details/7628371
五:程序源代码
package com.gloomyfish.image.moments;
import java.awt.image.BufferedImage;
import com.gloomyfish.filter.study.AbstractBufferedImageOp;
import com.gloomyfish.rice.analysis.FastConnectedComponentLabelAlg;
// Geometric Moments Computing
// low-order moments - calculate the center point
// second-order moments - get angle size
// projection -
public class GeometricMomentsFilter extends AbstractBufferedImageOp {
@Override
public BufferedImage filter(BufferedImage src, BufferedImage dest) {
int width = src.getWidth();
int height = src.getHeight();
if ( dest == null )
dest = createCompatibleDestImage( src, null );
// first step - make it as binary image output pixel
int[] inPixels = new int[width*height];
int[] outPixels = new int[width*height];
getRGB( src, 0, 0, width, height, inPixels );
int index = 0;
for(int row=0; row<height; row++) {
int tr = 0;
for(int col=0; col<width; col++) {
index = row * width + col;
tr = (inPixels[index] >> 16) & 0xff;
if(tr > 127)
{
outPixels[index] = 1;
}
else
{
outPixels[index] = 0;
}
}
}
// second step, connected component labeling algorithm
FastConnectedComponentLabelAlg ccLabelAlg = new FastConnectedComponentLabelAlg();
ccLabelAlg.setBgColor(0);
int[] labels = ccLabelAlg.doLabel(outPixels, width, height);
int max = 0;
for(int i=0; i<labels.length; i++)
{
if(max < labels[i])
{
System.out.println("Label Index = " + labels[i]);
max = labels[i];
}
}
// third step, calculate center point of each region area(connected component)
int[] input = new int[labels.length];
GeometricMomentsAlg momentsAlg = new GeometricMomentsAlg();
momentsAlg.setBACKGROUND(0);
double[][] labelCenterPos = new double[max][2];
for(int i=1; i<=max; i++)
{
for(int p=0; p<input.length; p++)
{
if(labels[p] == i)
{
input[p] = labels[p];
}
else
{
input[p] = 0;
}
}
labelCenterPos[i-1] = momentsAlg.getGeometricCenterCoordinate(input, width, height);
}
// render the each connected component center position
for(int row=0; row<height; row++) {
for(int col=0; col<width; col++) {
index = row * width + col;
if(labels[index] == 0)
{
outPixels[index] = (255 << 24) | (0 << 16) | (0 << 8) | 0; // make it as black for background
}
else
{
outPixels[index] = (255 << 24) | (0 << 16) | (0 << 8) | 100; // make it as blue for each region area
}
}
}
// make it as white color for each center position
for(int i=0; i<max; i++)
{
int crow = (int)labelCenterPos[i][0];
int ccol = (int)labelCenterPos[i][1];
index = crow * width + ccol;
outPixels[index] = (255 << 24) | (255 << 16) | (255 << 8) | 255;
}
setRGB( dest, 0, 0, width, height, outPixels );
return dest;
}
}
Moment算法代码:
package com.gloomyfish.image.moments;
public class GeometricMomentsAlg {
private int BACKGROUND = 0; // background color
private int labelIndex = 1;
public GeometricMomentsAlg()
{
System.out.println("Geometric Moments Algorithm Initialziation...");
}
public int getLabelIndex() {
return labelIndex;
}
public void setLabelIndex(int labelIndex) {
this.labelIndex = labelIndex;
}
public int getBACKGROUND() {
return BACKGROUND;
}
public void setBACKGROUND(int bACKGROUND) {
BACKGROUND = bACKGROUND;
}
public double[] getGeometricCenterCoordinate(int[] pixels, int width, int height)
{
double m00 = moments(pixels, width, height, 0, 0);
double xCr = moments(pixels, width, height, 1, 0) / m00; // row
double yCr = moments(pixels, width, height, 0, 1) / m00; // column
return new double[]{xCr, yCr};
}
public double moments(int[] pixels, int width, int height, int p, int q)
{
double mpq = 0.0;
int index = 0;
for(int row=0; row<height; row++)
{
for(int col=0; col<width; col++)
{
index = row * width + col;
if(pixels[index] == BACKGROUND) continue;
mpq += Math.pow(row, p) * Math.pow(col, q);
}
}
return mpq;
}
public double centralMoments(int[] pixel, int width, int height, int p, int q)
{
double m00 = moments(pixel, width, height, 0, 0);
double xCr = moments(pixel, width, height, 1, 0) / m00;
double yCr = moments(pixel, width, height, 0, 1) / m00;
double cMpq = 0.0;
int index = 0;
for(int row=0; row<height; row++)
{
for(int col=0; col<width; col++)
{
index = row * width + col;
if(pixel[index] == BACKGROUND) continue;
cMpq += Math.pow(row - xCr, p) * Math.pow(col - yCr, q);
}
}
return cMpq;
}
public double normalCentralMoments(int[] pixel, int width, int height, int p, int q)
{
double m00 = moments(pixel, width, height, 0, 0);
double normal = Math.pow(m00, ((double)(p+q+2))/2.0d);
return centralMoments(pixel, width, height, p, q)/normal;
}
}
觉得不错请支持一下