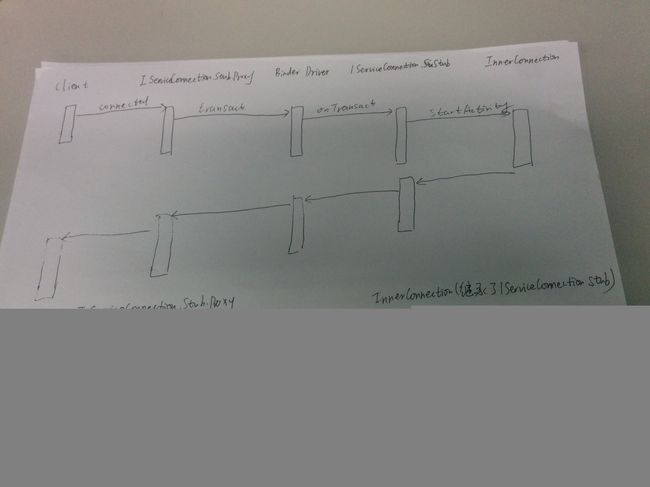
Android Service组件在进程内绑定(bindService)过程
本文参考Android应用程序绑定服务(bindService)的过程源代码分析http://blog.csdn.net/luoshengyang/article/details/6745181和《Android系统源代码情景分析》,作者罗升阳
一、Android Service组件在进程内绑定(bindService)过程
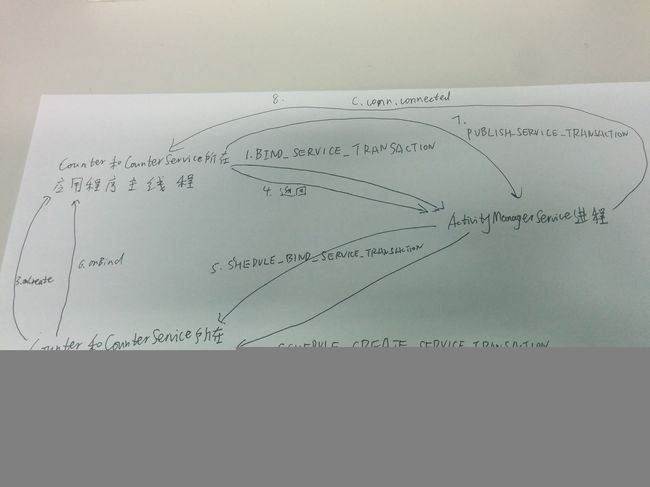
0、总图流程图如下:
1、Counter和CounterService所在应用程序主线程向ActivityManagerService进程发送BIND_SERVICE_TARNSATION
如下图:
如图:第一步
~/Android/frameworks/base/core/java/android/app
----ActivityManagerNative.java
class ActivityManagerProxy implements IActivityManager
{
......
public int bindService(IApplicationThread caller, IBinder token,
Intent service, String resolvedType, IServiceConnection connection,
int flags) throws RemoteException {
Parcel data = Parcel.obtain();
Parcel reply = Parcel.obtain();
data.writeInterfaceToken(IActivityManager.descriptor);
data.writeStrongBinder(caller != null ? caller.asBinder() : null);
data.writeStrongBinder(token);
service.writeToParcel(data, 0);
data.writeString(resolvedType);
data.writeStrongBinder(connection.asBinder());
data.writeInt(flags);
mRemote.transact(BIND_SERVICE_TRANSACTION, data, reply, 0);
reply.readException();
int res = reply.readInt();
data.recycle();
reply.recycle();
return res;
}
......
}
其中connection.asBinder()为InnerConnection对象。还有intent,主要关注这两个参数。
如图:第二步,省略binder_transaction传输过程,因为上面已经分析过了。
如图:第三步
~/Android/frameworks/base/core/java/android/app
----ActivityManagerNative.java
public abstract class ActivityManagerNative extends Binder implements IActivityManager
{
......
public boolean onTransact(int code, Parcel data, Parcel reply, int flags)
throws RemoteException {
switch (code) {
case BIND_SERVICE_TRANSACTION: {
data.enforceInterface(IActivityManager.descriptor);
IBinder b = data.readStrongBinder();
IApplicationThread app = ApplicationThreadNative.asInterface(b);
IBinder token = data.readStrongBinder();
Intent service = Intent.CREATOR.createFromParcel(data);
String resolvedType = data.readString();
b = data.readStrongBinder();
int fl = data.readInt();
IServiceConnection conn = IServiceConnection.Stub.asInterface(b);
int res = bindService(app, token, service, resolvedType, conn, fl);
reply.writeNoException();
reply.writeInt(res);
return true;
}
.......
} 其中conn为上图中IServiceConnection.Stub.Proxy对象,引用了
InnerConnection对象。
还有intent,主要关注这两个参数。
如图:第四步
~/Android/frameworks/base/services/java/com/android/server/am
----ActivityManagerService.java
public final class ActivityManagerService extends ActivityManagerNative
implements Watchdog.Monitor, BatteryStatsImpl.BatteryCallback {
......
public int bindService(IApplicationThread caller, IBinder token,
Intent service, String resolvedType,
IServiceConnection connection, int flags) {
......
synchronized(this) {
......
final ProcessRecord callerApp = getRecordForAppLocked(caller);
......
ActivityRecord activity = null;
if (token != null) {
int aindex = mMainStack.indexOfTokenLocked(token);
......
activity = (ActivityRecord)mMainStack.mHistory.get(aindex);
}
......
ServiceLookupResult res =
retrieveServiceLocked(service, resolvedType,
Binder.getCallingPid(), Binder.getCallingUid());
......
ServiceRecord s = res.record;
final long origId = Binder.clearCallingIdentity();
......
AppBindRecord b = s.retrieveAppBindingLocked(service, callerApp);
ConnectionRecord c = new ConnectionRecord(b, activity,
connection, flags, clientLabel, clientIntent);
IBinder binder = connection.asBinder();
ArrayList<ConnectionRecord> clist = s.connections.get(binder);
if (clist == null) {
clist = new ArrayList<ConnectionRecord>();
s.connections.put(binder, clist);
}
clist.add(c);
.......
if ((flags&Context.BIND_AUTO_CREATE) != 0) {
......
if (!bringUpServiceLocked(s, service.getFlags(), false)) {
return 0;
}
}
......
}
return 1;
}
......
}
主要做了以下几件事:
(1)创建ServiceRecord对象,并初始化它bindings变量,这个变量主要用来描述传递过来的intent。
(2)初始化它connections变量,这个变量主要用来描述传递过来的IServiceConnection.Stub.Proxy对象。
(3)ActivityManagerService进程向Counter和CounterService子线程发送SCHEDULE_CREATE_SERVICE_TRANSACTION。
2、ActivityManagerService进程向Counter和CounterService子线程发送SCHEDULE_CREATE_SERVICE_TRANSACTION
如总图中的第2步,过程可参考Android Activity组件的启动过程http://blog.csdn.net/jltxgcy/article/details/35984557中的第2步。
3、在Counter和CounterService主线程创建CounterService,并调用了它的onCreate方法
需要说明的一点是:
mServices.put(data.token, service);把刚创建的CounterService加入到mServices中了。
4、返回到ActivityManagerService进程
5、ActivityManagerService进程向Counter和CounterService子线程发送SCHEDULE_BIND_SERVICE_TRANSACTION
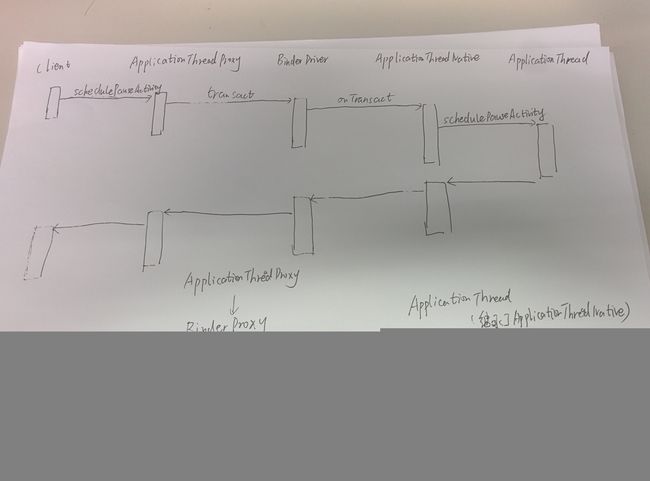
如图:第一步
~/Android/frameworks/base/core/java/android/app
----ApplicationThreadNative.java,ApplicationThreadProxy类
class ApplicationThreadProxy implements IApplicationThread {
......
public final void scheduleBindService(IBinder token, Intent intent, boolean rebind)
throws RemoteException {
Parcel data = Parcel.obtain();
data.writeInterfaceToken(IApplicationThread.descriptor);
data.writeStrongBinder(token);
intent.writeToParcel(data, 0);
data.writeInt(rebind ? 1 : 0);
mRemote.transact(SCHEDULE_BIND_SERVICE_TRANSACTION, data, null,
IBinder.FLAG_ONEWAY);
data.recycle();
}
......
}
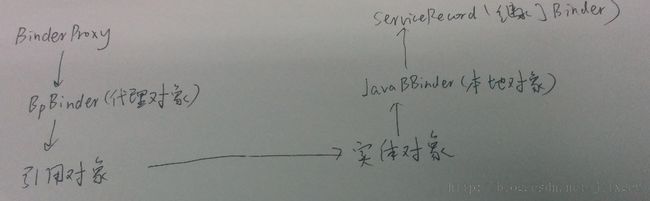
其中token为ServiceRecord对象,如下图,还有intent,主要关注这两个参数。
图1
如图:第二步,省略binder_transaction传输过程,因为上面已经分析过了。
如图:第三步
~/Android/frameworks/base/core/java/android/app
----ApplicationThreadNative.java
public abstract class ApplicationThreadNative extends Binder
implements IApplicationThread {
........
public boolean onTransact(int code, Parcel data, Parcel reply, int flags)
throws RemoteException {
switch (code) {
case SCHEDULE_BIND_SERVICE_TRANSACTION: {
data.enforceInterface(IApplicationThread.descriptor);
IBinder token = data.readStrongBinder();
Intent intent = Intent.CREATOR.createFromParcel(data);
boolean rebind = data.readInt() != 0;
scheduleBindService(token, intent, rebind);
return true;
}
.......
} 其中token为上图中的BinderProxy对象,引用了ServiceRecord。
还有intent,主要关注这两个参数。
如图:第四步
~/Android/frameworks/base/core/java/android/app
----ActivityThread.java
public final class ActivityThread {
......
public final void scheduleBindService(IBinder token, Intent intent,
boolean rebind) {
BindServiceData s = new BindServiceData();
s.token = token;
s.intent = intent;
s.rebind = rebind;
queueOrSendMessage(H.BIND_SERVICE, s);
}
......
}
6、在Counter和CounterService主线程绑定CounterService,并调用了它的onBind方法
主要做了以下几件事:
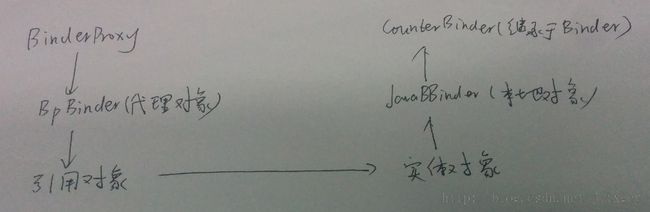
(1)获取了刚刚创建的service,并且调用onBind获取了CounterBinder对象,如下图:
图2
(2)Counter和CounterService主线程向ServiceManager进程发送PUBLISH_SERVICE_TRANSACTION
代码如下:
~/Android/frameworks/base/core/java/android/app
----ActivityThread.java
public final class ActivityThread {
......
private final void handleBindService(BindServiceData data) {
Service s = mServices.get(data.token);
if (s != null) {
try {
data.intent.setExtrasClassLoader(s.getClassLoader());
try {
if (!data.rebind) {
IBinder binder = s.onBind(data.intent);
ActivityManagerNative.getDefault().publishService(
data.token, data.intent, binder);
} else {
......
}
......
} catch (RemoteException ex) {
}
} catch (Exception e) {
......
}
}
}
......
}
public class CounterService extends Service implements ICounterService {
......
private final IBinder binder = new CounterBinder();
public class CounterBinder extends Binder {
public CounterService getService() {
return CounterService.this;
}
}
@Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
return binder;
}
......
}
7、Counter和CounterService主线程向ServiceManager进程发送PUBLISH_SERVICE_TRANSACTION
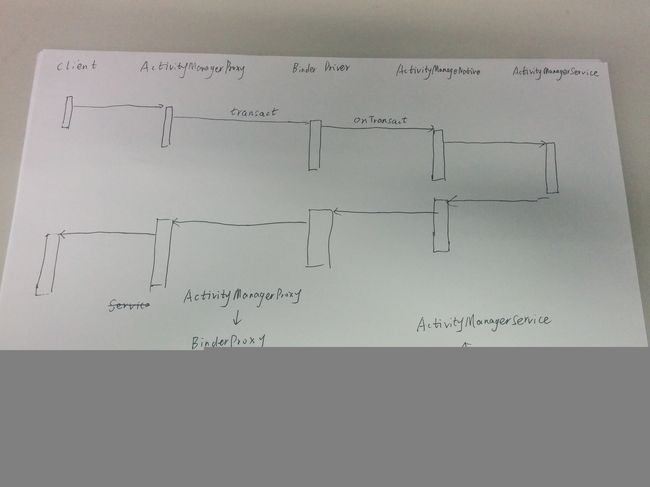
如图:第一步
~/Android/frameworks/base/core/java/android/app
----ActivityManagerNative.java
class ActivityManagerProxy implements IActivityManager
{
......
public void publishService(IBinder token,
Intent intent, IBinder service) throws RemoteException {
Parcel data = Parcel.obtain();
Parcel reply = Parcel.obtain();
data.writeInterfaceToken(IActivityManager.descriptor);
data.writeStrongBinder(token);
intent.writeToParcel(data, 0);
data.writeStrongBinder(service);
mRemote.transact(PUBLISH_SERVICE_TRANSACTION, data, reply, 0);
reply.readException();
data.recycle();
reply.recycle();
}
......
}
其中service为刚刚创建的 CounterBinder对象,如图2。其中token为其中token为上图中的BinderProxy对象,引用了ServiceRecord对象。如图1。
如图:第二步,省略binder_transaction传输过程,因为上面已经分析过了。
如图:第三步
~/Android/frameworks/base/core/java/android/app
----ActivityManagerNative.java
public abstract class ActivityManagerNative extends Binder implements IActivityManager
{
......
public boolean onTransact(int code, Parcel data, Parcel reply, int flags)
throws RemoteException {
switch (code) {
case PUBLISH_SERVICE_TRANSACTION: {
data.enforceInterface(IActivityManager.descriptor);
IBinder token = data.readStrongBinder();
Intent intent = Intent.CREATOR.createFromParcel(data);
IBinder service = data.readStrongBinder();
publishService(token, intent, service);
reply.writeNoException();
return true;
}
.......
} 其中service为BinderProxy对象,引用了CounterBinder对象,如图2。token为
ServiceRecord对象,如图1。
如图:第四步
~/Android/frameworks/base/services/java/com/android/server/am
----ActivityManagerService.java
public final class ActivityManagerService extends ActivityManagerNative
implements Watchdog.Monitor, BatteryStatsImpl.BatteryCallback {
......
public void publishService(IBinder token, Intent intent, IBinder service) {
......
synchronized(this) {
......
ServiceRecord r = (ServiceRecord)token;
......
......
if (r != null) {
Intent.FilterComparison filter
= new Intent.FilterComparison(intent);
IntentBindRecord b = r.bindings.get(filter);
if (b != null && !b.received) {
b.binder = service;
b.requested = true;
b.received = true;
if (r.connections.size() > 0) {
Iterator<ArrayList<ConnectionRecord>> it
= r.connections.values().iterator();
while (it.hasNext()) {
ArrayList<ConnectionRecord> clist = it.next();
for (int i=0; i<clist.size(); i++) {
ConnectionRecord c = clist.get(i);
......
try {
c.conn.connected(r.name, service);
} catch (Exception e) {
......
}
}
}
}
}
......
}
}
}
......
}
主要是获取ServiceRecord里面的ConnectionRecord对象,它的成员变量conn为 IServiceConnection.Stub.Proxy对象,引用了 InnerConnection对象。调用connected函数。
8、ActivityManagerS ervice进程向Counter和CounterService主线程发送connected命令
相关代码,请参考http://grepcode.com/file_/repository.grepcode.com/java/ext/com.google.android/android/2.0_r1/android/app/IServiceConnection.java/?v=source
经过一系列的传递,最终执行:
~/Android/frameworks/base/core/java/android/app
----LoadedApk.java
final class LoadedApk {
......
static final class ServiceDispatcher {
......
private static class InnerConnection extends IServiceConnection.Stub {
......
public void connected(ComponentName name, IBinder service) throws RemoteException {
LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher sd = mDispatcher.get();
if (sd != null) {
sd.connected(name, service);
}
}
......
}
......
}
......
}
由于执行了进程间通信,此时service为CounterBinder对象,如图2。所以可以向下转型。
public class MainActivity extends Activity implements OnClickListener {
......
private ServiceConnection serviceConnection = new ServiceConnection() {
public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName className, IBinder service) {
counterService = ((CounterService.CounterBinder)service).getService();
Log.i(LOG_TAG, "Counter Service Connected");
}
......
};
......
}