launcher修改--launcher架构解析
要想做好launcher,对其基本的架构了解是必须的,在这篇文章里,简单的介绍下launcher中类的构成和架构,首先,这篇文章中很多资源均从互联网中获得,感谢网友们的无私奉献,大家都共享,进步才会更快。
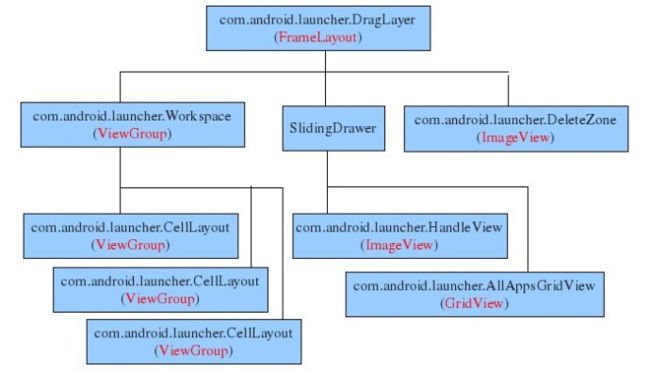
第一步,先看两张从网上找来的launcher的架构图。
第二张:
通过这两张图,简单的说下:
整个launcher,准确来说应该是homescreen更为合适,是一个包含三个child view的FrameLayout(com.android.launcher.DragLayer)。
第一个child就是桌面com.android.launcher.Workspace。这个桌面又包含5个child。每个child就对应一个桌 面。这就是你在Android上看到的五个桌面。每个桌面上可以放置下列对象:应用快捷方式,appwidget和folder。(第一张图应该是以前版本的,在2.2以前的版本应该是只有三个桌面,在2.3中,有五个桌面)
第二个child是一个SlidingDrawer控件,这个控件由两个子控件组成。一个是 com.android.launcher.HandleView,就是Android桌面下方的把手,当点击这个把手时,另一个子控 件,com.android.launcher.AllAppsGridView就会弹出,这个子控件列出系统中当前安装的所有类型为 category.launcher的Activity。
第三个child是com.android.launcher.DeleteZone。当用户在桌面上长按一个widget时,把手位置就会出现一个垃圾桶形状的控件,就是这个控件。(其实在2.2以后的版本中,在左下方和右下方添加了页面标记,来告诉用户当前在哪个桌面,其代码在launcher.xml代码中,
<ImageView
android:id="@+id/previous_screen"
android:layout_width="93dip"
android:layout_height="@dimen/button_bar_height"
android:layout_gravity="bottom|left"
android:layout_marginLeft="6dip"
android:scaleType="center"
android:src="@drawable/home_arrows_left"
android:onClick="previousScreen"
android:focusable="true"
android:clickable="true" />
<ImageView
android:id="@+id/next_screen"
android:layout_width="93dip"
android:layout_height="@dimen/button_bar_height"
android:layout_gravity="bottom|right"
android:layout_marginRight="6dip"
android:scaleType="center"
android:src="@drawable/home_arrows_right"
android:onClick="nextScreen"
android:focusable="true"
android:clickable="true" />下面就是launcher中主要类的简介:
AddAdapter:添加桌面元素的适配器, 维护了live fold , widget , shortcut , wallpaper 4个ListItem , 长按桌面会显示该列表
AllAppsGridView:Icon列表的的主界面,继承gridView。
ApplicationInfo:一个可启动的应用。
ApplicationsAdapter:gridview的adapter。
BubbleTextView:一个定制了的textview,主要用于显示应用图标。
DeleteZone:luancher的删除区域,继承ImageView。在平时是出于隐藏状态,在将item长按拖动的时候会显示出来,如果将item拖动到删除框位置时会删除item。 DeleteZone实现了DropTarget和DragListener两个接口。
DragController:拖动控制接口。为Drag定义的一个接口。包含一个接口,两个方法和两个静态常量。接口为DragListener(包含onDragStart(),onDragEnd()两个函数),onDragStart()是在刚开始拖动的时候被调用,onDragEnd()是在拖动完成时被调用。在launcher中典型的应用是DeleteZone,在长按拖动item时调用onDragStart()显示,在拖动结束的时候onDragEnd()隐藏。两个函数包括startDrag()和setDragItemInfo().startDrag()用于在拖动是传递要拖动的item的信息以及拖动的方式,setDragItemInfo()用于传递item的参数信息(包括位置以及大小)。两个常量为DRAG_ACTION_MOVE,DRAG_ACTION_COPY来标识拖动的方式,DRAG_ACTION_MOVE为移动,表示在拖动的时候需要删除原来的item,DRAG_ACTION_COPY为复制型的拖动,表示保留被拖动的item。
DragLayer:整个launcher的父节点,继承FrameLayout,实现接口DrayController,是内部支持拖拽的viewgroup。DragLayer实际上也是一个抽象的界面,用来处理拖动和对事件进行初步处理然后按情况分发下去,角色是一个controller。它首先用onInterceptTouchEvent(MotionEvent)来拦截所有的touch事件,如果是长按item拖动的话不把事件传下去,直接交由onTouchEvent()处理,这样就可以实现item的移动了,如果不是拖动item的话就把事件传到目标view,交有目标view的事件处理函数做相应处理。如过有要对事件的特殊需求的话可以修改onInterceptTouchEvent(MotionEvent)来实现所需要的功能。
DragSource:拖动源接口,定义了void onDropCompleted(View target, boolean success)。
DropTarget:拖动目标,定义很多拖动过程需要的方法:onDrop,onDragEnter,onDragOver,onDragExit,acceptDrop。
FastBitmapDrawable:工具
Folder:Icons的集合
FolderIcon:出现在workspace的icon 代表了一个folder
FolderInfo: ItemInfo子类
HandleView:launcher抽屉的开关,不过在android2.2已经没用抽屉了。
InstallShortcutReceiver,UninstallShortcutReceiver:一个broadcastrecier
ItemInfo:代表Launcher中一个Item(例如folder)对item的抽象,所有类型item的父类,item包含的属性有id(标识item的id),cellX(在横向位置上的位置,从0开始),cellY(在纵向位置上的位置,从0开始) ,spanX(在横向位置上所占的单位格),spanY(在纵向位置上所占的单位格),screen(在workspace的第几屏,从0开始),itemType(item的类型,有widget,search,application等),container(item所在的)。
Launcher:整个launcher的程序的入口,代码量最大的一个文件。
LauncherApplication:在VM中设置参数
LauncherAppWidgetHost,LauncherAppWidgetHostView,:Widget相关
LauncherModel: MVC中的M,里面有许多封装的对数据库的操作。包含几个线程,其中最主要的是ApplicationsLoader和DesktopItemsLoader。ApplicationsLoader在加载所有应用程序时使用,DesktopItemsLoader在加载workspace的时候使用。其他的函数就是对数据库的封装,比如在删除,替换,添加程序的时候做更新数据库和UI的工作。
LauncherProvider:launcher的数据库,一个contentprovider里面存储了桌面的item的信息。在创建数据库的时候会loadFavorites(db)方法,loadFavorites()会解析xml目录下的default_workspace.xml文件,把其中的内容读出来写到数据库中,这样就做到了桌面的预制。
LauncherSettings:设置相关的工具,数据库项的字符串定义,另外在这里定义了container的类型,还有itemType的定义,除此还有一些特殊的widget(如search,clock的定义等)的类型定义。
LiveFolder,LiveFolderAdapter,LiveFolderIcon,LiveFolderInfo: livefolder相关
Search: 搜索
UserFolder,UserFolderInfo:文件夹包含applications,shortcuts
Utilities:小工具
WallpaperChooser:选择wallpaper的activity
Workspace:整个界面layout,几个窗口就是他下面的子节点。widget : 代表启动的widget实例,例如搜索
在桌面中,有一下四种类型的对象:
1. ITEM_SHORTCUT,应用快捷方式,对应实现布局文件R.layout.application
2. ITEM_APPWIDGET,app widget 桌面组件
3. ITEM_LIVE_FOLDER,文件夹
--UserFolderInfo 对应实现布局文件R.layout.folder_icon
--LiveFolderInfo 对应实现布局文件R.layout.live_folder_icon
4. ITEM_WALLPAPER,墙纸。
下面,我们详细的来说一下launcher里面的详细功能:
1.DragLayer--DragLayer继承FrameLayout,并在此基础上组合了DragController实现拖放功能,DragLayer主要监听下面两个用户事件onInterceptTouchEvent和onTouchEvent
并交给DragController进行处理,DragController根据是否在拖放中等信息控制控件拖放过程处理。DragLayer 是Launcher这个activity的顶层view,其实在Launcher2这个应用只有Laucher.java这么一个activity。
2.DeleteZone--
<com.android.launcher2.DeleteZone
android:id="@+id/delete_zone"
android:layout_width="@dimen/delete_zone_size"
android:layout_height="@dimen/delete_zone_size"
android:paddingTop="@dimen/delete_zone_padding"
android:layout_gravity="bottom|center_horizontal"
android:scaleType="center"
android:src="@drawable/delete_zone_selector"
android:visibility="invisible"
launcher:direction="horizontal"
/>
在launcher.xml中,可以发现,DeleteZone默认是不显示的android:visibility="invisible",但是我们每次开始拖放图标的时候DeleteZone就显示了,这个功能是如何实现的呢?在代码中可以发现DeleteZone实现了DragController.DragListener接口,
public class DeleteZone extends ImageView implements DropTarget, DragController.DragListener
DragListener提供两个接口方法,
onDragStart:隐藏把手,显示DeleteZone
onDragEnd:显示把手,隐藏DeleteZone
在DeleteZone中,看一下代码:
public void onDragStart(DragSource source, Object info, int dragAction) {
final ItemInfo item = (ItemInfo) info;
if (item != null) {
mTrashMode = true;
createAnimations();
final int[] location = mLocation;
getLocationOnScreen(location);
mRegion.set(location[0], location[1], location[0] + mRight - mLeft,
location[1] + mBottom - mTop);
mDragController.setDeleteRegion(mRegion);
mTransition.resetTransition();
startAnimation(mInAnimation);
mHandle.startAnimation(mHandleOutAnimation);
setVisibility(VISIBLE);
}
}
public void onDragEnd() {
if (mTrashMode) {
mTrashMode = false;
mDragController.setDeleteRegion(null);
startAnimation(mOutAnimation);
mHandle.startAnimation(mHandleInAnimation);
setVisibility(GONE);
}
}
分别在开始DragController开始拖放和结束拖放的时候被调用.
另外DeleteZone实现了DropTarget接口的onDrop方法
public void onDrop(DragSource source, int x, int y, int xOffset, int yOffset,
DragView dragView, Object dragInfo) {
final ItemInfo item = (ItemInfo) dragInfo;
if (item.container == -1) return;
if (item.container == LauncherSettings.Favorites.CONTAINER_DESKTOP) {
if (item instanceof LauncherAppWidgetInfo) {
mLauncher.removeAppWidget((LauncherAppWidgetInfo) item);
}
} else {
if (source instanceof UserFolder) {
final UserFolder userFolder = (UserFolder) source;
final UserFolderInfo userFolderInfo = (UserFolderInfo) userFolder.getInfo();
// Item must be a ShortcutInfo otherwise it couldn't have been in the folder
// in the first place.
userFolderInfo.remove((ShortcutInfo)item);
}
}
if (item instanceof UserFolderInfo) {
final UserFolderInfo userFolderInfo = (UserFolderInfo)item;
LauncherModel.deleteUserFolderContentsFromDatabase(mLauncher, userFolderInfo);
mLauncher.removeFolder(userFolderInfo);
} else if (item instanceof LauncherAppWidgetInfo) {
final LauncherAppWidgetInfo launcherAppWidgetInfo = (LauncherAppWidgetInfo) item;
final LauncherAppWidgetHost appWidgetHost = mLauncher.getAppWidgetHost();
if (appWidgetHost != null) {
final int appWidgetId = launcherAppWidgetInfo.appWidgetId;
// Deleting an app widget ID is a void call but writes to disk before returning
// to the caller...
new Thread("deleteAppWidgetId") {
public void run() {
appWidgetHost.deleteAppWidgetId(launcherAppWidgetInfo.appWidgetId);
}
}.start();
}
}
LauncherModel.deleteItemFromDatabase(mLauncher, item);
}
当把图标拖放到DeleteZone,就会调用DeleteZone,实现的onDrop方法对应用图标进行删除处理。
3.屏幕左右移动按钮,就是使用的ImageView,
<ImageView
android:id="@+id/previous_screen"
android:layout_width="93dip"
android:layout_height="@dimen/button_bar_height"
android:layout_gravity="bottom|left"
android:layout_marginLeft="6dip"
android:scaleType="center"
android:src="@drawable/home_arrows_left"
android:onClick="previousScreen"
android:focusable="true"
android:clickable="true" />
<ImageView
android:id="@+id/next_screen"
android:layout_width="93dip"
android:layout_height="@dimen/button_bar_height"
android:layout_gravity="bottom|right"
android:layout_marginRight="6dip"
android:scaleType="center"
android:src="@drawable/home_arrows_right"
android:onClick="nextScreen"
android:focusable="true"
android:clickable="true" />
注意三点,
,ImageView通过把drawable传递给worksapce,当桌面切换时通过调用Drawable.setLevel()方法实现不同图标显示。
--2.当点击实现左右桌面切换,查看上面的布局文件中android:onClick="previousScreen",该属性定义了一个 onClick事件响应函数,在Launcher.java中的788行。
@SuppressWarnings({"UnusedDeclaration"})
publicvoid previousScreen(View v) {
if(!isAllAppsVisible()) {
mWorkspace.scrollLeft();
}
}
4.RelativeLayout--android:id="@+id/all_apps_button_cluster",如前面截图右边灰色竖状条,它是一个相对布局对象,上面承载了三个view
中间是一个HandleView,是一个进入allappview的按钮,HandleView的左面是拨号,右面是浏览器两个ImageView。
--HandleView
--1.点击事件 传递给Launcher.onClick进行处理 显示应用菜单view
--2.长按事件 传递给Launcher.onLongClick进行处理,方法执行显示5个桌面的预览微缩图显示
--拨号或者浏览器
--onClick响应:android:onClick="launchHotSeat"
5.Workspace--用户桌面包括5个workspace_screen,launcher:defaultScreen="2"在前面已经说过,表示默认桌面是第三个。
workspace继承了viewgroup,5个workspace_screen作为它的child,值得注意它只接收CellLayout类型的child,workspace重写了addview函数,添加了非CellLayout的child将抛异常--Workspace长按事件由launcher.onLongClick来监听
--Workspace实现了DropTarget, DragSource两个接口,意味着Workspace既是拖放源,又是拖放目的地
--Workspace实现DragScroller接口,DragScroller接口提供两个方法
void scrollLeft()和void scrollRight()在拖放过程被DragController调用实现桌面的左右滚动。
--CellLayout Workspace下的一个桌面布局,CellLayout也是ViewGroup的子类,
Workspace下有5个CellLayout顺序排列,Workspace下布局文件:android:scrollbars="horizontal"决定了5个CellLayout排列是横向还是纵向的
<com.android.launcher2.CellLayout
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:launcher="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/com.android.launcher"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:hapticFeedbackEnabled="false"
launcher:cellHeight="@dimen/workspace_cell_height"//每个cell的高度
launcher:longAxisStartPadding="8dip"//cell距离父view CellLayout左边距
launcher:longAxisEndPadding="78dip"//cell距离父view CellLayout右边距
launcher:shortAxisStartPadding="0dip"//cell距离父view CellLayout上边距
launcher:shortAxisEndPadding="0dip"//cell距离父view CellLayout下边距
launcher:shortAxisCells="4"//CellLayout cells行数
launcher:longAxisCells="4"//CellLayout cells列数 />
当纵向的控件不够cells排列时,cell将产生重叠,横向不产生重叠,横向每个cell间隔至少为0
--CellLayout覆盖重新实现了onMeasure方法,和onlayout方法,它限定了child view 使用的布局参数类型为CellLayout.LayoutParams因此企图通过修改
--CellLayout.LayoutParams说明,CellLayout.LayoutParams下有几个成员需要说明一下
--cellX:该child view占用的第几列的cell(若横向占用多个cell,表示最左边的cellx)
--cellY: 该child view占用的第几行的cell(若纵向占用多个cell,表示最上边的celly)
--cellHSpan:横向跨越的列数
--cellVSpan: 纵向跨越行数
--isDragging:该child是否正在被拖动
--regenerateId:是否重新生成view id
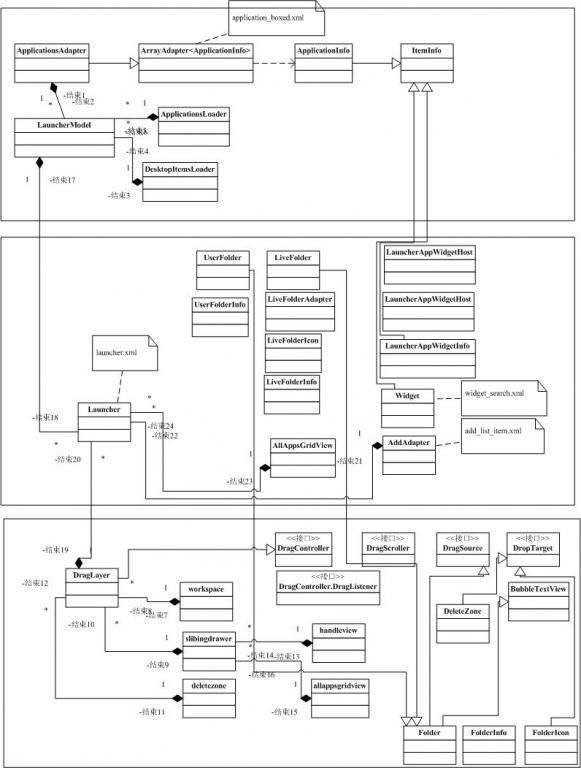
最后以网上淘来的launcher类的关系来结束这篇文章: