Vaadin Web应用开发教程(44): 使用Container接口管理一组Item
单个属性使用Property接口,一组Property使用Item接口来管理,Container接口则管理一组具有相同属性的Item。Container所包含的Item使用Item标识符(IID)来区分。
Item通过方法addItem()方法向Container添加Item。 查询某个属性可以先通过getItem()取得Item对象,然后再使用getItemProperty()方法,或者直接使用getContainerProperty 方法来读取。
Vaadin在设计Container接口考虑到灵活性和高效性,它包括了一些可选的接口一支持内部Item的排序,索引或者以层次关系来访问Item,从而为实现Table,Tree,Select等UI组件提供了实现基础。
和其它数据模型类似,Container接口也提供了数据变动事件的支持。
Container可以是无序的,有序的,带索引或是支持层次关系,因此可以支持几乎现实中所有数据模型。Vaadin 内部实现支持一些常用的数据源,比如简单的二维表(IndexedContainer)和文件系统(FileSystemContainer)等。
除了上面通用的Container实现,一些UI组件本身就实现了Container接口,比如Select组件。
使用BeanContainer
BeanContainer 为使用内存来管理JavaBean对象的Container类型。每个其中的Item为使用BeanItem封装的Java对象。Item的属性会根据setter, getter 自动识别,因此需要使用的Java Bean具有public 修饰符。也只有同类型的Java Bean对象才可以添加到BeanContainer中。
BeanContainer为一generic 类型,使用时给出所包含的Bean类型和Item 标识符的类型。参考下面例子:
// Here is a JavaBean
public class Bean implements Serializable {
String name;
double energy; // Energy content in kJ/100g
public Bean(String name, double energy) {
this.name = name;
this.energy = energy;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public double getEnergy() {
return energy;
}
public void setEnergy(double energy) {
this.energy = energy;
}
}
void basic(VerticalLayout layout) {
// Create a container for such beans with
// strings as item IDs.
BeanContainer<String, Bean> beans =
new BeanContainer<String, Bean>(Bean.class);
// Use the name property as the item ID of the bean
beans.setBeanIdProperty("name");
// Add some beans to it
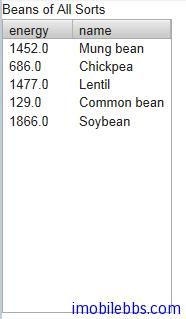
beans.addBean(new Bean("Mung bean", 1452.0));
beans.addBean(new Bean("Chickpea", 686.0));
beans.addBean(new Bean("Lentil", 1477.0));
beans.addBean(new Bean("Common bean", 129.0));
beans.addBean(new Bean("Soybean", 1866.0));
// Bind a table to it
Table table = new Table("Beans of All Sorts", beans);
layout.addComponent(table);
}
嵌套属性
如果Java Bean有个嵌套的Java Bean类型,而且具有和这个嵌套Java Bean具有1对1的关系,你可以将这个嵌套类的属性添加到Container中,就如同直接包含在其中Java Bean的属性一样。同样此时嵌套的Java Bean也必须具有public 修饰符。
如下例:
先定义两个Java Bean类型,其中EqCoord作为Star的嵌套类,一个Star类对应一个EqCoord,一一对应的关系。
/** Bean to be nested */
public class EqCoord implements Serializable {
double rightAscension; /* In angle hours */
double declination; /* In degrees */
... constructor and setters and getters for the properties ...
}
/** Bean containing a nested bean */
public class Star implements Serializable {
String name;
EqCoord equatorial; /* Nested bean */
... constructor and setters and getters for the properties ...
}
在创建好Container之后,可以通过方法addNestedContainerProperty将嵌套类的属性添加到Container中。
// Create a container for beans
final BeanItemContainer<Star> stars =
new BeanItemContainer<Star>(Star.class);
// Declare the nested properties to be used in the container
stars.addNestedContainerProperty("equatorial.rightAscension");
stars.addNestedContainerProperty("equatorial.declination");
// Add some items
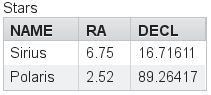
stars.addBean(new Star("Sirius", new EqCoord(6.75, 16.71611)));
stars.addBean(new Star("Polaris", new EqCoord(2.52, 89.26417)));
如果将这个Container绑定到一个TableUI组件,你可能需要为表的列定义列名称。嵌套类的属性也作为单独的列显示在表格中,如果需要隐藏某个列,可以通过方法setVisibleColumns修改例的可见性。
// Put them in a table
Table table = new Table("Stars", stars);
table.setColumnHeader("equatorial.rightAscension", "RA");
table.setColumnHeader("equatorial.declination", "Decl");
table.setPageLength(table.size());
// Have to set explicitly to hide the "equatorial" property
table.setVisibleColumns(new Object[]{"name",
"equatorial.rightAscension", "equatorial.declination"});
使用BeanItemContainer
BeanItemContainer 用来管理一组由BeanItem封装的Java Bean对象。Item的属性会根据setter, getter 自动识别,因此需要使用的Java Bean具有public 修饰符。也只有同类型的Java Bean对象才可以添加到BeanItemContainer中。
BeanItemContainer为BeanContainer的一个特别版本,它不需要指明Item 标识符的类型,而直接使用Item对象来区分Item。因此比BeanContainer使用更简单。
// Create a container for the beans
BeanItemContainer<Bean> beans =
new BeanItemContainer<Bean>(Bean.class);
// Add some beans to it
beans.addBean(new Bean("Mung bean", 1452.0));
beans.addBean(new Bean("Chickpea", 686.0));
beans.addBean(new Bean("Lentil", 1477.0));
beans.addBean(new Bean("Common bean", 129.0));
beans.addBean(new Bean("Soybean", 1866.0));
// Bind a table to it
Table table = new Table("Beans of All Sorts", beans);
遍历Container
Container 所包含的Item对象并不一定需要排过序,遍历整个Container可以通过Iterator接口。Container 的getItemIds()返回一个Collection集合支持枚举。下例为遍历一个Table,检查其中为Checkbox的某个列,选择出所有选中的Item。
// Collect the results of the iteration into this string.
String items = "";
// Iterate over the item identifiers of the table.
for (Iterator i = table.getItemIds().iterator(); i.hasNext();) {
// Get the current item identifier, which is an integer.
int iid = (Integer) i.next();
// Now get the actual item from the table.
Item item = table.getItem(iid);
// And now we can get to the actual checkbox object.
Button button = (Button)
(item.getItemProperty("ismember").getValue());
// If the checkbox is selected.
if ((Boolean)button.getValue() == true) {
// Do something with the selected item; collect the
// first names in a string.
items += item.getItemProperty("First Name")
.getValue() + " ";
}
}
// Do something with the results; display the selected items.
layout.addComponent (new Label("Selected items: " + items));
过滤Container
对应Container的Item对象,可以定义一些查询条件来过滤掉一些Item。如同数据查询时使用WHERE语句来查询表格。比如下面代码定义一个简单的过滤器来匹配name 列以Douglas 开头的Item
Filter filter = new SimpleStringFilter("name",
"Douglas", true, false);
table.addContainerFilter(filter);
Filter可以为单个(atomic)或是组合(Composite)类型。单个Filter 定义单独的一个条件,如上面的SimpleStringFilter,组合的Filter有多个单个的Filter通过NOT,OR,AND 组合而成。例如:
filter = new Or(new SimpleStringFilter("name",
"Douglas", true, false),
new Compare.Less("age", 42));
Vaadin定义了常用的Filter类型,如SimpleStringFilter,IsNull,Equal, Greater, Less, GreaterOrEqual, LessOrEqual,And, Or 和Not 等,也可以自定义一个Filter类型,如:
class MyCustomFilter implements Container.Filter {
protected String propertyId;
protected String regex;
public MyCustomFilter(String propertyId, String regex) {
this.propertyId = propertyId;
this.regex = regex;
}
/** Tells if this filter works on the given property. */
@Override
public boolean appliesToProperty(Object propertyId) {
return propertyId != null &&
propertyId.equals(this.propertyId);
}