Android Design Support Library使用详解
Google在2015的IO大会上,给我们带来了更加详细的Material Design设计规范,同时,也给我们带来了全新的Android Design Support Library,在这个support库里面,Google给我们提供了更加规范的MD设计风格的控件。最重要的是,Android Design Support Library的兼容性更广,直接可以向下兼容到Android 2.2。这不得不说是一个良心之作。
使用Support Library非常简单:
添加引用即可:
compile 'com.android.support:design:22.2.0'
下面我们来看看这些新控件的基本使用方法,我们从最简单的控件开始说起。
部分内容直接来自Android Developer Blog中的内容:
英文原文:
http://android-developers.blogspot.jp/2015/05/android-design-support-library.html
菠萝的翻译:
http://www.jcodecraeer.com/a/anzhuokaifa/developer/2015/0531/2958.html
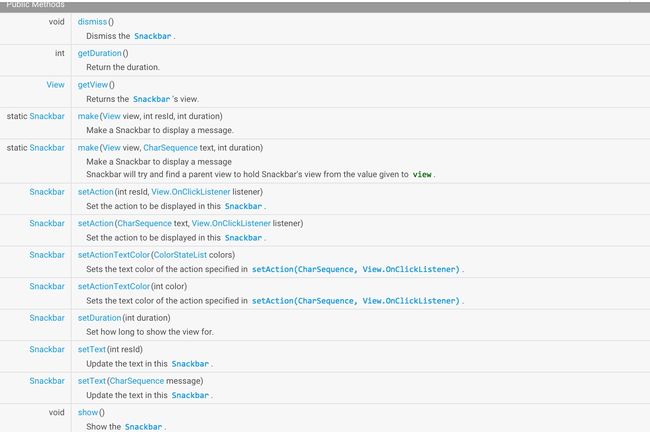
Snackbar
Snackbar提供了一个介于Toast和AlertDialog之间轻量级控件,它可以很方便的提供消息的提示和动作反馈。
Snackbar的使用与Toast的使用基本相同:
Snackbar.make(view, "Snackbar comes out", Snackbar.LENGTH_LONG)
.setAction("Action", new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
Toast.makeText(
MainActivity.this,
"Toast comes out",
Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
}).show();
需要注意的是,这里我们把第一个参数作为Snackbar显示的基准元素,而设置的Action也可以设置多个。
显示的效果就类似如下:
Snackbar在出现一定时间后,就会消失,这与Toast一模一样。
Google API Doc 官方说明:
http://developer.android.com/reference/android/support/design/widget/Snackbar.html
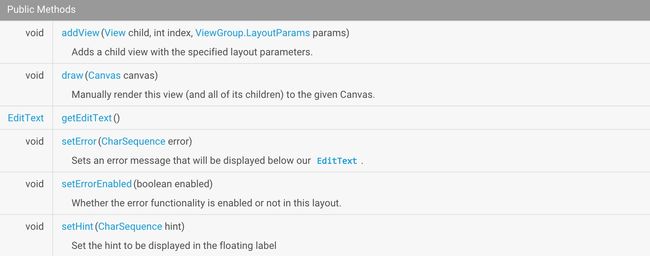
TextInputLayout
TextInputLayout作为一个父容器控件,包装了新的EditText。通常,单独的EditText会在用户输入第一个字母之后隐藏hint提示信息,但是现在你可以使用TextInputLayout 来将EditText封装起来,提示信息会变成一个显示在EditText之上的floating label,这样用户就始终知道他们现在输入的是什么。同时,如果给EditText增加监听,还可以给它增加更多的floating label。
下面我们来看这与一个TextInputLayout:
<android.support.design.widget.TextInputLayout
android:id="@+id/til_pwd"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content">
<EditText
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"/>
</android.support.design.widget.TextInputLayout>
一定要注意,他是把EditText包含起来的,不能单独使用。
在代码中,我们给它设置监听:
final TextInputLayout textInputLayout = (TextInputLayout) findViewById(R.id.til_pwd);
EditText editText = textInputLayout.getEditText();
textInputLayout.setHint("Password");
editText.addTextChangedListener(new TextWatcher() {
@Override
public void beforeTextChanged(CharSequence s, int start, int count, int after) {
if (s.length() > 4) {
textInputLayout.setError("Password error");
textInputLayout.setErrorEnabled(true);
} else {
textInputLayout.setErrorEnabled(false);
}
}
@Override
public void onTextChanged(CharSequence s, int start, int before, int count) {
}
@Override
public void afterTextChanged(Editable s) {
}
});
}
这样:显示效果如下:
当输入时:
下面我们给出Google API Doc上的说明,了解TextInputLayout的详细使用方法:
http://developer.android.com/reference/android/support/design/widget/TextInputLayout.html
Floating Action Button
floating action button 是一个负责显示界面基本操作的圆形按钮。Design library中的FloatingActionButton 实现了一个默认颜色为主题中colorAccent的悬浮操作按钮,like this:
FloatingActionButton——FAB使用非常简单,你可以指定在加强型FrameLayout里面——CoordinatorLayout,这个我们后面再将。
关于FAB的使用,你可以把它当做一个button即可。
<android.support.design.widget.FloatingActionButton
android:id="@+id/fab"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_gravity="end|bottom"
android:layout_margin="@dimen/fab_margin"
android:src="@drawable/ic_done"/>
通过指定layout_gravity就可以指定它的位置。
同样,你可以通过指定anchor,即显示位置的锚点:
<android.support.design.widget.FloatingActionButton
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
app:layout_anchor="@id/app_bar"
app:layout_anchorGravity="bottom|right|end"
android:src="@android:drawable/ic_done"
android:layout_margin="15dp"
android:clickable="true"/>
除了一般大小的悬浮操作按钮,它还支持mini size(fabSize=”mini”)。FloatingActionButton继承自ImageView,你可以使用android:src或者ImageView的任意方法,比如setImageDrawable()来设置FloatingActionButton里面的图标。
http://developer.android.com/reference/android/support/design/widget/FloatingActionButton.html
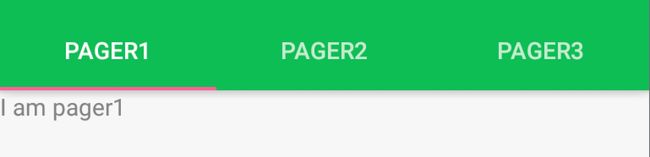
TabLayout
Tab滑动切换View并不是一个新的概念,但是Google却是第一次在support库中提供了完整的支持,而且,Design library的TabLayout 既实现了固定的选项卡 - view的宽度平均分配,也实现了可滚动的选项卡 - view宽度不固定同时可以横向滚动。选项卡可以在程序中动态添加:
TabLayout tabLayout = (TabLayout) findViewById(R.id.tabs);
tabLayout.addTab(tabLayout.newTab().setText("tab1"));
tabLayout.addTab(tabLayout.newTab().setText("tab2"));
tabLayout.addTab(tabLayout.newTab().setText("tab3"));
但大部分时间我们都不会这样用,通常滑动布局都会和ViewPager配合起来使用,所以,我们需要ViewPager来帮忙:
mViewPager = (ViewPager) findViewById(R.id.viewpager);
// 设置ViewPager的数据等
setupViewPager();
TabLayout tabLayout = (TabLayout) findViewById(R.id.tabs);
tabLayout.setupWithViewPager(mViewPager);
通过一句话setupWithViewPager,我们就把ViewPager和TabLayout结合了起来。
http://developer.android.com/reference/android/support/design/widget/TabLayout.html
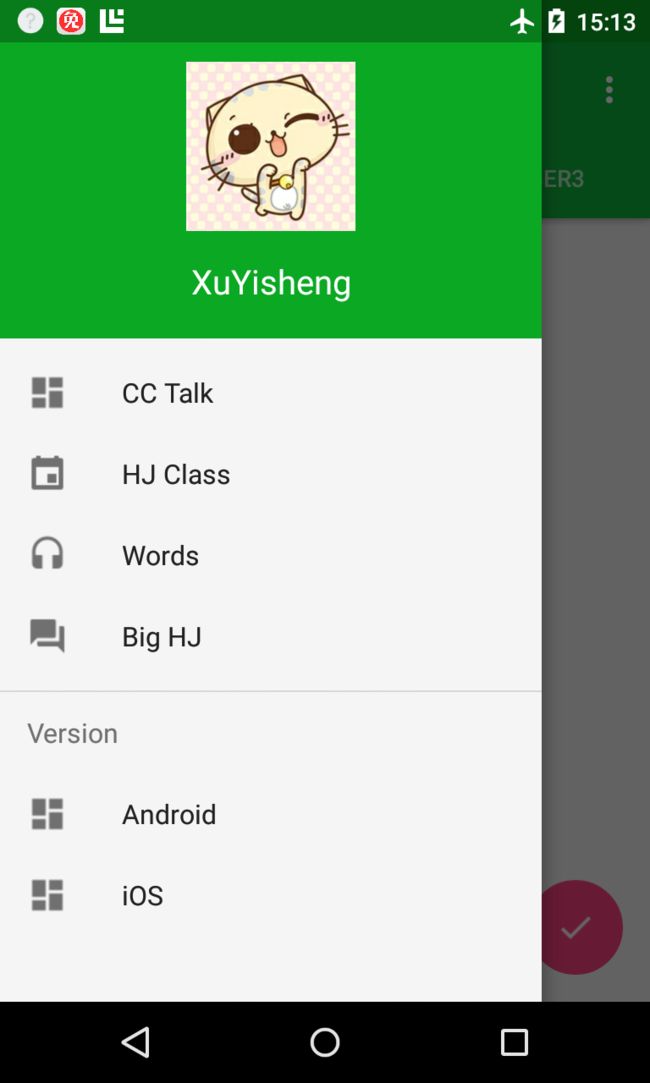
NavigationView
NavigationView在MD设计中非常重要,之前Google也提出了使用DrawerLayout来实现导航抽屉。这次,在support library中,Google提供了NavigationView来实现导航菜单界面,所以,新的导航界面可以这样写了:
<android.support.v4.widget.DrawerLayout
android:id="@+id/dl_main_drawer"
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:fitsSystemWindows="true">
<!-- 你的内容布局-->
<include layout="@layout/navigation_content"/>
<android.support.design.widget.NavigationView
android:id="@+id/nv_main_navigation"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_gravity="start"
app:headerLayout="@layout/navigation_header"
app:menu="@menu/drawer_view"/>
</android.support.v4.widget.DrawerLayout>
其中最重要的就是这两个属性:
app:headerLayout
app:menu
通过这两个属性,我们可以非常方便的指定导航界面的头布局和菜单布局:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="200dp"
android:background="?attr/colorPrimaryDark"
android:gravity="center"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:padding="16dp"
android:theme="@style/ThemeOverlay.AppCompat.Dark">
<ImageView
android:layout_width="100dp"
android:layout_height="100dp"
android:layout_marginTop="16dp"
android:background="@drawable/ic_user"/>
<TextView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginTop="16dp"
android:gravity="center"
android:text="XuYisheng"
android:textAppearance="@style/TextAppearance.AppCompat.Body1"
android:textSize="20sp"/>
</LinearLayout>
其中最上面的布局就是app:headerLayout所指定的头布局:
而下面的菜单布局,我们可以直接通过menu内容自动生成,而不需要我们来指定布局:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<menu xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android">
<group android:checkableBehavior="single">
<item
android:id="@+id/nav_home"
android:icon="@drawable/ic_dashboard"
android:title="CC Talk"/>
<item
android:id="@+id/nav_messages"
android:icon="@drawable/ic_event"
android:title="HJ Class"/>
<item
android:id="@+id/nav_friends"
android:icon="@drawable/ic_headset"
android:title="Words"/>
<item
android:id="@+id/nav_discussion"
android:icon="@drawable/ic_forum"
android:title="Big HJ"/>
</group>
<item android:title="Version">
<menu>
<item
android:icon="@drawable/ic_dashboard"
android:title="Android"/>
<item
android:icon="@drawable/ic_dashboard"
android:title="iOS"/>
</menu>
</item>
</menu>
你可以通过设置一个OnNavigationItemSelectedListener,使用其setNavigationItemSelectedListener()来获得元素被选中的回调事件。它为你提供被点击的 菜单元素 ,让你可以处理选择事件,改变复选框状态,加载新内容,关闭导航菜单,以及其他任何你想做的操作。例如这样:
private void setupDrawerContent(NavigationView navigationView) {
navigationView.setNavigationItemSelectedListener(
new NavigationView.OnNavigationItemSelectedListener() {
@Override
public boolean onNavigationItemSelected(MenuItem menuItem) {
menuItem.setChecked(true);
mDrawerLayout.closeDrawers();
return true;
}
});
}
可见,Google将这些东西封装的非常易于使用了。
AppBarLayout
AppBarLayout跟它的名字一样,把容器类的组件全部作为AppBar。like this:
这里就是把Toolbar和TabLayout放到了AppBarLayout中,让他们当做一个整体作为AppBar。
<android.support.design.widget.AppBarLayout
android:id="@+id/appbar"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:theme="@style/ThemeOverlay.AppCompat.Dark.ActionBar">
<android.support.v7.widget.Toolbar
android:id="@+id/toolbar"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="?attr/actionBarSize"
android:background="?attr/colorPrimary"
app:popupTheme="@style/ThemeOverlay.AppCompat.Light"/>
<android.support.design.widget.TabLayout
android:id="@+id/tabs"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"/>
</android.support.design.widget.AppBarLayout>
http://developer.android.com/reference/android/support/design/widget/AppBarLayout.html
CoordinatorLayout
CoordinatorLayout是这次新添加的一个增强型的FrameLayout。在CoordinatorLayout中,我们可以在FrameLayout的基础上完成很多新的操作。
Floating View
MD的一个新的特性就是增加了很多可悬浮的View,像我们前面说的Floating Action Button。我们可以把FAB放在任何地方,只需要通过:
android:layout_gravity="end|bottom"
来指定显示的位置。同时,它还提供了layout_anchor来供你设置显示坐标的锚点:
app:layout_anchor="@id/appbar"
创建滚动
CoordinatorLayout可以说是这次support library更新的重中之重。它从另一层面去控制子view之间触摸事件的布局,Design library中的很多控件都利用了它。
一个很好的例子就是当你将FloatingActionButton作为一个子View添加进CoordinatorLayout并且将CoordinatorLayout传递给 Snackbar.make(),在3.0及其以上的设备上,Snackbar不会显示在悬浮按钮的上面,而是FloatingActionButton利用CoordinatorLayout提供的回调方法,在Snackbar以动画效果进入的时候自动向上移动让出位置,并且在Snackbar动画地消失的时候回到原来的位置,不需要额外的代码。
官方的例子很好的说明了这一点:
<android.support.design.widget.CoordinatorLayout
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<! -- Your Scrollable View -->
<android.support.v7.widget.RecyclerView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
app:layout_behavior="@string/appbar_scrolling_view_behavior" />
<android.support.design.widget.AppBarLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content">
<android.support.v7.widget.Toolbar
...
app:layout_scrollFlags="scroll|enterAlways">
<android.support.design.widget.TabLayout
...
app:layout_scrollFlags="scroll|enterAlways">
</android.support.design.widget.AppBarLayout>
</android.support.design.widget.CoordinatorLayout>
其中,一个可以滚动的组件,例如RecyclerView、ListView(这里需要注意的是,貌似只支持RecyclerView、ListView,如果你用一个ScrollView,是没有效果的)。如果:
1、给这个可滚动组件设置了layout_behavior
2、给另一个控件设置了layout_scrollFlags
那么,当设置了layout_behavior的控件滑动时,就会触发设置了layout_scrollFlags的控件发生状态的改变。
设置的layout_scrollFlags有如下几种选项:
- scroll: 所有想滚动出屏幕的view都需要设置这个flag- 没有设置这个flag的view将被固定在屏幕顶部。
- enterAlways: 这个flag让任意向下的滚动都会导致该view变为可见,启用快速“返回模式”。
- enterAlwaysCollapsed: 当你的视图已经设置minHeight属性又使用此标志时,你的视图只能已最小高度进入,只有当滚动视图到达顶部时才扩大到完整高度。
- exitUntilCollapsed: this flag causes the view to scroll off until it is ‘collapsed’ (its minHeight) before exiting。
需要注意的是,后面两种模式基本只有在CollapsingToolbarLayout才有用,而前面两种模式基本是需要一起使用的,也就是说,这些flag的使用场景,基本已经固定了。
例如我们前面例子中的,也就是这种模式:
app:layout_scrollFlags="scroll|enterAlways"
PS : 所有使用scroll flag的view都必须定义在没有使用scroll flag的view的前面,这样才能确保所有的view从顶部退出,留下固定的元素。
http://developer.android.com/reference/android/support/design/widget/CoordinatorLayout.html
CollapsingToolbarLayout
CollapsingToolbarLayout提供了一个可以折叠的Toolbar,这也是Google+、photos中的效果。Google把它做成了一个标准控件,更加方便大家使用。
这里先看一个例子:
<android.support.design.widget.AppBarLayout
android:id="@+id/appbar"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="@dimen/detail_backdrop_height"
android:fitsSystemWindows="true"
android:theme="@style/ThemeOverlay.AppCompat.Dark.ActionBar">
<android.support.design.widget.CollapsingToolbarLayout
android:id="@+id/collapsing_toolbar"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:fitsSystemWindows="true"
app:contentScrim="?attr/colorPrimary"
app:expandedTitleMarginEnd="64dp"
app:expandedTitleMarginStart="48dp"
app:layout_scrollFlags="scroll|exitUntilCollapsed">
<ImageView
android:id="@+id/backdrop"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:fitsSystemWindows="true"
android:scaleType="centerCrop"
android:src="@drawable/ic_banner"
app:layout_collapseMode="parallax"/>
<android.support.v7.widget.Toolbar
android:id="@+id/toolbar"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="?attr/actionBarSize"
app:layout_collapseMode="pin"
app:popupTheme="@style/ThemeOverlay.AppCompat.Light"/>
</android.support.design.widget.CollapsingToolbarLayout>
</android.support.design.widget.AppBarLayout>
我们在CollapsingToolbarLayout中放置了一个ImageView和一个Toolbar。并把这个CollapsingToolbarLayout放到AppBarLayout中作为一个整体。在CollapsingToolbarLayout中,我们分别设置了ImageView和一个Toolbar的layout_collapseMode。
这里使用了CollapsingToolbarLayout的app:layout_collapseMode=”pin”来确保Toolbar在view折叠的时候仍然被固定在屏幕的顶部。当你让CollapsingToolbarLayout和Toolbar在一起使用的时候,title会在展开的时候自动变得大些,而在折叠的时候让字体过渡到默认值。必须注意,在这种情况下你必须在CollapsingToolbarLayout上调用setTitle(),而不是在Toolbar上。
除了固定住view,你还可以使用app:layout_collapseMode=”parallax”(以及使用app:layout_collapseParallaxMultiplier=”0.7”来设置视差因子)来实现视差滚动效果(比如CollapsingToolbarLayout里面的一个ImageView),这中情况和CollapsingToolbarLayout的app:contentScrim=”?attr/colorPrimary”属性一起配合更完美。
在这个例子中,我们同样设置了:
app:layout_scrollFlags="scroll|exitUntilCollapsed">
来接收一个:
app:layout_behavior="@string/appbar_scrolling_view_behavior">
这样才能产生滚动效果,而通过layout_collapseMode,我们就设置了滚动时内容的变化效果。
再来看一个官方的实例:
CoordinatorLayout与自定义view
有一件事情必须注意,那就是CoordinatorLayout并不知道FloatingActionButton或者AppBarLayout的内部工作原理 - 它只是以Coordinator.Behavior的形式提供了额外的API,该API可以使子View更好的控制触摸事件与手势以及声明它们之间的依赖,并通过onDependentViewChanged()接收回调。
可以使用CoordinatorLayout.DefaultBehavior(你的View.Behavior.class)注解或者在布局中使用app:layout_behavior=”com.example.app.你的View$Behavior”属性来定义view的默认行为。framework让任意view和CoordinatorLayout结合在一起成为了可能。
http://developer.android.com/reference/android/support/design/widget/CollapsingToolbarLayout.html
总结
经过几天的研究,Google这次提出的Android Design Support Library的意义其实并不在于给出了这些非常好的控件,其实这些控件在Github上基本都能找到相应的。它的目的在于Google给出了官方的设计指导,进一步完善了MD设计思想。这才是Android Design Support Library最重要的特性。当然,平心而论,这些控件的使用并不是非常的人性化,过多的封装导致整个效果不是非常的具有可定制性,但是,这毕竟是Google迈出的第一步,后面一定会更加牛逼。
Demo
最后,给出一个融合MD和Android Design Support Library的Demo供大家研究,相信结合文章和代码,大家一定能很快理解Android Design Support Library的使用方法。
DesignSupportLibraryDemo
https://github.com/xuyisheng/DesignSupportLibraryDemo 欢迎大家star、fork。
当前版本还未完善,很多画面还在处理中。后续会进一步丰富、完善,作为一个MD设计的Demo。