代码面试最常用的10大算法
4.Graph
与Graph相关的问题主要集中在深度优先搜索和宽度优先搜索。深度优先搜索非常简单,你可以从根节点开始循环整个邻居节点。下面是一个非常简单的宽度优先搜索例子,核心是用队列去存储节点。
第一步,定义一个GraphNode
class GraphNode{
int val;
GraphNode next;
GraphNode[] neighbors;
boolean visited;
GraphNode(int x) {
val = x;
}
GraphNode(int x, GraphNode[] n){
val = x;
neighbors = n;
}
public String toString(){
return "value: "+ this.val;
}
}
第二步,定义一个队列
class Queue{
GraphNode first, last;
public void enqueue(GraphNode n){
if(first == null){
first = n;
last = first;
}else{
last.next = n;
last = n;
}
}
public GraphNode dequeue(){
if(first == null){
return null;
}else{
GraphNode temp = new GraphNode(first.val, first.neighbors);
first = first.next;
return temp;
}
}
}第三步,使用队列进行宽度优先搜索
public class GraphTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
GraphNode n1 = new GraphNode(1);
GraphNode n2 = new GraphNode(2);
GraphNode n3 = new GraphNode(3);
GraphNode n4 = new GraphNode(4);
GraphNode n5 = new GraphNode(5);
n1.neighbors = new GraphNode[]{n2,n3,n5};
n2.neighbors = new GraphNode[]{n1,n4};
n3.neighbors = new GraphNode[]{n1,n4,n5};
n4.neighbors = new GraphNode[]{n2,n3,n5};
n5.neighbors = new GraphNode[]{n1,n3,n4};
breathFirstSearch(n1, 5);
}
public static void breathFirstSearch(GraphNode root, int x){
if(root.val == x)
System.out.println("find in root");
Queue queue = new Queue();
root.visited = true;
queue.enqueue(root);
while(queue.first != null){
GraphNode c = (GraphNode) queue.dequeue();
for(GraphNode n: c.neighbors){
if(!n.visited){
System.out.print(n + " ");
n.visited = true;
if(n.val == x)
System.out.println("Find "+n);
queue.enqueue(n);
}
}
}
}
}输出结果:
value: 2 value: 3 value: 5 Find value: 5
value: 4
实际中,基于Graph需要经常用到的算法:
- 克隆Graph
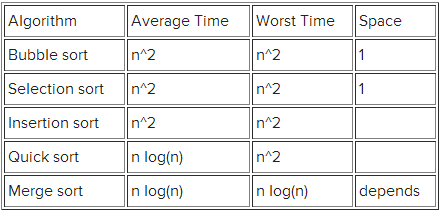
5.排序
不同排序算法的时间复杂度,大家可以到wiki上查看它们的基本思想。
BinSort、Radix Sort和CountSort使用了不同的假设,所有,它们不是一般的排序方法。
下面是这些算法的具体实例,另外,你还可以阅读: Java开发者在实际操作中是如何排序的。
- 归并排序
- 快速排序
- 插入排序
6.递归和迭代
下面通过一个例子来说明什么是递归。
问题:
这里有n个台阶,每次能爬1或2节,请问有多少种爬法?
步骤1:查找n和n-1之间的关系
为了获得n,这里有两种方法:一个是从第一节台阶到n-1或者从2到n-2。如果f(n)种爬法刚好是爬到n节,那么f(n)=f(n-1)+f(n-2)。
步骤2:确保开始条件是正确的
f(0) = 0;
f(1) = 1;
public static int f(int n){
if(n <= 2) return n;
int x = f(n-1) + f(n-2);
return x;
}
递归方法的时间复杂度指数为n,这里会有很多冗余计算。
f(5) f(4) + f(3) f(3) + f(2) + f(2) + f(1) f(2) + f(1) + f(2) + f(2) + f(1)该递归可以很简单地转换为迭代。
public static int f(int n) {
if (n <= 2){
return n;
}
int first = 1, second = 2;
int third = 0;
for (int i = 3; i <= n; i++) {
third = first + second;
first = second;
second = third;
}
return third;
}
在这个例子中,迭代花费的时间要少些。关于迭代和递归,你可以去 这里看看。
7.动态规划
动态规划主要用来解决如下技术问题:
- 通过较小的子例来解决一个实例;
- 对于一个较小的实例,可能需要许多个解决方案;
- 把较小实例的解决方案存储在一个表中,一旦遇上,就很容易解决;
- 附加空间用来节省时间。
上面所列的爬台阶问题完全符合这四个属性,因此,可以使用动态规划来解决:
public static int[] A = new int[100];
public static int f3(int n) {
if (n <= 2)
A[n]= n;
if(A[n] > 0)
return A[n];
else
A[n] = f3(n-1) + f3(n-2);//store results so only calculate once!
return A[n];
}
一些基于动态规划的算法:
- 编辑距离
- 最长回文子串
- 单词分割
- 最大的子数组
8.位操作
位操作符:
从一个给定的数n中找位i(i从0开始,然后向右开始)
public static boolean getBit(int num, int i){
int result = num & (1<<i);
if(result == 0){
return false;
}else{
return true;
}
}
例如,获取10的第二位:
i=1, n=10 1<<1= 10 1010&10=10 10 is not 0, so return true;典型的位算法:
- Find Single Number
- Maximum Binary Gap
9.概率
通常要解决概率相关问题,都需要很好地格式化问题,下面提供一个简单的例子:
有50个人在一个房间,那么有两个人是同一天生日的可能性有多大?(忽略闰年,即一年有365天)
算法:
public static double caculateProbability(int n){
double x = 1;
for(int i=0; i<n; i++){
x *= (365.0-i)/365.0;
}
double pro = Math.round((1-x) * 100);
return pro/100;
}结果:
calculateProbability(50) = 0.97
10.组合和排列
组合和排列的主要差别在于顺序是否重要。
例1:
1、2、3、4、5这5个数字,输出不同的顺序,其中4不可以排在第三位,3和5不能相邻,请问有多少种组合?
例2:
有5个香蕉、4个梨、3个苹果,假设每种水果都是一样的,请问有多少种不同的组合?
基于它们的一些常见算法
- 排列
- 排列2
- 排列顺序