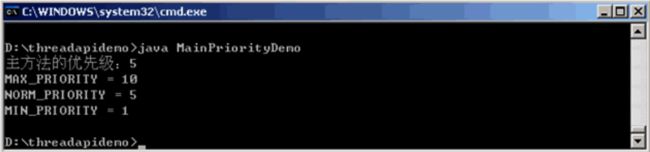
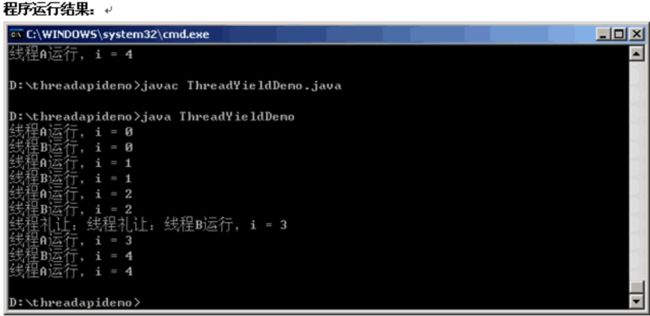
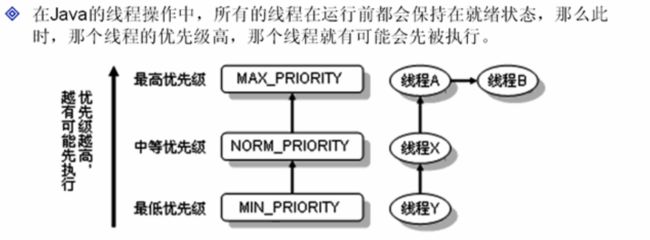
- OC语言多界面传值五大方式
Magnetic_h
iosui学习objective-c开发语言
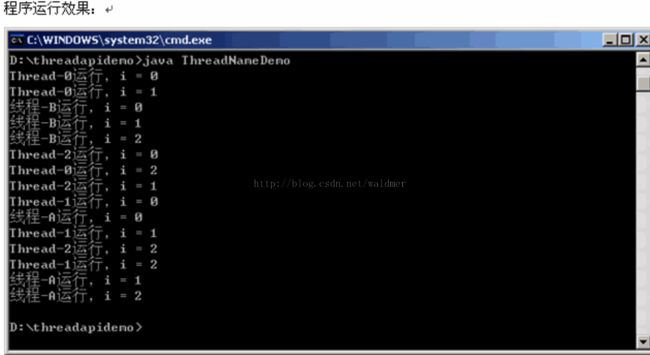
前言在完成暑假仿写项目时,遇到了许多需要用到多界面传值的地方,这篇博客来总结一下比较常用的五种多界面传值的方式。属性传值属性传值一般用前一个界面向后一个界面传值,简单地说就是通过访问后一个视图控制器的属性来为它赋值,通过这个属性来做到从前一个界面向后一个界面传值。首先在后一个界面中定义属性@interfaceBViewController:UIViewController@propertyNSSt
- 理解Gunicorn:Python WSGI服务器的基石
范范0825
ipythonlinux运维
理解Gunicorn:PythonWSGI服务器的基石介绍Gunicorn,全称GreenUnicorn,是一个为PythonWSGI(WebServerGatewayInterface)应用设计的高效、轻量级HTTP服务器。作为PythonWeb应用部署的常用工具,Gunicorn以其高性能和易用性著称。本文将介绍Gunicorn的基本概念、安装和配置,帮助初学者快速上手。1.什么是Gunico
- ArcGIS栅格计算器常见公式(赋值、0和空值的转换、补充栅格空值)
研学随笔
arcgis经验分享
我们在使用ArcGIS时通常经常用到栅格计算器,今天主要给大家介绍我日常中经常用到的几个公式,供大家参考学习。将特定值(-9999)赋值为0,例如-9999.Con("raster"==-9999,0,"raster")2.给空值赋予特定的值(如0)Con(IsNull("raster"),0,"raster")3.将特定的栅格值(如1)赋值为空值,其他保留原值SetNull("raster"==
- Python数据分析与可视化实战指南
William数据分析
pythonpython数据
在数据驱动的时代,Python因其简洁的语法、强大的库生态系统以及活跃的社区,成为了数据分析与可视化的首选语言。本文将通过一个详细的案例,带领大家学习如何使用Python进行数据分析,并通过可视化来直观呈现分析结果。一、环境准备1.1安装必要库在开始数据分析和可视化之前,我们需要安装一些常用的库。主要包括pandas、numpy、matplotlib和seaborn等。这些库分别用于数据处理、数学
- git常用命令笔记
咩酱-小羊
git笔记
###用习惯了idea总是不记得git的一些常见命令,需要用到的时候总是担心旁边站了人~~~记个笔记@_@,告诉自己看笔记不丢人初始化初始化一个新的Git仓库gitinit配置配置用户信息gitconfig--globaluser.name"YourName"gitconfig--globaluser.email"
[email protected]"基本操作克隆远程仓库gitclone查看
- 509. 斐波那契数(每日一题)
lzyprime
lzyprime博客(github)创建时间:2021.01.04qq及邮箱:2383518170leetcode笔记题目描述斐波那契数,通常用F(n)表示,形成的序列称为斐波那契数列。该数列由0和1开始,后面的每一项数字都是前面两项数字的和。也就是:F(0)=0,F(1)=1F(n)=F(n-1)+F(n-2),其中n>1给你n,请计算F(n)。示例1:输入:2输出:1解释:F(2)=F(1)+
- Git常用命令-修改远程仓库地址
猿大师
LinuxJavagitjava
查看远程仓库地址gitremote-v返回结果originhttps://git.coding.net/*****.git(fetch)originhttps://git.coding.net/*****.git(push)修改远程仓库地址gitremoteset-urloriginhttps://git.coding.net/*****.git先删除后增加远程仓库地址gitremotermori
- Day17笔记-高阶函数
~在杰难逃~
Python笔记python开发语言pycharm数据分析
高阶函数【重点掌握】函数的本质:函数是一个变量,函数名是一个变量名,一个函数可以作为另一个函数的参数或返回值使用如果A函数作为B函数的参数,B函数调用完成之后,会得到一个结果,则B函数被称为高阶函数常用的高阶函数:map(),reduce(),filter(),sorted()1.map()map(func,iterable),返回值是一个iterator【容器,迭代器】func:函数iterab
- Python爬虫解析工具之xpath使用详解
eqa11
python爬虫开发语言
文章目录Python爬虫解析工具之xpath使用详解一、引言二、环境准备1、插件安装2、依赖库安装三、xpath语法详解1、路径表达式2、通配符3、谓语4、常用函数四、xpath在Python代码中的使用1、文档树的创建2、使用xpath表达式3、获取元素内容和属性五、总结Python爬虫解析工具之xpath使用详解一、引言在Python爬虫开发中,数据提取是一个至关重要的环节。xpath作为一门
- mac电脑命令行获取电量
小米人er
我的博客macos命令行
在macOS上,有几个命令行工具可以用来获取电量信息,最常用的是pmset命令。你可以通过以下方式来查看电池状态和电量信息:查看电池状态:pmset-gbatt这个命令会返回类似下面的输出:Nowdrawingfrom'BatteryPower'-InternalBattery-0(id=1234567)95%;discharging;4:02remainingpresent:true输出中包括电
- Python开发常用的三方模块如下:
换个网名有点难
python开发语言
Python是一门功能强大的编程语言,拥有丰富的第三方库,这些库为开发者提供了极大的便利。以下是100个常用的Python库,涵盖了多个领域:1、NumPy,用于科学计算的基础库。2、Pandas,提供数据结构和数据分析工具。3、Matplotlib,一个绘图库。4、Scikit-learn,机器学习库。5、SciPy,用于数学、科学和工程的库。6、TensorFlow,由Google开发的开源机
- Shell、Bash、Zsh这都是啥啊
小白码上飞
bashlinux开发语言
Zsh和Bash都是我们常用的Shell,那先搞明白啥是shell吧。Shell作为一个单词,他是“壳”的意思,蛋壳坚果壳。之所以叫壳,是为了和计算机的“核”来区分,用它表示“为使用者提供的操作界面”。所以这个命名其实很形象,翻译成中文,直译过来叫“壳层”。个人认为这个叫法很奇怪,意译貌似也没有什么好的词汇来匹配。就还是叫shell吧。维基百科给的定义是:Incomputing,ashellisa
- ios GCD
_Waiting_
1.GCD任务和队列学习GCD之前,先来了解GCD中两个核心概念:任务和队列。任务:就是执行操作的意思,换句话说就是你在线程中执行的那段代码。在GCD中是放在block中的。执行任务有两种方式:同步执行(sync)和异步执行(async)。两者的主要区别是:是否等待队列的任务执行结束,以及是否具备开启新线程的能力。同步执行(sync):同步添加任务到指定的队列中,在添加的任务执行结束之前,会一直等
- 一文掌握python常用的list(列表)操作
程序员neil
pythonpython开发语言
目录一、创建列表1.直接创建列表:2.使用list()构造器3.使用列表推导式4.创建空列表二、访问列表元素1.列表支持通过索引访问元素,索引从0开始:2.还可以使用切片操作访问列表的一部分:三、修改列表元素四、添加元素1.append():在末尾添加元素2.insert():在指定位置插入元素五、删除元素1.del:删除指定位置的元素2.remove():删除指定值的第一个匹配项3.pop():
- 发现荞麦过敏这件事
怪小泊
荞麦在我这里不是常用的谷物。所以前二十年,我以为自己是很正常的,从街头小吃到包装零食到每日三餐,从来没有不能吃的。可是有天我突然病倒了,喉咙火辣辣的肿痛,口水都咽不下去,舌头发麻。当时我以为吃太多零食所致,因为那天我吃了很辣的泡椒凤爪。其实我是不怎么吃辣的。而那个泡椒凤爪真的超辣。当时我以为自己吃多了,并不知道自己对哪个食物过敏。因为不舒服我早早睡了,结果并没有睡着。肚子一阵一阵疼,非常痛苦,终于
- Linux vi常用命令
fengyehongWorld
Linuxlinux
参考资料viコマンド(vimコマンド)リファレンス目录一.保存系命令二.删除系命令三.移动系命令四.复制粘贴系命令一.保存系命令⏹保存并退出:wq⏹强制保存并退出:wq!⏹退出(文件未编辑):q⏹强制退出(忽略已编辑内容):q!⏹另存为:w新文件名二.删除系命令⏹删除当前行dd⏹清空整个文档gg:移动到文档顶部dG:删除到最后一行ggdG三.移动系命令⏹移动到文档顶部gg⏹移动到文档底部#方式1G
- 多线程之——ExecutorCompletionService
阿福德
在我们开发中,经常会遇到这种情况,我们起多个线程来执行,等所有的线程都执行完成后,我们需要得到个线程的执行结果来进行聚合处理。我在内部代码评审时,发现了不少这种情况。看很多同学都使用正确,但比较啰嗦,效率也不高。本文介绍一个简单处理这种情况的方法:直接上代码:publicclassExecutorCompletionServiceTest{@TestpublicvoidtestExecutorCo
- python多线程程序设计 之一
IT_Beijing_BIT
#Python程序设计语言python
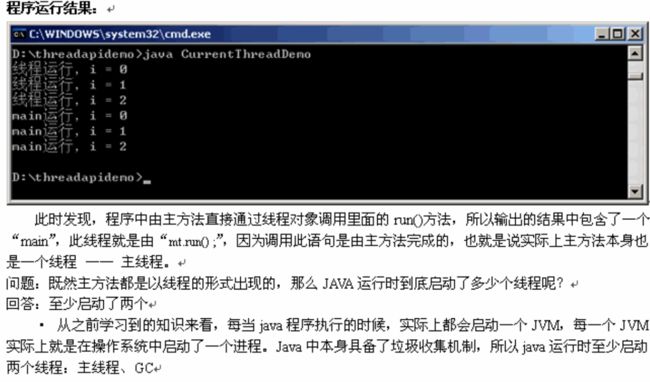
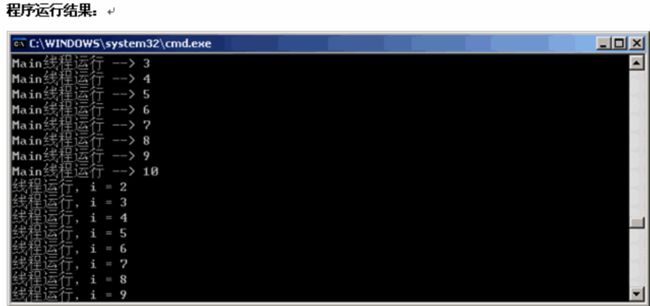
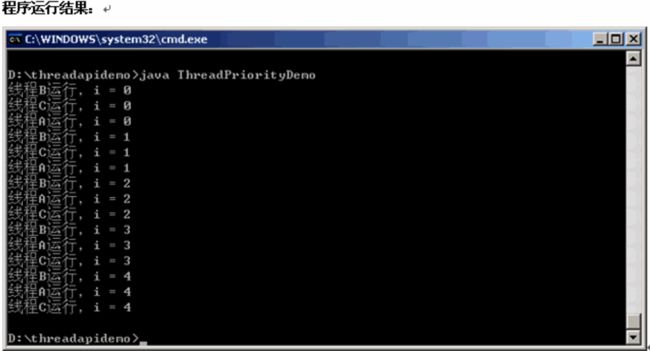
python多线程程序设计之一全局解释器锁线程APIsthreading.active_count()threading.current_thread()threading.excepthook(args,/)threading.get_native_id()threading.main_thread()threading.stack_size([size])线程对象成员函数构造器start/ru
- 语文主题教学学习笔记之87
东哥杂谈
“语文主题教学”学习笔记之八十七(0125)今天继续学习小学语文主题教学的实践样态。板块三:教学中体现“书艺”味道。作为四大名著之一的《水浒传》,堪称我国文学宝库之经典。对从《水浒传》中摘选的单元,教师就要了解其原生态,即评书体特点。这也要求教师要了解一些常用的评书行话术语,然后在教学时适时地加入一些,让学生体味其文本中原有的特色。学生也要尽可能地通过朗读的方式,而不单是分析讲解的方式进行学习。细
- Linux查看服务器日志
TPBoreas
运维linux运维
一、tail这个是我最常用的一种查看方式用法如下:tail-n10test.log查询日志尾部最后10行的日志;tail-n+10test.log查询10行之后的所有日志;tail-fn10test.log循环实时查看最后1000行记录(最常用的)一般还会配合着grep用,(实时抓包)例如:tail-fn1000test.log|grep'关键字'(动态抓包)tail-fn1000test.log
- MongoDB知识概括
GeorgeLin98
持久层mongodb
MongoDB知识概括MongoDB相关概念单机部署基本常用命令索引-IndexSpirngDataMongoDB集成副本集分片集群安全认证MongoDB相关概念业务应用场景:传统的关系型数据库(如MySQL),在数据操作的“三高”需求以及应对Web2.0的网站需求面前,显得力不从心。解释:“三高”需求:①Highperformance-对数据库高并发读写的需求。②HugeStorage-对海量数
- mac 备份android 手机通讯录导入iphone,iphone如何导出通讯录(轻松教你iPhone备份通讯录的方法)...
weixin_39762838
mac备份android手机通讯录导入iphone
在日新月异的手机更替中,换手机已经成为一个非常稀松平常的事情,但将旧手机上面的通讯录导入到新手机还是让不少小伙伴为难,本篇将给大家详细讲解这方面的知识:“苹果手机通讯录怎么导入到新手机”及“安卓手机通讯录导入到新手机”的方法。一、苹果手机通讯录导入到新手机常用方法(SIM卡导入)在苹果手机主频幕上找到“设置”,单击进入设置菜单,下拉菜单列表,点击“邮件、通讯录、日历”,然后找到“导入SIM卡通讯录
- SpringCloudAlibaba—Sentinel(限流)
菜鸟爪哇
前言:自己在学习过程的记录,借鉴别人文章,记录自己实现的步骤。借鉴文章:https://blog.csdn.net/u014494148/article/details/105484410Sentinel介绍Sentinel诞生于阿里巴巴,其主要目标是流量控制和服务熔断。Sentinel是通过限制并发线程的数量(即信号隔离)来减少不稳定资源的影响,而不是使用线程池,省去了线程切换的性能开销。当资源
- 利用python实现图片格式之间的相互转换
难得北窗高卧
python开发语言
一、概要图片一般有多种格式,常见的图片格式包括:JPEG(.jpg或.jpeg):一种广泛使用的有损压缩格式,适用于摄影图像和网页上的图片。PNG(.png):一种无损压缩格式,支持透明度和更好的图像质量,常用于图标、图形和需要透明背景的图片。该图片是4通道的,外加一个透明通道。如截屏GIF(.gif):一种支持动画和透明度的格式,常用于简单的动画和图标。BMP(.bmp):一种无损格式,存储图像
- Python多线程实现大规模数据集高效转移
sand&wich
网络python服务器
背景在处理大规模数据集时,通常需要在不同存储设备、不同服务器或文件夹之间高效地传输数据。如果采用单线程传输方式,当数据量非常大时,整个过程会非常耗时。因此,通过多线程并行处理可以大幅提升数据传输效率。本文将分享一个基于Python多线程实现的高效数据传输工具,通过遍历源文件夹中的所有文件,将它们移动到目标文件夹。工具和库这个数据集转移工具主要依赖于以下Python标准库:os:用于文件系统操作,如
- Python实现下载当前年份的谷歌影像
sand&wich
python开发语言
在GIS项目和地图应用中,获取最新的地理影像数据是非常重要的。本文将介绍如何使用Python代码从Google地图自动下载当前年份的影像数据,并将其保存为高分辨率的TIFF格式文件。这个过程涉及地理坐标转换、多线程下载和图像处理。关键功能该脚本的核心功能包括:坐标转换:支持WGS-84与WebMercator投影之间转换,以及处理中国GCJ-02偏移。自动化下载:多线程下载地图瓦片,提高效率。图像
- 入门MySQL——查询语法练习
K_un
前言:前面几篇文章为大家介绍了DML以及DDL语句的使用方法,本篇文章将主要讲述常用的查询语法。其实MySQL官网给出了多个示例数据库供大家实用查询,下面我们以最常用的员工示例数据库为准,详细介绍各自常用的查询语法。1.员工示例数据库导入官方文档员工示例数据库介绍及下载链接:https://dev.mysql.com/doc/employee/en/employees-installation.h
- WebMagic:强大的Java爬虫框架解析与实战
Aaron_945
Javajava爬虫开发语言
文章目录引言官网链接WebMagic原理概述基础使用1.添加依赖2.编写PageProcessor高级使用1.自定义Pipeline2.分布式抓取优点结论引言在大数据时代,网络爬虫作为数据收集的重要工具,扮演着不可或缺的角色。Java作为一门广泛使用的编程语言,在爬虫开发领域也有其独特的优势。WebMagic是一个开源的Java爬虫框架,它提供了简单灵活的API,支持多线程、分布式抓取,以及丰富的
- 更改npm镜像源为淘宝镜像
骆小骆
基于node.js
npm常用指令后缀*最近复习了一下node.js整理了一下跟node.js相关的指令后缀*--save、-S参数意思是把模块的版本信息保存到dependencies(生产环境依赖)中,即你的package.json文件的dependencies字段中;–--save-dev、-D参数意思是把模块版本信息保存到devDependencies(开发环境依赖)中,即你的package.json文件的de
- 常见的 JVM 调优方法有哪些?
爪哇天下
jvm
常见的JVM调优方法有哪些?可以具体到调整哪个参数,调成什么值?对年轻代的EdenSurvivor的比例进行配置-XX:SurvivorRatio=8:表示设置2个Survivor区:1个Eden区的大小比值为2:8,这意味着Survivor区占整个年轻代的1/5,这个参数默认为8如果经常性的SurvivorTo放不下YGC的剩余的对象时候,可以适当的调整比例常用的CMS收集器:设置回收阈值,需要
- JVM StackMapTable 属性的作用及理解
lijingyao8206
jvm字节码Class文件StackMapTable
在Java 6版本之后JVM引入了栈图(Stack Map Table)概念。为了提高验证过程的效率,在字节码规范中添加了Stack Map Table属性,以下简称栈图,其方法的code属性中存储了局部变量和操作数的类型验证以及字节码的偏移量。也就是一个method需要且仅对应一个Stack Map Table。在Java 7版
- 回调函数调用方法
百合不是茶
java
最近在看大神写的代码时,.发现其中使用了很多的回调 ,以前只是在学习的时候经常用到 ,现在写个笔记 记录一下
代码很简单:
MainDemo :调用方法 得到方法的返回结果
- [时间机器]制造时间机器需要一些材料
comsci
制造
根据我的计算和推测,要完全实现制造一台时间机器,需要某些我们这个世界不存在的物质
和材料...
甚至可以这样说,这种材料和物质,我们在反应堆中也无法获得......
- 开口埋怨不如闭口做事
邓集海
邓集海 做人 做事 工作
“开口埋怨,不如闭口做事。”不是名人名言,而是一个普通父亲对儿子的训导。但是,因为这句训导,这位普通父亲却造就了一个名人儿子。这位普通父亲造就的名人儿子,叫张明正。 张明正出身贫寒,读书时成绩差,常挨老师批评。高中毕业,张明正连普通大学的分数线都没上。高考成绩出来后,平时开口怨这怨那的张明正,不从自身找原因,而是不停地埋怨自己家庭条件不好、埋怨父母没有给他创造良好的学习环境。
- jQuery插件开发全解析,类级别与对象级别开发
IT独行者
jquery开发插件 函数
jQuery插件的开发包括两种: 一种是类级别的插件开发,即给
jQuery添加新的全局函数,相当于给
jQuery类本身添加方法。
jQuery的全局函数就是属于
jQuery命名空间的函数,另一种是对象级别的插件开发,即给
jQuery对象添加方法。下面就两种函数的开发做详细的说明。
1
、类级别的插件开发 类级别的插件开发最直接的理解就是给jQuer
- Rome解析Rss
413277409
Rome解析Rss
import java.net.URL;
import java.util.List;
import org.junit.Test;
import com.sun.syndication.feed.synd.SyndCategory;
import com.sun.syndication.feed.synd.S
- RSA加密解密
无量
加密解密rsa
RSA加密解密代码
代码有待整理
package com.tongbanjie.commons.util;
import java.security.Key;
import java.security.KeyFactory;
import java.security.KeyPair;
import java.security.KeyPairGenerat
- linux 软件安装遇到的问题
aichenglong
linux遇到的问题ftp
1 ftp配置中遇到的问题
500 OOPS: cannot change directory
出现该问题的原因:是SELinux安装机制的问题.只要disable SELinux就可以了
修改方法:1 修改/etc/selinux/config 中SELINUX=disabled
2 source /etc
- 面试心得
alafqq
面试
最近面试了好几家公司。记录下;
支付宝,面试我的人胖胖的,看着人挺好的;博彦外包的职位,面试失败;
阿里金融,面试官人也挺和善,只不过我让他吐血了。。。
由于印象比较深,记录下;
1,自我介绍
2,说下八种基本类型;(算上string。楼主才答了3种,哈哈,string其实不是基本类型,是引用类型)
3,什么是包装类,包装类的优点;
4,平时看过什么书?NND,什么书都没看过。。照样
- java的多态性探讨
百合不是茶
java
java的多态性是指main方法在调用属性的时候类可以对这一属性做出反应的情况
//package 1;
class A{
public void test(){
System.out.println("A");
}
}
class D extends A{
public void test(){
S
- 网络编程基础篇之JavaScript-学习笔记
bijian1013
JavaScript
1.documentWrite
<html>
<head>
<script language="JavaScript">
document.write("这是电脑网络学校");
document.close();
</script>
</h
- 探索JUnit4扩展:深入Rule
bijian1013
JUnitRule单元测试
本文将进一步探究Rule的应用,展示如何使用Rule来替代@BeforeClass,@AfterClass,@Before和@After的功能。
在上一篇中提到,可以使用Rule替代现有的大部分Runner扩展,而且也不提倡对Runner中的withBefores(),withAfte
- [CSS]CSS浮动十五条规则
bit1129
css
这些浮动规则,主要是参考CSS权威指南关于浮动规则的总结,然后添加一些简单的例子以验证和理解这些规则。
1. 所有的页面元素都可以浮动 2. 一个元素浮动后,会成为块级元素,比如<span>,a, strong等都会变成块级元素 3.一个元素左浮动,会向最近的块级父元素的左上角移动,直到浮动元素的左外边界碰到块级父元素的左内边界;如果这个块级父元素已经有浮动元素停靠了
- 【Kafka六】Kafka Producer和Consumer多Broker、多Partition场景
bit1129
partition
0.Kafka服务器配置
3个broker
1个topic,6个partition,副本因子是2
2个consumer,每个consumer三个线程并发读取
1. Producer
package kafka.examples.multibrokers.producers;
import java.util.Properties;
import java.util.
- zabbix_agentd.conf配置文件详解
ronin47
zabbix 配置文件
Aliaskey的别名,例如 Alias=ttlsa.userid:vfs.file.regexp[/etc/passwd,^ttlsa:.:([0-9]+),,,,\1], 或者ttlsa的用户ID。你可以使用key:vfs.file.regexp[/etc/passwd,^ttlsa:.: ([0-9]+),,,,\1],也可以使用ttlsa.userid。备注: 别名不能重复,但是可以有多个
- java--19.用矩阵求Fibonacci数列的第N项
bylijinnan
fibonacci
参考了网上的思路,写了个Java版的:
public class Fibonacci {
final static int[] A={1,1,1,0};
public static void main(String[] args) {
int n=7;
for(int i=0;i<=n;i++){
int f=fibonac
- Netty源码学习-LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder
bylijinnan
javanetty
先看看LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder的官方API
http://docs.jboss.org/netty/3.1/api/org/jboss/netty/handler/codec/frame/LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder.html
API举例说明了LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder的解析机制,如下:
实
- AES加密解密
chicony
加密解密
AES加解密算法,使用Base64做转码以及辅助加密:
package com.wintv.common;
import javax.crypto.Cipher;
import javax.crypto.spec.IvParameterSpec;
import javax.crypto.spec.SecretKeySpec;
import sun.misc.BASE64Decod
- 文件编码格式转换
ctrain
编码格式
package com.test;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.OutputStream;
- mysql 在linux客户端插入数据中文乱码
daizj
mysql中文乱码
1、查看系统客户端,数据库,连接层的编码
查看方法: http://daizj.iteye.com/blog/2174993
进入mysql,通过如下命令查看数据库编码方式: mysql> show variables like 'character_set_%'; +--------------------------+------
- 好代码是廉价的代码
dcj3sjt126com
程序员读书
长久以来我一直主张:好代码是廉价的代码。
当我跟做开发的同事说出这话时,他们的第一反应是一种惊愕,然后是将近一个星期的嘲笑,把它当作一个笑话来讲。 当他们走近看我的表情、知道我是认真的时,才收敛一点。
当最初的惊愕消退后,他们会用一些这样的话来反驳: “好代码不廉价,好代码是采用经过数十年计算机科学研究和积累得出的最佳实践设计模式和方法论建立起来的精心制作的程序代码。”
我只
- Android网络请求库——android-async-http
dcj3sjt126com
android
在iOS开发中有大名鼎鼎的ASIHttpRequest库,用来处理网络请求操作,今天要介绍的是一个在Android上同样强大的网络请求库android-async-http,目前非常火的应用Instagram和Pinterest的Android版就是用的这个网络请求库。这个网络请求库是基于Apache HttpClient库之上的一个异步网络请求处理库,网络处理均基于Android的非UI线程,通
- ORACLE 复习笔记之SQL语句的优化
eksliang
SQL优化Oracle sql语句优化SQL语句的优化
转载请出自出处:http://eksliang.iteye.com/blog/2097999
SQL语句的优化总结如下
sql语句的优化可以按照如下六个步骤进行:
合理使用索引
避免或者简化排序
消除对大表的扫描
避免复杂的通配符匹配
调整子查询的性能
EXISTS和IN运算符
下面我就按照上面这六个步骤分别进行总结:
- 浅析:Android 嵌套滑动机制(NestedScrolling)
gg163
android移动开发滑动机制嵌套
谷歌在发布安卓 Lollipop版本之后,为了更好的用户体验,Google为Android的滑动机制提供了NestedScrolling特性
NestedScrolling的特性可以体现在哪里呢?<!--[if !supportLineBreakNewLine]--><!--[endif]-->
比如你使用了Toolbar,下面一个ScrollView,向上滚
- 使用hovertree菜单作为后台导航
hvt
JavaScriptjquery.nethovertreeasp.net
hovertree是一个jquery菜单插件,官方网址:http://keleyi.com/jq/hovertree/ ,可以登录该网址体验效果。
0.1.3版本:http://keleyi.com/jq/hovertree/demo/demo.0.1.3.htm
hovertree插件包含文件:
http://keleyi.com/jq/hovertree/css
- SVG 教程 (二)矩形
天梯梦
svg
SVG <rect> SVG Shapes
SVG有一些预定义的形状元素,可被开发者使用和操作:
矩形 <rect>
圆形 <circle>
椭圆 <ellipse>
线 <line>
折线 <polyline>
多边形 <polygon>
路径 <path>
- 一个简单的队列
luyulong
java数据结构队列
public class MyQueue {
private long[] arr;
private int front;
private int end;
// 有效数据的大小
private int elements;
public MyQueue() {
arr = new long[10];
elements = 0;
front
- 基础数据结构和算法九:Binary Search Tree
sunwinner
Algorithm
A binary search tree (BST) is a binary tree where each node has a Comparable key (and an associated value) and satisfies the restriction that the key in any node is larger than the keys in all
- 项目出现的一些问题和体会
Steven-Walker
DAOWebservlet
第一篇博客不知道要写点什么,就先来点近阶段的感悟吧。
这几天学了servlet和数据库等知识,就参照老方的视频写了一个简单的增删改查的,完成了最简单的一些功能,使用了三层架构。
dao层完成的是对数据库具体的功能实现,service层调用了dao层的实现方法,具体对servlet提供支持。
&
- 高手问答:Java老A带你全面提升Java单兵作战能力!
ITeye管理员
java
本期特邀《Java特种兵》作者:谢宇,CSDN论坛ID: xieyuooo 针对JAVA问题给予大家解答,欢迎网友积极提问,与专家一起讨论!
作者简介:
淘宝网资深Java工程师,CSDN超人气博主,人称“胖哥”。
CSDN博客地址:
http://blog.csdn.net/xieyuooo
作者在进入大学前是一个不折不扣的计算机白痴,曾经被人笑话过不懂鼠标是什么,