Hibernate之一对多关联映射
这里以顾客、订单为例。一个顾客对应着多个订单。
数据表如下:
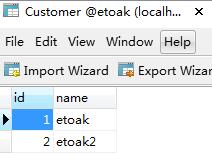
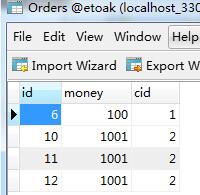
在双向一对多关联映射中,需要在”一“的一方添加set属性来存放”多“的一方,在属性上添加@OneToMany注解,mapping指向”一“的表。
同时在”多“的一方,添加”多“的对象属性,在并在这个属性上加上@ManyToOne注解 和@JoinColumn注解,后者的name值为”多“的一方的表中外键列的列名。
需要注意的是,一旦使用一对多关联映射,数据库中一定要添加外键,外键对应的是”一“的一方的主键,所以类型一定是一样的。
实体类:
@Entity
@Table(name = "customer", catalog = "etoak")
public class Customer implements java.io.Serializable {
private Integer id;
private String name;
private Set<Orders> orderses = new HashSet<Orders>(0);
public Customer() {
}
public Customer(String name, Set<Orders> orderses) {
this.name = name;
this.orderses = orderses;
}
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = IDENTITY)
@Column(name = "id", unique = true, nullable = false)
public Integer getId() {
return this.id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
@Column(name = "name", length = 32)
public String getName() {
return this.name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@OneToMany(cascade = CascadeType.ALL, fetch = FetchType.LAZY, mappedBy = "customer")
public Set<Orders> getOrderses() {
return this.orderses;
}
public void setOrderses(Set<Orders> orderses) {
this.orderses = orderses;
}
}@Entity
@Table(name = "orders", catalog = "etoak")
public class Orders implements java.io.Serializable {
private Integer id;
private Customer customer;
private Integer money;
public Orders() {
}
public Orders(Customer customer, Integer money) {
this.customer = customer;
this.money = money;
}
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = IDENTITY)
@Column(name = "id", unique = true, nullable = false)
public Integer getId() {
return this.id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
@ManyToOne(fetch = FetchType.LAZY)
@JoinColumn(name = "cid")
public Customer getCustomer() {
return this.customer;
}
public void setCustomer(Customer customer) {
this.customer = customer;
}
@Column(name = "money")
public Integer getMoney() {
return this.money;
}
public void setMoney(Integer money) {
this.money = money;
}
}dao层:
public interface IDao<T> {
public boolean add( T obj);
public boolean delete( T obj);
public boolean update (T obj);
public T get(Class<T> cls,int id);
}dao层实现类:
这里注意一下:在使用hibernate的时候必须要提交事务,不然的话执行完 没有错误,hibernate执行语句也打印出来了,但数据表里面就是没有添加数据。
public class DaoImpl<T> implements IDao<T> {
Session session = null;
Transaction tx = null;
@Override
public boolean add(T obj) {
try {
session = SF.getSession();
tx = session.beginTransaction();
session.save(obj);
tx.commit();
return true;
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return false;
}finally{
if(session!=null)session.close();
}
}
public boolean delete(T obj){
try{
session = SF.getSession();
tx = session.beginTransaction();
session.delete(obj);
tx.commit();
return true;
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
return false;
}finally{
if(session!=null)
session.close();
}
}
public boolean update(T obj){
try {
session = SF.getSession();
tx = session.beginTransaction();
session.update(obj);
tx.commit();
return true;
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return false;
}
}
@Override
public T get(Class<T> cls, int id) {
try {
session = SF.getSession();
tx = session.beginTransaction();
T t =(T) session.get(cls,id);
tx.commit();
return t;
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
}finally{
if(session!=null)session.close();
}
}
}测试类:
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//添加 一
/* 这里注意一下,在添加Customer也就是“一”时,必须要给orders setCustomer值,不然添加后,orders表添加的那一列外键值会为空。 */
Customer cus = new Customer();
cus.setName("etoak");
Orders o1 = new Orders();
o1.setMoney(100);
Orders o2 = new Orders();
o2.setMoney(200);
cus.getOrderses().add(o1);
cus.getOrderses().add(o2);
o1.setCustomer(cus);o2.setCustomer(cus);
IDao<Customer> dao = new DaoImpl<Customer>();
dao.add(cus);
//添加 多
Orders o1 = new Orders();
o1.setMoney(1001);
IDao<Customer> cusDao = new DaoImpl<Customer>();
Customer cus = cusDao.get(Customer.class, 2);
o1.setCustomer(cus);
IDao<Orders> dao = new DaoImpl<Orders>();
dao.add(o1);
//删除 多
/*Orders o1 = new Orders(); o1.setId(2); IDao<Orders> dao = new DaoImpl<Orders>(); dao.delete(o1);*/
//删除 一
/*Customer cus = new Customer(); cus.setId(2); IDao<Customer> dao = new DaoImpl<Customer>(); dao.delete(cus);*/
}
}session工厂类 :
这里要说明一下。 就是使用注解方式和非注解方式这个工厂类是有一点不同的。new 的configuration 不一样。注解方式用的是AnnotationConfiguration类
public class SF {
private static String CONFIG_FILE_LOCATION = "/hibernate.cfg.xml";
private static final ThreadLocal<Session> threadLocal = new ThreadLocal<Session>();
private static Configuration configuration = new AnnotationConfiguration();
private static org.hibernate.SessionFactory sessionFactory;
private static String configFile = CONFIG_FILE_LOCATION;
static {
try {
configuration.configure(configFile);
sessionFactory = configuration.buildSessionFactory();
} catch (Exception e) {
System.err
.println("%%%% Error Creating SessionFactory %%%%");
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private SF() {
}
public static Session getSession() throws HibernateException {
Session session = (Session) threadLocal.get();
if (session == null || !session.isOpen()) {
if (sessionFactory == null) {
rebuildSessionFactory();
}
session = (sessionFactory != null) ? sessionFactory.openSession()
: null;
threadLocal.set(session);
}
return session;
}
public static void rebuildSessionFactory() {
try {
configuration.configure(configFile);
sessionFactory = configuration.buildSessionFactory();
} catch (Exception e) {
System.err
.println("%%%% Error Creating SessionFactory %%%%");
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void closeSession() throws HibernateException {
Session session = (Session) threadLocal.get();
threadLocal.set(null);
if (session != null) {
session.close();
}
}
public static org.hibernate.SessionFactory getSessionFactory() {
return sessionFactory;
}
public static void setConfigFile(String configFile) {
SF.configFile = configFile;
sessionFactory = null;
}
public static Configuration getConfiguration() {
return configuration;
}
}hibernate.cfg.xml
<?xml version='1.0' encoding='UTF-8'?>
<!DOCTYPE hibernate-configuration PUBLIC "-//Hibernate/Hibernate Configuration DTD 3.0//EN" "http://hibernate.sourceforge.net/hibernate-configuration-3.0.dtd">
<hibernate-configuration>
<session-factory>
<property name="dialect">org.hibernate.dialect.MySQLDialect</property>
<property name="connection.url">jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/etoak</property>
<property name="connection.username">root</property>
<property name="connection.password">root</property>
<property name="connection.driver_class">com.mysql.jdbc.Driver</property>
<property name="myeclipse.connection.profile">mysql</property>
<property name="show_sql">true</property>
<property name="format_sql">true</property>
<mapping class="com.etoak.entity.Student"/>
<mapping class="com.etoak.entity.Classes"/>
</session-factory>
</hibernate-configuration>