连载:有限状态机以及维特比(Viterbi)译码器(一)
学习《通信原理》的时候,总是对维特比算法的实质有些把握不清楚,实现起来,颇煞费周章。这些天,赶上生病,好好思考了一下,总算有些领悟的意思了。
维特比算法并不是只针对卷积码的,可以说,它是一个普适的有限状态机算法(LSM)。只要有一个LSM,能够受不同输入的触发,在各个状态间跳转,并产生输出,就满足可基本条件,可根据状态机利用Viterbi 来从污染的输出中还原输入。
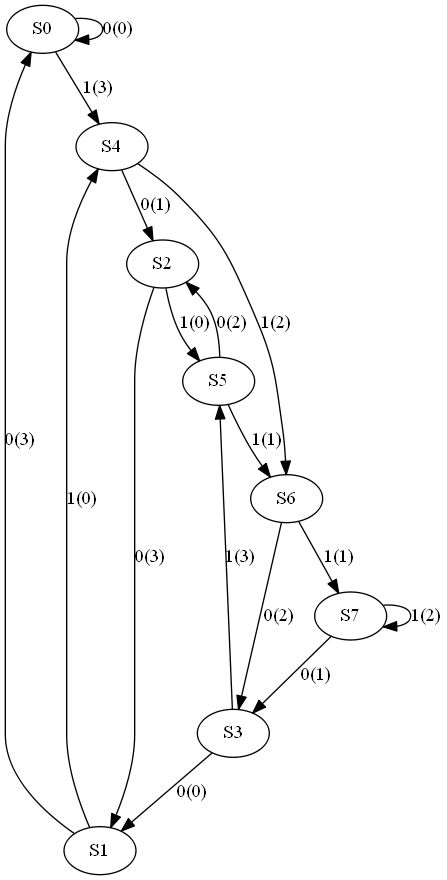
比如一个最简单的2,1,3码,其生成式八进制可以是13,17, 对应状态图(这是用 GraphViz自动生成的,后面代码会有)
寄存器有3个,状态共2^3 = 8个,由于输入不同,跳转也不同。维特比算法会找出一条最优的路径,按照这条路径跳转产生的输出,与接收到的实际输出之间空间距离(硬判决用汉明距离,即比特重量)最小。 比如,状态跳转为s0->s4->s2->s5->s6->s7->s3->s1->s0..., 会产生输出2,1,0,1,1,1,0,2...,但是,因为传输错误,接收到的输出为2,1,0,1,[0],1,0,2..,第五个输出错了。通过译码,可以还原出原始路径,理由是按照这条路径,产生的全路径误差最小。状态机是维特比的核心,具体输入什么,跳到哪去,完全取决于相应的编码。上述前向(无反馈)卷积码可以产生状态机,有反馈的feedback码,同样产生状态机。理论上,哪怕有人新发明一种纠错码,只要可用LSM来描述,就可以使用维特比译码。当然,要保证用好生成式确保好的代数性质,使得正确路径与其他路径产生的输出尽可能不同。
为了深入理解算法实现,玩转这个东东,而不只是限于用Matlab,动动手是比较有意思的! 因为状态机是实质,先打算抛开具体形式,实现一个基于状态机的编译码器。一旦这个通用编译码器实现了,向各类码型去特化变得非常容易。
最终目的,实现一个LSM通用译码模块,一次性解决前向卷积码、反馈卷积码、凿孔码等的维特比译码。具体实现想法:
1、搞出一个类,叫做通用维特比译码器,实现基于LSM(Limited Status Machine)的算法核心。这个类的状态机由具体形式的“填写器”初始化, 使用时类似
//定义一个通用编译码器 t_lcm_codec codec; //定义一个特定码型的状态生成器
int pins [] = {133,171};
t_fcmaker fc_maker(pins);
//用状态生成器初始化通用译码器
codec.init_status(fc_maker);
当然,为了灵活,实际代码比上面这个略复杂。我们可以为每个形式,建立一个填写器,比如前向码有前向码的填写器,反馈码有反馈码的,这样就可以使用同一个通用译码器,实现多种卷积纠错码的译码。
2、所有类的参数都是泛型的,可以支持任意具体的定义参数,比如定义速率,类似
//定义一个通用编译码器,有 //nRegStatus个状态, //每个状态到另一状态,有nInStatus 个跳转路径 //每次跳转,产生nOutputLen的输出 lsm_codec<nRegStatus,nInStatus,nOutputLen> lcm_codec; //定义一个前向卷积码状态机生成器 //码率为 n,k,约束 m ,生成式八进制是pins fconv_lsmaker<n,k,m> fcmaker(pins);
3、其他,为了研究,最好有GraphViz的接口,以便输出状态图。还有,最好支持打孔(速率调整)卷积码。这就动手吧!
首先是编译码器的实现,我们希望,这个编译码器可以这样处理数据,以便形式上分段,实质上连续的译码,以解决长数据的连续译码。
编码,
int nInitStatus = ...;//初态
hasData = fetch_Data(Data, &len);
while (hasData)
{
nInitStatus = lsm_codec.encode(Data,len,nOutputCode,nInitStatus);
hasData = fetch_Data(Data, &len);
}
译码类似:
bool Empty = fetchCode(Code , &buflen);
do{
lsm_codec.decode(Code, buflen);
int nPoped = pcodec->pop_data(nDecodedData,bufOut);
//存储一段数据
...
Empty = fetchCode(Code , &buflen);
}while (Empty==false);
好了,思路有了,动手实现。由于是泛型,所有东东全在一个文件里。后面部分的代码连起来,就是原始文件的内容分。先看看通用编译码器的描述(lsm_viterbi.h前半部分):
#define LSM_VITERBI_HEADER_VER 101
#include <vector>
#include <list>
#include <memory.h>
#include <functional>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
namespace LSMVIT{
/** \brief 有限状态机编译码器
* 有限状态机有若干状态,因用户输入的触发,在状态间跳转。跳转的过程中
* 跳转过程中,产生了跳转输出。受到信道污染的输出被重新送入译码器,
* 通过维特比算法,译码器会纠正一定量的错误。
*/
template < int reg_status /*寄存器状态数*/ , int data_status /*信息状态数*/ , int code_bitlen /*编码比特数*/, int L = 64 /*约束长度*/ >
class lsm_codec
{
protected:
//存储从当前状态到下一状态的跳转
struct tag_statusjmp_next{
int nNextStatus[data_status]; //下一状态
int nOutput[data_status]; //跳转输出
} m_table_nextjmp [reg_status];
//存储当前状态来自哪个旧状态的跳转
struct tag_statusjmp_last{
int nLastInput[data_status]; //上一次的触发
int nLastStatus[data_status]; //上一状态
int nLastOutput[data_status]; //跳转输出
} m_table_lastjmp [reg_status];
//最优路径表,采用double_buffer技术
struct tag_path{
int nCurrentHamming[2]; //当前全路径汉明
int nHamming[2][L]; //各个跳转的汉明
int nInChain[2][L]; //各个跳转的输入(触发)
int nOutChain[2][L]; //各个跳转的输出
int nRegChain[2][L]; //各步状态
} m_best_path[reg_status];
int m_nClock; //时钟
list<int> m_vec_decoded_data; //存储译码结果的缓存
int m_nBestHamming; //译码器当前的最优汉明
vector<int> m_nBestStatus; //所有最优路径的索引
int m_bitweight[16]; //用来称重的查表
public:
lsm_codec();
~lsm_codec(){}
//用回调函数对象cb_status (寄存器, 输入(触发),返回下一寄存器, 返回输出) 来初始化状态机。
bool init_status(function<bool (int ,int,int *,int *)> cb_status);
//重置状态机
void reset_status();
//进行编码
int encode(int inputArray[], int nLen, int outputArray[], int InitialStatus = 0);
//译码
int decode(int CodeArray[], int nLen, bool bfinished = false);
//弹出数据
int pop_data(int DataArray[], int nLen);
//生成GraphViz 状态图数据
string make_graph();
};
核心是两个数据结构,tag_statusjmp_next 和 tag_statusjmp_last,分别便于由状态机当前状态、输入触发查找下一状态、跳转速出,以及知道了当前状态,反差当前状态可能由哪些状态跳来,以及输出是什么。这两个结构分别用来编码、译码。
实现部分,首先是构造函数,初始化了比特称重器
template < int reg_status , int data_status, int code_bitlen, int L >
lsm_codec<reg_status,data_status,code_bitlen,L>::lsm_codec()
:m_nClock(-1)
,m_nBestHamming(0)
{
//用来量测比特重量的数组。
m_bitweight[0] = 0; m_bitweight[1] = 1; m_bitweight[2] = 1; m_bitweight[3] = 2;
m_bitweight[4] = 1; m_bitweight[5] = 2; m_bitweight[6] = 2; m_bitweight[7] = 3;
m_bitweight[8] = 1; m_bitweight[9] = 2; m_bitweight[10] = 2; m_bitweight[11] = 3;
m_bitweight[12] = 2; m_bitweight[13] = 3; m_bitweight[14] = 3; m_bitweight[15] = 4;
memset (&m_table_nextjmp,0, sizeof(m_table_nextjmp));
memset (&m_table_lastjmp,0, sizeof(m_table_lastjmp));
reset_status(); //重置状态
}
而后,是 重置译码器状态的函数,使得一个实例可以被多次使用。
/** \brief 重置译码器。如果译码器已经被初始化(m_nClock >=0),则会掷零
*/
template < int reg_status , int data_status, int code_bitlen, int L >
void lsm_codec<reg_status,data_status,code_bitlen,L>::reset_status()
{
memset (&m_best_path,0,sizeof(m_best_path));
if (m_nClock>=0) m_nClock = 0;
m_nBestHamming = 0;
m_nBestStatus.clear();
m_vec_decoded_data.clear();
for (int i = 0;i < reg_status; i++)
m_best_path[i].nRegChain[0][0] = i;
}
这是关键的状态机初始化函数,通过回调一个函数对象,实现用户自定义的状态初始化。有了它,用户自己可以设计状态机,解决特定的问题。
/** \brief 使用一个回调函数对象来初始化状态机
*
* \param cb_status fucntion <bool (int,int,int *, int * ) > 回调函数对象
* 注意,第一个参数是LSM当前状态,第二个是触发(输入),用户需要实现根据
* 前两个参数,计算下一状态、跳转输出的具体代码,并送入本回调。
* \return bool 成功失败标志
*/
template < int reg_status , int data_status, int code_bitlen, int L >
bool lsm_codec<reg_status,data_status,code_bitlen,L>::init_status(
function<
bool /*bSucceed*/(
int /*reg*/,
int /*data*/,
int * /*pNextReg*/,
int * /*pOutput*/
)
> cb_status
)
{
bool succeed = true;
for (int i=0;i<reg_status && succeed == true; i++)
{
for (int j=0;j<data_status && succeed == true; j++)
{
int nNextReg , nOutput;
//调用用户的函数
succeed = cb_status(i,j,&nNextReg,&nOutput);
if (succeed==true)
{
m_table_nextjmp[i].nNextStatus[j] = nNextReg;
m_table_nextjmp[i].nOutput[j] = nOutput;
//反差表初始化
for (int k=1;k<data_status;k++)
{
m_table_lastjmp[nNextReg].nLastInput[k-1] = m_table_lastjmp[nNextReg].nLastInput[k];
m_table_lastjmp[nNextReg].nLastOutput[k-1] = m_table_lastjmp[nNextReg].nLastOutput[k];
m_table_lastjmp[nNextReg].nLastStatus[k-1] = m_table_lastjmp[nNextReg].nLastStatus[k];
}
m_table_lastjmp[nNextReg].nLastStatus[data_status - 1] = i;
m_table_lastjmp[nNextReg].nLastInput[data_status - 1] = j;
m_table_lastjmp[nNextReg].nLastOutput[data_status - 1] = nOutput;
}// end if succeed
}//next j
}// next i
if (succeed==true)
m_nClock = 0 ;
else
m_nClock = -1;
reset_status();
return succeed;
}
接着,有了状态机,我们即可实现编码过程,可以直接查表解决。编码过程的输入是代表每次跳转的整数,对只有1排寄存器的卷积码,这个值取0-1,有2排寄存器的码,取值0-3。输出是一个个整数,如果是卷积码,则表示每个时钟后,送出的n路输出,第一路在最高位,最后一路在最低位,当然也可相反,完全取决于状态机生成器的嗜好
/** \brief 进行编码,利用用户所给的触发指令(输入信息),在状态间
* 跳转,并产生输出
* \param inputArray[] int 各个输入。输入为 [0 ~ data_status-1] 之间的任意值
* \param nLen int 有效输入数
* \param outputArray[] int 存放输出的数组,必须也要至少有nLen长
* \param InitialStatus int 编码器的初态。
* \return int 编码器现在的状态。对很长的数据,可以分段编码。
*
*/
template < int reg_status , int data_status, int code_bitlen, int L >
int lsm_codec<reg_status,data_status,code_bitlen,L>::encode(int inputArray[], int nLen, int outputArray[], int InitialStatus)
{
if (m_nClock < 0) return -1;
InitialStatus %= reg_status;
int nCurrStatus = InitialStatus;
for (int i = 0; i<nLen; i++)
{
int nInput = inputArray[i] % data_status;
//查表
outputArray [i] = m_table_nextjmp [ nCurrStatus].nOutput[nInput];
nCurrStatus = m_table_nextjmp[nCurrStatus].nNextStatus[nInput];
}
return nCurrStatus;
}
最关键的译码算法,其实并不长。为了防止路径计算时频繁的new, delete,设计了一对缓存,在每个时钟时刻,总是有一个缓存处于读(旧)态,另一个处于写(新)态,避免了内存频繁分配。由于窗口缓存L的存在,译码过程中会把过时的判决缓存到队列里,等待用户去取。代码:
/** \brief 维特比译码算法,最优的所有路径间,各个状态使用大数判决
*
* \param CodeArray[] int 输入译码器的编码后序列,每个元素取值 [0~2^code_bitlen-1]
* \param nLen int 序列长度
* \param bFinished bool 清空标志。是否把L约束长度内的所有元素全部输出,true 一般用于最后一批数据
* \return int 目前,缓存中有多少个判决可以读取。(调用 pop_data)
*
*/
template < int reg_status , int data_status, int code_bitlen, int L >
int lsm_codec<reg_status,data_status,code_bitlen,L>::decode(int CodeArray[], int nLen, bool bFinished)
{
if (m_nClock<0) return -1;
for (int cd = 0; cd < nLen; cd ++)
{
/*
对每次输入,m_nCLock ++, 对各个寄存器状态,查下 lastjmp 表,
从而知道每个新状态由哪些老的状态而来,同时计算汉明距离。
*/
m_nBestHamming = int (((unsigned int)-1)>>1);
m_nBestStatus.clear();
//对每个状态,统计最优路径
for (int i=0;i<reg_status; i++)
{
//用于记录最优路径的临时变量
int nBestLastStatus = 0, nBestInput = 0, nBestOutput = 0, nBestHamm = int (((unsigned int)-1)>>1),
nBestDHamm = 0;
//某个状态是由以下几个状态转来的
for (int j=0;j<data_status; j++)
{
//对每种可能的转换可能,计算有转换生成的输出与实际收到的码字的误差。
/*
为了处理打孔码,规定输入的卷积码符号每组表示为m...mm xx...x, 低code_bitlen位是符号,高位为掩码,
掩码表示对应符号位是否是删除比特,1为是,0为否
*/
unsigned int code = CodeArray[cd] % (1<< (unsigned int) code_bitlen);
unsigned int mask = (~((unsigned int)(CodeArray[cd]>>code_bitlen))) % (1<< (unsigned int) code_bitlen);
int nErr = (code ^ m_table_lastjmp[i].nLastOutput[j]);
nErr &= mask;
int nHamm = 0;
for (int yy = 0; yy <= code_bitlen /4; yy++)
{
//利用比特移位、称重,统计本次转换的汉明距离
nHamm += m_bitweight[nErr & 0x0f];
nErr >>= 4;
}
//全路径旧汉明距离
int nPathHamm = m_best_path[m_table_lastjmp[i].nLastStatus[j]].nCurrentHamming[m_nClock % 2];
//新距离
nPathHamm += nHamm;
if (nBestHamm > nPathHamm)
{
//如果本转换较优,则刷新纪录
nBestHamm = nPathHamm;
nBestLastStatus = m_table_lastjmp[i].nLastStatus[j];
nBestInput = m_table_lastjmp[i].nLastInput[j];
nBestOutput = m_table_lastjmp[i].nLastOutput[j];
nBestDHamm = nHamm;
}
} // end for j
//开始刷新镜像路径,双缓存,用找到的最优转换来做为新的路径
int mirror = (m_nClock + 1) %2;
int raw = m_nClock % 2;
//首先,补全旧的路径的转换参数
m_best_path[nBestLastStatus].nHamming [raw][0] = nBestDHamm;
m_best_path[nBestLastStatus].nInChain [raw][0] = nBestInput;
m_best_path[nBestLastStatus].nOutChain [raw][0] = nBestOutput;
//旧路径全部后移一个状态,腾出空间
for (int j=1;j<L;j++)
{
m_best_path[i].nHamming[mirror][j] = m_best_path[nBestLastStatus].nHamming[raw][j-1];
m_best_path[i].nInChain[mirror][j] = m_best_path[nBestLastStatus].nInChain[raw][j-1];
m_best_path[i].nOutChain[mirror][j] = m_best_path[nBestLastStatus].nOutChain[raw][j-1];
m_best_path[i].nRegChain[mirror][j] = m_best_path[nBestLastStatus].nRegChain[raw][j-1];
}
//更新汉明,旧路径最末 (L-1)的汉明由于跑出了范围,减去,同时,新的作为首部加入
m_best_path[i].nCurrentHamming[mirror] = m_best_path[nBestLastStatus].nCurrentHamming[raw];
m_best_path[i].nCurrentHamming[mirror] -= m_best_path[nBestLastStatus].nHamming[raw][L-1];
m_best_path[i].nCurrentHamming[mirror] += nBestDHamm;
//更新最前端(新)的节点
m_best_path[i].nHamming[mirror][0] = 0;
m_best_path[i].nInChain[mirror][0] = 0;
m_best_path[i].nOutChain[mirror][0] = 0;
m_best_path[i].nRegChain[mirror][0] = i;
//刷新最优路径纪录
if (m_nBestHamming > m_best_path[i].nCurrentHamming[mirror])
{
m_nBestHamming = m_best_path[i].nCurrentHamming[mirror];
m_nBestStatus.clear();
}
if (m_nBestHamming == m_best_path[i].nCurrentHamming[mirror])
m_nBestStatus.push_back(i);
}// end for i
//推进 clock
m_nClock ++;
//缓存输出
if (m_nClock >= L - 1 || bFinished == true )
{
if (cd + 1 < nLen && m_nClock < L - 1)
continue;
int raw = m_nClock % 2;
size_t nBests = m_nBestStatus.size();//最优的 n 条路径
for (size_t pos = L-1; pos >0 ; pos --)
{
//统计各个跳转的大数判决
int nStatusCounter[data_status];
memset(&nStatusCounter,0,sizeof(nStatusCounter));
for (size_t i=0;i< nBests ; i++)
nStatusCounter[m_best_path[m_nBestStatus[i]].nInChain[raw][pos]] ++;
int nBestStatus = 0;
int nMaxHit = 0;
for (int i=0;i<data_status;i++)
{
if (nMaxHit < nStatusCounter[i])
{
nMaxHit = nStatusCounter[i];
nBestStatus = i;
}
}// next i
m_vec_decoded_data.push_back(nBestStatus);
if (bFinished==false || cd + 1 < nLen)
break;
}//next Pos
}//end if m_nClock >= L - 1 || bFinished == true
}// next cd
if (bFinished == true)
{
m_nClock = 0;
for (int i=0;i<reg_status; i++)
m_best_path[i].nCurrentHamming[0] = m_best_path[i].nCurrentHamming[1] = 0;
}
return (int)m_vec_decoded_data.size();
}
当然,别忘了输出GraphViz状态图的方法
template < int reg_status , int data_status, int code_bitlen, int L >
int lsm_codec<reg_status,data_status,code_bitlen,L>::pop_data(int DataArray[], int nLen)
{
int nWritten = 0;
for (int i=0;i<nLen;i++)
{
DataArray[i] = * m_vec_decoded_data.begin();
m_vec_decoded_data.pop_front();
nWritten++;
if (m_vec_decoded_data.empty()==true)
break;
}
return nWritten;
}
template < int reg_status , int data_status, int code_bitlen, int L >
string lsm_codec<reg_status,data_status,code_bitlen,L>::make_graph()
{
string res;
res += "digraph G\n{";
for (int i=0;i<reg_status;i++)
{
for (int j=0;j<data_status;j++)
{
char buffer[1024];
sprintf(buffer,"\tS%d->S%d [label=\"%d(%d)\"];\n",
i,
m_table_nextjmp[i].nNextStatus[j],
j,
m_table_nextjmp[i].nOutput[j]
);
res += buffer;
}
}
res += "}";
return move(res);
}
};
#endif
用户可以随时通过pop_data函数取出结果
template < int reg_status , int data_status, int code_bitlen, int L >
int lsm_codec<reg_status,data_status,code_bitlen,L>::pop_data(int DataArray[], int nLen)
{
int nWritten = 0;
for (int i=0;i<nLen;i++)
{
DataArray[i] = * m_vec_decoded_data.begin();
m_vec_decoded_data.pop_front();
nWritten++;
if (m_vec_decoded_data.empty()==true)
break;
}
return nWritten;
}
这样,一个通用编码、译码器就完成了!下一篇,我们分别针对前向卷积码、反馈卷积码,实现回调状态机初始化类。