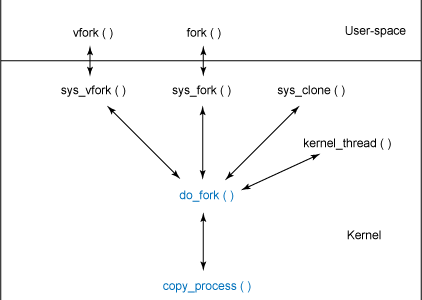
窥探 kernel --- sys_fork,sys_vfork,sys_clone,kernel_thread
本系列文章由张同浩编写,转载请注明出处:http://blog.csdn.net/muge0913/article/details/7479379
用户空间进程创建接口:fork,vfork,clone函数,这里只做简单说明。
fork:使用该系统调用时,子进程复制父进程的全部资源。由于要复制父进程进程描述符给子进程(进程描述的结构很大!!),这一过程开销是很大的。linux采用了”写时复制技术”(copy on write,COW),使子进程先共享父进程的物理页,只有子进程进行写操作时,再复制对应的物理页,避免了无用的复制开销,提高了系统的性能。
实现代码(x86):arch/x86/kernel/process.c
int sys_fork(struct pt_regs *regs)
{
return do_fork(SIGCHLD, regs->sp, regs,0, NULL, NULL);
}
实现代码(arm):arch/arm/kernel/sys_arm.c
/* Fork a newtask - this creates a new program thread.
* This is called indirectly via a smallwrapper
*/
asmlinkage int sys_fork(struct pt_regs *regs)
{
#ifdefCONFIG_MMU
return do_fork(SIGCHLD, regs->ARM_sp,regs, 0, NULL, NULL);
#else
/* can not support in nommu mode */
return(-EINVAL);
#endif
}
vfork:该系统调用创建的子进程,完全运行在父进程地址空间之上。子进程对地址空间任何数据的修改同样为父进程所见。vfork执行后父进程堵塞,知道子进程运行结束。
实现代码(x86):arch/x86/kernel/process.c
intsys_vfork(struct pt_regs *regs)
{
return do_fork(CLONE_VFORK | CLONE_VM |SIGCHLD, regs->sp, regs, 0,NULL, NULL);
}
实现代码(arm):arch/arm/kernel/sys_arm.c
asmlinkage intsys_vfork(struct pt_regs *regs)
{
return do_fork(CLONE_VFORK | CLONE_VM |SIGCHLD, regs->ARM_sp, regs, 0, NULL, NULL);
}
clone:该调用是linux系统所特有的,其NPTL的实现依赖此函数。与fork,vfork相比clone对进程创建有更好的控制能力,能控制子进程和父进程共享何种资源。
实现代码(x86):arch/x86/kernel/process.c
long sys_clone(unsignedlong clone_flags, unsigned long newsp,
void __user *parent_tid, void __user *child_tid, struct pt_regs *regs)
{
if (!newsp)
newsp = regs->sp;
return do_fork(clone_flags, newsp, regs, 0,parent_tid, child_tid);
}
实现代码(arm):arch/arm/kernel/sys_arm.c
/* Clone a task- this clones the calling program thread.
* This is called indirectly via a smallwrapper
*/
asmlinkage intsys_clone(unsigned long clone_flags, unsigned long newsp,
int __user *parent_tidptr, int tls_val,int__user *child_tidptr, struct pt_regs *regs)
{
if (!newsp)
newsp = regs->ARM_sp;
return do_fork(clone_flags, newsp, regs, 0,parent_tidptr, child_tidptr);
}
上面进程的创建最终依赖于:do_fork,只是向其传递了不同的参数。
longdo_fork(unsigned long clone_flags,
unsigned long stack_start,
struct pt_regs *regs,
unsigned long stack_size,
int __user *parent_tidptr,
int __user *child_tidptr)
参数clone_flags非常重要,fork把其设置为SIGCHLD,vfork把其设置为CLONE_VFORK|CLONE_VM|SIGCHLD,clone由用户调用时传递。总的来说,do_fork由clone_flags决定。其值可以自由组合决定。include/linux/sched.h中宏定义:
/* *cloning flags: */ #define CSIGNAL 0x000000ff /*signal mask to be sent at exit */ #define CLONE_VM 0x00000100 /* set if VM shared between processes */ #define CLONE_FS 0x00000200 /* set if fs info shared between processes*/ #define CLONE_FILES 0x00000400 /* set if open files shared betweenprocesses */ #define CLONE_SIGHAND 0x00000800 /* set if signal handlers and blockedsignals shared */ #define CLONE_PTRACE 0x00002000 /* set if we want to let tracing continue onthe child too */ #define CLONE_VFORK 0x00004000 /* set if the parent wants the child to wakeit up on mm_release */ #define CLONE_PARENT 0x00008000 /* set if we want to have the same parent asthe cloner */ #define CLONE_THREAD 0x00010000 /* Same thread group? */ #define CLONE_NEWNS 0x00020000 /* New namespace group? */ #define CLONE_SYSVSEM 0x00040000 /* share system V SEM_UNDO semantics */ #define CLONE_SETTLS 0x00080000 /* create a new TLS for the child */ #define CLONE_PARENT_SETTID 0x00100000 /*set the TID in the parent */ #define CLONE_CHILD_CLEARTID 0x00200000 /*clear the TID in the child */ #define CLONE_DETACHED 0x00400000 /* Unused,ignored */ #define CLONE_UNTRACED 0x00800000 /* set ifthe tracing process can't force CLONE_PTRACE on this clone */ #define CLONE_CHILD_SETTID 0x01000000 /*set the TID in the child */ #define CLONE_STOPPED 0x02000000 /* Start instopped state */ #define CLONE_NEWUTS 0x04000000 /* Newutsname group? */ #define CLONE_NEWIPC 0x08000000 /* Newipcs */ #defineCLONE_NEWUSER 0x10000000 /* New user namespace */ #define CLONE_NEWPID 0x20000000 /* New pidnamespace */ #define CLONE_NEWNET 0x40000000 /* Newnetwork namespace */ #define CLONE_IO 0x80000000 /* Clone io context */
上面的宏定义都占用了独立的bit,所以能或|组合使用。其低八位没有使用,是为了能和信号量组合使用。
内核线程创建接口:
内核线程是一种特殊的进程,它只能运行在内核态,不能访问用户空间的内容。内核线程除了各自的栈和硬件上下文外,共享所用资源。内核利用内核线程来完成一些后台工作如kswapd,ksoftirqd。内核线程有kernel_thread创建。
在linux2.6.xxx/arch/x86/include/asm/processor.h /* * create a kernel thread without removing itfrom tasklists */ extern intkernel_thread(int (*fn)(void *), void *arg, unsigned long flags);
在linux2.6.xxx/arch/arm/include/asm/processor.h
/* * Create a new kernel thread */ extern intkernel_thread(int (*fn)(void *), void *arg, unsigned long flags);
参数说明:
fn:新创建的内核线程要执行的函数。
arg:fn的参数。
flags:和do_fork中的clone_flags作用相似。
kernel_thread函数分析:
在linux2.6.xxx/arch/x86/kernel/process.c
/*
* Create a kernel thread
*/
intkernel_thread(int (*fn)(void *), void *arg, unsigned long flags)
{
struct pt_regs regs;//保存进程的硬件上下文
memset(®s, 0, sizeof(regs));
regs.si = (unsigned long) fn;
regs.di = (unsigned long) arg;
#ifdefCONFIG_X86_32
regs.ds = __USER_DS;
regs.es = __USER_DS;
regs.fs = __KERNEL_PERCPU;
regs.gs = __KERNEL_STACK_CANARY;
#else
regs.ss = __KERNEL_DS;
#endif
regs.orig_ax = -1;
regs.ip = (unsigned long)kernel_thread_helper;
regs.cs = __KERNEL_CS | get_kernel_rpl();
regs.flags = X86_EFLAGS_IF | 0x2;
/* Ok, create the new process.. */
return do_fork(flags | CLONE_VM |CLONE_UNTRACED, 0, ®s, 0, NULL, NULL);
}
分析:
从这段代码可知,内核线程的创建最终还是调用了do_fork。
arm架构的kernel_thread实现:
/*
* Create a kernel thread.
*/
pid_tkernel_thread(int (*fn)(void *), void *arg, unsigned long flags)
{
struct pt_regs regs;
memset(®s, 0, sizeof(regs));
regs.ARM_r4 = (unsigned long)arg;
regs.ARM_r5 = (unsigned long)fn;
regs.ARM_r6 = (unsignedlong)kernel_thread_exit;
regs.ARM_r7 = SVC_MODE | PSR_ENDSTATE |PSR_ISETSTATE;
regs.ARM_pc = (unsignedlong)kernel_thread_helper;
regs.ARM_cpsr = regs.ARM_r7 | PSR_I_BIT;
return do_fork(flags|CLONE_VM|CLONE_UNTRACED,0, ®s, 0, NULL, NULL);
}
/*
* Shuffle the argument into the correctregister before calling the
* thread function. r4 is the thread argument, r5 is the pointerto
* the thread function, and r6 points to theexit function.
*/
extern voidkernel_thread_helper(void);
asm( ".pushsection .text\n"
" .align\n"
" .type kernel_thread_helper,#function\n"
"kernel_thread_helper:\n"
#ifdefCONFIG_TRACE_IRQFLAGS
" bl trace_hardirqs_on\n"
#endif
" msr cpsr_c,r7\n"
" mov r0,r4\n"
" mov lr,r6\n"
" mov pc,r5\n"
" .size kernel_thread_helper,. - kernel_thread_helper\n"
" .popsection");