浅谈linux的LED驱动
转载请注明出处:http://blog.csdn.net/ruoyunliufeng/article/details/23561973
开发板mini2240.内核2.6.22.6
一.源代码
驱动源代码:
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/kernel.h>
#include <linux/fs.h>
#include <linux/init.h>
#include <linux/delay.h>
#include <asm/uaccess.h>
#include <asm/irq.h>
#include <asm/io.h>
#include <asm/arch/regs-gpio.h>
#include <asm/hardware.h>
#include <linux/device.h>
static struct class *firstdrv_class;
static struct class_device *firstdrv_class_dev;
volatile unsigned long *gpbcon = NULL;
volatile unsigned long *gpbdat = NULL;
static int first_drv_open(struct inode *inode, struct file *file)
{
//printk("first_drv_open\n");
/*
* LED1,LED2,LED4对应GPB5、GPB6、GPB7、GPB8
*/
/* 配置GPB5,6,7,8为输出 */
*gpbcon &= ~((0x3<<(5*2)) | (0x3<<(6*2)) | (0x3<<(7*2)) | (0x3<<(8*2))); //初始化
*gpbcon |= ((0x1<<(5*2)) | (0x1<<(6*2)) | (0x1<<(7*2)) | (0x1<<(8*2))); //01配置输出
return 0;
}
static ssize_t first_drv_write(struct file *file, const char __user *buf, size_t count, loff_t * ppos)
{
int val;
//printk("first_drv_write\n");
copy_from_user(&val, buf, count); //copy_to_user();
if (val == 1)
{
// 点灯
*gpbdat &= ~((1<<5) | (1<<6) | (1<<7) | (1<<8)); //0为亮
}
else
{
// 灭灯
*gpbdat |= (1<<5) | (1<<6) | (1<<7) | (1<<8); //1灭
}
return 0;
}
static struct file_operations first_drv_fops = {
.owner = THIS_MODULE, /* 这是一个宏,推向编译模块时自动创建的__this_module变量 */
.open = first_drv_open,
.write =first_drv_write,
}; //将应用的open与内核对应起来
int major;
static int first_drv_init(void) //驱动入口
{
major = register_chrdev(0, "first_drv", &first_drv_fops); // 注册, 告诉内核(主设备号,名字,结构体)将结构体,放入内核主设备好的数组。
firstdrv_class = class_create(THIS_MODULE, "firstdrv"); //创建一个类
firstdrv_class_dev = class_device_create(firstdrv_class, NULL, MKDEV(major, 0), NULL, "xyz"); // / dev/xyz 类下面建立设备
gpbcon = (volatile unsigned long *)ioremap(0x56000010, 16); //物理地址映射虚拟地址
gpbdat = gpbcon + 1; //这里是指针+1
return 0;
}
static void first_drv_exit(void)
{
unregister_chrdev(major, "first_drv"); // 卸载
class_device_unregister(firstdrv_class_dev);
class_destroy(firstdrv_class);
iounmap(gpbcon);
}
module_init(first_drv_init);//告诉内核first_drv_init为入口函数
module_exit(first_drv_exit);
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL"); //证书
测试程序源代码:
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <stdio.h>
/* firstdrvtest on
* firstdrvtest off
*/
int main(int argc, char **argv) //为参数,正常的话应该是两个一个是firstdrvtest一个是on或off
{
int fd;
int val = 1;
fd = open("/dev/xyz", O_RDWR);
if (fd < 0)
{
printf("can't open!\n");
}
if (argc != 2)
{
printf("Usage :\n");
printf("%s <on|off>\n", argv[0]);
return 0;
}
if (strcmp(argv[1], "on") == 0)
{
val = 1;
}
else
{
val = 0;
}
write(fd, &val, 4);
return 0;
}
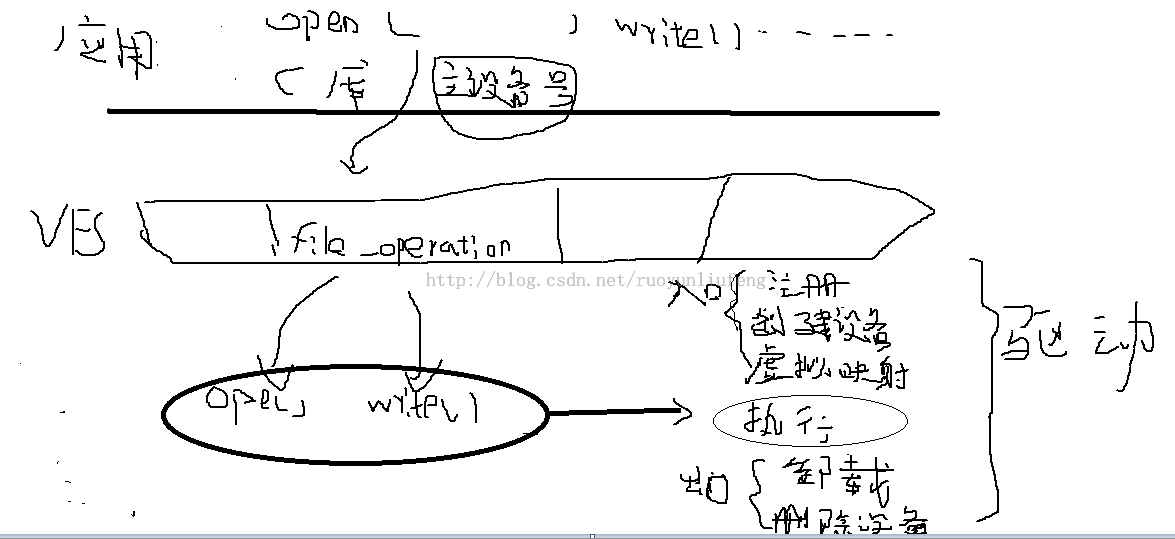
二.结构分析
1.应用程序:
应用程序是用户的操作硬件的第一个程序,程序进来第一件事就是打开设备文件(驱动程序自动创建的)如果打不开则提示错误。第二件事就是判断你输入的参数,如果不是两个则给出提示。然后判断第二个参数设置val的值,最后写入。
2.驱动程序:
应用程序并不能直接操作寄存器。从应用程序到驱动程序是需要一个连接的。连接的第一层是C库。第二层VFS(虚拟文件系统(VFS)是物理文件系统与服务之间的一个接口层,它对Linux的每个文件系统的所有细节进行抽象,使得不同的文件系统在Linux核心以及系统中运行的其他进程看来,都是相同的)。第三层就是注册的一个数组register_chrdev()数组根据主设备号,找到一个结构体file_operaation就是这个结构体将应用层的open()函数告诉内核驱动的。然后驱动根据应用程序传来的参数进行一系列操作。
模块加载后,本驱动程序支持,自动创建驱动文件。在入口创建一个类class_create();然后创建文件
class_device_create();在出口的时候进行删除。
三.图片解析
参考资料:韦东山视频第一期