Windows程序设计--文本输出(二)
今天要详细讲解一下TEXTOUT,它是显示文本最重要的GDI函数。CSDN是这样描述的:
The TextOut function writes a character string at the specified location, using the currently selected font, background color, and text color.
我们看看他的原型:
BOOL TextOut(
_In_ HDC hdc,
_In_ int nXStart,
_In_ int nYStart,
_In_ LPCTSTR lpString,
_In_ int cchString
);第一个参数就是设备环境句柄;
第二第三个参数决定了输出字符串在客户区的起始位置,注意的是该坐标为逻辑坐标,是相对于client的;
第四个参数是指向字符串的指针;
第五个参数是字符串中的字符数。
下面是简单应用:
// Obtain the window's client rectangle
GetClientRect(hwnd, &r);
// THE FIX: by setting the background mode
// to transparent, the region is the text itself
// SetBkMode(hdc, TRANSPARENT);
// Bracket begin a path
BeginPath(hdc);
// Send some text out into the world
TCHAR text[ ] = "Defenestration can be hazardous";
TextOut(hdc,r.left,r.top,text, ARRAYSIZE(text));
// Bracket end a path
EndPath(hdc);
// Derive a region from that path
SelectClipPath(hdc, RGN_AND);
// This generates the same result as SelectClipPath()
// SelectClipRgn(hdc, PathToRegion(hdc));
// Fill the region with grayness
FillRect(hdc, &r, GetStockObject(GRAY_BRUSH));
TextOut函数完成了文本的输出,但是输出文本的字体、大小等属性却不是由TextOut来控制的,还是需要我们之前所说的设备环境。
那接下来不得不提就是函数GetTextMetrics,该函数把程序当前的字体信息,存放到TEXTMETRIC中。
TEXTMETRIC又是什么鬼?
windows把字符尺寸的各种值复制到类型为TEXTMETRIC的结构中。这个结构体有20个字段,我们关心几个;
typedef struct tagTEXTMETRIC { /* tm */
int tmHeight; //字符高度
int tmAscent; //字符上部高度
int tmDescent; //字符下部高度
int tmInternalLeading;//由tmHeight定义的字符高度的顶部空间数目
int tmExternalLeading;//夹在两行之间的空间数目
int tmAveCharWidth; //平均字符宽度
int tmMaxCharWidth;//最宽字符的宽度
...
} TEXTMETRIC;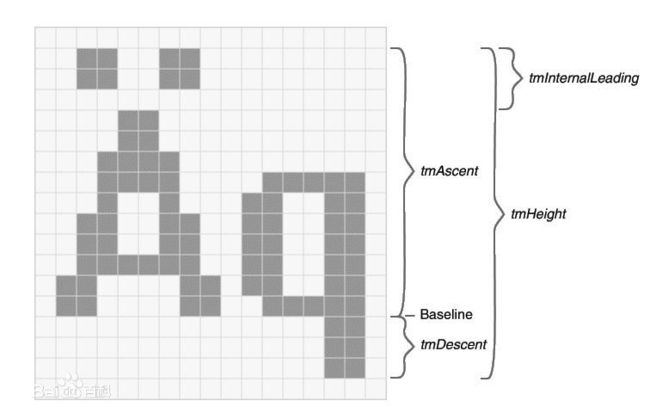
注意tmHeight = tmAscent+tmDescent。
现在是时候看下函数GetTextMetrics了,原型如下:
BOOL GetTextMetrics(HDC hdc, LPTEXTMETRIC lptm);hdc:设备环境句柄。
lptm:指向结构TEXTMETRIC的指针,该结构用于获得字体信息。
返回值:如果函数调用成功,返回值非零,如果函数调用失败,返回值是0。
TEXTMETRIC tm; hdc = GetDc(hwnd); GetTextMetrics(hdc, &tm); TextOut();