数据挖掘-基于Kmeans算法、MBSAS算法及DBSCAN算法的newsgroup18828文本聚类器的JAVA实现(上)
(update 2012.12.28 关于本项目下载及运行的常见问题 FAQ见 newsgroup18828文本分类器、文本聚类器、关联分析频繁模式挖掘算法的Java实现工程下载及运行FAQ )
本文要点如下:
对newsgroup文档集进行预处理,按照DF法及SVD分解法抽取特征词,实现降维
实现了K-Means,MBSAS,DBSCAN三种聚类算法用weka工具进行newsgroup文档聚类
计算各种算法聚类的熵,进行算法评价
1、newsgroup文档集预处理
newsgroup是常用的数据挖掘实验数据。文本预处理主要包括单词分片、去除标点等无关符号、去停用词等等,相关详细介绍见我的另一篇博文数据挖掘-基于贝叶斯算法及KNN算法的newsgroup18828文本分类器的JAVA实现(上),此处只给出文本预处理和向量化不同的部分代码。
文本预处理类DataPreProcess.java
package com.pku.yangliu;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
/**
* Newsgroups文档集预处理类
*/
public class DataPreProcess {
/**输入文件调用处理数据函数
* @param strDir newsgroup文件目录的绝对路径
* @throws IOException
*/
public void doProcess(String strDir) throws IOException{
File fileDir = new File(strDir);
if(!fileDir.exists()){
System.out.println("File not exist:" + strDir);
return;
}
String subStrDir = strDir.substring(strDir.lastIndexOf('/'));
String dirTarget = strDir + "/../../processedSample_includeNotSpecial"+subStrDir;
File fileTarget = new File(dirTarget);
if(!fileTarget.exists()){//注意processedSample需要先建立目录建出来,否则会报错,因为母目录不存在
fileTarget.mkdir();
}
File[] srcFiles = fileDir.listFiles();
String[] stemFileNames = new String[srcFiles.length];
for(int i = 0; i < srcFiles.length; i++){
String fileFullName = srcFiles[i].getCanonicalPath();
String fileShortName = srcFiles[i].getName();
if(!new File(fileFullName).isDirectory()){//确认子文件名不是目录如果是可以再次递归调用
System.out.println("Begin preprocess:"+fileFullName);
StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder();
stringBuilder.append(dirTarget + "/" + fileShortName);
createProcessFile(fileFullName, stringBuilder.toString());
stemFileNames[i] = stringBuilder.toString();
}
else {
fileFullName = fileFullName.replace("\\","/");
doProcess(fileFullName);
}
}
//下面调用stem算法
if(stemFileNames.length > 0 && stemFileNames[0] != null){
Stemmer.porterMain(stemFileNames);
}
}
/**进行文本预处理生成目标文件
* @param srcDir 源文件文件目录的绝对路径
* @param targetDir 生成的目标文件的绝对路径
* @throws IOException
*/
private static void createProcessFile(String srcDir, String targetDir) throws IOException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
FileReader srcFileReader = new FileReader(srcDir);
FileReader stopWordsReader = new FileReader("F:/DataMiningSample/stopwords.txt");
FileWriter targetFileWriter = new FileWriter(targetDir);
BufferedReader srcFileBR = new BufferedReader(srcFileReader);//装饰模式
BufferedReader stopWordsBR = new BufferedReader(stopWordsReader);
String line, resLine, stopWordsLine;
//用stopWordsBR够着停用词的ArrayList容器
ArrayList<String> stopWordsArray = new ArrayList<String>();
while((stopWordsLine = stopWordsBR.readLine()) != null){
if(!stopWordsLine.isEmpty()){
stopWordsArray.add(stopWordsLine);
}
}
while((line = srcFileBR.readLine()) != null){
resLine = lineProcess(line,stopWordsArray);
if(!resLine.isEmpty()){
//按行写,一行写一个单词
String[] tempStr = resLine.split(" ");//\s
for(int i = 0; i < tempStr.length; i++){
if(!tempStr[i].isEmpty()){
targetFileWriter.append(tempStr[i]+"\n");
}
}
}
}
targetFileWriter.flush();
targetFileWriter.close();
srcFileReader.close();
stopWordsReader.close();
srcFileBR.close();
stopWordsBR.close();
}
/**对每行字符串进行处理,主要是词法分析、去停用词和stemming
* @param line 待处理的一行字符串
* @param ArrayList<String> 停用词数组
* @return String 处理好的一行字符串,是由处理好的单词重新生成,以空格为分隔符
* @throws IOException
*/
private static String lineProcess(String line, ArrayList<String> stopWordsArray) throws IOException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
//step1 英文词法分析,去除数字、连字符、标点符号、特殊字符,所有大写字母转换成小写,可以考虑用正则表达式
String res[] = line.split("[^a-zA-Z]");
//这里要小心,防止把有单词中间有数字和连字符的单词 截断了,但是截断也没事
String resString = new String();
//step2去停用词
//step3stemming,返回后一起做
for(int i = 0; i < res.length; i++){
if(!res[i].isEmpty() && !stopWordsArray.contains(res[i].toLowerCase())){
resString += " " + res[i].toLowerCase() + " ";
}
}
return resString;
}
/**
* @param args
* @throws IOException
*/
public void BPPMain(String[] args) throws IOException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
DataPreProcess dataPrePro = new DataPreProcess();
dataPrePro.doProcess("F:/DataMiningSample/orginSample");
}
}
文本向量化表示主要基于TF-IDF值
ComputeWordsVector.java
package com.pku.yangliu;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.SortedMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;
import java.util.SortedSet;
import java.util.TreeMap;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.TreeSet;
/**计算文档的属性向量,将所有文档向量化
*
*/
public class ComputeWordsVector {
/**计算文档的TF-IDF属性向量,返回Map<文件名,Map<特征词,TF-IDF值>>
* @param testSampleDir 处理好的聚类样本测试样例集合
* @return Map<String,Map<String,Double>> 所有测试样例的属性向量构成的map
* @throws IOException
*/
public Map<String,Map<String,Double>> computeTFMultiIDF(String testSampleDir) throws IOException{
String word;
Map<String,Map<String,Double>> allTestSampleMap = new TreeMap<String,Map<String,Double>>();
Map<String, Double> idfPerWordMap = computeIDF(testSampleDir);
Map<String,Double> TFPerDocMap = new TreeMap<String,Double>();//计算每篇文档中含有各特征词数量
File[] samples = new File(testSampleDir).listFiles();
System.out.println("the total number of test files is" + samples.length);
for(int i = 0; i < samples.length; i++){
TFPerDocMap.clear();
FileReader samReader = new FileReader(samples[i]);
BufferedReader samBR = new BufferedReader(samReader);
Double wordSumPerDoc = 0.0;//计算每篇文档的总词数
while((word = samBR.readLine()) != null){
if(!word.isEmpty()){
wordSumPerDoc++;
if(TFPerDocMap.containsKey(word)){
Double count = TFPerDocMap.get(word);
TFPerDocMap.put(word, count + 1.0);
}
else {
TFPerDocMap.put(word, 1.0);
}
}
}
Double maxCount = 0.0, wordWeight;//记录出现次数最多的词出现的次数,用做归一化
Set<Map.Entry<String, Double>> tempTF = TFPerDocMap.entrySet();
for(Iterator<Map.Entry<String, Double>> mt = tempTF.iterator(); mt.hasNext();){
Map.Entry<String, Double> me = mt.next();
if(me.getValue() > maxCount) maxCount = me.getValue();
}
for(Iterator<Map.Entry<String, Double>> mt = tempTF.iterator(); mt.hasNext();){
Map.Entry<String, Double> me = mt.next();
Double IDF = Math.log(samples.length / idfPerWordMap.get(me.getKey())) / Math.log(10);
wordWeight = (me.getValue() / maxCount) * IDF;
TFPerDocMap.put(me.getKey(), wordWeight);
}
TreeMap<String,Double> tempMap = new TreeMap<String,Double>();
tempMap.putAll(TFPerDocMap);
allTestSampleMap.put(samples[i].getName(), tempMap);
}
//printTestSampleMap(allTestSampleMap);
return allTestSampleMap;
}
/**输出测试样例map内容,用于测试
* @param SortedMap<String,Double> 属性词典
* @throws IOException
*/
void printTestSampleMap(Map<String,Map<String,Double>> allTestSampleMap) throws IOException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
File outPutFile = new File("F:/DataMiningSample/KmeansClusterResult/allTestSampleMap.txt");
FileWriter outPutFileWriter = new FileWriter(outPutFile);
Set<Map.Entry<String,Map<String,Double>>> allWords = allTestSampleMap.entrySet();
for(Iterator<Map.Entry<String,Map<String,Double>>> it = allWords.iterator(); it.hasNext();){
Map.Entry<String,Map<String,Double>> me = it.next();
outPutFileWriter.append(me.getKey() + " ");
Set<Map.Entry<String,Double>> vecSet = me.getValue().entrySet();
for(Iterator<Map.Entry<String, Double>> jt = vecSet.iterator(); jt.hasNext();){
Map.Entry<String, Double> ne = jt.next();
outPutFileWriter.append(ne.getKey() + " "+ ne.getValue() + " ");
}
outPutFileWriter.append("\n");
outPutFileWriter.flush();
}
outPutFileWriter.close();
}
/**统计每个词的总的出现次数,返回出现次数大于n次的词汇构成最终的属性词典
* @param strDir 处理好的newsgroup文件目录的绝对路径
* @throws IOException
*/
public SortedMap<String,Double> countWords(String strDir,Map<String, Double> wordMap) throws IOException{
File sampleFile = new File(strDir);
File [] sampleDir = sampleFile.listFiles();
String word;
for(int j = 0; j < sampleDir.length; j++){
File[] sample = sampleDir[j].listFiles();
for(int i = 0; i < sample.length; i++){
if(sample[i].getName().contains("stemed")){
FileReader samReader = new FileReader(sample[i]);
BufferedReader samBR = new BufferedReader(samReader);
while((word = samBR.readLine()) != null){
if(!word.isEmpty() && wordMap.containsKey(word)){
double count = wordMap.get(word) + 1;
wordMap.put(word, count);
}
else {
wordMap.put(word, 1.0);
}
}
}
}
}
//去除停用词后,先用DF法选取特征词,后面再加入特征词的选取算法
SortedMap<String,Double> newWordMap = new TreeMap<String,Double>();
Set<Map.Entry<String,Double>> allWords = wordMap.entrySet();
for(Iterator<Map.Entry<String,Double>> it = allWords.iterator(); it.hasNext();){
Map.Entry<String, Double> me = it.next();
if(me.getValue() > 100){//DF法降维
newWordMap.put(me.getKey(),me.getValue());
}
}
return newWordMap;
}
/**计算IDF,即属性词典中每个词在多少个文档中出现过
* @param testSampleDir 聚类算法测试样本所在目录
* @return 单词的IDFmap 格式为SortedMap<String,Double> 即<单词,包含该单词的文档数>
* @throws IOException
*/
Map<String,Double> computeIDF(String testSampleDir) throws IOException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Map<String,Double> IDFPerWordMap = new TreeMap<String,Double>();
Set<String> alreadyCountWord = new HashSet<String>();//记下当前已经遇到过的该文档中的词
String word;
File[] samples = new File(testSampleDir).listFiles();
for(int i = 0; i < samples.length; i++){
alreadyCountWord.clear();
FileReader tsReader = new FileReader(samples[i]);
BufferedReader tsBR = new BufferedReader(tsReader);
while((word = tsBR.readLine()) != null){
if(!alreadyCountWord.contains(word)){
if(IDFPerWordMap.containsKey(word)){
IDFPerWordMap.put(word, IDFPerWordMap.get(word) + 1.0);
}
else IDFPerWordMap.put(word, 1.0);
alreadyCountWord.add(word);
}
}
}
return IDFPerWordMap;
}
/**创建聚类算法的测试样例集,主要是过滤出只含有特征词的文档写到一个目录下
* @param String srcDir 源目录,已经经过预处理但还没有过滤非特征词的文档目录
* @param String destDir 目的目录,聚类算法的测试样例目录
* @return String[] 创建测试样例集中特征词数组
* @throws IOException
*/
String[] createTestSamples( String srcDir, String destDir) throws IOException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
SortedMap<String,Double> wordMap = new TreeMap<String,Double>();
wordMap = countWords(srcDir, wordMap);
System.out.println("special words map sizes:" + wordMap.size());
String word, testSampleFile;
File[] sampleDir = new File(srcDir).listFiles();
for(int i = 0; i < sampleDir.length; i++){
File[] sample = sampleDir[i].listFiles();
for(int j = 0;j < sample.length; j++){
if(sample[j].getName().contains("stemed")){
testSampleFile = destDir + sampleDir[i].getName()+"_"+sample[j].getName();
FileReader samReader = new FileReader(sample[j]);
BufferedReader samBR = new BufferedReader(samReader);
FileWriter tsWriter = new FileWriter(new File(testSampleFile));
while((word = samBR.readLine()) != null){
if(wordMap.containsKey(word)){
tsWriter.append(word + "\n");
}
}
tsWriter.flush();
tsWriter.close();
}
}
}
//返回属性词典
String [] terms = new String[wordMap.size()];
int i = 0;
Set<Map.Entry<String,Double>> allWords = wordMap.entrySet();
for(Iterator<Map.Entry<String,Double>> it = allWords.iterator(); it.hasNext();){
Map.Entry<String, Double> me = it.next();
terms[i] = me.getKey();
i++;
}
return terms;
}
/**评估函数根据聚类结果文件统计熵和混淆矩阵
* @param clusterResultFile 聚类结果文件
* @param K 聚类数目
* @return double 聚类结果的熵值
* @throws IOException
*/
double evaluateClusterRes(String clusterResultFile, int K) throws IOException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Map<String,String> rightCate = new TreeMap<String,String>();
Map<String,String> resultCate = new TreeMap<String,String>();
FileReader crReader = new FileReader(clusterResultFile);
BufferedReader crBR = new BufferedReader(crReader);
String[] s;
String line;
while((line = crBR.readLine()) != null){
s = line.split(" ");
resultCate.put(s[0], s[1]);
//再把s[0]用_分片
rightCate.put(s[0], s[0].split("_")[0]);
}
return computeEntropyAndConfuMatrix(rightCate,resultCate,K);//返回熵
}
/**计算混淆矩阵并且输出,返回熵
* @param rightCate 正确类目对应map
* @param resultCate 聚类结果对应map
* @return double 返回聚类的熵
* @throws IOException
*/
private double computeEntropyAndConfuMatrix(Map<String, String> rightCate,
Map<String, String> resultCate, int K) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
int[][] confusionMatrix = new int[K][20];//K行20列,[i,j]表示聚类i中属于类目j的文件数
//首先求出类目对应的数组索引
SortedSet<String> cateNames = new TreeSet<String>();
Set<Map.Entry<String, String>> rightCateSet = rightCate.entrySet();
for(Iterator<Map.Entry<String, String>> it = rightCateSet.iterator(); it.hasNext();){
Map.Entry<String, String> me = it.next();
cateNames.add(me.getValue());
}
String[] cateNamesArray = cateNames.toArray(new String[0]);
Map<String,Integer> cateNamesToIndex = new TreeMap<String,Integer>();
for(int i = 0; i < cateNamesArray.length; i++){
cateNamesToIndex.put(cateNamesArray[i],i);
}
for(Iterator<Map.Entry<String, String>> it = rightCateSet.iterator(); it.hasNext();){
Map.Entry<String, String> me = it.next();
confusionMatrix[Integer.parseInt(resultCate.get(me.getKey()))][cateNamesToIndex.get(me.getValue())]++;
}
//输出混淆矩阵
double [] clusterSum = new double[K];//记录每个聚类的文件数
double[] everyClusterEntropy = new double[K];//记录每个聚类的熵
double clusterEntropy = 0;
System.out.print(" ");
for(int i = 0; i < 20; i++){
System.out.print(i + " ");
}
System.out.println();
for(int i = 0; i < K; i++){
System.out.print(i + " ");
for(int j = 0; j < 20; j++){
clusterSum[i] += confusionMatrix[i][j];
System.out.print(confusionMatrix[i][j]+" ");
}
System.out.println();
}
System.out.println();
for(int i = 0; i < K; i++){
if(clusterSum[i] != 0){
for(int j = 0; j < 20; j++){
double p = (double)confusionMatrix[i][j]/clusterSum[i];
if(p != 0){
everyClusterEntropy[i] += -p * Math.log(p);
}
}
clusterEntropy += clusterSum[i]/(double)rightCate.size() * everyClusterEntropy[i];
}
}
return clusterEntropy;
}
}
2、K-means算法
K-means算法是非常经典的聚类算法。其算法思路是: 先选K个初始聚类点作为初始中心点,然后计算其他所有点到K个聚类点的距离做聚类,将点分到最近的聚类,聚完类后中心点发生变化了,于是更新中心点。然后再计算其他所有点到这K个中心点的距离重新聚类,中心点又会发生变化,如此迭代下去。其伪代码如下:
K-means算法的实现有以下关键点:
初始点的选择策略:随机选、均匀抽样、最大最小法等
距离的度量 1-余弦相似度,欧式距离,1-向量内积,测试发现1-余弦相似度效果最好,而1-向量内积速度最快。
中心点的计算 向量各维取评价
算法停止条件 计算准则函数及设置最大迭代次数
空聚类的处理 注意空聚类导致的程序bug
K-means算法实现类KmeansCluster.java
package com.pku.yangliu;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;
import java.util.TreeMap;
import java.util.Vector;
/**Kmeans聚类算法的实现类,将newsgroups文档集聚成10类、20类、30类
* 算法结束条件:当每个点最近的聚类中心点就是它所属的聚类中心点时,算法结束
*
*/
public class KmeansCluster {
/**Kmeans算法主过程
* @param Map<String, Map<String, Double>> allTestSampleMap 聚类算法测试样本map
* @param int K 聚类的数量
* @return Map<String,Integer> 聚类的结果 即<文件名,聚类完成后所属的类别标号>
* @throws IOException
*/
private Map<String, Integer> doProcess(
Map<String, Map<String, Double>> allTestSampleMap, int K) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
//0、首先获取allTestSampleMap所有文件名顺序组成的数组
String[] testSampleNames = new String[allTestSampleMap.size()];
int count = 0, tsLength = allTestSampleMap.size();
Set<Map.Entry<String, Map<String, Double>>> allTestSampeleMapSet = allTestSampleMap.entrySet();
for(Iterator<Map.Entry<String, Map<String, Double>>> it = allTestSampeleMapSet.iterator(); it.hasNext(); ){
Map.Entry<String, Map<String, Double>> me = it.next();
testSampleNames[count++] = me.getKey();
}
//1、初始点的选择算法是随机选择或者是均匀分开选择,这里采用后者
Map<Integer, Map<String, Double>> meansMap = getInitPoint(allTestSampleMap, K);//保存K个中心点
double [][] distance = new double[tsLength][K];//distance[i][j]记录点i到聚类中心j的距离
//2、初始化K个聚类
int [] assignMeans = new int[tsLength];//记录所有点属于的聚类序号,初始化全部为0
Map<Integer, Vector<Integer>> clusterMember = new TreeMap<Integer,Vector<Integer>>();//记录每个聚类的成员点序号
Vector<Integer> mem = new Vector<Integer>();
int iterNum = 0;//迭代次数
while(true){
System.out.println("Iteration No." + (iterNum++) + "----------------------");
//3、计算每个点和每个聚类中心的距离
for(int i = 0; i < tsLength; i++){
for(int j = 0; j < K; j++){
distance[i][j] = getDistance(allTestSampleMap.get(testSampleNames[i]),meansMap.get(j));
}
}
//4、找出每个点最近的聚类中心
int[] nearestMeans = new int[tsLength];
for(int i = 0; i < tsLength; i++){
nearestMeans[i] = findNearestMeans(distance, i);
}
//5、判断当前所有点属于的聚类序号是否已经全部是其离得最近的聚类,如果是或者达到最大的迭代次数,那么结束算法
int okCount = 0;
for(int i = 0; i <tsLength; i++){
if(nearestMeans[i] == assignMeans[i]) okCount++;
}
System.out.println("okCount = " + okCount);
if(okCount == tsLength || iterNum >= 10) break;
//6、如果前面条件不满足,那么需要重新聚类再进行一次迭代,需要修改每个聚类的成员和每个点属于的聚类信息
clusterMember.clear();
for(int i = 0; i < tsLength; i++){
assignMeans[i] = nearestMeans[i];
if(clusterMember.containsKey(nearestMeans[i])){
clusterMember.get(nearestMeans[i]).add(i);
}
else {
mem.clear();
mem.add(i);
Vector<Integer> tempMem = new Vector<Integer>();
tempMem.addAll(mem);
clusterMember.put(nearestMeans[i], tempMem);
}
}
//7、重新计算每个聚类的中心点!
for(int i = 0; i < K; i++){
if(!clusterMember.containsKey(i)){//注意kmeans可能产生空聚类
continue;
}
Map<String, Double> newMean = computeNewMean(clusterMember.get(i), allTestSampleMap, testSampleNames);
Map<String, Double> tempMean = new TreeMap<String, Double>();
tempMean.putAll(newMean);
meansMap.put(i, tempMean);
}
}
//8、形成聚类结果并且返回
Map<String, Integer> resMap = new TreeMap<String, Integer>();
for(int i = 0; i < tsLength; i++){
resMap.put(testSampleNames[i], assignMeans[i]);
}
return resMap;
}
/**计算当前聚类新的中心,采用向量平均
* @param clusterM 该点到所有聚类中心的距离
* @param allTestSampleMap 所有测试样例的<文件名,向量>构成的map
* @param testSampleNames 所有测试样例文件名构成的数组
* @return Map<String, Double> 新的聚类中心的向量
* @throws IOException
*/
private Map<String, Double> computeNewMean(Vector<Integer> clusterM,
Map<String, Map<String, Double>> allTestSampleMap,
String[] testSampleNames) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
double memberNum = (double)clusterM.size();
Map<String, Double> newMeanMap = new TreeMap<String,Double>();
Map<String, Double> currentMemMap = new TreeMap<String,Double>();
for(Iterator<Integer> it = clusterM.iterator(); it.hasNext();){
int me = it.next();
currentMemMap = allTestSampleMap.get(testSampleNames[me]);
Set<Map.Entry<String, Double>> currentMemMapSet = currentMemMap.entrySet();
for(Iterator<Map.Entry<String, Double>> jt = currentMemMapSet.iterator(); jt.hasNext();){
Map.Entry<String, Double> ne = jt.next();
if(newMeanMap.containsKey(ne.getKey())){
newMeanMap.put(ne.getKey(), newMeanMap.get(ne.getKey()) + ne.getValue());
}
else {
newMeanMap.put(ne.getKey(), ne.getValue());
}
}
}
Set<Map.Entry<String, Double>> newMeanMapSet = newMeanMap.entrySet();
for(Iterator<Map.Entry<String, Double>> jt = newMeanMapSet.iterator(); jt.hasNext();){
Map.Entry<String, Double> ne = jt.next();
newMeanMap.put(ne.getKey(), newMeanMap.get(ne.getKey()) / memberNum);
}
return newMeanMap;
}
/**找出距离当前点最近的聚类中心
* @param double[][] 点到所有聚类中心的距离
* @return i 最近的聚类中心的序 号
* @throws IOException
*/
private int findNearestMeans(double[][] distance,int m) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
double minDist = 10;
int j = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < distance[m].length; i++){
if(distance[m][i] < minDist){
minDist = distance[m][i];
j = i;
}
}
return j;
}
/**计算两个点的距离
* @param map1 点1的向量map
* @param map2 点2的向量map
* @return double 两个点的欧式距离
*/
private double getDistance(Map<String, Double> map1, Map<String, Double> map2) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return 1 - computeSim(map1,map2);
}
/**计算两个文本的相似度
* @param testWordTFMap 文本1的<单词,词频>向量
* @param trainWordTFMap 文本2<单词,词频>向量
* @return Double 向量之间的相似度 以向量夹角余弦计算或者向量内积计算(效果相当而速度更快)
* @throws IOException
*/
private double computeSim(Map<String, Double> testWordTFMap,
Map<String, Double> trainWordTFMap) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
double mul = 0;//, testAbs = 0, trainAbs = 0;
Set<Map.Entry<String, Double>> testWordTFMapSet = testWordTFMap.entrySet();
for(Iterator<Map.Entry<String, Double>> it = testWordTFMapSet.iterator(); it.hasNext();){
Map.Entry<String, Double> me = it.next();
if(trainWordTFMap.containsKey(me.getKey())){
mul += me.getValue()*trainWordTFMap.get(me.getKey());
}
//testAbs += me.getValue() * me.getValue();
}
//testAbs = Math.sqrt(testAbs);
/*Set<Map.Entry<String, Double>> trainWordTFMapSet = trainWordTFMap.entrySet();
for(Iterator<Map.Entry<String, Double>> it = trainWordTFMapSet.iterator(); it.hasNext();){
Map.Entry<String, Double> me = it.next();
trainAbs += me.getValue()*me.getValue();
}
trainAbs = Math.sqrt(trainAbs);*/
return mul ;/// (testAbs * trainAbs);
}
/**获取kmeans算法迭代的初始点
* @param k 聚类的数量
* @param Map<String, Map<String, Double>> allTestSampleMap 所有测试样例的<文件名,向量>构成的map
* @return Map<Integer, Map<String, Double>> 初始中心点的Map
* @throws IOException
*/
private Map<Integer, Map<String, Double>> getInitPoint(Map<String, Map<String, Double>> allTestSampleMap, int K) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
int count = 0, i = 0;
Map<Integer, Map<String, Double>> meansMap = new TreeMap<Integer, Map<String, Double>>();//保存K个聚类中心点向量
System.out.println("本次聚类的初始点对应的文件为:");
Set<Map.Entry<String, Map<String,Double>>> allTestSampleMapSet = allTestSampleMap.entrySet();
for(Iterator<Map.Entry<String, Map<String,Double>>> it = allTestSampleMapSet.iterator();it.hasNext();){
Map.Entry<String, Map<String,Double>> me = it.next();
if(count == i * allTestSampleMapSet.size() / K){
meansMap.put(i, me.getValue());
System.out.println(me.getKey() + " map size is " + me.getValue().size());
i++;
}
count++;
}
return meansMap;
}
/**输出聚类结果到文件中
* @param kmeansClusterResultFile 输出文件目录
* @param kmeansClusterResult 聚类结果
* @throws IOException
*/
private void printClusterResult(Map<String, Integer> kmeansClusterResult, String kmeansClusterResultFile) throws IOException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
FileWriter resWriter = new FileWriter(kmeansClusterResultFile);
Set<Map.Entry<String,Integer>> kmeansClusterResultSet = kmeansClusterResult.entrySet();
for(Iterator<Map.Entry<String,Integer>> it = kmeansClusterResultSet.iterator(); it.hasNext(); ){
Map.Entry<String, Integer> me = it.next();
resWriter.append(me.getKey() + " " + me.getValue() + "\n");
}
resWriter.flush();
resWriter.close();
}
public void KmeansClusterMain(String testSampleDir) throws IOException {
//首先计算文档TF-IDF向量,保存为Map<String,Map<String,Double>> 即为Map<文件名,Map<特征词,TF-IDF值>>
ComputeWordsVector computeV = new ComputeWordsVector();
int[] K = {10, 20 ,30};
Map<String,Map<String,Double>> allTestSampleMap = computeV.computeTFMultiIDF(testSampleDir);
for(int i = 0; i < K.length; i++){
System.out.println("开始聚类,聚成" + K[i] + "类");
String KmeansClusterResultFile = "F:/DataMiningSample/KmeansClusterResult/";
Map<String,Integer> KmeansClusterResult = new TreeMap<String, Integer>();
KmeansClusterResult = doProcess(allTestSampleMap, K[i]);
KmeansClusterResultFile += K[i];
printClusterResult(KmeansClusterResult,KmeansClusterResultFile);
System.out.println("The Entropy for this Cluster is " + computeV.evaluateClusterRes(KmeansClusterResultFile, K[i]));
}
}
}
聚类器主类ClusterMain.java
package com.pku.yangliu;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
/**聚类器主类,提供主函数入口
*
*/
public class ClusterMain {
/**
* @param args
* @throws IOException
*/
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
DataPreProcess DataPP = new DataPreProcess();
ComputeWordsVector computeV = new ComputeWordsVector();
//KmeansSVDCluster kmeansCluster1 = new KmeansSVDCluster();
KmeansCluster kmeansCluster2 = new KmeansCluster();
DataPP.BPPMain(args);//数据预处理,注意如果已经完成数据预处理,此函数可以不执行
//下面创建聚类算法的测试样例集合
String srcDir = "F:/DataMiningSample/processedSample_includeNotSpecial/";
String destDir = "F:/DataMiningSample/clusterTestSample/";
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
String beginTime = sdf.format(new java.util.Date());
System.out.println("程序开始执行时间:"+beginTime);
String[] terms = computeV.createTestSamples(srcDir, destDir);
//kmeansCluster1.KmeansClusterMain(destDir, terms);
kmeansCluster2.KmeansClusterMain(destDir);
String endTime = sdf.format(new java.util.Date());
System.out.println("程序结束执行时间:"+endTime);
}
}3、K-means算法聚类结果
K-means算法对newsgroup文本聚类的结果用聚类结果的熵值来度量,熵值定义如下
对newsgroup文本聚类的结果混淆矩阵如下:
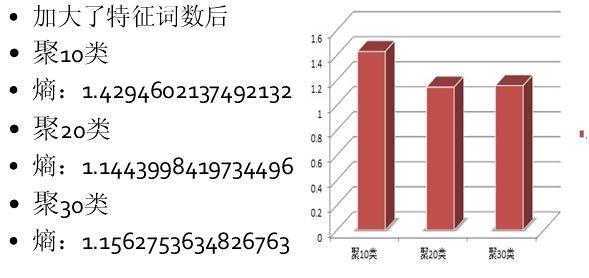
这是用DF法降维到6070词的聚类结果,熵值已经比较小了聚20类时只有1.144,特征词抽取降维是数据挖掘研究中的一个重要内容,我还尝试了用LSI中的SVD分解来进行特征降维,详细介绍实现和其他两种聚类算法的聚类结果对比见下一篇博文数据挖掘-基于Kmeans算法、MBSAS算法及DBSCAN算法的newsgroup18828文本聚类器的JAVA实现(下)