Collection of algorithm for sorting. 常见排序算法集(三) —— Quick Sort
Quick Sort
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
update: 2015.01.15
Add three different implementationin Python
The best one is the third version.
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
update: 2015.01.12
Python 实现
If you have no idea about Quick Sort. I recommend you to
read the Python version but not C : )
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
update: 2014.09.21
今天用这个自己写的QS做中值滤波的时候发现有个bug!现在已经消除了.
欢迎测试,如果发现有bug,请不吝赐教.
#bug fix up:
之前会出现 left > right的报警,是由于没有考虑quick_sort传入参数
small_region_index == bigger_region_index 的情况
添加if语句进行条件筛选即可.
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
快排,一个排序方法能直接享受这样的名称殊荣,呵呵,可见其威力与重要性.
其中最重要的思想就是 “分治”—— divide and conquer !
这里排序用到的思想极其简单,却是很实用的!小孩子都会的简单想法.
先把所有数据分成三个部分. 在所有数据中选取某一元素X,比X小的放左边,比X大的放右边.
接着把这一思想同样分别施加在X元素的左边和右边部分,同样继续划分,选出一个元素X’ 比X‘小的放左边比X’大的放右边。
继续施加这种划分策略,直到划分的元素很少(实现的时候是选取的3为阈值),那么就对其进行简单排序(我这里选取的插入排序方法)。
整个算法就这么简单,漂亮!
想提一下,感觉《DSAA》里面的算法demo小点问题,数组会溢出,我已经测试过了,下面的代码实现是其修补改进.
只是参考了《算法导论》,实现的细节可能和算导略微不同.
Implementation In C
quick_sort.h
#ifndef _QUICK_SORT_H #define _QUICK_SORT_H #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> void swap(int* x,int* y); int median(int* array,int left,int right); void quick_sort(int* array,int left,int right); void Qsort(int* array,int size); #endif
swap.c
交换 x,y 指向的值,这里用了一个小技巧 没有使用第三个变量(通常是tmp)交换两个数据的值.
/************************************************ code writer : EOF code date : 2014.09.20 code file : swap.c e-mail : [email protected] ************************************************/ #include "quick_sort.h" void swap(int* x,int* y) { /* ** Don't panic :) */ *y = *x - *y; *x = *x - *y; *y = *x + *y; }
median.c
用于确保排序的不等关系式的条件 left < center < right
最后的hide pivot是把中间值和最右侧值交换, 便于比较以及数据的交换
/************************************************ code writer : EOF code date : 2014.09.20 code file : median.c e-mail : [email protected] ************************************************/ int median(int* array,int left,int right) { int center = (left+right)/2; if(array[left] > array[right]) { swap(&array[left],&array[right]); } if(array[left] > array[center]) { swap(&array[left],&array[center]); } if(array[center] > array[right]) { swap(&array[center],&array[right]); } /* ** There are three if-statement here, ** just make sure that : ** A[left] <= A[center] <= A[right] */ /* ** Hide pivot */ swap(&array[center],&array[right]); return array[right]; }
quick_sort.c 算法核心部分
/************************************************ code writer : EOF code date : 2014.09.20 code file : quick_sort.c e-mail : [email protected] ************************************************/ #include "quick_sort.h" #define CUT_OFF 3 void quick_sort(int* array,int left,int right) { if(!array) { printf("You passed NULL into function %s()\n",__FUNCTION__); return; } if(left > right) { printf("Parameter @left and @right error!\ @left should less or equal to @right\n"); return ; } int pivot = 0; int smaller_region_index = left; int bigger_region_index = right-1; int tmp = 0; int index = 0; int sentinel = 0; if(left + CUT_OFF <= right) { pivot = median(array,left,right); for(smaller_region_index -=1, bigger_region_index += 1;;) { while(array[++smaller_region_index] < pivot) { /* ** DON'T do ++smaller_region_index here! ** That must be hide a bug! */ } while(array[--bigger_region_index] > pivot) { /* ** DON'T do --bigger_region_index here! ** That must be hide a bug! */ } if(smaller_region_index < bigger_region_index) { swap(&array[smaller_region_index],&array[bigger_region_index]); } else { break; } } /* ** Restore pivot */ swap(&array[smaller_region_index],&array[right]); if(left == smaller_region_index) { quick_sort(array,left,smaller_region_index); } else { quick_sort(array,left,smaller_region_index-1); } if(right == bigger_region_index) { quick_sort(array,bigger_region_index,right); } else { quick_sort(array,bigger_region_index+1,right); } } else { /* ** Insertion sort. */ tmp = 0; index = 0; for(tmp = left; tmp <= right;tmp++) { sentinel = array[tmp]; for(index = tmp;array[index-1] > sentinel && index > left;index--) { array[index] = array[index - 1]; } array[index] = sentinel; } } } void Qsort(int* array,int size) { quick_sort(array,0,size-1); }
Qsort_test.c
/************************************************ code writer : EOF code date : 2014.09.20 code file : Qsort_test.c e-mail : [email protected] ************************************************/ #include "quick_sort.h" int main() { int array[] = {13,81,92,43,31,65,31,57,26,75,0}; int size = sizeof(array)/sizeof(array[0]); int tmp = 0; Qsort(array,size); for(tmp = 0;tmp < size;tmp++) { printf("%4d",array[tmp]); } printf("\n"); return 0; }
----------------------------------------------------------------
update: 2015.01.12
Python 实现1
Stack depth theta{n}
Average time complexity O{n*lg(n)}
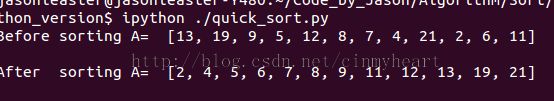
""" code writer : EOF code date : 2015.01.12 code file : quick_sort.c e-mail : [email protected] Code description: Quick Sort is implemented in Python """ def quick_sort(A, p, r) : if p < r : q = partition(A, p, r) A = quick_sort(A, p, q-1) A = quick_sort(A, q+1, r) return A # resorting in place def partition(A, p, r) : x = A[r] i = p-1 for j in range(p, r) : if A[j] <= x : i += 1 tmp = A[i] A[i] = A[j] A[j] = tmp tmp = A[i+1] A[i+1] = A[r] A[r] = tmp return i+1 A = [13,19,9,5,12,8,7,4,21,2,6,11] print "Before sorting A= " , A, "\n" A = quick_sort(A,0,len(A)-1) print "After sorting A= " , A, "\n"
------------------------------------
2015.01.15
Python 实现2
Just changed the function @quick_sort()
stack depth theta{n}
time complexity O{n*lg(n)}
#****************************
def quick_sort(A, p, r) :
while p < r :
q = partition(A, p, r)
quick_sort(A, p, q-1)
p = q + 1
#*****************************
Python 实现3 (the best one)
Just changed the function @quick_sort()
stack depth theta{lg(n)}
time complexity O{n*lg(n)}
The same time cost but the stack depth is smaller that the another version.
#**************************************************
def quick_sort(A, p, r) :
while p < r :
q = partition(A, p, r)
# partion and sort the smaller subarray first
if q - p < r - q :
quick_sort(A, p, q-1)
p = q + 1
else :
quick_sort(A, q+1, r)
r = q -1
#**************************************************
灰暗的农庄 莱昂•奥古斯丁•莱尔米特 1844―1925年 法国 画布油画 1910年 85.10×71.10厘米
作为现实主义画派的领军人物,莱尔米特一生主要以农村为题材作画,并有幸成为这一杰出艺术流派的最后一位画家。莱尔米特生活的时代,正是法国的城市和农村的社会角色开始大变革的时期。整个国家正在迅速地现代化,城市也在加速实现工业化。文明、进步的北方和布满农庄和农民的南方,形成泾渭分明的态势,各大区之间几乎没有人口的流动。作为国际性大都会巴黎的居民,巴黎人开始把法国南部看成依旧保持原生态田园风情的乐土。生活在城市的巴黎精英们遂将城郊变成怀旧的天地,许多艺术家和作家也把这片土地当成创作的乐园。农民的形象依然是工业化前的社会生活的标志,于是我们就在这幅追忆性的图画中,看到了一个农民牵着他的牲畜,在周围一片寂静之中,独自彳亍前行。