android自定义属性的使用
我们在做android界面的时候,经常会在xml文件中写如下代码:
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
android:orientation="horizontal" >
<include layout="@layout/layout_menu" />
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
android:background="@drawable/qq" >
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:onClick="toggleMenu"
android:text="button" />
</LinearLayout>
</LinearLayout>可以看到这里使用了大量的属性,如android:layout_width,android:layout_height,android:background等等,这里我记录下如何自定义属性。
我们的例子是这样的,使用自定义的属性定义圆的半径和圆心坐标,然后在自定义的MyView(继承自View)中将这个圆画出来
要自定义属性,我们首先需要在xml文件中定义这些属性,在res/values/attrs.xml文件中(如果没有就创建这个文件)加入如下代码:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<resources>
<declare-styleable name="MyView">
<attr name="radius" format="float"></attr>
<attr name="cx" format="float"></attr>
<attr name="cy" format="float"></attr>
</declare-styleable>
</resources>上面的代码定义了三个属性,radius代表圆的半径,cx和cy代表圆心坐标,在declare-styleable标签中有一个name属性,name属性的值可以随意取,这个值将会在我们做界面时用到。
下面我们定义MyView控件,这个控件继承了View,复写了onDraw方法,在onDraw中画圆,代码如下:
package com.example.testattrs;
import android.content.Context;
import android.content.res.TypedArray;
import android.graphics.Canvas;
import android.graphics.Color;
import android.graphics.Paint;
import android.util.AttributeSet;
import android.view.View;
public class MyView extends View {
private float radius;//半径
private float cx;//圆心横坐标
private float cy;//圆心纵坐标
private Paint paint;//画圆用到的画笔
/**构造方法,在其中获取我们在xml文件中定义的属性,并初始化一些数据*/
public MyView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyle) {
super(context, attrs, defStyle);
//设置画笔的属性
paint = new Paint();
paint.setStrokeWidth(5);
paint.setColor(Color.RED);
//获取xml中定义的属性
TypedArray a = context.obtainStyledAttributes(attrs, R.styleable.MyView);
//得到属性的总个数
final int N = a.getIndexCount();
//通过循环获取我们自定义的属性的值
for(int i = 0; i < N; i++){
int attr = a.getIndex(i);
switch(attr){
case R.styleable.MyView_radius:
radius = a.getFloat(attr, 5.0f);
break;
case R.styleable.MyView_cx:
cx = a.getFloat(attr, 10f);
break;
case R.styleable.MyView_cy:
cy = a.getFloat(attr, 10f);
break;
}
}
//TypedArray使用完毕后一定要调用recycle()方法
a.recycle();
}
public MyView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
//调用了第一个构造方法
this(context, attrs, 0);
}
public MyView(Context context) {
//调用了第一个构造方法
this(context, null, 0);
}
@Override
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {
super.onDraw(canvas);
//画出圆
canvas.drawCircle(cx, cy, radius, paint);
}
}
可以看到,上面的switch语句中,每一个case后都是R.styleable.MyView_+属性名,这里的MyView_就是我们在属性文件中declare-styleable标签中定义的name属性的值。
然后是Activity中布局文件的使用了,这里先上布局文件:
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
xmlns:myview="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/com.example.testattrs"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent" >
<com.example.testattrs.MyView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
myview:radius="80.0"
myview:cx="100.0"
myview:cy="100.0"
android:layout_centerHorizontal="true"
android:layout_centerVertical="true" />
</RelativeLayout>
在布局文件中,我们加入了一个自定义的MyView,这里最需要注意的是RelativeLayout中的
xmlns:myview="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/com.example.testattrs"
因为使用了我们自定义的属性,所以这里要加上新的命名空间,命名空间的写法为:xmlns:[名称]="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/[控件所在包名]",布局文件中使用自定义属性的方法,就是命名空间+属性名,如myview:radius、myview:cx、myview:cy。
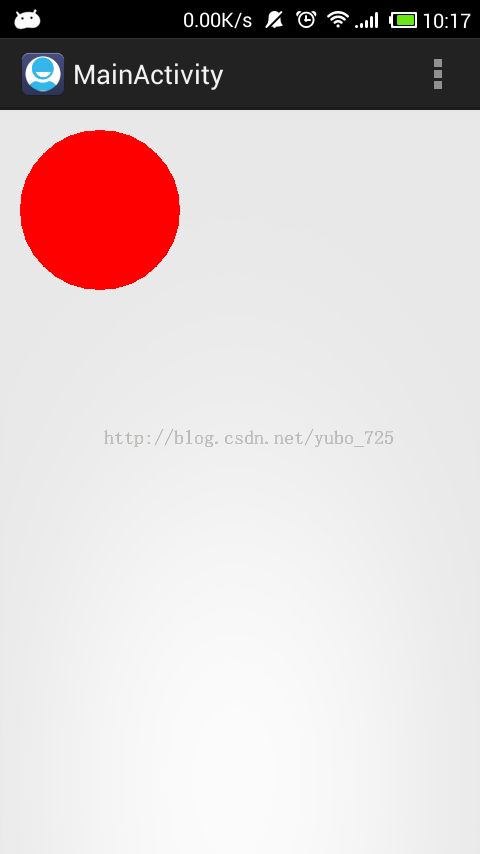
到这里基本上就完成所有代码了,我们运行程序,效果如下: