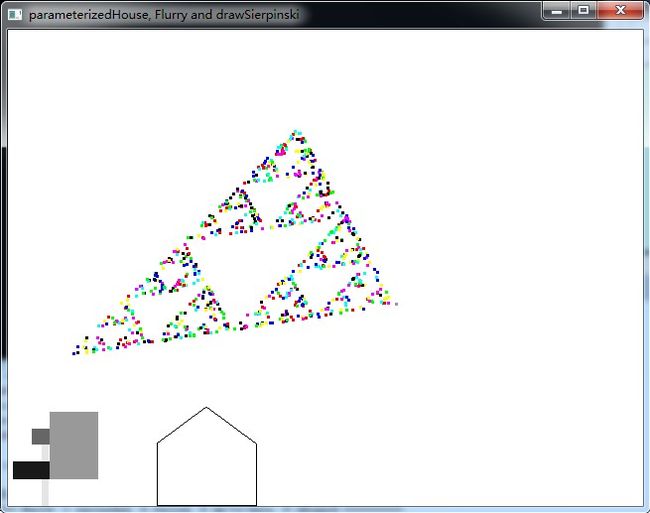
OpenGL 基础图形绘制与投影变换
本文参考《Computer Graphics Using OpenGL》,第一个例子绘制了
1. 参数定义的House
2. a flurry of filled rectangles
3. Sierpinski曲线
含有鼠标和键盘响应函数onmouse和onkeyboard。
/************************************************************************/
/* CreateTime:2013-2-18
**Author:@Rachel Zhang
**Discription: Draw Parameter House, Flurry and Sierpinski
**3rd-party:OpenGL*/
/************************************************************************/
#include "GL/glut.h"
#include "stdlib.h"
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#define screenHeight 480
class GLintPoint{
public:
GLint x, y;
};
// Create a number between 0 and m(a number which will be given)
// the input m must be less than 32767 according to P49 in <Computer Graphics Using OpenGL>
int random(int m)
{
return rand()%m;
}
void drawDot (GLint x, GLint y)
{
glPointSize(3);
glBegin(GL_POINTS);
glVertex2i(x,y);
glEnd();
}
typedef struct
{
GLfloat r, g, b;
} GLfloatRGBColour;
GLfloatRGBColour colour[8] = { {0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f}, {0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f},
{0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f}, {1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f},
{0.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f}, {1.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f},
{1.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f}, {1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f}};
void setPenColour(GLfloatRGBColour newColour)
{
glColor3f(newColour.r, newColour.g, newColour.b);
}
/************************************************************************/
/* Draw Functions */
/************************************************************************/
void parameterizedHouse(GLintPoint peak, GLint width, GLint height)
// the top of house is at the peak; the size of house is given
// by height and width
{
glBegin(GL_LINE_LOOP);
glVertex2i(peak.x, peak.y); // draw shell of house
glVertex2i(peak.x + width / 2, peak.y - 3 * height /8);
glVertex2i(peak.x + width / 2, peak.y - height);
glVertex2i(peak.x - width / 2, peak.y - height);
glVertex2i(peak.x - width / 2, peak.y - 3 * height /8);
glEnd();
}
void drawFlurry(int num, int Width, int Height)
// draw num random rectangles in a Width by Height rectangle
{
for (int i = 0; i < num; i++)
{
GLint x1 = random(Width); // place corner randomly
GLint y1 = random(Height);
GLint x2 = random(Width); // pick the size so it fits
GLint y2 = random(Height);
GLfloat lev = random(10)/10.0; // random value, in range 0 to 1
glColor3f(lev,lev,lev); // set the gray level
glRecti(x1, y1, x2, y2); // draw the rectangle
}
glFlush();
}
void drawSierpinski(GLintPoint corner[3])
{
int i, index, tcolour=0;
GLintPoint point;
point = corner[random(3)];
drawDot(point.x, point.y);
for (i = 0; i < 1000; i++)
{
index = random(3);
point.x = (point.x + corner[index].x)/2;
point.y = (point.y + corner[index].y)/2;
tcolour = (++tcolour)%7; // col = (col + 1) mod 7;
setPenColour(colour[tcolour]);
drawDot(point.x, point.y);
}
}
/************************************************************************/
/* Mouse Listener and keyboard Listener */
/************************************************************************/
void myMouse(int button, int state, int x, int y)
{
static GLintPoint corners[3];
static int numCorners;
if (button == GLUT_LEFT_BUTTON && state == GLUT_DOWN)
{
corners[numCorners].x = x;
corners[numCorners].y = screenHeight - y - 1;
if (++numCorners == 3)
{
drawSierpinski(corners);
numCorners = 0;
}
}
else if (button==GLUT_RIGHT_BUTTON)
glClear(GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT);
glFlush();
}
void onKeyBoard(unsigned char key,int mousex, int mousey)
{
switch (key)
{
case 'q':
exit(0);
case 'r':
static GLintPoint corners[3];
for (int i=0;i<3;i++)
{
corners[i].x = random(640);
corners[i].y = random(screenHeight);
}
drawSierpinski(corners);
default:
break;
}
}
// Initialization
void Init(void)
{
glClearColor(1.0,1.0,1.0,0.0); // Set white background color
glColor3f(0.0f,0.0f,0.0f); // Set the drawing color
glMatrixMode(GL_PROJECTION);
glLoadIdentity();
gluOrtho2D(0.0,640.0,0.0,480.0);
}
void myDisplay()
{
glClear(GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT); //clear the screen
GLintPoint Mypoint = {200,100};
parameterizedHouse(Mypoint,100,100);
drawFlurry(4,100,100);
glFlush();
}
void main(int argc,char *argv[])
{
glutInit(&argc, argv); // Initialize the toolkit
glutInitDisplayMode(GLUT_RGB | GLUT_SINGLE); // Set display mode
glutInitWindowPosition(100, 150); // Set window pozition on screen
glutInitWindowSize(640, 480); // Set window size
glutCreateWindow("parameterizedHouse, Flurry and drawSierpinski"); // Open the screen window
glutDisplayFunc(myDisplay); // Register redraw function
glutMouseFunc(myMouse);
glutKeyboardFunc(onKeyBoard);
Init();
glutMainLoop(); // Go into a perpetual loop
}
效果图:
第二个例子绘制了这样一系列图形:
在其中有空间投影变换,主要应用了三个函数:
投影变换函数glViewport(), 矩阵平移函数glTranslated() 和正射投影函数 glOrtho()
上图实现代码参考《计算机图形学-用OpenGL实现第2版》:
#include <windows.h> //suitable when using Windows 95/98/NT
#include <gl/Gl.h>
#include <gl/Glu.h>
#include <gl/glut.h>
//<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<< axis >>>>>>>>>>>>>>
void axis(double length)
{ // draw a z-axis, with cone at end
glPushMatrix();
glBegin(GL_LINES);
glVertex3d(0, 0, 0); glVertex3d(0,0,length); // along the z-axis
glEnd();
glTranslated(0, 0,length -0.2);
glutWireCone(0.04, 0.2, 12, 9);
glPopMatrix();
}
//<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<< displayWire >>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>
void displayWire(void)
{
glMatrixMode(GL_PROJECTION); // set the view volume shape
glLoadIdentity();
glOrtho(-2.0*64/48.0, 2.0*64/48.0, -2.0, 2.0, 0.1, 100);//正射投影函数
glMatrixMode(GL_MODELVIEW); // position and aim the camera
glLoadIdentity();
gluLookAt(2.0, 2.0, 2.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 0.0);//define viewpoint transformation
//Draw axis
glClear(GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT); // clear the screen
glColor3d(0,0,0); // draw black lines
axis(0.5); // z-axis
glPushMatrix();
glRotated(90, 0,1.0, 0);
axis(0.5); // y-axis
glRotated(-90.0, 1, 0, 0);
axis(0.5); // z-axis
glPopMatrix();
//Draw Cube
glPushMatrix();
glTranslated(0.5, 0.5, 0.5); // multiply by a translation matrix, define center (0.5, 0.5, 0.5)
glutWireCube(1.0);
glPopMatrix();
//Draw Sphere
glPushMatrix();
glTranslated(1.0,1.0,0); // sphere at (1,1,0)
glutWireSphere(0.25, 10, 8);
glPopMatrix();
//Draw Cone
glPushMatrix();
glTranslated(1.0,0,1.0); // cone at (1,0,1)
glutWireCone(0.2, 0.5, 10, 8);
glPopMatrix();
//Draw Teapot
glPushMatrix();
glTranslated(1,1,1);
glutWireTeapot(0.2); // teapot at (1,1,1)
glPopMatrix();
//Draw Torus
glPushMatrix();
glTranslated(0, 1.0 ,0); // torus at (0,1,0)
glRotated(90.0, 1,0,0);
glutWireTorus(0.1, 0.3, 10,10);
glPopMatrix();
//十二面体
glPushMatrix();
glTranslated(1.0, 0 ,0); // dodecahedron at (1,0,0)
glScaled(0.15, 0.15, 0.15);
glutWireDodecahedron();
glPopMatrix();
glPushMatrix();
glTranslated(0, 1.0 ,1.0); // small cube at (0,1,1)
glutWireCube(0.25);
glPopMatrix();
glPushMatrix();
glTranslated(0, 0 ,1.0); // cylinder at (0,0,1)
GLUquadricObj * qobj;
qobj = gluNewQuadric();
gluQuadricDrawStyle(qobj,GLU_LINE);
gluCylinder(qobj, 0.2, 0.2, 0.4, 8,8);
glPopMatrix();
glFlush();
}
//<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<< main >>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>
void main(int argc, char **argv)
{
glutInit(&argc, argv);
glutInitDisplayMode(GLUT_SINGLE | GLUT_RGB );
glutInitWindowSize(640,480);
glutInitWindowPosition(100, 100);
glutCreateWindow("Transformation testbed - wireframes");
glutDisplayFunc(displayWire);
glClearColor(1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f,0.0f); // background is white
glViewport(0, 0, 640, 480);//投影变换函数
glutMainLoop();
}
Reference:
http://www.oocities.org/uniq_friq/c_files/openGL/1lab/dots.htm