- android系统selinux中添加新属性property
辉色投像
1.定位/android/system/sepolicy/private/property_contexts声明属性开头:persist.charge声明属性类型:u:object_r:system_prop:s0图12.定位到android/system/sepolicy/public/domain.te删除neverallow{domain-init}default_prop:property
- LocalDateTime 转 String
igotyback
java开发语言
importjava.time.LocalDateTime;importjava.time.format.DateTimeFormatter;publicclassMain{publicstaticvoidmain(String[]args){//获取当前时间LocalDateTimenow=LocalDateTime.now();//定义日期格式化器DateTimeFormatterformat
- 每日一题——第九十题
互联网打工人no1
C语言程序设计每日一练c语言
题目:判断子串是否与主串匹配#include#include#include//////判断子串是否在主串中匹配//////主串///子串///boolisSubstring(constchar*str,constchar*substr){intlenstr=strlen(str);//计算主串的长度intlenSub=strlen(substr);//计算子串的长度//遍历主字符串,对每个可能得
- C#中使用split分割字符串
互联网打工人no1
c#
1、用字符串分隔:usingSystem.Text.RegularExpressions;stringstr="aaajsbbbjsccc";string[]sArray=Regex.Split(str,"js",RegexOptions.IgnoreCase);foreach(stringiinsArray)Response.Write(i.ToString()+"");输出结果:aaabbbc
- python是什么意思中文-在python中%是什么意思
编程大乐趣
Python中%有两种:1、数值运算:%代表取模,返回除法的余数。如:>>>7%212、%操作符(字符串格式化,stringformatting),说明如下:%[(name)][flags][width].[precision]typecode(name)为命名flags可以有+,-,''或0。+表示右对齐。-表示左对齐。''为一个空格,表示在正数的左侧填充一个空格,从而与负数对齐。0表示使用0填
- python os 环境变量
CV矿工
python开发语言numpy
环境变量:环境变量是程序和操作系统之间的通信方式。有些字符不宜明文写进代码里,比如数据库密码,个人账户密码,如果写进自己本机的环境变量里,程序用的时候通过os.environ.get()取出来就行了。os.environ是一个环境变量的字典。环境变量的相关操作importos"""设置/修改环境变量:os.environ[‘环境变量名称’]=‘环境变量值’#其中key和value均为string类
- Redis系列:Geo 类型赋能亿级地图位置计算
Ly768768
redisbootstrap数据库
1前言我们在篇深刻理解高性能Redis的本质的时候就介绍过Redis的几种基本数据结构,它是基于不同业务场景而设计的:动态字符串(REDIS_STRING):整数(REDIS_ENCODING_INT)、字符串(REDIS_ENCODING_RAW)双端列表(REDIS_ENCODING_LINKEDLIST)压缩列表(REDIS_ENCODING_ZIPLIST)跳跃表(REDIS_ENCODI
- ARM驱动学习之基础小知识
JT灬新一
ARM嵌入式arm开发学习
ARM驱动学习之基础小知识•sch原理图工程师工作内容–方案–元器件选型–采购(能不能买到,价格)–原理图(涉及到稳定性)•layout画板工程师–layout(封装、布局,布线,log)(涉及到稳定性)–焊接的一部分工作(调试阶段板子的焊接)•驱动工程师–驱动,原理图,layout三部分的交集容易发生矛盾•PCB研发流程介绍–方案,原理图(网表)–layout工程师(gerber文件)–PCB板
- C++ | Leetcode C++题解之第409题最长回文串
Ddddddd_158
经验分享C++Leetcode题解
题目:题解:classSolution{public:intlongestPalindrome(strings){unordered_mapcount;intans=0;for(charc:s)++count[c];for(autop:count){intv=p.second;ans+=v/2*2;if(v%2==1andans%2==0)++ans;}returnans;}};
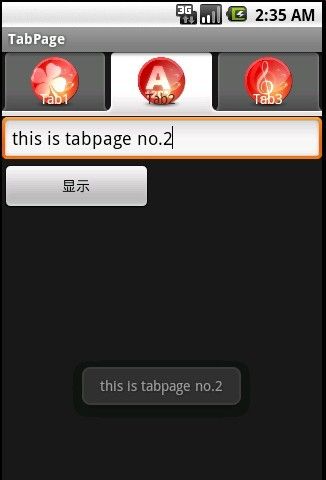
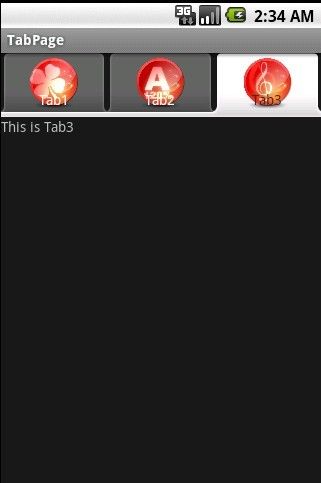
- 2.2.6 通知类控件 Toast、Menu
常思行
本文例程下载:WillFlow_Toast、WillFlowMenu一、什么是Toast?Toast也被叫做吐司,是Android系统提供的一种非常好的提醒方式,在程序中可以使用它将一些短小的信息通知给用户,它有如下两个特点:Toast是没有焦点的Toast显示的时间有限过一定的时间就会自动消失所以一般来讲Toast的使用并不会影响我们的正常操作,并且它通常不会占用太大的屏幕空间,有着良好的用户体
- 用Python实现读取统计单词个数
程序媛了了
python游戏java
完整实例代码:fromcollectionsimportCounterdefpythonit():danci={}withopen("pythonit.txt","r",encoding="utf-8")asf:foriinf:words=i.strip().split()forwordinwords:ifwordnotindanci:danci[word]=1else:danci[word]+=
- 2024.9.6 Python,华为笔试题总结,字符串格式化,字符串操作,广度优先搜索解决公司组织绩效互评问题,无向图
RaidenQ
python华为leetcode算法力扣广度优先无向图
1.字符串格式化name="Alice"age=30formatted_string="Name:{},Age:{}".format(name,age)print(formatted_string)或者name="Alice"age=30formatted_string=f"Name:{name},Age:{age}"print(formatted_string)2.网络健康检查第一行有两个整数m
- mac 备份android 手机通讯录导入iphone,iphone如何导出通讯录(轻松教你iPhone备份通讯录的方法)...
weixin_39762838
mac备份android手机通讯录导入iphone
在日新月异的手机更替中,换手机已经成为一个非常稀松平常的事情,但将旧手机上面的通讯录导入到新手机还是让不少小伙伴为难,本篇将给大家详细讲解这方面的知识:“苹果手机通讯录怎么导入到新手机”及“安卓手机通讯录导入到新手机”的方法。一、苹果手机通讯录导入到新手机常用方法(SIM卡导入)在苹果手机主频幕上找到“设置”,单击进入设置菜单,下拉菜单列表,点击“邮件、通讯录、日历”,然后找到“导入SIM卡通讯录
- android 更改窗口的层次,浮窗开发之窗口层级
Ms.Bu
android更改窗口的层次
最近在项目中遇到了这样的需求:需要在特定的其他应用之上悬浮自己的UI交互(拖动、输入等复杂的UI交互),和九游的浮窗类似,不过我们的比九游的体验更好,我们越过了很多授权的限制。浮窗效果很多人都知道如何去实现一个简单的浮窗,但是却很少有人去深入的研究背后的流程机制,由于项目中浮窗交互比较复杂,遇到了些坑查看了很多资料,故总结浮窗涉及到的知识点:窗口层级关系(浮窗是如何“浮”的)?浮窗有哪些限制,如何
- Android应用性能优化
轻口味
Android
Android手机由于其本身的后台机制和硬件特点,性能上一直被诟病,所以软件开发者对软件本身的性能优化就显得尤为重要;本文将对Android开发过程中性能优化的各个方面做一个回顾与总结。Cache优化ListView缓存:ListView中有一个回收器,Item滑出界面的时候View会回收到这里,需要显示新的Item的时候,就尽量重用回收器里面的View;每次在getView函数中inflate新
- JAVA·一个简单的登录窗口
MortalTom
java开发语言学习
文章目录概要整体架构流程技术名词解释技术细节资源概要JavaSwing是Java基础类库的一部分,主要用于开发图形用户界面(GUI)程序整体架构流程新建项目,导入sql.jar包(链接放在了文末),编译项目并运行技术名词解释一、特点丰富的组件提供了多种可视化组件,如按钮(JButton)、文本框(JTextField)、标签(JLabel)、下拉列表(JComboBox)等,可以满足不同的界面设计
- 非对称加密算法原理与应用2——RSA私钥加密文件
私语茶馆
云部署与开发架构及产品灵感记录RSA2048私钥加密
作者:私语茶馆1.相关章节(1)非对称加密算法原理与应用1——秘钥的生成-CSDN博客第一章节讲述的是创建秘钥对,并将公钥和私钥导出为文件格式存储。本章节继续讲如何利用私钥加密内容,包括从密钥库或文件中读取私钥,并用RSA算法加密文件和String。2.私钥加密的概述本文主要基于第一章节的RSA2048bit的非对称加密算法讲述如何利用私钥加密文件。这种加密后的文件,只能由该私钥对应的公钥来解密。
- Android实现监听事件的方法
Amy木婉清
1.通过内部类实现2.通过匿名内部类实现3.通过事件源所在类实现4.通过外部类实现5.布局文件中onclick属性(针对点击事件)1.通过内部类实现代码:privateButtonmBtnEvent;//oncreate中mBtnEvent.setOnClickListener(newOnClick());//内部类实现监听classOnClickimplementsView.OnClickLis
- Golang语言基础知识点总结
最帅猪猪侠
golang开发语言后端
Golang语言基础知识点小总结1.go语言有两大类型:值类型:数值类型,bool,string,数组,struct结构体变量直接存储值,内存通常在栈中分配,修改值,不会对源对象产生影响引用类型:指针,slice切片,管道chan,map,interface变量存储的是一个地址,这个地址对应的空间才真正存储数据值,内存通常在堆上分配,当没有任何变量引用这个地址时,该地址对应的数据空间就成为一个垃圾
- string trim的实现
JamesSawyer
if(typeofString.prototype.trim!=='function'){String.prototype.trim=function(){//这个正则的意思是//'^''$'表示结束和开始//'^\s*'表示任意以空格开头的空格//'\s*$'表示任意以空格结尾的空格//'\S*'表示任意非空字符//'$1'表示'(\S*(\s*\S*)*)'returnthis.replace
- 高级UI<第二十四篇>:Android中用到的矩阵常识
NoBugException
(1)定义在数学中,矩阵(Matrix)是一个按照长方阵列排列的复数或实数集合。由m×n个数aij排成的m行n列的数表称为m行n列的矩阵,简称m×n矩阵。记作:图片.png这m×n个数称为矩阵A的元素,简称为元,数aij位于矩阵A的第i行第j列,称为矩阵A的(i,j)元,以数aij为(i,j)元的矩阵可记为(aij)或(aij)m×n,m×n矩阵A也记作Amn。元素是实数的矩阵称为实矩阵,元素是复
- [Swift]LeetCode943. 最短超级串 | Find the Shortest Superstring
黄小二哥
swift
★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★➤微信公众号:山青咏芝(shanqingyongzhi)➤博客园地址:山青咏芝(https://www.cnblogs.com/strengthen/)➤GitHub地址:https://github.com/strengthen/LeetCode➤原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/streng
- [Swift]LeetCode767. 重构字符串 | Reorganize String
weixin_30591551
swiftruntime
★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★➤微信公众号:山青咏芝(shanqingyongzhi)➤博客园地址:山青咏芝(https://www.cnblogs.com/strengthen/)➤GitHub地址:https://github.com/strengthen/LeetCode➤原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/streng
- RK3229_Android9.0_Box 4G模块EC200A调试
suifen_
网络
0、kernel修改这部分完全可以参考Linux的移植:RK3588EC200A-CN【4G模块】调试_rkec200a-cn-CSDN博客1、修改device/rockchip/rk322xdiff--gita/device.mkb/device.mkindexec6bfaa..e7c32d1100755---a/device.mk+++b/device.mk@@-105,6+105,8@@en
- golang获取用户输入的几种方式
余生逆风飞翔
golang开发语言后端
一、定义结构体typeUserInfostruct{Namestring`json:"name"`Ageint`json:"age"`Addstring`json:"add"`}typeReturnDatastruct{Messagestring`json:"message"`Statusstring`json:"status"`DataUserInfo`json:"data"`}二、get请求的
- golang实现从服务器下载文件到本地指定目录
余生逆风飞翔
golang服务器开发语言
一、连接服务器,采用sftp连接模式packagemiddlewaresimport("fmt""time""github.com/pkg/sftp""golang.org/x/crypto/ssh")//建立服务器连接funcConnect(user,password,hoststring,portint)(*sftp.Client,error){var(auth[]ssh.AuthMethod
- spring mvc @RequestBody String类型参数
zoyation
spring-mvcspringmvc
通过如下配置:text/html;charset=UTF-8application/json;charset=UTF-8在springmvc的Controller层使用@RequestBody接收Content-Type为application/json的数据时,默认支持Map方式和对象方式参数@RequestMapping(value="/{code}/saveUser",method=Requ
- el-table实现全选整表,单元一页复选框功能
周bro
vue.jselementuijavascript前端
全选整表单选一页0":popper-append-to-body="false":total="tableData.length":page-size="pageObj.pagesize":page-sizes="[10,50,100]"layout="total,sizes,prev,pager,next"@size-change="handleSizeChange"@current-chang
- 处理标签包裹的字符串,并取出前250字符
周bro
前端javascript开发语言
//假设这是你的HTML字符串varhtmlString=`这是一个段落。这是一个标题这是另一个段落,包含一些链接。`;//解析HTML字符串并提取文本functionextractTextFromHTML(html){varparser=newDOMParser();vardoc=parser.parseFromString(html,"text/html");vartextContent=do
- kt文件和java文件_Java与Kotlin之间怎样进行互操作
铭空间
kt文件和java文件
Java与Kotlin之间怎样进行互操作发布时间:2021-02-0210:50:43来源:亿速云阅读:98作者:小新这篇文章主要介绍了Java与Kotlin之间怎样进行互操作,具有一定借鉴价值,感兴趣的朋友可以参考下,希望大家阅读完这篇文章之后大有收获,下面让小编带着大家一起了解一下。前言目前kotlin是谷歌首推的开发Android的语言,但由于历史原因,我们绝大部分项目依旧还是以Java为主
- 强大的销售团队背后 竟然是大数据分析的身影
蓝儿唯美
数据分析
Mark Roberge是HubSpot的首席财务官,在招聘销售职位时使用了大量数据分析。但是科技并没有挤走直觉。
大家都知道数理学家实际上已经渗透到了各行各业。这些热衷数据的人们通过处理数据理解商业流程的各个方面,以重组弱点,增强优势。
Mark Roberge是美国HubSpot公司的首席财务官,HubSpot公司在构架集客营销现象方面出过一份力——因此他也是一位数理学家。他使用数据分析
- Haproxy+Keepalived高可用双机单活
bylijinnan
负载均衡keepalivedhaproxy高可用
我们的应用MyApp不支持集群,但要求双机单活(两台机器:master和slave):
1.正常情况下,只有master启动MyApp并提供服务
2.当master发生故障时,slave自动启动本机的MyApp,同时虚拟IP漂移至slave,保持对外提供服务的IP和端口不变
F5据说也能满足上面的需求,但F5的通常用法都是双机双活,单活的话还没研究过
服务器资源
10.7
- eclipse编辑器中文乱码问题解决
0624chenhong
eclipse乱码
使用Eclipse编辑文件经常出现中文乱码或者文件中有中文不能保存的问题,Eclipse提供了灵活的设置文件编码格式的选项,我们可以通过设置编码 格式解决乱码问题。在Eclipse可以从几个层面设置编码格式:Workspace、Project、Content Type、File
本文以Eclipse 3.3(英文)为例加以说明:
1. 设置Workspace的编码格式:
Windows-&g
- 基础篇--resources资源
不懂事的小屁孩
android
最近一直在做java开发,偶尔敲点android代码,突然发现有些基础给忘记了,今天用半天时间温顾一下resources的资源。
String.xml 字符串资源 涉及国际化问题
http://www.2cto.com/kf/201302/190394.html
string-array
- 接上篇补上window平台自动上传证书文件的批处理问卷
酷的飞上天空
window
@echo off
: host=服务器证书域名或ip,需要和部署时服务器的域名或ip一致 ou=公司名称, o=公司名称
set host=localhost
set ou=localhost
set o=localhost
set password=123456
set validity=3650
set salias=s
- 企业物联网大潮涌动:如何做好准备?
蓝儿唯美
企业
物联网的可能性也许是无限的。要找出架构师可以做好准备的领域然后利用日益连接的世界。
尽管物联网(IoT)还很新,企业架构师现在也应该为一个连接更加紧密的未来做好计划,而不是跟上闸门被打开后的集成挑战。“问题不在于物联网正在进入哪些领域,而是哪些地方物联网没有在企业推进,” Gartner研究总监Mike Walker说。
Gartner预测到2020年物联网设备安装量将达260亿,这些设备在全
- spring学习——数据库(mybatis持久化框架配置)
a-john
mybatis
Spring提供了一组数据访问框架,集成了多种数据访问技术。无论是JDBC,iBATIS(mybatis)还是Hibernate,Spring都能够帮助消除持久化代码中单调枯燥的数据访问逻辑。可以依赖Spring来处理底层的数据访问。
mybatis是一种Spring持久化框架,要使用mybatis,就要做好相应的配置:
1,配置数据源。有很多数据源可以选择,如:DBCP,JDBC,aliba
- Java静态代理、动态代理实例
aijuans
Java静态代理
采用Java代理模式,代理类通过调用委托类对象的方法,来提供特定的服务。委托类需要实现一个业务接口,代理类返回委托类的实例接口对象。
按照代理类的创建时期,可以分为:静态代理和动态代理。
所谓静态代理: 指程序员创建好代理类,编译时直接生成代理类的字节码文件。
所谓动态代理: 在程序运行时,通过反射机制动态生成代理类。
一、静态代理类实例:
1、Serivce.ja
- Struts1与Struts2的12点区别
asia007
Struts1与Struts2
1) 在Action实现类方面的对比:Struts 1要求Action类继承一个抽象基类;Struts 1的一个具体问题是使用抽象类编程而不是接口。Struts 2 Action类可以实现一个Action接口,也可以实现其他接口,使可选和定制的服务成为可能。Struts 2提供一个ActionSupport基类去实现常用的接口。即使Action接口不是必须实现的,只有一个包含execute方法的P
- 初学者要多看看帮助文档 不要用js来写Jquery的代码
百合不是茶
jqueryjs
解析json数据的时候需要将解析的数据写到文本框中, 出现了用js来写Jquery代码的问题;
1, JQuery的赋值 有问题
代码如下: data.username 表示的是: 网易
$("#use
- 经理怎么和员工搞好关系和信任
bijian1013
团队项目管理管理
产品经理应该有坚实的专业基础,这里的基础包括产品方向和产品策略的把握,包括设计,也包括对技术的理解和见识,对运营和市场的敏感,以及良好的沟通和协作能力。换言之,既然是产品经理,整个产品的方方面面都应该能摸得出门道。这也不懂那也不懂,如何让人信服?如何让自己懂?就是不断学习,不仅仅从书本中,更从平时和各种角色的沟通
- 如何为rich:tree不同类型节点设置右键菜单
sunjing
contextMenutreeRichfaces
组合使用target和targetSelector就可以啦,如下: <rich:tree id="ruleTree" value="#{treeAction.ruleTree}" var="node" nodeType="#{node.type}"
selectionChangeListener=&qu
- 【Redis二】Redis2.8.17搭建主从复制环境
bit1129
redis
开始使用Redis2.8.17
Redis第一篇在Redis2.4.5上搭建主从复制环境,对它的主从复制的工作机制,真正的惊呆了。不知道Redis2.8.17的主从复制机制是怎样的,Redis到了2.4.5这个版本,主从复制还做成那样,Impossible is nothing! 本篇把主从复制环境再搭一遍看看效果,这次在Unbuntu上用官方支持的版本。 Ubuntu上安装Red
- JSONObject转换JSON--将Date转换为指定格式
白糖_
JSONObject
项目中,经常会用JSONObject插件将JavaBean或List<JavaBean>转换为JSON格式的字符串,而JavaBean的属性有时候会有java.util.Date这个类型的时间对象,这时JSONObject默认会将Date属性转换成这样的格式:
{"nanos":0,"time":-27076233600000,
- JavaScript语言精粹读书笔记
braveCS
JavaScript
【经典用法】:
//①定义新方法
Function .prototype.method=function(name, func){
this.prototype[name]=func;
return this;
}
//②给Object增加一个create方法,这个方法创建一个使用原对
- 编程之美-找符合条件的整数 用字符串来表示大整数避免溢出
bylijinnan
编程之美
import java.util.LinkedList;
public class FindInteger {
/**
* 编程之美 找符合条件的整数 用字符串来表示大整数避免溢出
* 题目:任意给定一个正整数N,求一个最小的正整数M(M>1),使得N*M的十进制表示形式里只含有1和0
*
* 假设当前正在搜索由0,1组成的K位十进制数
- 读书笔记
chengxuyuancsdn
读书笔记
1、Struts访问资源
2、把静态参数传递给一个动作
3、<result>type属性
4、s:iterator、s:if c:forEach
5、StringBuilder和StringBuffer
6、spring配置拦截器
1、访问资源
(1)通过ServletActionContext对象和实现ServletContextAware,ServletReque
- [通讯与电力]光网城市建设的一些问题
comsci
问题
信号防护的问题,前面已经说过了,这里要说光网交换机与市电保障的关系
我们过去用的ADSL线路,因为是电话线,在小区和街道电力中断的情况下,只要在家里用笔记本电脑+蓄电池,连接ADSL,同样可以上网........
- oracle 空间RESUMABLE
daizj
oracle空间不足RESUMABLE错误挂起
空间RESUMABLE操作 转
Oracle从9i开始引入这个功能,当出现空间不足等相关的错误时,Oracle可以不是马上返回错误信息,并回滚当前的操作,而是将操作挂起,直到挂起时间超过RESUMABLE TIMEOUT,或者空间不足的错误被解决。
这一篇简单介绍空间RESUMABLE的例子。
第一次碰到这个特性是在一次安装9i数据库的过程中,在利用D
- 重构第一次写的线程池
dieslrae
线程池 python
最近没有什么学习欲望,修改之前的线程池的计划一直搁置,这几天比较闲,还是做了一次重构,由之前的2个类拆分为现在的4个类.
1、首先是工作线程类:TaskThread,此类为一个工作线程,用于完成一个工作任务,提供等待(wait),继续(proceed),绑定任务(bindTask)等方法
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding:utf8 -*-
- C语言学习六指针
dcj3sjt126com
c
初识指针,简单示例程序:
/*
指针就是地址,地址就是指针
地址就是内存单元的编号
指针变量是存放地址的变量
指针和指针变量是两个不同的概念
但是要注意: 通常我们叙述时会把指针变量简称为指针,实际它们含义并不一样
*/
# include <stdio.h>
int main(void)
{
int * p; // p是变量的名字, int *
- yii2 beforeSave afterSave beforeDelete
dcj3sjt126com
delete
public function afterSave($insert, $changedAttributes)
{
parent::afterSave($insert, $changedAttributes);
if($insert) {
//这里是新增数据
} else {
//这里是更新数据
}
}
- timertask
shuizhaosi888
timertask
java.util.Timer timer = new java.util.Timer(true);
// true 说明这个timer以daemon方式运行(优先级低,
// 程序结束timer也自动结束),注意,javax.swing
// 包中也有一个Timer类,如果import中用到swing包,
// 要注意名字的冲突。
TimerTask task = new
- Spring Security(13)——session管理
234390216
sessionSpring Security攻击保护超时
session管理
目录
1.1 检测session超时
1.2 concurrency-control
1.3 session 固定攻击保护
- 公司项目NODEJS实践0.3[ mongo / session ...]
逐行分析JS源代码
mongodbsessionnodejs
http://www.upopen.cn
一、前言
书接上回,我们搭建了WEB服务端路由、模板等功能,完成了register 通过ajax与后端的通信,今天主要完成数据与mongodb的存取,实现注册 / 登录 /
- pojo.vo.po.domain区别
LiaoJuncai
javaVOPOJOjavabeandomain
POJO = "Plain Old Java Object",是MartinFowler等发明的一个术语,用来表示普通的Java对象,不是JavaBean, EntityBean 或者 SessionBean。POJO不但当任何特殊的角色,也不实现任何特殊的Java框架的接口如,EJB, JDBC等等。
即POJO是一个简单的普通的Java对象,它包含业务逻辑
- Windows Error Code
OhMyCC
windows
0 操作成功完成.
1 功能错误.
2 系统找不到指定的文件.
3 系统找不到指定的路径.
4 系统无法打开文件.
5 拒绝访问.
6 句柄无效.
7 存储控制块被损坏.
8 存储空间不足, 无法处理此命令.
9 存储控制块地址无效.
10 环境错误.
11 试图加载格式错误的程序.
12 访问码无效.
13 数据无效.
14 存储器不足, 无法完成此操作.
15 系
- 在storm集群环境下发布Topology
roadrunners
集群stormtopologyspoutbolt
storm的topology设计和开发就略过了。本章主要来说说如何在storm的集群环境中,通过storm的管理命令来发布和管理集群中的topology。
1、打包
打包插件是使用maven提供的maven-shade-plugin,详细见maven-shade-plugin。
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.
- 为什么不允许代码里出现“魔数”
tomcat_oracle
java
在一个新项目中,我最先做的事情之一,就是建立使用诸如Checkstyle和Findbugs之类工具的准则。目的是制定一些代码规范,以及避免通过静态代码分析就能够检测到的bug。 迟早会有人给出案例说这样太离谱了。其中的一个案例是Checkstyle的魔数检查。它会对任何没有定义常量就使用的数字字面量给出警告,除了-1、0、1和2。 很多开发者在这个检查方面都有问题,这可以从结果
- zoj 3511 Cake Robbery(线段树)
阿尔萨斯
线段树
题目链接:zoj 3511 Cake Robbery
题目大意:就是有一个N边形的蛋糕,切M刀,从中挑选一块边数最多的,保证没有两条边重叠。
解题思路:有多少个顶点即为有多少条边,所以直接按照切刀切掉点的个数排序,然后用线段树维护剩下的还有哪些点。
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <vector&