GCC Coverage代码分析-gcov-dump原理分析
本博客(http://blog.csdn.net/livelylittlefish)贴出作者(阿波)相关研究、学习内容所做的笔记,欢迎广大朋友指正!
Content
1.序
2. gcov-dump原理分析
2.1 gcov-dump程序结构
2.2 dump_file函数分析
2.3处理各种tag的callback定义
2.4基本读取函数gcov_read_words
2.5分配空间函数gcov_allocate
2.6重要数据结构gcov_var
3.处理tag的callback分析
3.1FUNCTION tag: tag_function()函数
3.2BLOCKS tag: tag_blocks()函数
3.3ARCS tag: tag_arcs()函数
3.4LINES tag: tag_lines()函数
3.5COUNTER tag: tag_counters()函数
3.6OBJECT/PROGRAM SUMMARY tag: tag_summary()函数
4.小结
1.序
gcov的相关文件.gcda(data文件)/.gcno(note文件)文件是以二进制方式写入的(fwrite),普通编辑文件打开看到的只是乱码,用ultraedit打开也只是看到十六进制的数据。如果你了解.gcda/.gcno的文件格式(可以参考"Linux平台代码覆盖率测试工具GCOV相关文件分析"),看起来会好些;否则,看起来便不知所云,除非有一种工具或程序能将其内容按照有意义的(文件)格式dump出来,如果再加上一些提示,就更好了。
——这就是gcov-dump程序。
gcov-dump是一个dump程序,输入是一个gcov的文件,或者.gcda,即gcov的data文件;或者.gcno,即gcov的note文件。
有了"Linux平台代码覆盖率测试工具GCOV相关文件分析"和"Linux平台代码覆盖率测试-GCC如何编译生成gcov/gcov-dump程序及其bug分析"这两篇文章做基础,gcov-dump的原理就很好理解了。本文不予详细叙述,只做一些代码注释和简单记录,便于用到的时候查询。好头脑赶不上烂笔头嘛。
本文例子所用的gcov-dump程序来自"Linux平台代码覆盖率测试-从GCC源码中抽取gcov/gcov-dump程序"一文。
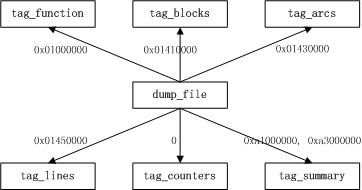
2. gcov-dump原理分析
图中实线表示调用,实线旁边的数字表示tag值。tag的值请参考gcov_io.h文件,或者"Linux平台代码覆盖率测试工具GCOV相关文件分析"。
2.2 dump_file函数分析
gcov-dump程序的主函数main,是靠调用dump_file()函数来完成文件内容的输出。该函数定义如下。其中的注释为笔者所加。
static void
dump_file (const char *filename)
{
unsigned tags[4];
unsigned depth = 0;
if (! gcov_open (filename, 1)) /* it will open .gcda/.gcno file, and save information into gcov_var */
{
fprintf (stderr, "%s:cannot open\n", filename);
return;
}
/* magic */
{
unsigned magic = gcov_read_unsigned ();
unsigned version;
const char *type = NULL;
int endianness = 0;
char m[4], v[4];
/***** compare magic read just now with "gcda" or "gcno" to confirm file type */
if ((endianness = gcov_magic (magic, GCOV_DATA_MAGIC)))
type = "data";
else if ((endianness = gcov_magic (magic, GCOV_NOTE_MAGIC)))
type = "note";
else
{
printf ("%s:not a gcov file\n", filename);
gcov_close ();
return;
}
/***** read version, an unsigned word */
version = gcov_read_unsigned ();
/***** Convert a magic or version number to a 4 character string with ASCII */
GCOV_UNSIGNED2STRING (v, version);
GCOV_UNSIGNED2STRING (m, magic);
printf ("%s:%s:magic `%.4s':version `%.4s'%s\n", filename, type,
m, v, endianness < 0 ? " (swapped endianness)" : "");
if (version != GCOV_VERSION)
{
char e[4];
GCOV_UNSIGNED2STRING (e, GCOV_VERSION);
printf ("%s:warning:current version is `%.4s'\n", filename, e);
}
}
/* stamp */
{
unsigned stamp = gcov_read_unsigned ();
printf ("%s:stamp %lu\n", filename, (unsigned long)stamp);
}
while (1)
{
gcov_position_t base, position = gcov_position ();
unsigned tag, length; tag_format_t const *format; unsigned tag_depth;
int error;
unsigned mask;
/***** read a tag, for example, 0x01000000, 0x01a10000, 0xa1000000, etc */
tag = gcov_read_unsigned ();
if (! tag) /***** tag=0x00000000, then, to the end of file, break *****/
break;
/***** read its length tag */
length = gcov_read_unsigned ();
base = gcov_position ();
/***** for example, tag=0x01000000, then, tag- 1=0xFFFFFF,
* then, GCOV_TAG_MASK (tag)=0x1FFFFFF, then, mask = 0x1FFFFFF/ 2 = 0xFFFFFF
*/
mask = GCOV_TAG_MASK (tag) >> 1;
/****** validate the tag */
for (tag_depth = 4; mask; mask >>= 8)
{
if ((mask & 0xff) != 0xff)
{
printf ("%s:tag `%08x' is invalid\n", filename, tag);
break;
}
tag_depth-- ;
}
/***** find the tag in tag_table, if found, then call its procedure */
for (format = tag_table; format- >name; format++)
if (format- >tag == tag)
goto found;
format = &tag_table[GCOV_TAG_IS_COUNTER (tag) ? 2: 1];
found:
;
if (tag)
{
if (depth && depth < tag_depth)
{
if (! GCOV_TAG_IS_SUBTAG (tags[depth - 1], tag))
printf ("%s:tag `%08x' is incorrectly nested\n",
filename, tag);
}
depth = tag_depth;
tags[depth - 1] = tag;
}
/***** print some spaces to represent the depth level */
print_prefix (filename, tag_depth, position);
printf ("%08x:%4u:%s", tag, length, format- >name);
/***** call the procedure of this tag stored in tag_table */
if (format- >proc)
(*format- >proc) (filename, tag, length); //此处调用相应的tag处理函数
printf ("\n");
if (flag_dump_contents && format- >proc)
{
unsigned long actual_length = gcov_position () - base;
if (actual_length > length)
printf ("%s:record size mismatch %lu bytes overread\n",
filename, actual_length - length);
else if (length > actual_length)
printf ("%s:record size mismatch %lu bytes unread\n",
filename, length - actual_length);
}
/***** base stands for the base position of a tag, then, synchronize the pointer */
gcov_sync (base, length);
if ((error = gcov_is_error ()))
{
printf (error < 0 ? "%s:counter overflow at %lu\n" :
"%s:read error at %lu\n", filename,
(long unsigned) gcov_position ());
break;
}
}
gcov_close ();
}
dump_file函数首先通过gcov_open打开.gcda/.gcno文件,将文件信息保存到全局变量gcov_var(稍后介绍该变量),接着读取文件头信息,包括magic,version,stamp,然后循环读取每个tag,length,并通过函数指针处理该tag,直到文件结束(0x00000000)。下面介绍各种tag的callback。
2.3处理各种tag的callback定义
处理tag的callback函数定义如下。
static const tag_format_t tag_table[] =
{
{0,"NOP", NULL},
{0,"UNKNOWN", NULL},
{0,"COUNTERS", tag_counters},
{GCOV_TAG_FUNCTION, "FUNCTION", tag_function},
{GCOV_TAG_BLOCKS, "BLOCKS", tag_blocks},
{GCOV_TAG_ARCS, "ARCS", tag_arcs},
{GCOV_TAG_LINES, "LINES", tag_lines},
{GCOV_TAG_OBJECT_SUMMARY, "OBJECT_SUMMARY", tag_summary},
{GCOV_TAG_PROGRAM_SUMMARY, "PROGRAM_SUMMARY", tag_summary},
{0, NULL, NULL}
};
其类型tag_format_t为一个结构,分别由tag本身,tag name和处理该tag的函数指针组成,定义如下。
typedef struct tag_format
{
unsigned tag;
char const *name;
void (*proc) (const char *, unsigned, unsigned);
} tag_format_t;
2.4基本读取函数gcov_read_words
对.gcda/.gcno文件的读取/写入,均以4字节(1个words)为单位进行。下面分析从.gcda/.gcno文件中读取words的基本读取函数gcov_read_words。代码如下。其中的注释为笔者所加。
/ * Return a pointer to read BYTES bytes from the gcov file. Returns
NULL on failure (read past EOF). */
static const gcov_unsigned_t *
gcov_read_words (unsigned words)
{
const gcov_unsigned_t *result;
/**excess is the number of words which can be excessed*/
unsigned excess = gcov_var.length - gcov_var.offset;
gcc_assert (gcov_var.mode > 0);
if (excess < words)
{
gcov_var.start += gcov_var.offset;
#if IN_LIBGCOV
if (excess)
{
gcc_assert (excess == 1);
memcpy (gcov_var.buffer, gcov_var.buffer + gcov_var.offset, 4);
}
#else
//在gcov-dump程序中,执行memmove
memmove (gcov_var.buffer, gcov_var.buffer + gcov_var.offset, excess * 4);
#endif
gcov_var.offset = 0;
gcov_var.length = excess;
#if IN_LIBGCOV
gcc_assert (! gcov_var.length || gcov_var.length == 1);
excess = GCOV_BLOCK_SIZE;
#else
//在gcov-dump程序中,执行gcov_allocate
if (gcov_var.length + words > gcov_var.alloc)
/** allocate space, the space pointer is saved in gcov_var.buffer */
gcov_allocate (gcov_var.length + words);
excess = gcov_var.alloc - gcov_var.length; /** if program can run here, then, excess = 2050 */
#endif
/*****
* >>2, that is, divided by 4, it is for 4 Bytes as a unit.
* for example, a file with 168B, then, will read 168B, but excess is 168/ 4=42.
* gcov_var.buffer will save the file content.
*/
excess = fread (gcov_var.buffer + gcov_var.length, 1, excess << 2, gcov_var.file) >> 2;
gcov_var.length += excess;
if (gcov_var.length < words)
{
gcov_var.overread += words - gcov_var.length;
gcov_var.length = 0;
return 0;
}
}
/***** then, return an unsigned word */
result = &gcov_var.buffer[gcov_var.offset]; gcov_var.offset += words;
return result;
}
第一次调用该函数时,gcov_var.alloc=0,然后一定会调用gcov_allocate,调用gcov_allocate后,gcov_var.alloc=2050。跟踪执行发现,第一次调用fread之前,excess = gcov_var.alloc - gcov_var.length = 2050,调用fread后,仍以test.c产生的test.gcda为例(可参考前面的文章),excess=168/4=42。因为test.gcda较小,只有168字节,故调用fread后,gcov_var.buffer中就存放了整个文件的内容(168字节),如下所示,虽然为gcov_var.buffer分配了8200自己的空间。
(gdb) p gcov_var
$1 = {
file = 0x810c008, //文件指针
start = 0,
offset = 0,
length = 0,
overread = 4294967295, //4294967295=0xffffffff=-1
error = 0,
mode = 1,
endian = 0,
alloc = 2050,
buffer = 0x810c170
}
(gdb) x /42w 0x810c170 //查看buffer中的前42个字,共168字节,就是test.gcda文件的内容
0x810c170: 0x67636461 0x34303170 0xc5ecae39 0x01000000
0x810c180: 0x00000002 0x00000003 0xeb65a768 0x01a10000
0x810c190: 0x0000000a 0x0000000a 0x00000000 0x00000000
0x810c1a0: 0x00000000 0x00000001 0x00000000 0x00000000
0x810c1b0: 0x00000000 0x00000001 0x00000000 0xa1000000
0x810c1c0: 0x00000009 0x00000000 0x00000005 0x00000001
0x810c1d0: 0x0000000c 0x00000000 0x0000000a 0x00000000
0x810c1e0: 0x0000000a 0x00000000 0xa3000000 0x00000009
0x810c1f0: 0x51924f98 0x00000005 0x00000001 0x0000000c
0x810c200: 0x00000000 0x0000000a 0x00000000 0x0000000a
0x810c210: 0x00000000 0x00000000
其中,前3个字(4字节/字)即为magic, version, stamp;蓝色部分即为tag,可以参考"Linux平台代码覆盖率测试-GCC如何编译生成gcov/gcov-dump程序及其bug分析"一文的3.3和3.4节,也可以参考本文第3节。
为什么为gcov_var.buffer分配了8200字节的空间?
——这就是gcov_allocate完成的。
2.5分配空间函数gcov_allocate
代码如下。其中的注释为笔者加入。
#if ! IN_LIBGCOV
static void
gcov_allocate (unsigned length)
{
size_t new_size = gcov_var.alloc;
if (! new_size)
new_size = GCOV_BLOCK_SIZE; /***** if new_size==0, then, new_size=1024(GCOV_BLOCK_SIZE=1024) */
new_size += length; /***** if length==1, then, new_size=1025 */
new_size *= 2; /***** then, new_size=1025*2=2050 */
gcov_var.alloc = new_size;
gcov_var.buffer = xrealloc (gcov_var.buffer, new_size << 2); /***** size=1025*4=8200 */
}
#endif
实际上gcov_var.alloc是一个内存block,以4字节为一个单位。由代码及其注释可以看出,当length=1时,gcov_var.alloc=2050,调用gcov_allocate后,实际上分配了2050*4=8200个字节的空间给gcov_var.buffer。
此处,不得不介绍一下gcov_var。
2.6重要数据结构gcov_var
gcov_var是个全局变量,其作用就是在gcov/gcov-dump程序运行期间保存操作的文件信息,例如,文件指针、某个block的start/offset/length、文件内容buffer等信息,定义如下。
/* Optimum number of gcov_unsigned_t's read from or written to disk. */
#define GCOV_BLOCK_SIZE (1<< 10)
GCOV_LINKAGE struct gcov_var
{
FILE *file;
gcov_position_t start; /* Position of first byte of block */
unsigned offset; /* Read/ write position within the block. */
unsigned length; /* Read limit in the block. */
unsigned overread; /* Number of words overread. */
int error; /* < 0 overflow, > 0 disk error. */
int mode; /* < 0 writing, > 0 reading */
#if IN_LIBGCOV
/* Holds one block plus 4 bytes, thus all coverage reads & writes
fit within this buffer and we always can transfer GCOV_BLOCK_SIZE
to and from the disk. libgcov never backtracks and only writes 4 or 8 byte objects. */
gcov_unsigned_t buffer[GCOV_BLOCK_SIZE + 1];
#else
int endian; /* Swap endianness. */
/* Holds a variable length block, as the compiler can write strings and needs to backtrack. */
size_t alloc;
gcov_unsigned_t *buffer;
#endif
}gcov_var ATTRIBUTE_HIDDEN;
在gcov-dump程序中,sizeof(gcov_type)=sizeof(gcov_unsigned_t)=4,sizeof(gcov_var)=40。gcov_var的值一个例子可以参考2.4节,此处不再赘述。
3.处理tag的callback分析
3.1FUNCTION tag: tag_function()函数
static void
tag_function (const char *filename ATTRIBUTE_UNUSED,
unsigned tag ATTRIBUTE_UNUSED, unsigned length ATTRIBUTE_UNUSED)
{
unsigned long pos = gcov_position ();
/***** for function, it will print ident and checksum */
printf (" ident=%u", gcov_read_unsigned ());
printf (", checksum=0x%08x", gcov_read_unsigned ());
if (gcov_position () - pos < length) //一般对于.gcno文件该条件才满足,才能执行该clause
{
const char *name;
name = gcov_read_string (); //该函数读取length(4字节)和length个words(4*length字节),读取函数名字
printf (", `%s'", name ? name : "NULL");
name = gcov_read_string (); //读取源文件名字
printf (" %s", name ? name : "NULL");
printf (":%u", gcov_read_unsigned ()); //读取该函数在该源文件中的行号
}
}
输出格式:
.gcda文件输出:ident=3, checksum=0xeb65a768
.gcno文件输出:ident=3, checksum=0xeb65a768, `main' test.c:4
其中,划线部分分别为:函数名源文件名:行号
3.2BLOCKS tag: tag_blocks()函数
static void
tag_blocks (const char *filename ATTRIBUTE_UNUSED,
unsigned tag ATTRIBUTE_UNUSED, unsigned length ATTRIBUTE_UNUSED)
{
unsigned n_blocks = GCOV_TAG_BLOCKS_NUM (length);
printf (" %u blocks", n_blocks);
if (flag_dump_contents)
{
unsigned ix;
for (ix = 0; ix != n_blocks; ix++)
{
if (! (ix & 7)) //如果blocks较多,则每8个为1行输出,且按0,8,16,...输出序号
{
printf ("\n");
print_prefix (filename, 0, gcov_position ());
printf ("\t\t%u", ix); //输出序号
}
printf (" %04x", gcov_read_unsigned ());
}
}
}
其中,flag_dump_contents是打印开关,flag_dump_contents非0时将打印COUNTER的内容。
输出格式:
n blocks
0 block0 block1 ... block7 //每8个1行输出,前面的0表示序号
8 block8 block9 ... block15 //前面的8表示序号
...
当然,需要注意前导符或者输出位置。
3.3ARCS tag: tag_arcs()函数
static void
tag_arcs (const char *filename ATTRIBUTE_UNUSED,
unsigned tag ATTRIBUTE_UNUSED, unsigned length ATTRIBUTE_UNUSED)
{
unsigned n_arcs = GCOV_TAG_ARCS_NUM (length);
printf (" %u arcs", n_arcs); //输出提示信息,几个arcs
if (flag_dump_contents)
{
unsigned ix;
unsigned blockno = gcov_read_unsigned ();
for (ix = 0; ix != n_arcs; ix++)
{
unsigned dst, flags;
if (! (ix & 3)) //如果arcs较多,则每4个为1行输出,且每行前面输出blockno
{
printf ("\n");
print_prefix (filename, 0, gcov_position ());
printf ("\tblock %u:", blockno);
}
dst = gcov_read_unsigned (); //读取目的blockno
flags = gcov_read_unsigned ();
printf (" %u:%04x", dst, flags);
}
}
}
输出格式:
n arcs //n个arcs,每4个为1行输出
blockno: dst0:flags0 dst1:flags1 dst2:flags2 dst3:flags3
blockno: dst4:flags4 dst5:flags5 dst6:flags6 dst7:flags7
...
同上,需要注意前导符或者输出位置。dst0, ...,表示目的block的blockno。
3.4LINES tag: tag_lines()函数
static void
tag_lines (const char *filename ATTRIBUTE_UNUSED,
unsigned tag ATTRIBUTE_UNUSED, unsigned length ATTRIBUTE_UNUSED)
{
if (flag_dump_contents)
{
unsigned blockno = gcov_read_unsigned ();
char const *sep = NULL;
while (1)
{
gcov_position_t position = gcov_position ();
const char *source = NULL;
unsigned lineno = gcov_read_unsigned ();
if (! lineno) //lineno=0时才会执行该clause,因此lineno=0即为以后的新的文件的标志
{
source = gcov_read_string (); //该函数读取length(4字节)和length个words(4*length字节)
if (! source) //source即为文件名,没有源文件了,就退出
break;
sep = NULL;
}
if (! sep) //sep=NULL才会执行该clause,那么什么时候会为NULL呢?——就是新的文件开始,实际上就是lineno=0
{
printf ("\n");
print_prefix (filename, 0, position);
printf ("\tblock %u:", blockno);
sep = "";
}
if (lineno)
{
printf ("%s%u", sep, lineno);
sep = ", ";
}
else
{
printf ("%s`%s'", sep, source); //lineno=0时,输出该文件名,之后sep=":"
sep = ":";
}
}
}
}
输出格式:
block blockno:'filename':lineno1, lineno2, ...
例如:block 1:'test.c':4, 7, 9
其中,前面的block为提示信息。同上,需要注意前导符或者输出位置。
3.5COUNTER tag: tag_counters()函数
static void
tag_counters (const char *filename ATTRIBUTE_UNUSED,
unsigned tag ATTRIBUTE_UNUSED, unsigned length ATTRIBUTE_UNUSED)
{
static const char *const counter_names[] = GCOV_COUNTER_NAMES;
unsigned n_counts = GCOV_TAG_COUNTER_NUM (length);
printf (" %s %u counts",
counter_names[GCOV_COUNTER_FOR_TAG (tag)], n_counts);
if (flag_dump_contents)
{
unsigned ix;
for (ix = 0; ix != n_counts; ix++)
{
gcov_type count;
if (! (ix & 7)) //如果counter较多,则每8个1行输出,且按0,8,16,...输出序号
{
printf ("\n");
print_prefix (filename, 0, gcov_position ());
printf ("\t\t%u", ix); //输出序号
}
count = gcov_read_counter (); //读取该counter,读取8字节,但返回4字节
printf (" ");
printf (HOST_WIDEST_INT_PRINT_DEC, count);
}
}
}
关于GCOV_TAG_COUNTER_NUM和GCOV_COUNTER_FOR_TAG,请参考源代码。
counter的名字定义如下。
/* A list of human readable names of the counters */
#define GCOV_COUNTER_NAMES {"arcs", "interval", "pow2", "single", "delta"}
输出格式:
arcsn counts //arcs即为counter的名字,如上
0 counter0 counter1 ... counter7 //每8个1行输出,前面的0表示序号
8 counter8 counter9 ... counter15 //前面的8表示序号
...
同上,需要注意前导符或者输出位置。
3.6OBJECT/PROGRAM SUMMARY tag: tag_summary()函数
static void
tag_summary (const char *filename ATTRIBUTE_UNUSED,
unsigned tag ATTRIBUTE_UNUSED, unsigned length ATTRIBUTE_UNUSED)
{
struct gcov_summary summary;
unsigned ix;
/***** initialize all members with 0 *****/
memset(&summary, 0, sizeof(summary));
unsigned count = gcov_read_summary (&summary); //读取该summary
printf (" checksum=0x%08x", summary.checksum);
/* for (ix = 0; ix ! = GCOV_COUNTERS; ix++) */ /* 原来的代码 */
for (ix = 0; ix < count; ix++) /* 应该如此修改*/
{
printf ("\n");
print_prefix (filename, 0, 0);
printf ("\t\tcounts=%u, runs=%u", summary.ctrs[ix].num, summary.ctrs[ix].runs);
printf (", sum_all=" HOST_WIDEST_INT_PRINT_DEC, (HOST_WIDEST_INT)summary.ctrs[ix].sum_all);
printf (", run_max=" HOST_WIDEST_INT_PRINT_DEC, (HOST_WIDEST_INT)summary.ctrs[ix].run_max);
printf (", sum_max=" HOST_WIDEST_INT_PRINT_DEC, (HOST_WIDEST_INT)summary.ctrs[ix].sum_max);
}
}
输出格式:
checksum=0x51924f98
counts=5, runs=1, sum_all=12, run_max=10, sum_max=10
同上,也需要注意前导符或者输出位置。
其中,gcov_read_summary函数是修改后的函数,在"Linux平台代码覆盖率测试-GCC如何编译生成gcov/gcov-dump程序及其bug分析"一文没有列出该修改后的函数,其实这篇文章中的bug与该函数有关。此处列出其代码。
GCOV_LINKAGE unsigned
gcov_read_summary (struct gcov_summary *summary)
{
unsigned ix;
struct gcov_ctr_summary *csum;
summary- >checksum = gcov_read_unsigned (); /***** checksum is a words (4Bytes) *****/
/***** that is, a summry is 32Bytes (sizeof(gcov_type)=4) or 20Bytes (sizeof(gcov_type)=8) *****/
for (csum = summary- >ctrs, ix = GCOV_COUNTERS_SUMMABLE; ix-- ; csum++)
{
csum- >num = gcov_read_unsigned (); /***** 4Bytes *****/
csum- >runs = gcov_read_unsigned (); /***** 4Bytes *****/
csum- >sum_all = gcov_read_counter (); /***** 8Bytes, but return 4Bytes *****/
csum- >run_max = gcov_read_counter (); /***** 8Bytes, but return 4Bytes *****/
csum- >sum_max = gcov_read_counter (); /***** 8Bytes, but return 4Bytes *****/
}
return GCOV_COUNTERS_SUMMABLE; /* zubo modified to return the nubmer */
}
gcov_summary及gcov_ctr_summary结构的定义可参考源代码或者"Linux平台代码覆盖率测试工具GCOV相关文件分析"。
4.小结
本文详细叙述了gcov-dump程序的结构和实现原理。也从中学习了其处理各种tag用到的callback方法,如果你想深入跟踪或学习gcc源码,请注意callback的使用,因为gcc源码中大量地使用了callback。
Reference
http://blog.csdn.net/livelylittlefish/archive/2011/04/13/6321909.aspx
http://blog.csdn.net/livelylittlefish/archive/2011/05/01/6382489.aspx
http://blog.csdn.net/livelylittlefish/archive/2011/05/26/6448799.aspx
Technorati 标签: 覆盖率测试,GCC,gcov,gcov-dump