Android debuggerd 源码分析
debuggerd 简介
Android系统自带一个实用的程序异常退出的诊断daemon debuggerd。此进程可以侦测到程序崩溃,并将崩溃时的进程状态信息输出到文件和串口中,以供开发人员分析调试使用。Debuggerd的数据被保存在/data/tombstone/目录下,共可保存10个文件,当超过10个时,会覆盖重写最早生产的文件。串口中,则直接用DEBUG的tag,输出logcat信息。 Linux kernel有自己的一套signal机制,在应用程序崩溃时,通常系统内核都会发送signal到出问题的进程,以通知进程出现什么异常,这些进程可以捕获这些signal并对其做相应的处理。通常对于程序异常信号的处理,就是退出。Android在此机制上实现了一个更实用的功能:拦截这些信号,dump进程信息以供调试。
debuggerd的运行原理
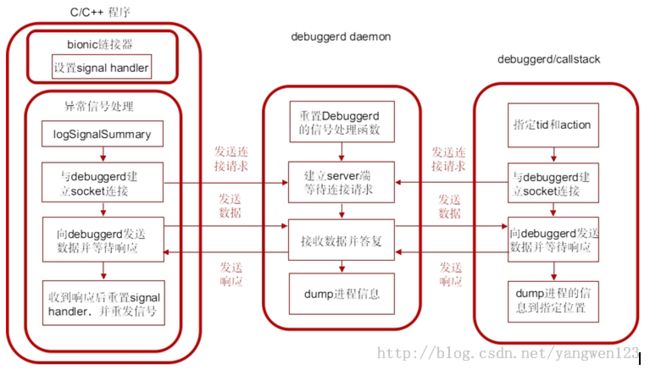
debuggerd创建一个名为 “Android:debuggerd”的socket,作为server端等待其他client端进程的连接,接收client端进程发送来的tid和action信息将由tid指定的那个进程的运行信息,按照由action指定的动作dump到文件或者控制台中可以作为debuggerd的client端的进程主要有几种:
1. 异常的C/C++程序
这种程序由bionic的linker安装异常信号的处理函数,当程序产生异常信号时,进入信号处理函数,与debuggerd建立。
2. debuggerd程序
debuggerd可以在控制台中以命令debuggerd -b [<tid>]启动 ,然后与debuggerd daemon建立连接。这样debuggerd可以在不中断进程执行的情况下dump由tid指定的进程的信息。
3. dumpstate
控制台中运行命令dumpstate,并指定必要的参数,命令中会调用dump_backtrace_to_file与debuggerd交互。
debuggerd的使用方法
产生异常信号的C/C++程序与debuggerd建立连接后,debuggerd将进程信息dump到tombstone_XX文件中保存到/data/tombstone/文件夹下。可通过查看tombstone_XX分析异常进程的堆栈信息。
在控制台中以命令debuggerd -b [<tid>]启动。如果加上-b参数,则由tid指定的进程的信息将dump到控制台上,否则dump到tombstone文件中。控制台中运行命令callstack/dumpstate,进程信息会写入这两个命令指定的文件中。
应用程序异常处理过程
应用程序入口属于bionic实现的一部分,则对所有android的程序有效。在应用程序入口地址__start后,__linker_init中调用debugger_init()函数来注册异常信号处理handler,以实现拦截系统异常的几个singal:SIGILL,SIGABRT, SIGBUS, SIGFPE,SIGSEGV和SIGPIPE:
linker/arch/arm/begin.S
start:
mov r0, sp
mov r1, #0
bl __linker_init
bionic\linker\ Linker.cpp
extern "C" Elf32_Addr __linker_init(void* raw_args) {
…
Elf32_Addr start_address = __linker_init_post_relocation(args, linker_addr);
set_soinfo_pool_protection(PROT_READ);
// Return the address that the calling assembly stub should jump to.
return start_address;
}
static Elf32_Addr __linker_init_post_relocation(KernelArgumentBlock& args, Elf32_Addr linker_base) {
...
debuggerd_init();
...
}
bionic\linker\Debugger.c
void debugger_init()
{
struct sigaction act;
memset(&act, 0, sizeof(act));
act.sa_sigaction = debugger_signal_handler;
act.sa_flags = SA_RESTART | SA_SIGINFO;
sigemptyset(&act.sa_mask);
sigaction(SIGILL, &act, NULL);
sigaction(SIGABRT, &act, NULL);
sigaction(SIGBUS, &act, NULL);
sigaction(SIGFPE, &act, NULL);
sigaction(SIGSEGV, &act, NULL);
sigaction(SIGSTKFLT, &act, NULL);
sigaction(SIGPIPE, &act, NULL);
}
bionic库中的链接器会对以下七种信号设置Handler(debugger_signal_handler):
- SIGILL(非法指令异常)
- SIGABRT(abort退出异常)
- SIGBUS(硬件访问异常)
- SIGFPE(浮点运算异常)
- SIGSEGV(内存访问异常)
- SIGSTKFLT(协处理器栈异常)
- SIGPIPE(管道异常)
debugger_init中act.sa_flags = SA_RESTART | SA_SIGINFO的涵义:
1) SA_RESTART
如果指定该参数,表示若信号中断了进程的某个系统调用,则系统自动启动该系统调用。如果不指定该参数,则被中断的系统调用返回失败,错误码为EINTR。这个标志位只要用于处理慢系统调用(可能会被阻塞的系统调用)。比如调用write系统调用写某个设备被阻塞,这时进程捕获某个信号且进入相应信号处理函数返回时,该系统调用可能要返回ENINTR错误。指定这个参数后,系统调用会重启,与RETRY_ON_EINTR宏配合使用则可以保证写操作的完成
2) SA_SIGINFO
如果指定该参数,表示信号附带的参数(siginfo_t结构体)可以被传递到信号处理函数中。
链接到bionic库上的C/C++程序崩溃时,内核会发送相应的signal,进程收到异常信号后,会转入debugger_signal_handler函数中进行处理。
void debugger_signal_handler(int n, siginfo_t* info, void* unused)
{
char msgbuf[128];
unsigned tid;
int s;
logSignalSummary(n, info);
tid = gettid();
//"android:debuggerd"
s = socket_abstract_client(DEBUGGER_SOCKET_NAME, SOCK_STREAM);
if (s >= 0) {
/* debugger knows our pid from the credentials on the
* local socket but we need to tell it our tid. It
* is paranoid and will verify that we are giving a tid
* that's actually in our process
*/
int ret;
debugger_msg_t msg;
msg.action = DEBUGGER_ACTION_CRASH;
msg.tid = tid;
RETRY_ON_EINTR(ret, write(s, &msg, sizeof(msg)));
if (ret == sizeof(msg)) {
/* if the write failed, there is no point to read on
* the file descriptor. */
RETRY_ON_EINTR(ret, read(s, &tid, 1));
int savedErrno = errno;
notify_gdb_of_libraries();
errno = savedErrno;
}
if (ret < 0) {
/* read or write failed -- broken connection? */
format_buffer(msgbuf, sizeof(msgbuf),
"Failed while talking to debuggerd: %s", strerror(errno));
__libc_android_log_write(ANDROID_LOG_FATAL, "libc", msgbuf);
}
close(s);
} else {
/* socket failed; maybe process ran out of fds */
format_buffer(msgbuf, sizeof(msgbuf),
"Unable to open connection to debuggerd: %s", strerror(errno));
__libc_android_log_write(ANDROID_LOG_FATAL, "libc", msgbuf);
}
/* remove our net so we fault for real when we return */
signal(n, SIG_DFL);
/*
* These signals are not re-thrown when we resume. This means that
* crashing due to (say) SIGPIPE doesn't work the way you'd expect it
* to. We work around this by throwing them manually. We don't want
* to do this for *all* signals because it'll screw up the address for
* faults like SIGSEGV.
*/
switch (n) {
case SIGABRT:
case SIGFPE:
case SIGPIPE:
case SIGSTKFLT:
(void) tgkill(getpid(), gettid(), n);
break;
default: // SIGILL, SIGBUS, SIGSEGV
break;
}
}
debugger_signal_handler函数处理流程:
1) 调用logSignalSummary将signal信息写入文件;
static void logSignalSummary(int signum, const siginfo_t* info)
{
char buffer[128];
char threadname[MAX_TASK_NAME_LEN + 1]; // one more for termination
char* signame;
switch (signum) {
case SIGILL: signame = "SIGILL"; break;
case SIGABRT: signame = "SIGABRT"; break;
case SIGBUS: signame = "SIGBUS"; break;
case SIGFPE: signame = "SIGFPE"; break;
case SIGSEGV: signame = "SIGSEGV"; break;
case SIGSTKFLT: signame = "SIGSTKFLT"; break;
case SIGPIPE: signame = "SIGPIPE"; break;
default: signame = "???"; break;
}
if (prctl(PR_GET_NAME, (unsigned long)threadname, 0, 0, 0) != 0) {
strcpy(threadname, "<name unknown>");
} else {
// short names are null terminated by prctl, but the manpage
// implies that 16 byte names are not.
threadname[MAX_TASK_NAME_LEN] = 0;
}
format_buffer(buffer, sizeof(buffer),
"Fatal signal %d (%s) at 0x%08x (code=%d), thread %d (%s)",
signum, signame, info->si_addr, info->si_code, gettid(), threadname);
__libc_android_log_write(ANDROID_LOG_FATAL, "libc", buffer);
}
获取异常信号的名字和thread名字,并格式化字符串,调用函数__libc_android_log_write函数写入”/dev/log/main”中。
2) 调用socket_abstract_client函数与debuggerd建立socket连接;
s = socket_abstract_client(DEBUGGER_SOCKET_NAME, SOCK_STREAM);
3) 如果连接建立成功,则设置结构体debugger_msg_t,并发送给debuggerd;
msg.action = DEBUGGER_ACTION_CRASH;//告诉debuggerd采取何种行 msg.tid = tid;//线程号 RETRY_ON_EINTR(ret, write(s, &msg, sizeof(msg)));
4) 等待debuggerd的回复,阻塞在下面的调用中,收到回复后接着执行下面的流程;
RETRY_ON_EINTR(ret, read(s, &tid, 1));
5) 重新设置信号处理函数为SIG_DFL,即采取默认的动作;
signal(n, SIG_DFL);
6) 重新发送信号,进程从当前信号处理函数返回后,会处理这个信号,进行默认的信号处理动作,即中断进程。
debuggerd的源码分析
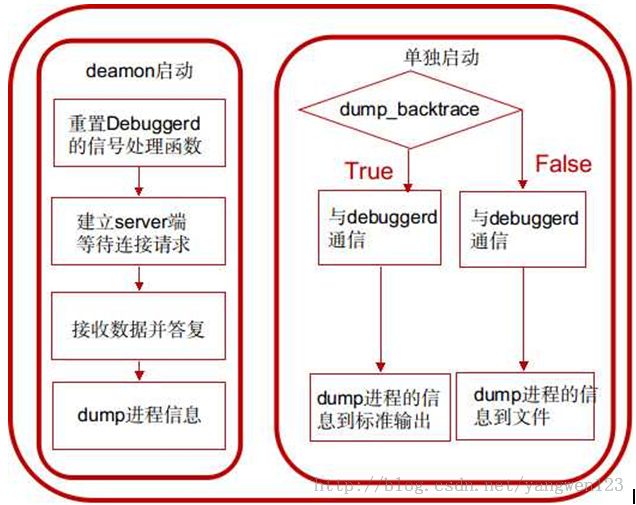
1. 在init进程中以deamon的方式启动,在init.rc中
service debuggerd /system/bin/debuggerd class main
以这种方式启动的话,进入main函数后,将调用do_server函数,作为server端为其他进程提供dump进程信息的服务。
2. 直接运行system/bin/debuggerd可执行文件,需要指定参数,用法为:
debuggerd -b [<tid>] //参数-b表示在控制台中输出backtrace
以这种方式启动的话,进入main函数后,将调用do_explicit_dump函数与debuggerd daemon通信,将指定进程的信息dump到文件或控制台。
服务启动方式
int main(int argc, char** argv) {
if (argc == 1) {
return do_server();
}
}
当启动debuggerd进程传递的参数个数为1时,此时启动的debuggerd将作为一个后台服务进程,专门接收应用程序异常退出消息而产生tombstone。
static int do_server() {
int s;
struct sigaction act;
int logsocket = -1;
/*
* debuggerd crashes can't be reported to debuggerd. Reset all of the
* crash handlers.
*/
signal(SIGILL, SIG_DFL);
signal(SIGABRT, SIG_DFL);
signal(SIGBUS, SIG_DFL);
signal(SIGFPE, SIG_DFL);
signal(SIGSEGV, SIG_DFL);
signal(SIGPIPE, SIG_IGN);
signal(SIGSTKFLT, SIG_DFL);
logsocket = socket_local_client("logd",
ANDROID_SOCKET_NAMESPACE_ABSTRACT, SOCK_DGRAM);
if(logsocket < 0) {
logsocket = -1;
} else {
fcntl(logsocket, F_SETFD, FD_CLOEXEC);
}
act.sa_handler = SIG_DFL;
sigemptyset(&act.sa_mask);
sigaddset(&act.sa_mask,SIGCHLD);
act.sa_flags = SA_NOCLDWAIT;
sigaction(SIGCHLD, &act, 0);
s = socket_local_server(DEBUGGER_SOCKET_NAME,
ANDROID_SOCKET_NAMESPACE_ABSTRACT, SOCK_STREAM);
if(s < 0) return 1;
fcntl(s, F_SETFD, FD_CLOEXEC);
LOG("debuggerd: " __DATE__ " " __TIME__ "\n");
//check corefile limit.
(void)check_corefile_limit();
for(;;) {
struct sockaddr addr;
socklen_t alen;
int fd;
alen = sizeof(addr);
XLOG("waiting for connection\n");
fd = accept(s, &addr, &alen);
if(fd < 0) {
XLOG("accept failed: %s\n", strerror(errno));
continue;
}
fcntl(fd, F_SETFD, FD_CLOEXEC);
handle_request(fd);
}
return 0;
}
1. 忽略debuggerd自身crash的处理;
2. 建立socket通信的server端;
3. 进入无限循环中,等待并接收客户端进程连接请求,并通过handle_request()函数处理请求;
handle_request
static void handle_request(int fd) {
XLOG("handle_request(%d)\n", fd);
debugger_request_t request;
int status = read_request(fd, &request);
if (!status) {
XLOG("BOOM: pid=%d uid=%d gid=%d tid=%d\n",
request.pid, request.uid, request.gid, request.tid);
/* At this point, the thread that made the request is blocked in
* a read() call. If the thread has crashed, then this gives us
* time to PTRACE_ATTACH to it before it has a chance to really fault.
*
* The PTRACE_ATTACH sends a SIGSTOP to the target process, but it
* won't necessarily have stopped by the time ptrace() returns. (We
* currently assume it does.) We write to the file descriptor to
* ensure that it can run as soon as we call PTRACE_CONT below.
* See details in bionic/libc/linker/debugger.c, in function
* debugger_signal_handler().
*/
if (ptrace(PTRACE_ATTACH, request.tid, 0, 0)) {
LOG("ptrace attach failed: %s\n", strerror(errno));
} else {
bool detach_failed = false;
bool attach_gdb = should_attach_gdb(&request);
if (TEMP_FAILURE_RETRY(write(fd, "\0", 1)) != 1) {
LOG("failed responding to client: %s\n", strerror(errno));
} else {
char* tombstone_path = NULL;
if (request.action == DEBUGGER_ACTION_CRASH) {
close(fd);
fd = -1;
}
int total_sleep_time_usec = 0;
for (;;) {
int signal = wait_for_signal(request.tid, &total_sleep_time_usec);
if (signal < 0) {
break;
}
switch (signal) {
case SIGSTOP:
if (request.action == DEBUGGER_ACTION_DUMP_TOMBSTONE) {
XLOG("stopped -- dumping to tombstone\n");
tombstone_path = engrave_tombstone(request.pid, request.tid,
signal, true, true, &detach_failed,
&total_sleep_time_usec);
} else if (request.action == DEBUGGER_ACTION_DUMP_BACKTRACE) {
XLOG("stopped -- dumping to fd\n");
dump_backtrace(fd, request.pid, request.tid, &detach_failed,
&total_sleep_time_usec);
} else {
XLOG("stopped -- continuing\n");
status = ptrace(PTRACE_CONT, request.tid, 0, 0);
if (status) {
LOG("ptrace continue failed: %s\n", strerror(errno));
}
continue; /* loop again */
}
break;
case SIGILL:
case SIGABRT:
case SIGBUS:
case SIGFPE:
case SIGSEGV:
case SIGSTKFLT: {
XLOG("stopped -- fatal signal\n");
/*
* Send a SIGSTOP to the process to make all of
* the non-signaled threads stop moving. Without
* this we get a lot of "ptrace detach failed:
* No such process".
*/
kill(request.pid, SIGSTOP);
/* don't dump sibling threads when attaching to GDB because it
* makes the process less reliable, apparently... */
tombstone_path = engrave_tombstone(request.pid, request.tid,
signal, !attach_gdb, false, &detach_failed,
&total_sleep_time_usec);
break;
}
case SIGPIPE:
LOG("socket-client process stopped due to SIGPIPE! \n");
break;
default:
XLOG("stopped -- unexpected signal\n");
LOG("process stopped due to unexpected signal %d\n", signal);
break;
}
break;
}
if (request.action == DEBUGGER_ACTION_DUMP_TOMBSTONE) {
if (tombstone_path) {
write(fd, tombstone_path, strlen(tombstone_path));
}
close(fd);
fd = -1;
}
free(tombstone_path);
}
XLOG("detaching\n");
if (attach_gdb) {
/* stop the process so we can debug */
kill(request.pid, SIGSTOP);
/* detach so we can attach gdbserver */
if (ptrace(PTRACE_DETACH, request.tid, 0, 0)) {
LOG("ptrace detach from %d failed: %s\n", request.tid, strerror(errno));
detach_failed = true;
}
/*
* if debug.db.uid is set, its value indicates if we should wait
* for user action for the crashing process.
* in this case, we log a message and turn the debug LED on
* waiting for a gdb connection (for instance)
*/
wait_for_user_action(request.pid);
} else {
/* just detach */
if (ptrace(PTRACE_DETACH, request.tid, 0, 0)) {
LOG("ptrace detach from %d failed: %s\n", request.tid, strerror(errno));
detach_failed = true;
}
}
/* resume stopped process (so it can crash in peace). */
kill(request.pid, SIGCONT);
/* If we didn't successfully detach, we're still the parent, and the
* actual parent won't receive a death notification via wait(2). At this point
* there's not much we can do about that. */
if (detach_failed) {
LOG("debuggerd committing suicide to free the zombie!\n");
kill(getpid(), SIGKILL);
}
}
}
if (fd >= 0) {
close(fd);
}
}
1) 调用read_request函数读取client端进程发送来的数据:
static int read_request(int fd, debugger_request_t* out_request) {
struct ucred cr;
int len = sizeof(cr);
int status = getsockopt(fd, SOL_SOCKET, SO_PEERCRED, &cr, &len);
if (status != 0) {
LOG("cannot get credentials\n");
return -1;
}
XLOG("reading tid\n");
fcntl(fd, F_SETFL, O_NONBLOCK);
struct pollfd pollfds[1];
pollfds[0].fd = fd;
pollfds[0].events = POLLIN;
pollfds[0].revents = 0;
status = TEMP_FAILURE_RETRY(poll(pollfds, 1, 3000));
if (status != 1) {
LOG("timed out reading tid\n");
return -1;
}
debugger_msg_t msg;
status = TEMP_FAILURE_RETRY(read(fd, &msg, sizeof(msg)));
if (status < 0) {
LOG("read failure? %s\n", strerror(errno));
return -1;
}
if (status != sizeof(msg)) {
LOG("invalid crash request of size %d\n", status);
return -1;
}
out_request->action = msg.action;
out_request->tid = msg.tid;
out_request->pid = cr.pid;
out_request->uid = cr.uid;
out_request->gid = cr.gid;
if (msg.action == DEBUGGER_ACTION_CRASH) {
/* Ensure that the tid reported by the crashing process is valid. */
char buf[64];
struct stat s;
snprintf(buf, sizeof buf, "/proc/%d/task/%d", out_request->pid, out_request->tid);
if(stat(buf, &s)) {
LOG("tid %d does not exist in pid %d. ignoring debug request\n",
out_request->tid, out_request->pid);
return -1;
}
} else if (cr.uid == 0
|| (cr.uid == AID_SYSTEM && msg.action == DEBUGGER_ACTION_DUMP_BACKTRACE)) {
/* Only root or system can ask us to attach to any process and dump it explicitly.
* However, system is only allowed to collect backtraces but cannot dump tombstones. */
status = get_process_info(out_request->tid, &out_request->pid,
&out_request->uid, &out_request->gid);
if (status < 0) {
LOG("tid %d does not exist. ignoring explicit dump request\n",
out_request->tid);
return -1;
}
} else {
/* No one else is not allowed to dump arbitrary processes. */
return -1;
}
return 0;
}
☞ 从socket中读取client端进程的pid uid gid
getsockopt(fd, SOL_SOCKET, SO_PEERCRED, &cr, &len);
☞ 轮询socket句柄
struct pollfd pollfds[1]; pollfds[0].fd = fd; pollfds[0].events = POLLIN; pollfds[0].revents = 0; status = TEMP_FAILURE_RETRY(poll(pollfds, 1, 3000));
☞ 从socket上读取debugger_msg_t结构体
debugger_msg_t msg;
status = TEMP_FAILURE_RETRY(read(fd, &msg, sizeof(msg)));
if (status < 0) {
LOG("read failure? %s\n", strerror(errno));
return -1;
}
if (status != sizeof(msg)) {
LOG("invalid crash request of size %d\n", status);
return -1;
}
out_request->action = msg.action;
out_request->tid = msg.tid;
out_request->pid = cr.pid;
out_request->uid = cr.uid;
out_request->gid = cr.gid;
☞ 如果debugger_msg_t中设置的action为DEBUGGER_ACTION_CRASH,说明是crash的C/C++进程发来的请求,则判断传进来的tid是否有效。
if (msg.action == DEBUGGER_ACTION_CRASH) {
/* Ensure that the tid reported by the crashing process is valid. */
char buf[64];
struct stat s;
snprintf(buf, sizeof buf, "/proc/%d/task/%d", out_request->pid, out_request->tid);
if(stat(buf, &s)) {
LOG("tid %d does not exist in pid %d. ignoring debug request\n",
out_request->tid, out_request->pid);
return -1;
}
}
☞ 如果debugger_msg_t中设置的action为DEBUGGER_ACTION_DUMP_BACKTRACE说明是其他方式(debuggerd)发来的请求,则要求必须为root权限或者system权限,然后再判断tid是否有效。
2) 从read_request返回后,调用ptrace函数attach到tid指定的进程,此时debuggerd将变为被attache进程的父进程,然后ptrace函数会向子进程发送SIGSTOP信号将子进程停下来。此时,父进程有机会检查子进程核心image和寄存器的值。
ptrace(PTRACE_ATTACH, request.tid, 0, 0)
3) 调用下面的语句给client端子进程回复消息,使clinet端的进程能从read调用中返回。
TEMP_FAILURE_RETRY(write(fd, "\0", 1)
4) 在for循环中等待子进程停止。
int signal = wait_for_signal(request.tid, &total_sleep_time_usec);
5) 子进程根据收到的不同信号、不同的action进行不同的处理
switch (signal) {
case SIGSTOP:
if (request.action == DEBUGGER_ACTION_DUMP_TOMBSTONE) {
XLOG("stopped -- dumping to tombstone\n");
tombstone_path = engrave_tombstone(request.pid, request.tid,
signal, true, true, &detach_failed,
&total_sleep_time_usec);
} else if (request.action == DEBUGGER_ACTION_DUMP_BACKTRACE) {
XLOG("stopped -- dumping to fd\n");
dump_backtrace(fd, request.pid, request.tid, &detach_failed,
&total_sleep_time_usec);
} else {
XLOG("stopped -- continuing\n");
status = ptrace(PTRACE_CONT, request.tid, 0, 0);
if (status) {
LOG("ptrace continue failed: %s\n", strerror(errno));
}
continue; /* loop again */
}
break;
case SIGILL:
case SIGABRT:
case SIGBUS:
case SIGFPE:
case SIGSEGV:
case SIGSTKFLT: {
XLOG("stopped -- fatal signal\n");
kill(request.pid, SIGSTOP);
tombstone_path = engrave_tombstone(request.pid, request.tid,
signal, !attach_gdb, false, &detach_failed,
&total_sleep_time_usec);
break;
}
case SIGPIPE:
LOG("socket-client process stopped due to SIGPIPE! \n");
break;
default:
XLOG("stopped -- unexpected signal\n");
LOG("process stopped due to unexpected signal %d\n", signal);
break;
}
☞子进程收到SIGSTOP说明进程并没有发生crash,根据action不同将进程信息写入tombstone文件。
☞子进程收到七种异常信号说明是进程发生crash,调用engrave_tombstone直接将dump的信息写到tombstone。
6) 调用ptrace(PTRACE_DETACH, request.tid, 0, 0)解除对子进程的追踪;
if (attach_gdb) {
kill(request.pid, SIGSTOP);
if (ptrace(PTRACE_DETACH, request.tid, 0, 0)) {
LOG("ptrace detach from %d failed: %s\n", request.tid, strerror(errno));
detach_failed = true;
}
wait_for_user_action(request.pid);
} else {
if (ptrace(PTRACE_DETACH, request.tid, 0, 0)) {
LOG("ptrace detach from %d failed: %s\n", request.tid, strerror(errno));
detach_failed = true;
}
}
如果运行了类似以下指令:adb shell setprop debug.db.uid 10000;则所有uid<10000的进程发生crash的时候attach_gdb为true,将停止crash进程,并调用ptrace(PTRACE_DETACH, request.tid, 0, 0) 解除对crash进程的追踪后,开始等待gdb的连接。
adb forward tcp:5039 tcp:5039
adb shell gdbserver :5039 --attach pid &
用户按下HOME或者VOLUME DOWN按键,可以使进程继续进行,自然crash
attach_gdb为false时,只会解除对子进程的追踪。
7) 调用kill(request.pid, SIGCONT)恢复被停止的子进程,并让其自然终止;
engrave_tombstone
char* engrave_tombstone(pid_t pid, pid_t tid, int signal,
bool dump_sibling_threads, bool quiet, bool* detach_failed,
int* total_sleep_time_usec) {
mkdir(TOMBSTONE_DIR, 0755);
chown(TOMBSTONE_DIR, AID_SYSTEM, AID_SYSTEM);
//dump maps & check corefile limit .
dump_creash_maps(pid); //creat maps file
int fd;
char* path = find_and_open_tombstone(&fd);
if (!path) {
*detach_failed = false;
return NULL;
}
log_t log;
log.tfd = fd;
log.quiet = quiet;
*detach_failed = dump_crash(&log, pid, tid, signal, dump_sibling_threads,
total_sleep_time_usec);
close(fd);
return path;
}
对于crash的C/C++进程,主要通过这个函数dump进程信息
1.创建”/data/tombstones”文件夹并修改权限
2.调用函数find_and_open_tombstone,tombstone_XX文件最多10个,超过则覆盖最早的
3.调用dump_crash将所有信息dump到tombstone文件:
☞ dump_build_info(log);
☞ dump_thread_info(log, pid, tid, true);
☞ dump_fault_addr(log, tid, signal);
☞ dump_thread(context, log, tid, true, total_sleep_time_usec) dump进程的上下文信息
☞ dump_logs(log, pid, true);
☞ dump_sibling_thread_report(context, log, pid, tid, total_sleep_time_usec);
dump_backtrace
void dump_backtrace(int fd, pid_t pid, pid_t tid, bool* detach_failed,
int* total_sleep_time_usec) {
log_t log;
log.tfd = fd;
log.quiet = true;
ptrace_context_t* context = load_ptrace_context(tid);
dump_process_header(&log, pid);
dump_thread(&log, tid, context, true, detach_failed, total_sleep_time_usec);
char task_path[64];
snprintf(task_path, sizeof(task_path), "/proc/%d/task", pid);
DIR* d = opendir(task_path);
if (d) {
struct dirent debuf;
struct dirent *de;
while (!readdir_r(d, &debuf, &de) && de) {
if (!strcmp(de->d_name, ".") || !strcmp(de->d_name, "..")) {
continue;
}
char* end;
pid_t new_tid = strtoul(de->d_name, &end, 10);
if (*end || new_tid == tid) {
continue;
}
dump_thread(&log, new_tid, context, false, detach_failed, total_sleep_time_usec);
}
closedir(d);
}
dump_process_footer(&log, pid);
free_ptrace_context(context);
}
☞ dump_process_header(&log, pid);
☞ dump_thread(&log, tid, context, true, detach_failed, total_sleep_time_usec);
☞ dump_process_footer(&log, pid);
调试工具方式
int main(int argc, char** argv) {
bool dump_backtrace = false;
bool have_tid = false;
pid_t tid = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < argc; i++) {
if (!strcmp(argv[i], "-b")) {
dump_backtrace = true;
} else if (!have_tid) {
tid = atoi(argv[i]);
have_tid = true;
} else {
usage();
return 1;
}
}
if (!have_tid) {
usage();
return 1;
}
return do_explicit_dump(tid, dump_backtrace);
}
通过do_explicit_dump函数dump出指定进程的栈信息等
static int do_explicit_dump(pid_t tid, bool dump_backtrace) {
fprintf(stdout, "Sending request to dump task %d.\n", tid);
if (dump_backtrace) {
fflush(stdout);
if (dump_backtrace_to_file(tid, fileno(stdout)) < 0) {
fputs("Error dumping backtrace.\n", stderr);
return 1;
}
} else {
char tombstone_path[PATH_MAX];
if (dump_tombstone(tid, tombstone_path, sizeof(tombstone_path)) < 0) {
fputs("Error dumping tombstone.\n", stderr);
return 1;
}
fprintf(stderr, "Tombstone written to: %s\n", tombstone_path);
}
return 0;
}
☞ dump_backtrace_to_file(tid, fileno(stdout))
☞ dump_tombstone(tid, tombstone_path, sizeof(tombstone_path))