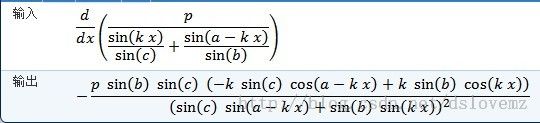ACMICPC 2013 长沙 F 题Curve in Circle
题目链接
http://acm.zju.edu.cn/changsha/showProblem.do?problemId=27
题目大意
一个半径为 R 的洞里面有一个半径为 r 的圆盘, 圆盘内部有个凸包,每个点给你。用一支笔画住洞和圆盘连线延长线的凸包上点,在凸包上转一圈,问形成的路径长度是多少。
Tag
计算几何·凸包、点
数值积分·自适应辛普森、路径积分
求导
解法
1、计算几何部分
因为没有说到底是顺时针还是逆时针给的凸包,索性再求一次凸包,整理成逆时针顺序。
对于每条边来说
以 AB 边为例,当圆盘 o 在 O 洞上旋转的时候,Oo 长度保持不变,逆时针旋转,而剩下的长度是oA向oB滑动。总长度 = Oo + o->凸包上距离。
综上所述,对于Oo与水平夹角(设为alpha) 我们都可以算出来 O - > 凸包上距离 这个长度。那么就可以用含 alpha 的参数方程来表示正在划线的这个点,设为 (f(alpha) , g(alpha))。
根据 神·室友的理论,路径积分长度是积分 sqrt((f'(alpha))^2 + (g‘(alpha))^2) -> 根号下 f函数倒数的平方 加上 g 函数倒数的平方。于是就是数值积分的故事了。。。
注意一点,在 小圆盘上转的角度不等于大圆上转的角度!!因为线速度一样,所以设小圆盘上转的角度为 beta = alpha * r / R . 不妨设 k = R / r.
那么我们只用看oAB 这个三角形就可以了。
更简单的是,给的坐标就是以 o 为坐标系的,所以直接可以算出 A , B , C 的角度值(余弦定理),如果要求精度可以用点积。。。
2.积分部分
为了方便我们把 oAB 变成 ABC (点对应)。那么转过的角度就是 k * alpha.
这时候我们设 AD 长度为 x , 那么我们尽量来表示 BD 长度 和 DC 长度。 又根据定理——三角形边长 比 对边角度的 sin值都相等,我们很容易就能列出方程
那么 AD 的长度就解出来了,是根据 beta 也就是根据 alpha 的方程。设 BC 长度为 p , AD 长度为 T(alpha)
那么 O->凸包上点 的长度就是 R - r + AD. 我们设为 T(alpha)
我懒了,用 mathmatics 求得T 的导数 dT(x) 为
那么我们很容易就表示出那个划线的点是 (Tcos(alpha) , Tsin(alpha))
于是乎
f() = T'cos() - T sin() 也就是 T 导数 乘以 cos 减去 T 乘以 sin
g() = T'sin + Tcos 也就是 T 导数 乘以 sin 加上 T 乘以 cos
那么对于一条线来说,我们的要积分的就可以做了。
有一点想通就好——对于每条线段我们要积分的是一个分段函数,而且相互独立!那么我们对于每条线单算一发就好了。
这个题目就这样愉快的结束了。
Code
namespace Geo{
#define typec double
const typec eps=1e-8;
int dblcmp(double d){
if (fabs(d)<eps)return 0;
return d>eps?1:-1;
}
int sgn(double a) {return a<-eps?-1:a>eps;}
inline double sqr(double x){return x*x;}
struct Point2D{
typec x,y;
Point2D(){}
Point2D(typec _x,typec _y):x(_x),y(_y){};
void input(){
RF(x , y);
}
void output(){
printf("%.2f %.2f\n",x,y);
}
bool operator==(Point2D a)const{
return dblcmp(a.x-x)==0&&dblcmp(a.y-y)==0;
}
bool operator<(Point2D a)const{
return dblcmp(a.x-x)==0?dblcmp(y-a.y)<0:x<a.x;
}
typec len(){
return hypot(x,y);
}
typec len2(){
return x*x+y*y;
}
Point2D operator + (const Point2D &A) const{
return Point2D(x + A.x , y + A.y);
}
Point2D operator - (const Point2D &A) const{
return Point2D(x - A.x , y - A.y);
}
Point2D operator * (const typec _x) const{
return Point2D(x * _x , y * _x);
}
typec operator * (const Point2D &A) const{
return x * A.x + y * A.y;
}
typec operator ^ (const Point2D &A) const{
return x * A.y - y * A.x;
}
Point2D operator / (const typec _p) const{
return Point2D(x / _p , y / _p);
}
typec distance(Point2D p){
return hypot(x-p.x,y-p.y);
}
Point2D add(Point2D p){
return Point2D(x+p.x,y+p.y);
}
Point2D sub(Point2D p){
return Point2D(x-p.x,y-p.y);
}
Point2D mul(typec b){
return Point2D(x*b,y*b);
}
Point2D div(typec b){
return Point2D(x/b,y/b);
}
typec dot(Point2D p){
return x*p.x+y*p.y;
}
typec det(Point2D p){
return x*p.y-y*p.x;
}
typec rad(Point2D a,Point2D b){
Point2D p=*this;
return fabs(atan2(fabs(a.sub(p).det(b.sub(p))),a.sub(p).dot(b.sub(p))));
}
Point2D trunc(typec r){
typec l=len();
if (!dblcmp(l))return *this;
r/=l;
return Point2D(x*r,y*r);
}
Point2D rotleft(){
return Point2D(-y,x);
}
Point2D rotright(){
return Point2D(y,-x);
}
Point2D rotate(Point2D p,typec angle)//èÆμãpÄæê±ÕëDy×aangle½Ç¶è
{
Point2D v=this->sub(p);
typec c=cos(angle),s=sin(angle);
return Point2D(p.x+v.x*c-v.y*s,p.y+v.x*s+v.y*c);
}
};
typec cross(Point2D a,Point2D b,Point2D c){
return (b.sub(a)).det(c.sub(a));
}
}using namespace Geo;
/* .................................................................................................................................. */
const int maxp = 100;
struct Polygon2D{
int n;
Point2D p[maxp];
void copy(Polygon2D & A){
A.n=n;
for (int i=0;i<n;++i){
A.p[i]=p[i];
}
}
void input()
{
for (int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
p[i].input();
}
}
struct cmp
{
Point2D p;
cmp(const Point2D &p0){p=p0;}
bool operator()(const Point2D &aa,const Point2D &bb)
{
Point2D a=aa,b=bb;
int d=dblcmp(a.sub(p).det(b.sub(p)));
if (d==0)
{
return dblcmp(a.distance(p)-b.distance(p))<0;
}
return d>0;
}
};
void norm()
{
Point2D mi=p[0];
for (int i=1;i<n;i++)mi=min(mi,p[i]);
sort(p,p+n,cmp(mi));
}
void getconvex(Polygon2D &convex)
{
int i,j,k;
sort(p,p+n);
convex.n=n;
for (i=0;i<min(n,2);i++)
{
convex.p[i]=p[i];
}
if (n<=2)return;
int &top=convex.n;
top=1;
for (i=2;i<n;i++)
{
while (top&&dblcmp(convex.p[top].sub(p[i]).det(convex.p[top-1].sub(p[i])))<=0)
top--;
convex.p[++top]=p[i];
}
int temp=top;
convex.p[++top]=p[n-2];
for (i=n-3;i>=0;i--)
{
while (top!=temp&& dblcmp(convex.p[top].sub(p[i]).det(convex.p[top-1].sub(p[i])))<=0)
top--;
convex.p[++top]=p[i];
}
}
};
double R , r , la , A , B , C , k;
double T(double x){
double fm = sin(k * x) / sin(C) + sin(A - k * x) / sin(B);
double ret = la / fm + R - r;
return ret;
}
double dT(double x){
double fz = la * sin(B) * sin(C) * (-k * sin(C) * cos(A - k * x) + k * sin(B) * cos(k * x));
double fm = sqr(sin(C) * sin(A - k * x) + sin(B) * sin(k * x));
return -fz / fm;
}
DB f0(DB x){ // Input the function
double dx = dT(x) * cos(x) - T(x) * sin(x);
double dy = dT(x) * sin(x) + T(x) * cos(x);
return sqrt(sqr(dx) + sqr(dy));
}
/* helper function of adaptive_simpsons */
DB adaptive_simpsons_aux(DB (*f)(DB), DB a, DB b,
DB eps, DB s, DB fa, DB fb, DB fc, int depth) {
DB c = (a + b) / 2, h = b - a;
DB d = (a + c) / 2, e = (c + b) / 2;
DB fd = f(d), fe = f(e);
DB sl = (fa + 4 * fd + fc) * h / 12;
DB sr = (fc + 4 * fe + fb) * h / 12;
DB s2 = sl + sr;
if (depth <= 0 || fabs(s2 - s) <= 15 * eps)
return s2 + (s2 - s) / 15;
return adaptive_simpsons_aux(f, a, c, eps / 2, sl, fa, fc, fd, depth - 1) +
adaptive_simpsons_aux(f, c, b, eps / 2, sr, fc, fb, fe, depth - 1);
}
/* Adaptive Simpson's Rule, integral of f at [a, b],
* max error of eps, max depth of depth */
DB adaptive_simpsons(DB (*f)(DB), DB a, DB b,
DB eps, int depth) {
DB c = (a + b) / 2, h = b - a;
DB fa = f(a), fb = f(b), fc = f(c);
DB s = (fa + 4 * fc + fb) * h / 6;
return adaptive_simpsons_aux(f, a, b, eps, s, fa, fb, fc, depth);
}
Polygon2D p , q;
void solve(){
k = R / r;
p.input();
p.getconvex(q);
double ans = 0;
q.norm();
for (int i = 0 ; i < q.n ; ++i){
int j = (i + 1) % q.n;
double t = atan2(q.p[j].y, q.p[j].x)- atan2(q.p[i].y , q.p[i].x);
if (dblcmp(t) < 0) t += PI * 2.;
la = (q.p[i] - q.p[j]).len();
double lb = q.p[j].len() , lc = q.p[i].len();
A = (sqr(lc) + sqr(lb) - sqr(la)) / 2. / lb / lc;
A = acos(A);
B = (sqr(lc) + sqr(la) - sqr(lb)) / 2. / la / lc;
B = acos(B);
C = (sqr(la) + sqr(lb) - sqr(lc)) / 2. / la / lb;
C = acos(C);
ans += adaptive_simpsons(f0 , 0 , t / k , eps , 20);
}
printf("%.3lf\n" , ans + eps);
}
int main(){
while(~scanf("%lf%lf%d", &R , &r , &p.n)) solve();
}