Exception Handling in Asp.net MVC
From :
http://www.codeproject.com/Articles/731913/Exception-Handling-in-MVC
Introduction
In this article we will discuss about Exception handling in MVC in detail. If you are completely new to MVC then please read day 1 from our MVC step by step article.
Initial setup for our lab
Before we go and start our step by step demo on exception handling lets create a sample demo.
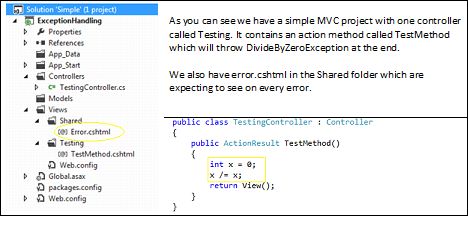
Local level Exception Handling
1. Simply Try…Catch approach
public ActionResult TestMethod() { try { //.... return View(); } catch (Exception e) { //Handle Exception; return View("Error"); } }
Limitation:
Problem with the above approach is we cannot reuse the exception handling logic across multiple action methods. That where our second approach comes to picture.2. Override OnException method in controller
protected override void OnException(ExceptionContext filterContext) { Exception e = filterContext.Exception; //Log Exception e filterContext.ExceptionHandled=true; filterContext.Result = new ViewResult() { ViewName = "Error" }; }
Advantage
Now we can share error handling logic across all the actions in a controllerLimitation:
Problem with the above approach is we cannot reuse the exception handling logic across multiple controllers. That where global error handling comes to picture.Global level Exception Handling
Step 1
In Web.Config simply enable custom error as follows and execute our application.
<customerrors mode="On" />Output
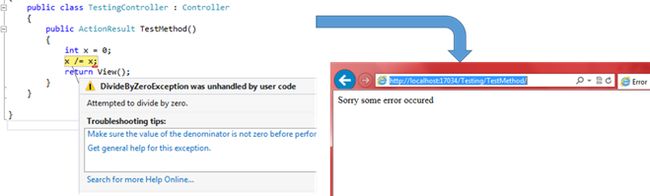
It seems that only step 1 done all the work, but how? We have not specified the error page (view) name anywhere, still in response we get error view whenever error occurs.
Let’s understand how?
FilterConfig class
public class FilterConfig { public static void RegisterGlobalFilters(GlobalFilterCollection filters) { filters.Add(new HandleErrorAttribute()); } }
As you can see HandleErrorAttrubute is added to global filter collection.
Where RegisterGlobalFilters method is invoked?
In Global.asax file in Applicaion_Start RegisterGlobalFilters method is invoked.

What it does?
It handles all the exceptions raised by all action methods in all the controllers and return error view present inside shared folder.
HandleError at controller level?
- Remove the code written in FilterConfig class
- Add HandleErrorAttribute to Controller class as follows,
Now errors raised by all action methods present inside TestingController method will be handled. Other exceptions will be considered as unhandled exceptions.
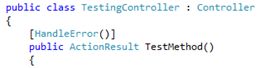
HandleError at Action level
Add HandleErrorAttribute to Action method as follows,
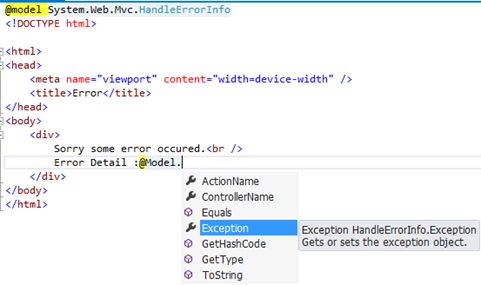
Displaying error detail in Error view
For that we will make our error view strongly typed view of model System.Web.Mvc.HandleErrorInfo and then as usual using @Model keyword we can access the members. One of the member is Exception object.
Different views for Different Exceptions
For that we will use overloaded version of HandleErrorAttribute constructor as follows.
Limitations of HandleErrorAttribute
- Error won’t get logged anywhere.
- Exceptions raised outside controllers will not be handled. Example- exception raised because of invalid url won’t be handled.
- Exception Handling based on scenario is not possible. Example – So one error page when request comes via ajax and different one when comes via normal request.
Extending HandleErrorAttribute
Some of the above limitations can be overcame by extending the default HandleErrorAttribute as follow.
private bool IsAjax(ExceptionContext filterContext) { return filterContext.HttpContext.Request.Headers["X-Requested-With"] == "XMLHttpRequest"; } public override void OnException(ExceptionContext filterContext) { if (filterContext.ExceptionHandled || !filterContext.HttpContext.IsCustomErrorEnabled) { return; } // if the request is AJAX return JSON else view. if (IsAjax(filterContext)) { //Because its a exception raised after ajax invocation //Lets return Json filterContext.Result = new JsonResult(){Data=filterContext.Exception.Message, JsonRequestBehavior=JsonRequestBehavior.AllowGet}; filterContext.ExceptionHandled = true; filterContext.HttpContext.Response.Clear(); } else { //Normal Exception //So let it handle by its default ways. base.OnException(filterContext); } // Write error logging code here if you wish. //if want to get different of the request //var currentController = (string)filterContext.RouteData.Values["controller"]; //var currentActionName = (string)filterContext.RouteData.Values["action"]; }
Advantages of extending Handle Error Attribute
- Now we can log errors.
- More control over exception handling. Now we have full control over exception handling code so we can simply check whether it’s an Ajax request or normal request and proceed accordingly.
“Resource cannot be found” Exception
This is the one which cannot be handled by neither HandleErroAttribute nor CustomHandleErrorAttribute.
But we can follow the traditional web.config approach as follows.
<customerrors mode="On"> <error statuscode="404" redirect="~/Testing/NoPageFound"> </error></customerrors>
How Global level HandleErrorAttribute is different from Application_Error?
Application_Error is an application level event, we define in the global.asax file. It will be executed whenever there is an unhandled exception in the application.
If this is the point, why we won’t use Application_Error always?
Here are the advantages of HandleError over Application_Error,
- With HandleErrorAttribute we get more control over exception handling. HandleError allow us to handle error differently for different controllers and actions easily where in Application_Error to get this feature we take the help of switch loop.
- Once you are into Application_Error you are out of MVC and you will lose ControllerContext and then we cannot do much things which will easily possible with HandleError.
Thanks for reading. Hope you have enjoyed reading this article. In case you are interested in any
technical training related to MVC, WCF, Design Patterns, WPF, Angular.js, TFS,UML or BI visit www.sukesh-Marla.comor contact [email protected]
See 600+ above FAQ questions and answers in .NET, C#, ASP.NET, SQL, WCF, WPF, WWF, SharePoint, Design patterns, UML etc.