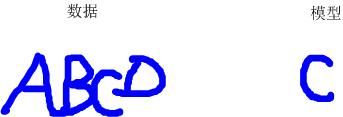ransac算法(随机抽样一致性)
对于运行不了几次,一次运行不了多久的方法,我们不需要考虑性能优化,对于那些需要经常运行几百次几千次的方法,我们头脑里还是要有性能这根弦。C#太优雅方便了,以至于很多人写程序时根本就把性能抛到脑后了,不愿意耗费心思去进行代码优化和算法优化,结果写出来的程序奇慢无比。不明真相的群众把这怪罪给C#语言。这不是C#的杯具,是程序员的无能。
2个月前,我研究sift(一种重要的图像分析算法)。最先找到了一个C#实现的library——libsift,这个library处理一张正常大小的图像,要耗时2-3分钟。后来,又找到一个C实现的library,处理同样的图像,耗时在1秒以内——秒杀。
昨天,我写Ransac(随机抽样一致性)算法代码时参考了libsift里的Ransac实现。不看不知道,一看吓一跳。那代码性能低下得无以复加。我随手优化了一下算法,就将随机抽样那部分的性能提高了上千倍。
下面详细道出。
一、Ransac
Ransac是用途很广泛的算法,详细介绍请看http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/RANSAC。下面简单介绍一下(没兴趣的可以略过不看)。
我们分析世界,需要对世界建模,把世界中的现象抽象成模型。每个模型,又存在一些参数,通过调节参数,可以得到不同的实例,进行推演。我们观察现象,得到一堆数据。如何为这堆数据找一个合适的模型,再确定合适的模型参数,这是很重要的问题,是人类理性的基础。
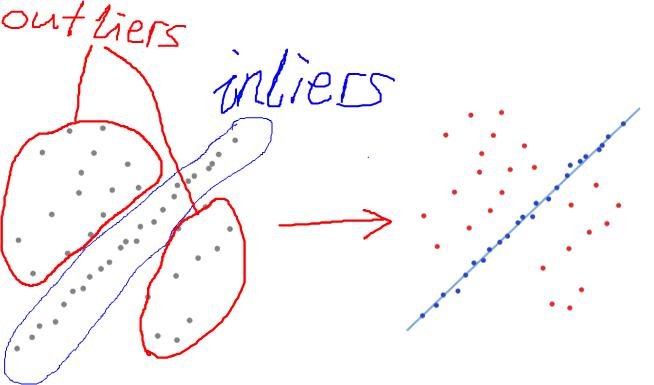
数据分两种:有效数据(inliers)和无效数据(outliers)。那些偏差不大的数据是有效数据,偏差大的数据是无效数据。
如果有效数据占大多数,无效数据只是很少量时,我们可以通过最小二乘法或类似的方法来确定模型的参数和误差。如果无效数据很多(比如,超过了50%的数据是无效数据),最小二乘法就失效了,我们需要新的算法。
上图左图是观察的数据。直觉可以看出,外面的散点是outliers,中间近似分布为一直线的是inliers。怎么设计一个算法,算出这条直线,使它对inliers的拟合度较高(如上图右图所示)?
再举一个更直观的例子:
上图左侧是一个验证码,我们将它看作“数据”。右侧是一个字符,我们将它看作“模型”,如何通过算法去除“数据”中的outlier,剩下inliner来和“模型”进行匹配
Ransac 是解决这类问题的代表性算法。它是一种随机算法,步骤如下:
输入:k,n,t,d,model,data
BestModel = null;
迭代k次——
(1) 从data中随机取出n个点,用这n个点去拟合model和模型的model,将得到的带参数的model记为MaybeBestModel。
(2) 依次取出剩下的点,计算该点对应MaybeBestModel模型的误差,如果这个误差小于阈值t,则认为这个点是有效的,把这个点也放进MaybeBestModel中。
(3) 所有点取完了。这时,MaybeBestModel中有效点的数量是否大于或等于d,如果是,则对于MaybeBestModel,重新计算一下它的模型参数。
(4) 评估一下MaybeBestModel和BestModel哪一个好?如果MaybeBestModel更好,则将MaybeBestModel 记做新的 BestModel。
二、libsift中Ransac算法的实现
Ransac算法中,model,model的拟合,不同参数model之间的比较都是因问题不同而不同,因此,可以将model抽象成接口。将model 抽象之后,Ransac 算法的骨干就只剩下一个随机采样的过程:
迭代k次——(1) 从data中随机抽取n个点,然后do something
(2) 依次取出剩下的点,然后do something
下面是libsift中Ransac算法的实现代码:
1 using System;
2 using System.Collections;
3
4 public class RANSAC
5 {
6 public interface IRANSACModel : ICloneable, IComparable
7 {
8 // Fit the model to the samples given. The number of samples is equal
9 // to or larger than the smallest number of points required for a fit
10 // ('n').
11 // Return true if the fit can be done, false otherwise.
12 bool FitModel (ArrayList points);
13
14 // Return the fitting error of a single point against the current
15 // model.
16 double FittingErrorSingle (object point);
17
18 // Threshhold the given fit error of a point.
19 // Return true if the fitting error is small enough and the point is
20 // fitting.
21 // Return false if the point is not fitting.
22 bool ThreshholdPoint (double fitError);
23
24 // The overall fitting error of all points in FittingGround. This
25 // value is calculated by averaging all individual fitting errors of
26 // the points in the FittingGround.
27 double FittingErrorSum {
28 get;
29 set;
30 }
31
32 // All the points used to fit. Has to be set explicitly.
33 ArrayList FittingGround {
34 get;
35 set;
36 }
37 }
38
39 // Smallest number of points to be able to fit the model.
40 private int n;
41
42 // The number of iterations required.
43 private int k;
44
45 private RANSAC ()
46 {
47 }
48
49 // n: Smallest number of points to be able to fit the model.
50 // k: The number of iterations required.
51 public RANSAC (int n, int k)
52 {
53 this.n = n;
54 this.k = k;
55 }
56
57 // ArrayList of Model's, sorted by summed fitting error.
58 // model: Model to fit
59 // points: List of point data to fit
60 // d: Number of nearby points required for a model to be accepted
61 public ArrayList FindModels (IRANSACModel model, ArrayList points, int d)
62 {
63 Random rand = new Random ();
64 ArrayList result = new ArrayList ();
65
66 if (points.Count < n)
67 throw (new ArgumentException
68 ("List of data is smaller than minimum fit requires."));
69
70 for (int ki = 0 ; ki < k ; ++ki) {
71 ArrayList samples = new ArrayList ();
72
73 // Build random samples
74 for (int ri = 0 ; ri < n ; ++ri) {
75 object sampleToAdd;
76 sampleToAdd = points[rand.Next (0, points.Count)];
77
78 if (samples.Contains (sampleToAdd))
79 continue;
80
81 samples.Add (sampleToAdd);
82 }
83
84 if (model.FitModel (samples) == false)
85 continue;
86
87 ArrayList good = new ArrayList ();
88 double overAllFittingError = 0.0;
89
90 // Check all non-sample points for fit.
91 foreach (object point in points) {
92 if (samples.Contains (point))
93 continue;
94
95 double fitError = model.FittingErrorSingle (point);
96 if (model.ThreshholdPoint (fitError)) {
97 good.Add (point);
98 overAllFittingError += fitError;
99 }
100 }
101
102 // good contains a list of all fitting points now. Check if there
103 // are more than d points near our model.
104 if (good.Count >= d) {
105 good.AddRange (samples);
106 IRANSACModel modelGood = (IRANSACModel) model.Clone ();
107
108 modelGood.FitModel (good);
109 modelGood.FittingErrorSum = overAllFittingError / good.Count;
110 modelGood.FittingGround = good;
111
112 result.Add (modelGood);
113 }
114 }
115 result.Sort ();
116 //Console.WriteLine ("got {0} modelfits", result.Count);
117
118 return (result);
119 }
120
121 // Calculate the expected number of draws required when a fraction of
122 // 'goodFraction' of the sample points is good and at least 'n' points are
123 // required to fit the model. Add 'sdM' times the standard deviation to be
124 // sure.
125 // n: > 0
126 // goodFraction: > 0.0 and <= 1.0
127 // sdM: >= 0
128 // return the guess for k, the expected number of draws.
129 public static int GetKFromGoodfraction (int n, double goodFraction, int sdM)
130 {
131 double result;
132
133 result = Math.Pow (goodFraction, -n);
134 if (sdM > 0)
135 result += sdM * Math.Sqrt (1.0 - Math.Pow (goodFraction, n));
136
137 return ((int) (result + 0.5));
138 }
139
140 // Test Main
141 public static void Main (string[] args)
142 {
143 Console.WriteLine ("n = 3, goodFraction = 0.3, sdM = 0: {0}",
144 GetKFromGoodfraction (3, 0.3, 0));
145 Console.WriteLine ("n = 3, goodFraction = 0.3, sdM = 10: {0}",
146 GetKFromGoodfraction (3, 0.3, 10));
147 }
148 }
149
150
不考虑Model部分,只考虑单次迭代过程中的随机抽样,可抽象出这样一个过程:
(1)假设数据集是points,它的类型是List<T>;(2)从points中随机选取n个对象,放入容器samples中;
(3)依次处理剩下的对象,根据处理结果决定放入samples或不放入samples
我把libsift的Ransac代码中上述逻辑部分单独提取出来了,并作了以下简化:
(1) 直接令points是List<int>类型1 public class CaseLibSift
2 {
3 Random rand = new Random ();
4
5 public List<int> RandomSample(List<int> points, int n)
6 {
7 List<int> samples = new List<int>();
8
9 // Build random samples
10 for (int ri = 0; ri < n; ++ri)
11 {
12 int sampleToAdd;
13 sampleToAdd = points[rand.Next(0, points.Count)];
14
15 if (samples.Contains(sampleToAdd))
16 continue;
17
18 samples.Add(sampleToAdd);
19 }
20
21 // Check all non-sample points for fit.
22 foreach (int point in points)
23 {
24 if (samples.Contains(point))
25 continue;
26 else
27 samples.Add(point);
28 }
29 return samples;
30 }
31 }
准备测试数据,进行性能测试:
<!--
Code highlighting produced by Actipro CodeHighlighter (freeware)
http://www.CodeHighlighter.com/
--> 1 static int loops;
2 static int dataLength;
3 static int n;
4
5 static List<int> data;
6
7 static RandomSampleCompareCase()
8 {
9 loops = 50;
10 dataLength = 10000;
11 n = 4000;
12 data = new List<int>(dataLength);
13 for (int i = 0; i < dataLength; i++)
14 data.Add(i);
15 }
16
17 public static void Test()
18 {
19 CaseLibSift c0 = new CaseLibSift();
20 CodeTimer.Time("CaseLibSift", loops, () => { c0.RandomSample(data, n); });
21 // CodeTimer.Time("MyCase", loops, () => { data.RandomSampleSplitOnSite(n); });
22 Console.Read();
23 }
这个测试中假设共有10000个数据,一共进行50次迭代,每次迭代的n值为4000。用老赵的CodeTimer测量运行时间,结果为:
CaseLibSiftTime Elapsed: 24,492ms
CPU Cycles: 44,426,562,664
Gen 0: 6
Gen 1: 0
Gen 2: 0
24.5秒!雷人的慢!
为什么会这样呢?主要问题出在这两句中:
if (samples.Contains(sampleToAdd))
if (samples.Contains(point))
您有更好的方案吗?
四、我的方案
再回顾一下问题:
(1)假设数据集是points,它的类型是List<T>;
(2)从points中随机选取n个对象,放入容器samples中;
(3)依次处理剩下的对象,根据处理结果决定放入samples或不放入samples
我采用的洗牌算法的变种。所谓洗牌问题,就是给定一个数组,编写程序将这个数组打乱。下面是一个经典的洗牌算法:
对于N个元素的数组
(1) 从N个元素中随机取出一个元素,与数组最后一个元素调换
(2) 从前N-1个元素中随机取出一个元素,与倒数第二个元素调换
(3) ……
将上述洗牌算法稍微改变一下,就得到本文问题的答案:
对于N个元素的数组
(1) 从N个元素中随机取出一个元素,与数组第一个元素调换
(2) 从后N-1个元素中随机取出一个元素,与第二个元素调换
……
(n) 从后N-(n-1)个元素中随机取出一个元素,与第n个元素调换
这样,前n个元素就是随机取出的元素了。再考虑这样一个问题,就是n>N/2的情况,这时,n>N-n。我们不需要随机取出n个元素,只需要取出N-n个元素即可,剩下n个元素便是我们想要的随机采样结果。
把整个算法写成了扩展方法,代码如下:
<!--
Code highlighting produced by Actipro CodeHighlighter (freeware)
http://www.CodeHighlighter.com/
--> 1 /// <summary>
2 /// 代表IList中的一段[Start,End)
3 /// </summary>
4 /// <typeparam name="T"></typeparam>
5 public struct ListSegment<T>
6 {
7 public IList<T> Data;
8 public int Start;
9 public int End;
10 }
11
12 ……
13
14 public static ListSegment<T> RandomSampleSplit<T>(this IList<T> data, int number)
15 {
16 IList<T> clone = new List<T>(data.Count);
17 clone.AddRange(data);
18 return clone.RandomSampleSplitOnSite(number);
19 }
20
21 public static ListSegment<T> RandomSampleSplitOnSite<T>(this IList<T> data, int number)
22 {
23 int count = data.Count;
24 if (number < 1 || number >= count) throw new ArgumentException("number 必须大于 0 并且小于data中的元素数量。");
25
26 int loops = number;
27
28 if (number > (count >> 1)) // number 太大
29 {
30 loops = count - number;
31
32 //从N个数中随机取出一个和最后一个元素交换,再从前面N-1个数中随机取一个和倒数第二个交换…
33 for (int i = 0; i < loops; i++)
34 {
35 int index0 = Random.Next(0, count - i);
36 int index1 = count - i - 1;
37 T tmp = data[index0];
38 data[index0] = data[index1];
39 data[index1] = tmp;
40 }
41 }
42 else
43 {
44 //从N个数中随机取出一个和第一个元素交换,再从后面N-1个数中随机取一个和第二个交换…
45 for (int i = 0; i < loops; i++)
46 {
47 int index0 = Random.Next(i, count);
48 int index1 = i;
49 T tmp = data[index0];
50 data[index0] = data[index1];
51 data[index1] = tmp;
52 }
53 }
54
55 ListSegment<T> seg = new ListSegment<T>();
56 seg.Start = 0;
57 seg.End = number;
58 seg.Data = data;
59 return seg;
60 }
同CaseLibSift对比性能:
<!--
Code highlighting produced by Actipro CodeHighlighter (freeware)
http://www.CodeHighlighter.com/
-->1 public static void Test()
2 {
3 CaseLibSift c0 = new CaseLibSift();
4 CodeTimer.Time("CaseLibSift", loops, () => { c0.RandomSample(data, n); });
5 CodeTimer.Time("MyCase", loops, () => { data.RandomSampleSplitOnSite(n); });
6 Console.Read();
7 }
结果为:
(1)datalenth=10000;n=1000;loops=100时的测试结果:
CaseLibSift
Time Elapsed: 43,750ms
CPU Cycles: 78,647,268,469
Gen 0: 12
Gen 1: 1
Gen 2: 0
MyCase
Time Elapsed: 20ms
CPU Cycles: 29,902,543
Gen 0: 0
Gen 1: 0
Gen 2: 0
(2)datalenth=10000;n=4000;loops=50时的测试结果:
CaseLibSift
Time Elapsed: 24,626ms
CPU Cycles: 44,217,626,002
Gen 0: 6
Gen 1: 1
Gen 2: 0
MyCase
Time Elapsed: 30ms
CPU Cycles: 48,109,204
Gen 0: 0
Gen 1: 0
Gen 2: 0
对比可见,性能提高了千倍。
下面是我的Ransac完整实现代码:
<!--
Code highlighting produced by Actipro CodeHighlighter (freeware)
http://www.CodeHighlighter.com/
--> 1 public interface IRansacModel : ICollection<Vector>, ICloneable
2 {
3 double Error { get; }
4 void Update();
5 bool FitPoint(Vector point);
6 /// <summary>
7 /// 比较IRansacModel的优劣。
8 /// </summary>
9 /// <param name="other"></param>
10 /// <returns></returns>
11 bool BestThan(IRansacModel other);
12 }
13
14 public abstract class RansacModelBase : List<Vector>, IRansacModel
15 {
16 public double Error { get; private set; }
17
18 public RansacModelBase():base()
19 { }
20
21 public RansacModelBase(int capacity):base(capacity)
22 { }
23
24 public abstract void Update();
25
26 public abstract bool FitPoint(Vector point);
27
28 protected void CloneBaseFrom(RansacModelBase other)
29 {
30 this.Error = other.Error;
31 this.Clear();
32 this.AddRange(other);
33 }
34
35 /// <summary>
36 /// 比较IRansacModel的优劣。
37 /// 默认情况下比较两者的 Error,Error 小则认为较优。
38 /// </summary>
39 /// <param name="other"></param>
40 /// <returns></returns>
41 public virtual bool BestThan(IRansacModel other)
42 {
43 return this.Error < other.Error;
44 }
45
46 #region ICloneable Members
47
48 public abstract object Clone();
49
50 #endregion
51
52 }
53
54 public class Ransac<TModel> where TModel : IRansacModel
55 {
56 private int m_minNumberFitted;
57 private TModel m_model;
58 private Random m_rand = new Random();
59 private int m_iteration;
60
61 private Ransac()
62 {
63 }
64
65 public Ransac(TModel model, int minNumberFitted, int iteration)
66 {
67 this.m_minNumberFitted = minNumberFitted;
68 this.m_iteration = iteration;
69 m_model = model;
70 }
71
72 public TModel Match(IList<Vector> points, int d)
73 {
74 if (points.Count < m_minNumberFitted) return default(TModel);
75
76 TModel bestModel = default(TModel);
77
78 for (int ki = 0; ki < m_iteration; ++ki)
79 {
80 TModel tmpModel = (TModel)this.m_model.Clone();
81
82 // 随机采样
83 ListSegment<Vector> v = points.RandomSampleSplitOnSite(m_minNumberFitted);
84
85 for (int i = v.Start; i < v.End; i++)
86 {
87 tmpModel.Add(points[i]);
88 }
89
90 tmpModel.Update();
91
92 IList<Vector> good = new List<Vector>();
93
94 // Check all non-sample points for fit.
95 for (int i = v.End; i < points.Count; i++)
96 {
97 Vector point = points[i];
98 if (tmpModel.FitPoint(point) == true) tmpModel.Add(point);
99 }
100
101 if (tmpModel.Count >= d)
102 {
103 tmpModel.Update();
104 if (bestModel == null) bestModel = tmpModel;
105 else if (tmpModel.BestThan(bestModel)) bestModel = tmpModel;
106 }
107 }
108 return (bestModel);
109 }
110 }