Nmap源码分析(脚本引擎)
Nmap源码分析(脚本引擎)
2012年9月6日
Nmap提供了强大的脚本引擎(NSE),以支持通过Lua编程来扩展Nmap的功能。目前脚本库已经包含300多个常用的Lua脚本,辅助完成Nmap的主机发现、端口扫描、服务侦测、操作系统侦测四个基本功能,并补充了其他扫描能力:如执行HTTP服务详细的探测、暴力破解简单密码、检查常见的漏洞信息等等。如果用户需要对特定的应用做更深入的探究,可以按照NSE脚本格式编写Lua脚本来增强Nmap的扫描能力。
1 简单引入
1.1 实现原理
NSE(Nmap Scripting Engine)是Nmap最为强大、最为灵活的功能之一。
NSE主要分为两大部分:内嵌Lua解释器与NSE library。
解释器:Nmap采用嵌入的Lua解释器来支持Lua脚本语言。Lua语言小巧简单而且扩展灵活,能够很好地与Nmap自身的C/C++语言融合。
NSE library:为Lua脚本与Nmap提供了连接,负责完成基本初始化及提供脚本调度、并发执行、IO框架及异常处理,并且提供了默认的实用的脚本程序。
1.2 脚本分类
NSE中提供的Lua脚本分为不同的类别(Category),目前的类别如下:
- auth 负责处理鉴权证书(绕开鉴权)的脚本
- broadcast 在局域网内探查更多服务开启状况,如dhcp/dns/sqlserver等服务。
- brute 提供暴力破解方式,针对常见的应用如http/snmp等
- default 这是使用-sC或-A选项扫描时候默认的脚本,提供基本脚本扫描能力
- discovery 对网络进行更多的信息,如SMB枚举、SNMP查询等
- dos 用于进行拒绝服务攻击(denial of service)
- exploit 利用已知的漏洞入侵系统
- external 利用第三方的数据库或资源,例如进行whois解析
- fuzzer 模糊测试的脚本,发送异常的包到目标机,探测出潜在漏洞
- intrusive 入侵性的脚本,此类脚本可能引发对方的IDS/IPS的记录或屏蔽
- malware 探测目标机是否感染了病毒、开启了后门等信息
- safe 此类与intrusive相反,属于安全性脚本
- version 负责增强服务与版本扫描(Version Detection)功能的脚本。
- vuln 负责检查目标机是否有常见的漏洞(Vulnerability),如是否有MS08_067。
1.3 命令行选项
Nmap提供的命令行参数如下:
-sC: 等价于--script=default,使用默认类别的脚本进行扫描。 --script=<Lua scripts>: <Lua scripts>使用某个或某类脚本进行扫描,支持通配符描述 --script-args=<n1=v1,[n2=v2,...]>: 为脚本提供默认参数 --script-args-file=filename: 使用文件来为脚本提供参数 --script-trace: 显示脚本执行过程中发送与接收的数据 --script-updatedb: 更新脚本数据库 --script-help=<Lua scripts>: 显示脚本的帮助信息,其中<Lua scripts>部分可以逗号分隔的文件或脚本类别。
2 实现框架
2.1 文件组织
Nmap脚本引擎所需要的的文件:
- nse_main.cc/nse_main.h/nse_main.lua,这是核心流程文件,负责脚本的初始化与调度执行。
- nmap/nse_*文件,nmap源码目录下以nse开头的文件,负责为NSE提供调用库,例如提供dnet、nsock、ssl、pcrelib、fs、bit等操作的库函数。
- liblua目录,提供Lua语言默认的源码C语言文件(提供Lua库函数与解释器相关代码)
- nselib目录,Nmap实现的NSE库文件,以Lua语言形式提供基本的库函数
- scripts目录,Nmap内置的实用脚本,即对具体扫描任务相关的操作脚本。Nmap目前支持300多个脚本(14个类别)。
2.2 代码流程
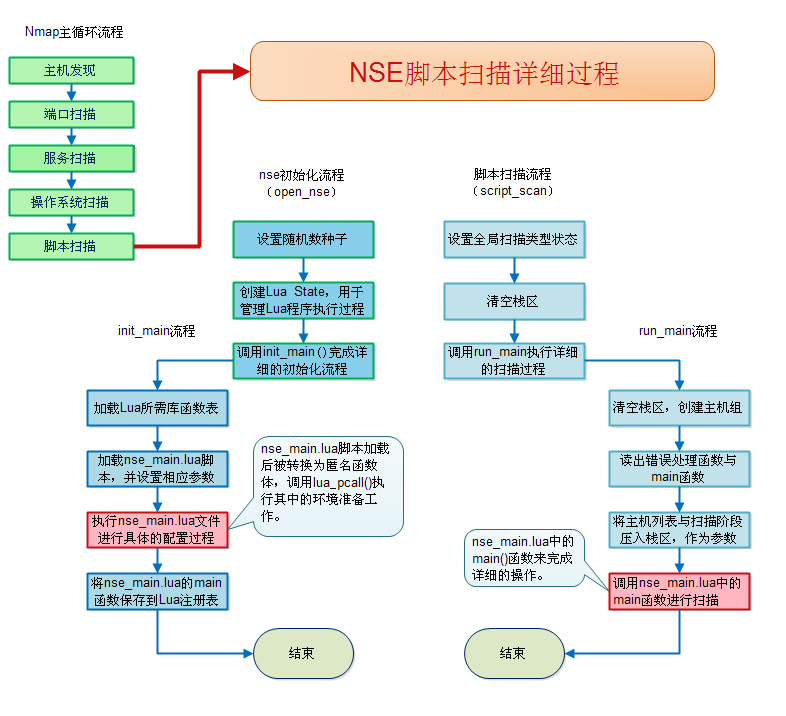
2.2.1代码流程图
2.2.2流程解析
初始化流程
在命令行参数中指定脚本(--script/-sC)或指定-A选项或指定-sV选项,都会触发Nmap启动脚本引擎。其中-A选项表示aggressive scan,会调用default类别的脚本扫描;而-sV选项表示应用与版本侦测,会调用Version类别的脚本,辅助侦测服务详细信息。
在Nmap.cc的nmap_main()函数中,若判断到需要启动脚本引擎,那么调用open_nse()函数进行NSE环境的准备。在open_nse()中主要创建luaState(管理Lua解释器的执行的全局变量),然后调用init_main()进行详细的初始化过程。
进入init_main()函数,首先加载Lua标准库与Nmap的扩展库,随后准备参数环境,然后加载并执行nse_main.lua文件。
nse_main.lua脚本为后续的脚本执行准备Lua环境,加载用户选择的需要调用的脚本(例如,用户--script discovery,那么会将该类别中所有的脚本加载进来),返回一个main()函数对象给init_main(),该main()是否后续脚本扫描需要的主函数,被保存在Lua的环境的注册表中。
在nse_main.lua中,定义两个核心的类,Script和Thread,Script用于管理NSE脚本,当新的脚本被加载时,调用Script.new创建脚本对象,该对象被保存下来在后续的扫描过程中使用;Thread用于管理脚本的执行,该类中也包含对脚本健全性的检查(sanity check,如是否包含Action函数)。在脚本执行时,如果脚本之间存在依赖关系,那么会将基础的无依赖的脚本统一执行完毕,再执行依赖性的脚本。
脚本扫描流程
执行脚本扫描时,从nmap_main()中调用script_scan()函数。
在进入script_scan()后,会标记扫描阶段类型,然后进入到初始化阶段返回的main()函数(来自nse_main.lua脚本中的main)中,在函数中解析具体的扫描类型。
main()函数负责处理三种类型的脚本扫描:预扫描(SCRIPT_PRE_SCAN)、脚本扫描(SCRIPT_SCAN)、后扫描(SCRIPT_POST_SCAN)。预扫描即在Nmap调用的最前面(没有进行主机发现、端口扫描等操作)执行的脚本扫描,通常该类扫描用于准备基本的信息,例如到第三服务器查询相关的DNS信息。而脚本扫描,是使用NSE脚本来扫描目标主机,这是最核心的扫描方式。后扫描,是整个扫描结束后,做一些善后处理的脚本,比如优化整理某些扫描。
在NSE脚本中都会定义触发规则(rule),确定在什么阶段什么条件执行该脚本。NSE共有4中规则,prerule(),如果脚本定义该规则,则在预扫描阶段该脚本会被执行;hostrule(host)该规则在检测到主机在线时候才执行;port(host,port),检测主机某个端口开放时才执行,通常用于侦查特定的服务类型;postrule(),在所有主机都被扫描完毕后执行。
在main()函数中核心操作由run函数负责。而run()函数的本身设计用于执行所有同一级别的脚本(根据依赖关系划分的级别),直到所有线程执行完毕才退出。
run()函数中实现三个队列:执行队列(Running Queue)、等待队列(Waiting Queue)、挂起队列(Pending Queue),并管理三个队列中线程的切换,直到全部队列为空或出错而退出。
3 源码分析
///L_NSE用于保存Lua程序的状态
static lua_State *L_NSE = NULL;
///open_nse用于创建Lua状态,准备Lua解释器环境
///调用init_main()完成初始化操作。
void open_nse (void)
{
if (L_NSE == NULL) ///全局维护一份Lua状态
{
/*
Set the random seed value on behalf of scripts. Since Lua uses the
C rand and srand functions, which have a static seed for the entire
program, we don't want scripts doing this themselves.
*/
srand(get_random_uint());
///创建Lua状态机,用于管理整个Lua程序的执行
if ((L_NSE = luaL_newstate()) == NULL)
fatal("%s: failed to open a Lua state!", SCRIPT_ENGINE);
lua_atpanic(L_NSE, panic); ///注册发生严重故障的回调函数为panic函数
#if 0
/* Lua 5.2 */
lua_pushcfunction(L_NSE, init_main);
lua_pushlightuserdata(L_NSE, &o.chosenScripts);
if (lua_pcall(L_NSE, 1, 0, 0))
#else
///此处lua_cpcall()以保护模式执行C语言函数init_main()
if (lua_cpcall(L_NSE, init_main, &o.chosenScripts))
#endif
fatal("%s: failed to initialize the script engine:\n%s\n", SCRIPT_ENGINE,
lua_tostring(L_NSE, -1));
}
}
///scipt_scan函数具体执行脚本扫描的过程
///设置扫描状态;调用run_main()函数执行具体脚本扫描过程。
void script_scan (std::vector<Target *> &targets, stype scantype)
{
///设置全局的扫描状态为此处状态(可能是SCRIPT_PRE_SCAN/SCRIPT_SCAN/SCRIPT_POST_SCAN)
o.current_scantype = scantype;
///断言L_NSE非空,并清空栈区(C与Lua调用交互过程均会在栈内完成)
assert(L_NSE != NULL);
lua_settop(L_NSE, 0); /* clear the stack */
#if 0
/* Lua 5.2 */
lua_pushcfunction(L_NSE, run_main);
lua_pushlightuserdata(L_NSE, &targets);
if (lua_pcall(L_NSE, 1, 0, 0))
#else
///此处lua_cpcall()以保护模式执行C语言函数run_main()
if (lua_cpcall(L_NSE, run_main, &targets))
#endif
error("%s: Script Engine Scan Aborted.\nAn error was thrown by the "
"engine: %s", SCRIPT_ENGINE, lua_tostring(L_NSE, -1));
}
void close_nse (void)
{
///关闭Lua状态
if (L_NSE != NULL)
{
lua_close(L_NSE);
L_NSE = NULL;
}
}
static int init_main (lua_State *L)
{
char path[MAXPATHLEN];
std::vector<std::string> *rules = (std::vector<std::string> *)
lua_touserdata(L, 1);
/* Load some basic libraries */
luaL_openlibs(L); ///加载Lua自身的库
set_nmap_libraries(L); ///加载Nmap扩展的Lua库
lua_newtable(L);
lua_setfield(L, LUA_REGISTRYINDEX, NSE_CURRENT_HOSTS);
/* Load debug.traceback for collecting any error tracebacks */
lua_settop(L, 0); /* clear the stack */
lua_getglobal(L, "debug");
lua_getfield(L, -1, "traceback");
lua_replace(L, 1); // debug.traceback stack position 1
lua_pushvalue(L, 1);
lua_setfield(L, LUA_REGISTRYINDEX, NSE_TRACEBACK); /* save copy */
/* Load main Lua code, stack position 2 */
///将nse_main.lua文件加载进来,文件被转换为匿名函数(栈索引为2),后续调用lua_pcall()执行它。
if (nmap_fetchfile(path, sizeof(path), "nse_main.lua") != 1)
luaL_error(L, "could not locate nse_main.lua");
if (luaL_loadfile(L, path) != 0)
luaL_error(L, "could not load nse_main.lua: %s", lua_tostring(L, -1));
/* The first argument to the NSE Main Lua code is the private nse
* library table which exposes certain necessary C functions to
* the Lua engine.
*/
///加载提供给nse_main.lua调用的C语言函数表(栈索引为3)
open_cnse(L); // stack index 3
/* The second argument is the script rules, including the
* files/directories/categories passed as the userdata to this function.
*/
///将脚本规则作为参数压入栈区(栈索引为4)
lua_createtable(L, rules->size(), 0); // stack index 4
for (std::vector<std::string>::iterator si = rules->begin();
si != rules->end(); si++)
{
lua_pushstring(L, si->c_str());
lua_rawseti(L, 4, lua_objlen(L, 4) + 1);
}
/* Get Lua main function */
///调用由nse_main.lua转换后的匿名函数(栈索引2):
///传入2个参数(栈索引3/4),输出1个结果(执行完毕后放在栈顶),
///错误处理函数对应的栈区索引为1(即debug.traceback)。
///功能:在nse_main.lua会加载用户选择的所有的脚本,并初始化Script/Thread类
if (lua_pcall(L, 2, 1, 1) != 0) lua_error(L); /* we wanted a traceback */
///将执行nse_main.lua返回的结果(nse_main.lua中的main函数对象)放入注册表中,
///以便后续的脚本扫描过程直接调用此main函数。
lua_setfield(L, LUA_REGISTRYINDEX, NSE_MAIN);
return 0;
}
static int run_main (lua_State *L)
{
std::vector<Target *> *targets = (std::vector<Target*> *)
lua_touserdata(L, 1);
lua_settop(L, 0); ///清空栈区
/* New host group */
lua_newtable(L); ///清空当前主机组
lua_setfield(L, LUA_REGISTRYINDEX, NSE_CURRENT_HOSTS);
///读出error traceback函数
lua_getfield(L, LUA_REGISTRYINDEX, NSE_TRACEBACK); /* index 1 */
///获取nse_main.lua中的main()函数
lua_getfield(L, LUA_REGISTRYINDEX, NSE_MAIN); /* index 2 */
assert(lua_isfunction(L, -1)); ///若不是函数,那此处必然有错
/* The first and only argument to main is the list of targets.
* This has all the target names, 1-N, in a list.
*/
///main (hosts, scantype)
///main函数需要两个参数,被扫描的主机组与扫描类型(PRE/SCRIPT/POST)
///以下代码将逐次加入等待扫描主机到NSE_CURRENT_HOSTS表中
lua_createtable(L, targets->size(), 0); // stack index 3
lua_getfield(L, LUA_REGISTRYINDEX, NSE_CURRENT_HOSTS); /* index 4 */
for (std::vector<Target *>::iterator ti = targets->begin();
ti != targets->end(); ti++)
{
Target *target = (Target *) *ti;
const char *TargetName = target->TargetName();
const char *targetipstr = target->targetipstr();
lua_newtable(L);
set_hostinfo(L, target);
lua_rawseti(L, 3, lua_objlen(L, 3) + 1);
if (TargetName != NULL && strcmp(TargetName, "") != 0)
lua_pushstring(L, TargetName);
else
lua_pushstring(L, targetipstr);
lua_pushlightuserdata(L, target);
lua_rawset(L, 4); /* add to NSE_CURRENT_HOSTS */
}
lua_pop(L, 1); /* pop NSE_CURRENT_HOSTS */
///设置main()第二个参数,扫描类型
/* push script scan type phase */
switch (o.current_scantype)
{
case SCRIPT_PRE_SCAN:
lua_pushstring(L, NSE_PRE_SCAN);
break;
case SCRIPT_SCAN:
lua_pushstring(L, NSE_SCAN);
break;
case SCRIPT_POST_SCAN:
lua_pushstring(L, NSE_POST_SCAN);
break;
default:
fatal("%s: failed to set the script scan phase.\n", SCRIPT_ENGINE);
}
///以保护模式运行main()函数,两个参数,0个返回值,错误处理函数在栈区的index1位置
if (lua_pcall(L, 2, 0, 1) != 0) lua_error(L); /* we wanted a traceback */
return 0;
}