SVD Recommendataion System
(1) 这里,将对SVD如何应用在推荐系统中,进行详尽的描述。
引用一段对SVD的英文描述:
SVD methods are a direct consequence of a theorem in linear algebra:
Any MxN matrix A whose number of rows M is greater than or equal to its number of columns N, can be written as the product of an MxM column-orthogonal matrix U, and MxN diagonal matrix S with positive or zero elements (singular values), and the transpose of an NxN orthogonal matrix V.
降维处理的时候,如我们需要降维到k维,这时候,就可以取U矩阵前K列元素,S的前K*K子矩阵,
矩阵VT的前K行元素。
(2) SVD在推荐系统中表现。设定一个用户矩阵M,M 矩阵的每一列代表一个用户,每一行代表一个物品(实验中我们采用用户对 a Family Guy season的平分)。下面的一个图表表示的就是推荐所使用的用户矩阵。
上面的用户矩阵M:6*4. 使用SVD对M进行分解的时候,可以得到3个部分:U(6*6),S(6*4),VT(4*4)。降维处理的时候,我们把M映射到二维空间。
在二维空间里,可以画出物品,用户位置图,在图中,我们可以方便的看到,物品之间,用户之间的相近程度。下面,我们绘制的二维图:
其中X轴,Y轴的描述如下:对用物品的坐标,可以从矩阵U中得到,U 矩阵第一列表示X轴坐标,第二列表示Y轴坐标;比如U矩阵的第一行表示season1的坐标(-0.4472,0.5373); 对于用户的坐标,通过矩阵V得到,同样V 矩阵第一列表示X轴坐标,第二列表示Y轴坐标,比如用户Ben的坐标(-0.5710,0.2228). 从图表中看到:Ben与Fried很近的,s6和s5很近的。(3)寻找相似用户。
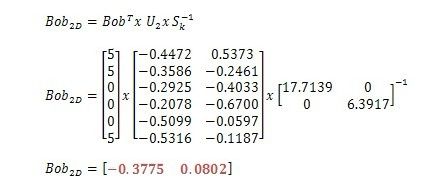
假设用户Bob对season1-6的评分如下:[5,5,0,0,0,5] 。我们如何查找和Bob相似的用户?首先,要做的就是把Bob的评分向量映射到二维空间。
计算公式如下:
得到Bob的二维映射向量Bob2d后,我们就可以计算Bob与每个用户的相似度,一般采用Cosin 相似度方法,实验中,我们把相似度低于0.9的用户滤除。
最后于Bob最近的用户是Ben(0.987),Fred(0.955)。
我们采用把最相近的用户Ben对物品season1-6的评分来代表Bob没评分项。如Bob对season5的评分将会是5,对season3的评分将会是3.(这里最终的评分有待考虑,是否加权处理会更好?比如season4 ,Ben也没评分,这时候,如何处理呢?)
下面贴上,我们实验过程中代码(采用Python语言撰写):
# SVD Recomendation
# file_name: svd_recommendation_test.py
#!/usr/bin/python
from numpy import *
from numpy.linalg.linalg import *
users = ["Ben","Tom", "John", "Fred" ]
m = matrix([
#Ben, Tom, John, Fred
[5,5,0,5], # season 1
[5,0,3,4], # season 2
[3,4,0,3], # season 3
[0,0,5,3], # season 4
[5,4,4,5], # season 5
[5,4,5,5] # season 6
])
# Compute the SVD Decomposition
u, s, vt = svd(m)
vt = transpose (vt)
#print u
#print s
#print vt
# Take the 2-rank approximation of the Matrix
# - Take first and second columns of u (6x2)
# - Take first and second columns of vt (4x2)
# - Take the first two eigen-values (2x2)
u2 = u[:,0:2]
v2 = vt[:,0:2]
eig2 = matrix([[s[0],0],[0,s[1]]])
# Here comes Bob, our new user
bob = matrix([[5,5,0,0,0,5]])
bobEmbed = bob * u2 * inv(eig2)
# Compute the cosine similarity between Bob and every other User in our 2-D space
user_sim = []
count = 1
for i in range(shape(v2)[0]):
x=v2[i,:]
user_sim.append((bobEmbed *transpose(x)/ (norm(x) * norm(bobEmbed)), i) )
# Remove all users who fall below the 0.90 cosine similarity cutoff and sort by similarity
user_sim = filter(lambda x: x[0]>0.9,user_sim)
# user_sim = [item for item in user_sim if item[0] >= 0.9]
user_sim.sort()
user_sim.reverse()
for i in range(len(user_sim)):
print '%s (ID: %d, Similarity: %0.3f) \n' %(users[i], user_sim[i][1], user_sim[i][0])
# We'll use a simple strategy in this case:
# 1) Select the most similar user
# 2) Compare all items rated by this user against your own and select items that you have not yet rated
# 3) Return the ratings for items I have not yet seen, but the most similar user has rated
similarUsersItems = m[:,user_sim[0][1]]
myItems = transpose(bob)
not_seen_yet = []
for i in range(shape(myItems)[0]):
if myItems[i] == 0 and similarUsersItems[i] != 0:
not_seen_yet.append((similarUsersItems[i],i))
print '\n %s recommends: \n' %users[user_sim[0][1]]
not_seen_yet.sort()
not_seen_yet.reverse()
for i in range(len(not_seen_yet)):
print '\tSeason %d .. I gave it a rating of %d \n' %(not_seen_yet[i][1]+1,not_seen_yet[i][0])
if len(not_seen_yet)== 0:
print "We've seen all the same seasons, bugger!"
程序运行结果:
参考文献:
【1】http://www.igvita.com/2007/01/15/svd-recommendation-system-in-ruby/
【2】http://www.slideshare.net/bmabey/svd-and-the-netflix-dataset-presentation
【3】http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Collaborative_filtering
【4】http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Singular_value_decomposition