跳跃表
本文将总结一种数据结构:跳跃表。前半部分跳跃表性质和操作的介绍直接摘自《让算法的效率跳起来--浅谈“跳跃表”的相关操作及其应用》上海市华东师范大学第二附属中学 魏冉。之后将附上跳跃表的源代码,以及本人对其的了解。难免有错误之处,希望指正,共同进步。谢谢。
跳跃表(Skip List)是1987年才诞生的一种崭新的数据结构,它在进行查找、插入、删除等操作时的期望时间复杂度均为O(logn),有着近乎替代平衡树的本领。而且最重要的一点,就是它的编程复杂度较同类的AVL树,红黑树等要低得多,这使得其无论是在理解还是在推广性上,都有着十分明显的优势。
首先,我们来看一下跳跃表的结构
跳跃表由多条链构成(S0,S1,S2 ……,Sh),且满足如下三个条件:
每条链必须包含两个特殊元素:+∞ 和 -∞(其实不需要)
S0包含所有的元素,并且所有链中的元素按照升序排列。
每条链中的元素集合必须包含于序数较小的链的元素集合。
操作
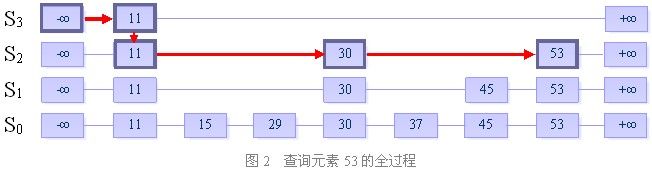
一、查找
目的:在跳跃表中查找一个元素x
在跳跃表中查找一个元素x,按照如下几个步骤进行:
1. 从最上层的链(Sh)的开头开始
2. 假设当前位置为p,它向右指向的节点为q(p与q不一定相邻),且q的值为y。将y与x作比较
(1) x=y 输出查询成功及相关信息
(2) x>y 从p向右移动到q的位置
(3) x<y 从p向下移动一格
3. 如果当前位置在最底层的链中(S0),且还要往下移动的话,则输出查询失败
二、插入
目的:向跳跃表中插入一个元素x
首先明确,向跳跃表中插入一个元素,相当于在表中插入一列从S0中某一位置出发向上的连续一段元素。有两个参数需要确定,即插入列的位置以及它的“高度”。
关于插入的位置,我们先利用跳跃表的查找功能,找到比x小的最大的数y。根据跳跃表中所有链均是递增序列的原则,x必然就插在y的后面。
而插入列的“高度”较前者来说显得更加重要,也更加难以确定。由于它的不确定性,使得不同的决策可能会导致截然不同的算法效率。为了使插入数据之后,保持该数据结构进行各种操作均为O(logn)复杂度的性质,我们引入随机化算法(Randomized Algorithms)。
我们定义一个随机决策模块,它的大致内容如下:
产生一个0到1的随机数r r ← random()
如果r小于一个常数p,则执行方案A, if r<p then do A
否则,执行方案B else do B
初始时列高为1。插入元素时,不停地执行随机决策模块。如果要求执行的是A操作,则将列的高度加1,并且继续反复执行随机决策模块。直到第i次,模块要求执行的是B操作,我们结束决策,并向跳跃表中插入一个高度为i的列。
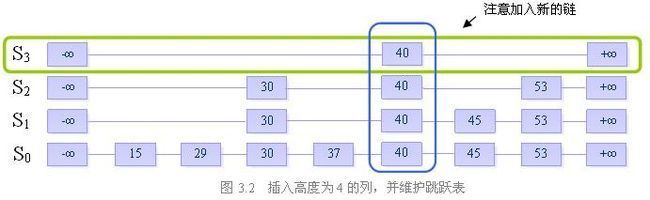
我们来看一个例子:
假设当前我们要插入元素“40”,且在执行了随机决策模块后得到高度为4
步骤一:找到表中比40小的最大的数,确定插入位置
步骤二:插入高度为4的列,并维护跳跃表的结构
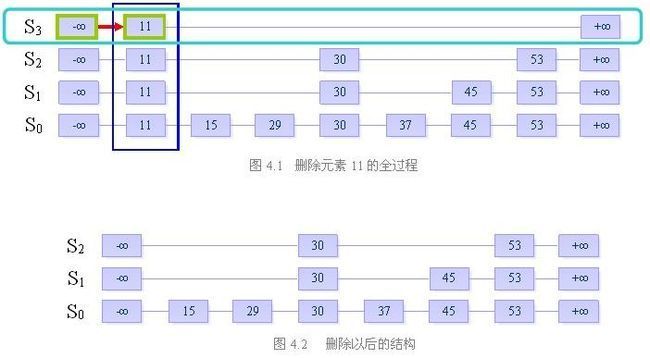
三、删除
目的:从跳跃表中删除一个元素x
删除操作分为以下三个步骤:
在跳跃表中查找到这个元素的位置,如果未找到,则退出
将该元素所在整列从表中删除
将多余的“空链”删除
我们来看一下跳跃表的相关复杂度:
空间复杂度: O(n) (期望)
跳跃表高度: O(logn) (期望)
相关操作的时间复杂度:
查找: O(logn) (期望)
插入: O(logn) (期望)
删除: O(logn) (期望)
之所以在每一项后面都加一个“期望”,是因为跳跃表的复杂度分析是基于概率论的。有可能会产生最坏情况,不过这种概率极其微小。
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
以下是自己学习时碰到的一些问题
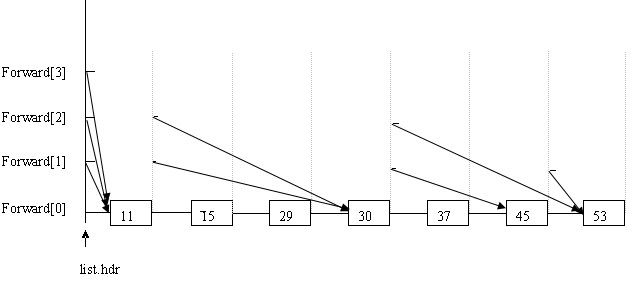
首先分配一个链表,用list.hdr指向,长度为跳跃表规定的最高层,说是链表,在以下代码中只是分配了一段连续的空间,用来指向每一层的开始位置。我们看到结构体nodeType中,有一个key,一个rec(用户数据),还有一个指向结构体的指针数组。
一开始的那些图容易给人误解。如上图所示,例如每个节点的forward[2],就认为是跳跃表的第3层。List.hdr的forward[2]指向11,11的forward[2]指向30,30的forward[2]指向53。这就是跳跃表的第3层:11---30-----53。(准确的说每个forward都指向新节点,新节点的同层forward又指向另一个节点,从而构成一个链表,而数据只有一个,并不是像开始途中所画的那样有N个副本)。本人天资愚钝,看了挺长时间才把它在内存里的结构看清楚了,呵呵。
以下是在网上搜到的一个实现代码
代码中主要注释了insert函数,剩下的两个函数差不多,就不一一注释了
#include < stdio.h >
#include < stdlib.h >
/* implementation dependent declarations */
typedef enum {
STATUS_OK,
STATUS_MEM_EXHAUSTED,
STATUS_DUPLICATE_KEY,
STATUS_KEY_NOT_FOUND
} statusEnum;
typedef int keyType; /* type of key */
/* user data stored in tree */
typedef struct {
int stuff; /* optional related data */
} recType;
#define compLT(a,b) (a < b)
#define compEQ(a,b) (a == b)
/* levels range from (0 .. MAXLEVEL) */
#define MAXLEVEL 15
typedef struct nodeTag {
keyType key; /* key used for searching */
recType rec; /* user data */
struct nodeTag * forward[ 1 ]; /* skip list forward pointer */
} nodeType;
/* implementation independent declarations */
typedef struct {
nodeType * hdr; /* list Header */
int listLevel; /* current level of list */
} SkipList;
SkipList list; /* skip list information */
#define NIL list.hdr
static int count = 0 ;
statusEnum insert(keyType key, recType * rec) {
int i, newLevel;
nodeType * update[MAXLEVEL + 1 ];
nodeType * x;
count ++ ;
/* **********************************************
* allocate node for data and insert in list *
********************************************** */
/* find where key belongs */
/* 从高层一直向下寻找,直到这层指针为NIL,也就是说
后面没有数据了,到头了,并且这个值不再小于要插入的值。
记录这个位置,留着向其后面插入数据 */
x = list.hdr;
for (i = list.listLevel; i >= 0 ; i -- ) {
while (x -> forward[i] != NIL
&& compLT(x -> forward[i] -> key, key))
x = x -> forward[i];
update[i] = x;
}
/* 现在让X指向第0层的X的后一个节点 */
x = x -> forward[ 0 ];
/* 如果相等就不用插入了 */
if (x != NIL && compEQ(x -> key, key))
return STATUS_DUPLICATE_KEY;
/* 随机的计算要插入的值的最高level */
for (
newLevel = 0 ;
rand() < RAND_MAX / 2 && newLevel < MAXLEVEL;
newLevel ++ );
/* 如果大于当前的level,则更新update数组并更新当前level */
if (newLevel > list.listLevel) {
for (i = list.listLevel + 1 ; i <= newLevel; i ++ )
update[i] = NIL;
list.listLevel = newLevel;
}
/* 给新节点分配空间,分配newLevel个指针,则这个
节点的高度就固定了,只有newLevel。更高的层次将
不会再有这个值 */
if ((x = malloc( sizeof (nodeType) + newLevel * sizeof (nodeType * ))) == 0 )
return STATUS_MEM_EXHAUSTED;
x -> key = key;
x -> rec = * rec;
/* 给每层都加上这个值,相当于往链表中插入一个数 */
for (i = 0 ; i <= newLevel; i ++ ) {
x -> forward[i] = update[i] -> forward[i];
update[i] -> forward[i] = x;
}
return STATUS_OK;
}
statusEnum delete(keyType key) {
int i;
nodeType * update[MAXLEVEL + 1 ], * x;
/* ******************************************
* delete node containing data from list *
****************************************** */
/* find where data belongs */
x = list.hdr;
for (i = list.listLevel; i >= 0 ; i -- ) {
while (x -> forward[i] != NIL
&& compLT(x -> forward[i] -> key, key))
x = x -> forward[i];
update[i] = x;
}
x = x -> forward[ 0 ];
if (x == NIL || ! compEQ(x -> key, key)) return STATUS_KEY_NOT_FOUND;
/* adjust forward pointers */
for (i = 0 ; i <= list.listLevel; i ++ ) {
if (update[i] -> forward[i] != x) break ;
update[i] -> forward[i] = x -> forward[i];
}
free (x);
/* adjust header level */
while ((list.listLevel > 0 )
&& (list.hdr -> forward[list.listLevel] == NIL))
list.listLevel -- ;
return STATUS_OK;
}
statusEnum find(keyType key, recType * rec) {
int i;
nodeType * x = list.hdr;
/* ******************************
* find node containing data *
****************************** */
for (i = list.listLevel; i >= 0 ; i -- ) {
while (x -> forward[i] != NIL
&& compLT(x -> forward[i] -> key, key))
x = x -> forward[i];
}
x = x -> forward[ 0 ];
if (x != NIL && compEQ(x -> key, key)) {
* rec = x -> rec;
return STATUS_OK;
}
return STATUS_KEY_NOT_FOUND;
}
void initList() {
int i;
/* *************************
* initialize skip list *
************************* */
if ((list.hdr = malloc(
sizeof (nodeType) + MAXLEVEL * sizeof (nodeType * ))) == 0 ) {
printf ( " insufficient memory (initList)\n " );
exit( 1 );
}
for (i = 0 ; i <= MAXLEVEL; i ++ )
list.hdr -> forward[i] = NIL;
list.listLevel = 0 ;
}
int main( int argc, char ** argv) {
int i, maxnum, random;
recType * rec;
keyType * key;
statusEnum status;
/* command-line:
*
* skl maxnum [random]
*
* skl 2000
* process 2000 sequential records
* skl 4000 r
* process 4000 random records
*
*/
maxnum = 20 ;
random = argc > 2 ;
initList();
if ((rec = malloc(maxnum * sizeof (recType))) == 0 ) {
fprintf (stderr, " insufficient memory (rec)\n " );
exit( 1 );
}
if ((key = malloc(maxnum * sizeof (keyType))) == 0 ) {
fprintf (stderr, " insufficient memory (key)\n " );
exit( 1 );
}
if (random) {
/* fill "a" with unique random numbers */
for (i = 0 ; i < maxnum; i ++ ) key[i] = rand();
printf ( " ran, %d items\n " , maxnum);
} else {
for (i = 0 ; i < maxnum; i ++ ) key[i] = i;
printf ( " seq, %d items\n " , maxnum);
}
for (i = 0 ; i < maxnum; i ++ ) {
status = insert(key[i], & rec[i]);
if (status) printf( " pt1: error = %d\n " , status);
}
for (i = maxnum - 1 ; i >= 0 ; i -- ) {
status = find(key[i], & rec[i]);
if (status) printf( " pt2: error = %d\n " , status);
}
for (i = maxnum - 1 ; i >= 0 ; i -- ) {
status = delete(key[i]);
if (status) printf( " pt3: error = %d\n " , status);
}
return 0 ;
}