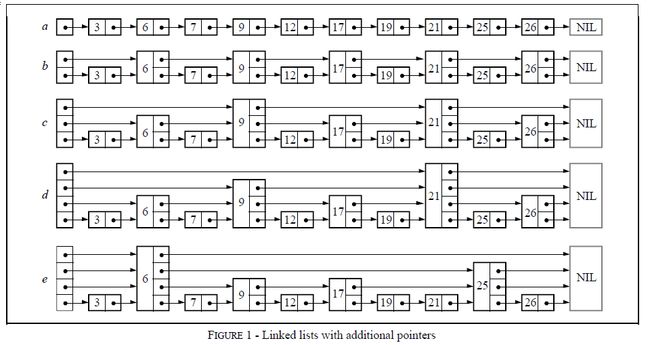
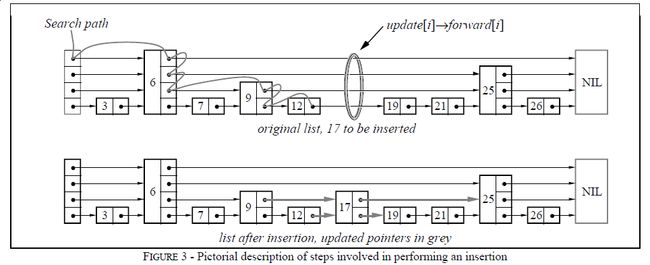
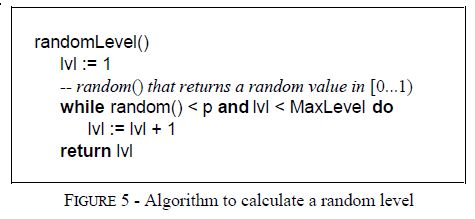
skip list
简单实现了建skip list的过程,至于查找,删除,有了参考文献[1]的算法,很容易实现的,这里就不赘述了。
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <assert.h> #include <time.h> #define INT_MIN ((int)(1 << 31)) #define INT_MAX ((int)((unsigned int)(1 << 31) - 1)) #define MAXLEVEL 10 #define PROBABILITY 0.1 #define DEBUG typedef struct Node{ int key; struct Node *next, *down; }Node; static Node NIL = {INT_MAX, NULL, NULL}; static Node *head = NULL; static int skiplist_level = 0; static void skiplist_print() { int i; Node *node, *t = head; for(i = skiplist_level; i >= 0; i--){ printf("%d: ", i); for (node = t; node; node = node->next){ printf("%d ", node->key); } t = t->down; printf("/n"); } } Node *new_node(int key, Node *next, Node *down) { Node *node = (Node *)malloc(sizeof(Node)); #if 0 printf("%d/n", INT_MIN); #endif if (!node){ printf("no mem to malloc/n"); exit(1); } node->key = key; node->next = next; node->down = down; return node; } static inline float gen_p() { return (float)random() / RAND_MAX; //[0, 1] // return 0; } static int skiplist_randlevel() { int level = 0; while (gen_p() < PROBABILITY && level < MAXLEVEL - 1){ level++; } return level; } static Node *skiplist_insert(int key) { Node *update[MAXLEVEL]; Node *node, *tmp; int level; int i; for (node = head, i = skiplist_level; i >= 0; i--){ while (node->next->key < key){ node = node->next; } /*node->key < key <= node->next->key*/ update[i] = node; if (i){ node = node->down; } } /*level 0*/ node = node->next; /*insert*/ if (1 /*node->key != key*/){ level = skiplist_randlevel(); if (level > skiplist_level){ for (i = skiplist_level + 1; i <= level; i++){ update[i] = new_node(INT_MIN, &NIL, head); head = update[i]; } skiplist_level = level; } /*has got insertion place*/ tmp = NULL; #ifdef DEBUG printf("level: %d update: ", level); #endif for (i = 0; i <= skiplist_level; i++){ node = new_node(key, update[i]->next, tmp); update[i]->next = node; #ifdef DEBUG printf("%d ", update[i]->key); #endif tmp = node; } #ifdef DEBUG printf("/n"); #endif } return head; } static Node *build_skiplist(FILE *file) { int key; //build empty skiplist head = new_node(INT_MIN, &NIL, NULL); skiplist_level = 0; while (EOF != fscanf(file, "%d", &key)){ #ifdef DEBUG skiplist_print(); printf("*********************/n"); printf("%d/n", key); #endif skiplist_insert(key); } #ifdef DEBUG skiplist_print(); printf("*********************/n"); #endif return head; } static void foo(FILE *file) { srandom((unsigned int)time(NULL)); head = build_skiplist(file); //TODO } int main(int argc, char **argv) { FILE *file; file = fopen("skiplist.input", "r"); if (!file){ perror("fopen"); exit(1); } foo(file); fclose(file); return 0; }
参考文献
[1] William Pugh. Skip lists: a probabilistic alternative to balanced trees. In Communications of the ACM. page 668-676, 1990.