Windows API一日一练(87)CreateProcess函数收藏
新一篇: Windows API一日一练(88)EnumProcesses函数 | 旧一篇: Windows API一日一练(88)EnumProcesses函数
Trackback: http://tb.blog.csdn.net/TrackBack.aspx?PostId=1930256
发表于 @ 2007年12月15日 20:11:00|评论(0)|编辑
新一篇: Windows API一日一练(88)EnumProcesses函数 | 旧一篇: Windows API一日一练(88)EnumProcesses函数
CreateProcess使用心得收藏
新一篇: 在Java中处理日志记录 | 旧一篇: NT Service的几个注意点和示例代码
1、我们用CreateProcess执行一个外部程序时,怎样才能得到这个程序的输入输出呢?CreateProcess已经替我们准备好了,在CreateProcess的STARTUPINFO参数里有这样几个hStdInput、hStdOutput、hStdError东东,用来为创建的进程指定输入输出,例如用CreateFile创建一个文件,接着把得到的文件句柄指定给hStdOutput,并且把dwFlags的值设为USESTDHANDLES,这样外部程序的输出就会输到这个文件里。注意:CreateFile的SECURITY_ATTRIBUTES.bInheritHandle参数要设为TRUE。
?
2、在Create系列函数中通常都会有一个叫SECURITY_ATTRIBUTES的参数,
? SECURITY_ATTRIBUTES sa;
????????? sa.nLength = sizeof(SECURITY_ATTRIBUTES);
????????? sa.lpSecurityDescriptor = NULL;
????????? sa.bInheritHandle = TRUE;
? 如果把bInheritHandle的值设为TRUE,意思就是它所创建出来的东西是可以被其他的子进程使用的,例如用CreatePipe创建的管道可以用在CreateProcess创建的进程中。
?
3、用CreateProcess创建子进程时通过lpCurrentDirectory参数指定子进程运行的路径。
发表于 @ 2004年06月23日 12:43:00|评论(1)|编辑
新一篇: 在Java中处理日志记录 | 旧一篇: NT Service的几个注意点和示例代码
孙鑫VC学习笔记:第十七讲 用匿名管道实现进程间的通信收藏
新一篇: 孙鑫VC学习笔记:第十七讲 用命名管道实现进程间的通信 | 旧一篇: 孙鑫VC学习笔记:第十七讲 用剪贴板实现进程间的通信
用匿名管道实现进程间的通信:
匿名管道只能在本地主机上,父子进程之间完成通信:
步骤:
1.新建一个项目Parent
2.增加“匿名管道”子菜单以及“创建管道”、“读取数据”与“写入数据”三个菜单项。
3.在CParentView 中添加两个成员句柄:
HANDLE m_hWrite;
HANDLE m_hRead;
4.为“创建管道”菜单项实现创建管道的功能
代码如下:
注:
关闭进程和线程对象的句柄
CloseHandle (pi.hProcess); //关闭所返回的子进程句柄
CloseHandle (pi.hThread); //关闭子进程中主线程句柄
在创建新进程时,系统会建立一个主进程内核对象和一个线程内核对象,内核对象都有使用计数,
系统为内核对象赋初始的使用计数1,当CreateProgress在内部打开内核对象时,
每个对象的使用计数变为2,我们在父进程中如果不需要使用这两个句柄,
调用CloseHandle 关闭这两个句柄,
系统会将子进程的进程内核对象和线程内核对象减1,
当子进程中止运行时,系统会再将使用计数减一,此时内核对象实用计数为零,
进程内核对象和线程内核对象才能够被释放。
我们应该在不需要使用内核对象句柄的时候使用CloseHandle关闭句柄。
将结构体中所有成员置为零可以使用函数:
void ZeroMemory(PVOID Destination,SIZE_T Length);
要获得标准输入输出或标准错误句柄,使用函数:
HANDLE GetStdHandle(DWORD nStdHandle);
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
5.接下来完成读取与写入数据的功能了
“读取数据”菜单项
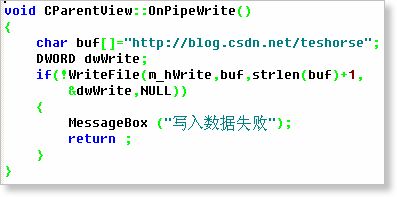
“写入数据”菜单项
注.
在父进程创建管道,返回管道的读写句柄,调用CreateProcess启动子进程,
通过将子进程的标准输入输出句柄设置为管道的读写句柄,
相当于对管道的读写句柄做上标记然后传递给子进程。
在子进程中得到自己的标准输入输出句柄,相当于得到了管道的读写句柄。
匿名管道只能在父子进程间进行通信,因为匿名管道没有名字,
所以我们只有在调用CreateProcess时将管道的读写句柄传递给子进程。
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
下面编写子线程程序:
1.新建一个项目Child添加到当前工作区
2.增加“匿名管道”子菜单以及“读取数据”与“写入数据”两个菜单项。
3.增加一个虚函数:CChildView::OnInitialUpdate(),
首先在CChildView中添加两个成员句柄:
HANDLE m_hWrite;
HANDLE m_hRead;
然后在CChildView::OnInitialUpdate()函数中得到标准输入输出句柄
m_hRead = GetStdHandle(STD_INPUT_HANDLE);
m_hWrite = GetStdHandle(STD_OUTPUT_HANDLE);
4.接下来完成读取与写入数据的功能了
读取代码与前面父进程的代码完全一样
写入代码只改了一个字符串
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
至此,我们的程序完成了。
值得注意的是,
子进程必须由父进程打开(点击“匿名管道”菜单的“创建管道”项),它才与父进程有父子关系。
如果先打开子进程,再打开父进程,那么这两个进程并无任何关系。
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
创建管道相关函数说明:
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
CreatePipe
创建一个命名管道,返回一个管道的读写句柄。
The CreatePipe function creates an anonymous pipe, and returns handles to the read and write ends of the pipe.
BOOL CreatePipe(
PHANDLE hReadPipe, // pointer to read handle 用来接收管道的读取句柄
PHANDLE hWritePipe, // pointer to write handle 用来接收管道的写入句柄
LPSECURITY_ATTRIBUTES lpPipeAttributes, // pointer to security attributes
DWORD nSize // 指定管道缓冲区大小
);
参数3:lpPipeAttributes用来检测返回的句柄是否可以被子进程继承。
这里不能设置为NULL,因为管道只能在父子进程间通信,
子进程要获得父进程的管道句柄只能通过继承得到。
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
启动进程:
CreateProcess
The CreateProcess function creates a new process and its primary thread. The new process executes the specified executable file.
BOOL CreateProcess(
LPCTSTR lpApplicationName, //
LPTSTR lpCommandLine, // pointer to command line string 传递命令行参数
LPSECURITY_ATTRIBUTES lpProcessAttributes, // process security attributes
LPSECURITY_ATTRIBUTES lpThreadAttributes, // thread security attributes
BOOL bInheritHandles, // handle inheritance flag
DWORD dwCreationFlags, //用来指定控制优先级类和进程创建的附加标记
LPVOID lpEnvironment, // pointer to new environment block
LPCTSTR lpCurrentDirectory, //指向完整路径的字符指针,指定子进程当前的驱动器和目录
LPSTARTUPINFO lpStartupInfo, // pointer to STARTUPINFO 指定新进程主窗口如何出现
LPPROCESS_INFORMATION lpProcessInformation
// pointer to PROCESS_INFORMATION,用来接收关于新的进程的标识信息。
);
Parameters
lpApplicationName
Pointer to a null-terminated string that specifies the module to execute.
用来指定一个可执行模块的名字。也就是可以用来设定一个可执行程序的名字
The string can specify the full path and filename of the module to execute or it can specify a partial name.
这个字符串可以指定可执行文件的完整+文件名或者指定部分名字。
In the case of a partial name, the function uses the current drive and current directory to complete the specification.
如果指定部分名字,则应用程序在当前的驱动器、当前的目录下面搜索它,如果搜索失败也不会使用搜索路径。注意:指定名字时要指定扩展名。
The lpApplicationName parameter can be NULL. In that case, the module name must be the first white space-delimited token in the lpCommandLine string.
该参数可以为NULL,这时文件的名称由第二个参数lpCommandLine 中的第一个空格以前的字符指定。
If you are using a long filename that contains a space, use quoted strings to indicate where the filename ends and the arguments begin, otherwise, the filename is ambiguous.
lpCommandLine
Pointer to a null-terminated string that specifies the command line to execute. The system adds a null character to the command line, trimming the string if necessary, to indicate which file was actually used.
The lpCommandLine parameter can be NULL. In that case, the function uses the string pointed to by lpApplicationName as the command line.
If both lpApplicationName and lpCommandLine are non-NULL, *lpApplicationName specifies the module to execute, and *lpCommandLine specifies the command line. The new process can use GetCommandLine to retrieve the entire command line. C runtime processes can use the argc and argv arguments.
如果第一个参数为NULL,也就是用第二个参数来指定文件名,那么这人参数的第一个空格以前的字符会被认为是文件的名字,如果是长文件字,需要用引号把它括起来;如果没有加扩展名,则会自动加上.exe的扩展名;如果没有写全路径,则会按下下面6个路径进行搜索。
If lpApplicationName is NULL, the first white space-delimited token of the command line specifies the module name. If you are using a long filename that contains a space, use quoted strings to indicate where the filename ends and the arguments begin (see the explanation for the lpApplicationName parameter). If the filename does not contain an extension, .EXE is assumed. If the filename ends in a period (.) with no extension, or the filename contains a path, .EXE is not appended. If the filename does not contain a directory path, the system searches for the executable file in the following sequence:
- The directory from which the application loaded.
- The current directory for the parent process.
- Windows 95 and Windows 98: The Windows system directory. Use the GetSystemDirectory function to get the path of this directory.
Windows NT: The 32-bit Windows system directory. Use the GetSystemDirectory function to get the path of this directory. The name of this directory is SYSTEM32. - Windows NT: The 16-bit Windows system directory. There is no Win32 function that obtains the path of this directory, but it is searched. The name of this directory is SYSTEM.
- The Windows directory. Use the GetWindowsDirectory function to get the path of this directory.
- The directories that are listed in the PATH environment variable.
If the process to be created is an MS-DOS - based or 16-bit Windows-based application, lpCommandLine should be a full command line in which the first element is the application name. Because this also works well for Win32-based applications, it is the most robust way to set lpCommandLine.
lpProcessAttributes
Pointer to a SECURITY_ATTRIBUTES structure that determines whether the returned handle can be inherited by child processes. If lpProcessAttributes is NULL, the handle cannot be inherited.
用来设定新进程的安全性,以及指定父进程以后生成的子进程是否具有这个对象的句柄。
Windows NT: The lpSecurityDescriptor member of the structure specifies a security descriptor for the new process. If lpProcessAttributes is NULL, the process gets a default security descriptor.
lpThreadAttributes
Pointer to a SECURITY_ATTRIBUTES structure that determines whether the returned handle can be inherited by child processes. If lpThreadAttributes is NULL, the handle cannot be inherited.
用来设定新线程的安全性,以及指定父进程以后生成的子进程是否具有这个对象的句柄。
Windows NT: The lpSecurityDescriptor member of the structure specifies a security descriptor for the main thread. If lpThreadAttributes is NULL, the thread gets a default security descriptor.
bInheritHandles
Indicates whether the new process inherits handles from the calling process. 指定新的进程是否可以从调用进程继承句柄。
If TRUE, each inheritable open handle in the calling process is inherited by the new process. Inherited handles have the same value and access privileges as the original handles.
如果为真,则任何可继承的打开句柄都可以被新的进程所继承,
继承的句柄和原始句柄拥有同样的值和访问特权。
Return Values
If the function succeeds, the return value is nonzero.
If the function fails, the return value is zero. To get extended error information, call GetLastError.
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
其中STARTUPINFO结构体定义如下:
STARTUPINFO
The STARTUPINFO structure is used with the CreateProcess function to specify main window properties if a new window is created for the new process. For graphical user interface (GUI) processes, this information affects the first window created by the CreateWindow function and shown by the ShowWindow function. For console processes, this information affects the console window if a new console is created for the process. A process can use the GetStartupInfo function to retrieve the STARTUPINFO structure specified when the process was created.
typedef struct _STARTUPINFO { // si
DWORD cb;
LPTSTR lpReserved;
LPTSTR lpDesktop;
LPTSTR lpTitle;
DWORD dwX;
DWORD dwY;
DWORD dwXSize;
DWORD dwYSize;
DWORD dwXCountChars;
DWORD dwYCountChars;
DWORD dwFillAttribute;
DWORD dwFlags;
WORD wShowWindow;
WORD cbReserved2;
LPBYTE lpReserved2;
HANDLE hStdInput;
HANDLE hStdOutput;
HANDLE hStdError;
} STARTUPINFO, *LPSTARTUPINFO;
Members
cb 指示结构体的大小,以字节为单位。
Specifies the size, in bytes, of the structure.
dwFlags
This is a bit field that determines whether certain STARTUPINFO members are used when the process creates a window. Any combination of the following values can be specified:
Value
STARTF_USESHOWWINDOW
STARTF_USEPOSITION
STARTF_USESIZE
STARTF_USECOUNTCHARS
这个值没有被指定,则 dwXCountChars
与dwYCountChars成员被忽略。
STARTF_USEFILLATTRIBUTE
STARTF_FORCEONFEEDBACK
STARTF_FORCEOFFFEEDBACK
STARTF_USESTDHANDLES
用来设定我们所创建的进程的标准输入、标准输出和标准错误句柄。
The CreateProcess function's fInheritHandles parameter must be set to TRUE for this to work properly.
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
PROCESS_INFORMATION
The PROCESS_INFORMATION structure is filled in by the CreateProcess function with information about a newly created process and its primary thread.
typedef struct _PROCESS_INFORMATION { // pi HANDLE hProcess; HANDLE hThread; DWORD dwProcessId; DWORD dwThreadId; } PROCESS_INFORMATION;
Members
hProcess
Returns a handle to the newly created process. The handle is used to specify the process in all functions that perform operations on the process object.
hThread
Returns a handle to the primary thread of the newly created process. The handle is used to specify the thread in all functions that perform operations on the thread object.
dwProcessId
Returns a global process identifier (全局进程标识符)that can be used to identify a process. The value is valid from the time the process is created until the time the process is terminated.
dwThreadId
Returns a global thread identifiers (全局线程标识符)that can be used to identify a thread. The value is valid from the time the thread is created until the time the thread is terminated.
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
GetStdHandle
The GetStdHandle function returns a handle for the standard input, standard output, or standard error device.
HANDLE GetStdHandle(
DWORD nStdHandle // input, output, or error device
);
Parameters
nStdHandle
Specifies the device for which to return the handle. This parameter can have one of the following values:
Value Meaning
STD_INPUT_HANDLE
Standard input handle
STD_OUTPUT_HANDLE
Standard output handle
STD_ERROR_HANDLE
Standard error handle
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
发表于 @ 2006年08月22日 22:34:00|评论(0)|编辑
新一篇: 孙鑫VC学习笔记:第十七讲 用命名管道实现进程间的通信 | 旧一篇: 孙鑫VC学习笔记:第十七讲 用剪贴板实现进程间的通信
ShellExecute
有几个API函数都可以实现这些功能,但是在大多数情况下ShellExecute是更多的被使用的,同时它并不是太复杂。
ShellExecute函数原型及参数含义如下:
ShellExecute(
HWND hwnd, //父窗口句柄 (如:NULL,Handle等)
LPCSTR lpOperation, //操作类型 (如:"open")*要加英文双引号
LPCSTR lpFile, //要进行操作的文件或路径
LPCSTR lpParameters, //当lpOperation为“explore”时指定要传递的参数,通常设为NULL
LPCSTR lpDirectory, //指定默认目录,通常设为NULL
INT nShowCmd //文件打开的方式,以通常方式还是最大化或最小化显示,一般为SW_SHOWNORMAL
)
例子如下:
//调用计算器
ShellExecute(NULL,"open","calc.exe",NULL,NULL,SW_SHOWNORMAL);
//调用记事本
ShellExecute(NULL,"open","NOTEPAD.EXE",NULL,NULL,SW_SHOWNORMAL);
●hWnd:用于指定父窗口句柄。当函数调用过程出现错误时,它将作为Windows消息窗口 的父窗口。例如,可以将其设置为应用程序主窗口句柄,即Application.Handle,也可以将其设置为桌面窗口句柄(用 GetDesktopWindow函数获得)。
●Operation:用于指定要进行的操作。其中“open”操作表示执行由 FileName参数指定的程序,或打开由FileName参数指定的文件或文件夹;“print”操作表示打印由FileName参数指定的文件; “explore”操作表示浏览由FileName参数指定的文件夹。当参数设为nil时,表示执行默认操作“open”。
●FileName:用于指定要打开的文件名、要执行的程序文件名或要浏览的文件夹名。
●Parameters:若FileName参数是一个可执行程序,则此参数指定命令行参数,否则此参数应为nil或PChar(0)。
●Directory:用于指定默认目录。
●ShowCmd:若FileName参数是一个可执行程序,则此参数指定程序窗口的初始显示方式,否则此参数应设置为0。
若ShellExecute函数调用成功,则返回值为被执行程序的实例句柄。若返回值小于32,则表示出现错误。
上述仅仅是ShellExecute函数的标准用法,下面将介绍它的特殊用法。
2.特殊用法
如果将FileName参数设置为“http:”协议格式,那么该函数将打开默认浏览器并链接 到指定的URL地址。若用户机器中安装了多个浏览器,则该函数将根据Windows 9x/NT注册表中http协议处理程序(Protocols Handler)的设置确定启动哪个浏览器。
格式一:http://网站域名。
如:ShellExecute(Handle, "open", http:// ;
www.neu.edu.cn’, NULL, NULL, SW_SHOWNORMAL);
格式二:http://网站域名/网页文件名。
如:ShellExecute(Handle, "open", http:// ;
www.neu.edu.cn/default.htm',NULL,NULL,
SW_SHOWNORMAL);
如果将FileName参数设置为“mailto:”协议格式,那么该函数将启动默认邮件客户 程序,如Microsoft Outlook(也包括Microsoft Outlook Express)或Netscape Messanger。若用户机器中安装了多个邮件客户程序,则该函数将根据Windows 9x/NT注册表中mailto协议处理程序的设置确定启动哪个邮件客户程序。
格式一:mailto:
如:ShellExecute(Handle,"open", "mailto:", NULL, NULL, SW_SHOWNORMAL);打开新邮件窗口。
格式二:mailto:用户账号@邮件服务器地址
如:ShellExecute(Handle, "open"," mailto:[email protected]", NULL, NULL, SW_SHOWNORMAL);打开新邮件窗口,并自动填入收件人地址。若指定多个收件人地址,则收件人地址之间必须用分号或逗号分隔开(下同)。
格式三:mailto:用户账号@邮件服务器地址?subject=邮件主题&body=邮件正文
如:ShellExecute(handle, ‘open’, ‘ mailto:[email protected]?subject=Hello&Body=This is a test’, nil, nil, SW_SHOWNORMAL);打开新邮件窗口,并自动填入收件人地址、邮件主题和邮件正文。若邮件正文包括多行文本,则必须在每行文本之间加入换行转义 字符%0a。
例子(delphi):
在一个应用程序调用c:/Project1.exe;
ShellExecute(handle, 'open','c:/Project1.exe','字串内容',nil, SW_SHOWNORMAL);
在Project1.exe里可以调用:
procedure TForm1.FormCreate(Sender: TObject);
var i:integer;
begin
for i:=1 to paramcount do
if ParamStr(i)<>'' then showmessage(ParamStr(i));
end;
最后的那个参数,为窗口指定可视性方面的一个命令。
请用下述任何一个常数
SW_HIDE 隐藏窗口,活动状态给另一个窗口
SW_MINIMIZE 最小化窗口,活动状态给另一个窗口
SW_RESTORE 用原来的大小和位置显示一个窗口,同时令其进入活动状态
SW_SHOW 用当前的大小和位置显示一个窗口,同时令其进入活动状态
SW_SHOWMAXIMIZED 最大化窗口,并将其激活
SW_SHOWMINIMIZED 最小化窗口,并将其激活
SW_SHOWMINNOACTIVE 最小化一个窗口,同时不改变活动窗口
SW_SHOWNA 用当前的大小和位置显示一个窗口,不改变活动窗口
SW_SHOWNOACTIVATE 用最近的大小和位置显示一个窗口,同时不改变活动窗口
SW_SHOWNORMAL 与SW_RESTORE相同
参考链接:
http://hi.baidu.com/ce%5Fken/blog/item/01e93a33d26fb4fa1a4cffd3.html
我知道的有
CreateProgress
WinExec
ShellExecute
system