【存档】QT和OpenCV 显示视频
2010-12-08 21:20:29| 分类: 默认分类 |字号 订阅
Qt开发的程序一般都要借助qmake生成makefile文件。因此为了加入opencv库就要修改.pro文件,下面是Linux下该文件的配置。(增加的部分)
 INCLUDEPATH
+=
.
/
usr
/
local
/
include
/
opencv
INCLUDEPATH
+=
.
/
usr
/
local
/
include
/
opencv
 LIBS
+=
/
usr
/
local
/
lib
/
libcv.so \
LIBS
+=
/
usr
/
local
/
lib
/
libcv.so \
 /
usr
/
local
/
lib
/
libcvaux.so \
/
usr
/
local
/
lib
/
libcvaux.so \
 /
usr
/
local
/
lib
/
libcxcore.so \
/
usr
/
local
/
lib
/
libcxcore.so \
 /
usr
/
local
/
lib
/
libhighgui.so \
/
usr
/
local
/
lib
/
libhighgui.so \
 /
usr
/
local
/
lib
/
libml.so
/
usr
/
local
/
lib
/
libml.so
Opencv中通过摄像头捕捉到的每帧图像的数据结构是IplImage类型的,要把它显示到Qt窗口中就需要把它转化为QImage类型的图像。
 #include
<
QVector
>
#include
<
QVector
>
 #include
<
cstring
>
#include
<
cstring
>

 QImage MyThread::IplImageToQImage(
const
IplImage
*
iplImage,
double
mini,
double
maxi)
QImage MyThread::IplImageToQImage(
const
IplImage
*
iplImage,
double
mini,
double
maxi)
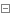 {
{
 uchar *qImageBuffer = NULL;
uchar *qImageBuffer = NULL;

 int width = iplImage->width;
int width = iplImage->width;

 /* Note here that OpenCV image is stored so that each lined is
/* Note here that OpenCV image is stored so that each lined is
 32-bits aligned thus
32-bits aligned thus
 * explaining the necessity to "skip" the few last bytes of each
* explaining the necessity to "skip" the few last bytes of each
 line of OpenCV image buffer.
line of OpenCV image buffer.
 */
*/
 int widthStep = iplImage->widthStep;
int widthStep = iplImage->widthStep;
 int height = iplImage->height;
int height = iplImage->height;

 switch (iplImage->depth)
switch (iplImage->depth)
 {
{
 case IPL_DEPTH_8U:
case IPL_DEPTH_8U:
 if(iplImage->nChannels == 1)
if(iplImage->nChannels == 1)
 {
{
 /* OpenCV image is stored with one byte grey pixel. We convert it
/* OpenCV image is stored with one byte grey pixel. We convert it
 to an 8 bit depth QImage.
to an 8 bit depth QImage.
 */
*/

 qImageBuffer = (uchar *) malloc(width*height*sizeof(uchar));
qImageBuffer = (uchar *) malloc(width*height*sizeof(uchar));
 uchar *QImagePtr = qImageBuffer;
uchar *QImagePtr = qImageBuffer;
 const uchar *iplImagePtr = (const uchar *) iplImage->imageData;
const uchar *iplImagePtr = (const uchar *) iplImage->imageData;

 for(int y = 0; y < height; y++)
for(int y = 0; y < height; y++)
 {
{
 // Copy line by line
// Copy line by line
 memcpy(QImagePtr, iplImagePtr, width);
memcpy(QImagePtr, iplImagePtr, width);
 QImagePtr += width;
QImagePtr += width;
 iplImagePtr += widthStep;
iplImagePtr += widthStep;
 }
}

 }
}
 else if(iplImage->nChannels == 3)
else if(iplImage->nChannels == 3)
 {
{
 /* OpenCV image is stored with 3 byte color pixels (3 channels).
/* OpenCV image is stored with 3 byte color pixels (3 channels).
 We convert it to a 32 bit depth QImage.
We convert it to a 32 bit depth QImage.
 */
*/
 qImageBuffer = (uchar *) malloc(width*height*4*sizeof(uchar));
qImageBuffer = (uchar *) malloc(width*height*4*sizeof(uchar));
 uchar *QImagePtr = qImageBuffer;
uchar *QImagePtr = qImageBuffer;
 const uchar *iplImagePtr = (const uchar *) iplImage->imageData;
const uchar *iplImagePtr = (const uchar *) iplImage->imageData;
 for(int y = 0; y < height; y++)
for(int y = 0; y < height; y++)
 {
{
 for (int x = 0; x < width; x++)
for (int x = 0; x < width; x++)
 {
{
 // We cannot help but copy manually.
// We cannot help but copy manually.
 QImagePtr[0] = iplImagePtr[0];
QImagePtr[0] = iplImagePtr[0];
 QImagePtr[1] = iplImagePtr[1];
QImagePtr[1] = iplImagePtr[1];
 QImagePtr[2] = iplImagePtr[2];
QImagePtr[2] = iplImagePtr[2];
 QImagePtr[3] = 0;
QImagePtr[3] = 0;

 QImagePtr += 4;
QImagePtr += 4;
 iplImagePtr += 3;
iplImagePtr += 3;
 }
}
 iplImagePtr += widthStep-3*width;
iplImagePtr += widthStep-3*width;
 }
}

 }
}
 else
else
 {
{
 qDebug("IplImageToQImage: image format is not supported : depth=8U and %d channels ", iplImage->nChannels);
qDebug("IplImageToQImage: image format is not supported : depth=8U and %d channels ", iplImage->nChannels);
 }
}
 break;
break;
 case IPL_DEPTH_16U:
case IPL_DEPTH_16U:
 if(iplImage->nChannels == 1)
if(iplImage->nChannels == 1)
 {
{
 /* OpenCV image is stored with 2 bytes grey pixel. We convert it
/* OpenCV image is stored with 2 bytes grey pixel. We convert it
 to an 8 bit depth QImage.
to an 8 bit depth QImage.
 */
*/
 qImageBuffer = (uchar *) malloc(width*height*sizeof(uchar));
qImageBuffer = (uchar *) malloc(width*height*sizeof(uchar));
 uchar *QImagePtr = qImageBuffer;
uchar *QImagePtr = qImageBuffer;
 //const uint16_t *iplImagePtr = (const uint16_t *);
//const uint16_t *iplImagePtr = (const uint16_t *);
 const unsigned int *iplImagePtr = (const unsigned int *)iplImage->imageData;
const unsigned int *iplImagePtr = (const unsigned int *)iplImage->imageData;
 for (int y = 0; y < height; y++)
for (int y = 0; y < height; y++)
 {
{
 for (int x = 0; x < width; x++)
for (int x = 0; x < width; x++)
 {
{
 // We take only the highest part of the 16 bit value. It is
// We take only the highest part of the 16 bit value. It is
 //similar to dividing by 256.
//similar to dividing by 256.
 *QImagePtr++ = ((*iplImagePtr++) >> 8);
*QImagePtr++ = ((*iplImagePtr++) >> 8);
 }
}
 iplImagePtr += widthStep/sizeof(unsigned int)-width;
iplImagePtr += widthStep/sizeof(unsigned int)-width;
 }
}
 }
}
 else
else
 {
{
 qDebug("IplImageToQImage: image format is not supported : depth=16U and %d channels ", iplImage->nChannels);
qDebug("IplImageToQImage: image format is not supported : depth=16U and %d channels ", iplImage->nChannels);

 }
}
 break;
break;
 case IPL_DEPTH_32F:
case IPL_DEPTH_32F:
 if(iplImage->nChannels == 1)
if(iplImage->nChannels == 1)
 {
{
 /* OpenCV image is stored with float (4 bytes) grey pixel. We
/* OpenCV image is stored with float (4 bytes) grey pixel. We
 convert it to an 8 bit depth QImage.
convert it to an 8 bit depth QImage.
 */
*/
 qImageBuffer = (uchar *) malloc(width*height*sizeof(uchar));
qImageBuffer = (uchar *) malloc(width*height*sizeof(uchar));
 uchar *QImagePtr = qImageBuffer;
uchar *QImagePtr = qImageBuffer;
 const float *iplImagePtr = (const float *) iplImage->imageData;
const float *iplImagePtr = (const float *) iplImage->imageData;
 for(int y = 0; y < height; y++)
for(int y = 0; y < height; y++)
 {
{
 for(int x = 0; x < width; x++)
for(int x = 0; x < width; x++)
 {
{
 uchar p;
uchar p;
 float pf = 255 * ((*iplImagePtr++) - mini) / (maxi - mini);
float pf = 255 * ((*iplImagePtr++) - mini) / (maxi - mini);
 if(pf < 0) p = 0;
if(pf < 0) p = 0;
 else if(pf > 255) p = 255;
else if(pf > 255) p = 255;
 else p = (uchar) pf;
else p = (uchar) pf;

 *QImagePtr++ = p;
*QImagePtr++ = p;
 }
}
 iplImagePtr += widthStep/sizeof(float)-width;
iplImagePtr += widthStep/sizeof(float)-width;
 }
}
 }
}
 else
else
 {
{
 qDebug("IplImageToQImage: image format is not supported : depth=32F and %d channels ", iplImage->nChannels);
qDebug("IplImageToQImage: image format is not supported : depth=32F and %d channels ", iplImage->nChannels);
 }
}
 break;
break;
 case IPL_DEPTH_64F:
case IPL_DEPTH_64F:
 if(iplImage->nChannels == 1)
if(iplImage->nChannels == 1)
 {
{
 /* OpenCV image is stored with double (8 bytes) grey pixel. We
/* OpenCV image is stored with double (8 bytes) grey pixel. We
 convert it to an 8 bit depth QImage.
convert it to an 8 bit depth QImage.
 */
*/
 qImageBuffer = (uchar *) malloc(width*height*sizeof(uchar));
qImageBuffer = (uchar *) malloc(width*height*sizeof(uchar));
 uchar *QImagePtr = qImageBuffer;
uchar *QImagePtr = qImageBuffer;
 const double *iplImagePtr = (const double *) iplImage->imageData;
const double *iplImagePtr = (const double *) iplImage->imageData;
 for(int y = 0; y < height; y++)
for(int y = 0; y < height; y++)
 {
{
 for(int x = 0; x < width; x++)
for(int x = 0; x < width; x++)
 {
{
 uchar p;
uchar p;
 double pf = 255 * ((*iplImagePtr++) - mini) / (maxi - mini);
double pf = 255 * ((*iplImagePtr++) - mini) / (maxi - mini);

 if(pf < 0) p = 0;
if(pf < 0) p = 0;
 else if(pf > 255) p = 255;
else if(pf > 255) p = 255;
 else p = (uchar) pf;
else p = (uchar) pf;

 *QImagePtr++ = p;
*QImagePtr++ = p;
 }
}
 iplImagePtr += widthStep/sizeof(double)-width;
iplImagePtr += widthStep/sizeof(double)-width;
 }
}
 }
}
 else
else
 {
{
 qDebug("IplImageToQImage: image format is not supported : depth=64F and %d channels ", iplImage->nChannels);
qDebug("IplImageToQImage: image format is not supported : depth=64F and %d channels ", iplImage->nChannels);
 }
}
 break;
break;
 default:
default:
 qDebug("IplImageToQImage: image format is not supported : depth=%d and %d channels ", iplImage->depth, iplImage->nChannels);
qDebug("IplImageToQImage: image format is not supported : depth=%d and %d channels ", iplImage->depth, iplImage->nChannels);
 }
}

 QImage qImage;
QImage qImage;
 QVector<QRgb> vcolorTable;
QVector<QRgb> vcolorTable;
 if(iplImage->nChannels == 1)
if(iplImage->nChannels == 1)
 {
{
 // We should check who is going to destroy this allocation.
// We should check who is going to destroy this allocation.
 QRgb *colorTable = new QRgb[256];
QRgb *colorTable = new QRgb[256];
 for(int i = 0; i < 256; i++)
for(int i = 0; i < 256; i++)
 {
{
 colorTable[i] = qRgb(i, i, i);
colorTable[i] = qRgb(i, i, i);
 vcolorTable[i] = colorTable[i];
vcolorTable[i] = colorTable[i];
 }
}
 qImage = QImage(qImageBuffer, width, height, QImage::Format_Indexed8).copy();
qImage = QImage(qImageBuffer, width, height, QImage::Format_Indexed8).copy();
 qImage.setColorTable(vcolorTable);
qImage.setColorTable(vcolorTable);
 }
}
 else
else
 {
{
 qImage = QImage(qImageBuffer, width, height, QImage::Format_RGB32).copy();
qImage = QImage(qImageBuffer, width, height, QImage::Format_RGB32).copy();
 }
}
 free(qImageBuffer);
free(qImageBuffer);
 return qImage;
return qImage;
 }
}
于是你可以下面的代码(部分)测试一下:摄像头获取每一帧IplImage*类型的图像,转化为QImage类型的图像,用update()发出一个paintEvent(QPaintEvent*)事件,如此不断更新图像。(IplImageToQImage中的mini和maxi默认初始化为0)
 void
ImageViewer::paintEvent(QPaintEvent
*
)
{
void
ImageViewer::paintEvent(QPaintEvent
*
)
{
 QPainter painter(this);
QPainter painter(this);
 painter.drawImage(QPoint(0,0), *image);
painter.drawImage(QPoint(0,0), *image);
 }
}

 bool
ImageViewer::ShowImage()
{
bool
ImageViewer::ShowImage()
{
 IplImage *pImage = NULL;
IplImage *pImage = NULL;
 CvCapture *pCapture = NULL;
CvCapture *pCapture = NULL;
 if((pCapture = cvCaptureFromCAM(-1)) == NULL){
if((pCapture = cvCaptureFromCAM(-1)) == NULL){
 cout << "Open camera failed! ";
cout << "Open camera failed! ";
 return false;
return false;
 }
}
 while((pImage = cvQueryFrame(pCapture)) != NULL){
while((pImage = cvQueryFrame(pCapture)) != NULL){
 image = IplImageToQImage(pImage);
image = IplImageToQImage(pImage);
 update();
update();
 }
}
 cvReleaseImage(&pImage);
cvReleaseImage(&pImage);
 cvReleaseCapture(&pCapture);
cvReleaseCapture(&pCapture);
 return true;
return true;
 }
}
Opencv中通过摄像头捕捉到的每帧图像的数据结构是IplImage类型的,要把它显示到Qt窗口中就需要把它转化为QImage类型的图像。
于是你可以下面的代码(部分)测试一下:摄像头获取每一帧IplImage*类型的图像,转化为QImage类型的图像,用update()发出一个paintEvent(QPaintEvent*)事件,如此不断更新图像。(IplImageToQImage中的mini和maxi默认初始化为0)