Postorder for Binary Tree
Post order accesing the binary tree with a flag to recording what kind of node is accessed.
flag == 0 means made left move or accessed a left node.
flag == 1 means made right move or accessed a right node.
according to the move action and information between child and parent, we could get and set
this flag value during the accessing.
Here is a simple implementation of my idea with out full test. Just for example.
Any bug report will be appreciated.
My stdext.h for pstack implementation
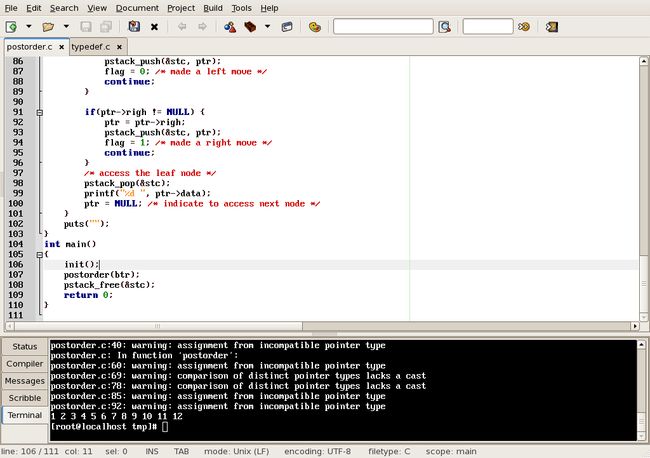
flag == 0 means made left move or accessed a left node.
flag == 1 means made right move or accessed a right node.
according to the move action and information between child and parent, we could get and set
this flag value during the accessing.
Here is a simple implementation of my idea with out full test. Just for example.
Any bug report will be appreciated.
#include
<
stdio.h
>
#include < stdlib.h >
#include < stdext.h >
typedef struct {
int data;
struct node * left;
struct node * righ;
} node;
typedef node btree;
btree * btr = NULL;
void init()
{
int siz = sizeof (node);
btr = (node * )malloc(siz); btr -> data = 12 ;
node * n1 = (node * )malloc(siz); node * n2 = (node * )malloc(siz);
node * n3 = (node * )malloc(siz); node * n4 = (node * )malloc(siz);
node * n5 = (node * )malloc(siz); node * n6 = (node * )malloc(siz);
node * n7 = (node * )malloc(siz); node * n8 = (node * )malloc(siz);
node * n9 = (node * )malloc(siz); node * na = (node * )malloc(siz);
node * nb = (node * )malloc(siz); node * nc = (node * )malloc(siz);
n1 -> data = 12 ; n2 -> data = 8 ; n3 -> data = 11 ;
n4 -> data = 6 ; n5 -> data = 7 ; n6 -> data = 9 ;
n7 -> data = 10 ; n8 -> data = 5 ; n9 -> data = 2 ;
na -> data = 4 ; nb -> data = 1 ; nc -> data = 3 ;
n1 -> left = n2; n1 -> righ = n3;
n2 -> left = n4; n2 -> righ = n5;
n3 -> left = n6; n3 -> righ = n7;
n4 -> left = NULL; n4 -> righ = n8;
n5 -> left = NULL; n5 -> righ = NULL;
n6 -> left = NULL; n6 -> righ = NULL;
n7 -> left = NULL; n7 -> righ = NULL;
n8 -> left = n9; n8 -> righ = na;
n9 -> left = NULL; n9 -> righ = nb;
na -> left = NULL; na -> righ = nc;
nb -> left = NULL; nb -> righ = NULL;
nc -> left = NULL; nc -> righ = NULL;
btr = n1;
}
pstack * stc = NULL;
void postorder(btree * root)
{
assert(root != NULL);
node * ptr = root;
pstack_push( & stc, ptr);
short flag;
while (pstack_hasmore(stc)) {
if (ptr == NULL && pstack_hasmore(stc)) {
if (flag == 0 ) { /* a left node is accessed */
ptr = pstack_top(stc);
if (ptr -> righ != NULL) { /* stack right node */
ptr = ptr -> righ;
pstack_push( & stc, ptr);
flag = 1 ; /* made a right move */
}
else {
pstack_pop( & stc); /* no right node */
printf( " %d " , ptr -> data);
if (pstack_isempty(stc)) break ;
node * prt = pstack_top(stc); /* get parent node */
if (prt -> left != ptr) flag = 1 ; /* right node accessed */
ptr = NULL;
}
}
else { /* flag == 1 */
ptr = pstack_pop( & stc);
printf( " %d " , ptr -> data);
if (pstack_isempty(stc)) break ;
node * prt = pstack_top(stc); /* get parent */
if (prt -> left == ptr) flag = 0 ; /* left node accessed */
ptr = NULL;
}
continue ;
}
if (ptr -> left != NULL) {
ptr = ptr -> left;
pstack_push( & stc, ptr);
flag = 0 ; /* made a left move */
continue ;
}
if (ptr -> righ != NULL) {
ptr = ptr -> righ;
pstack_push( & stc, ptr);
flag = 1 ; /* made a right move */
continue ;
}
/* access the leaf node */
pstack_pop( & stc);
printf( " %d " , ptr -> data);
ptr = NULL; /* indicate to access next node */
}
puts( "" );
}
int main()
{
init();
postorder(btr);
pstack_free( & stc);
return 0 ;
}
#include < stdlib.h >
#include < stdext.h >
typedef struct {
int data;
struct node * left;
struct node * righ;
} node;
typedef node btree;
btree * btr = NULL;
void init()
{
int siz = sizeof (node);
btr = (node * )malloc(siz); btr -> data = 12 ;
node * n1 = (node * )malloc(siz); node * n2 = (node * )malloc(siz);
node * n3 = (node * )malloc(siz); node * n4 = (node * )malloc(siz);
node * n5 = (node * )malloc(siz); node * n6 = (node * )malloc(siz);
node * n7 = (node * )malloc(siz); node * n8 = (node * )malloc(siz);
node * n9 = (node * )malloc(siz); node * na = (node * )malloc(siz);
node * nb = (node * )malloc(siz); node * nc = (node * )malloc(siz);
n1 -> data = 12 ; n2 -> data = 8 ; n3 -> data = 11 ;
n4 -> data = 6 ; n5 -> data = 7 ; n6 -> data = 9 ;
n7 -> data = 10 ; n8 -> data = 5 ; n9 -> data = 2 ;
na -> data = 4 ; nb -> data = 1 ; nc -> data = 3 ;
n1 -> left = n2; n1 -> righ = n3;
n2 -> left = n4; n2 -> righ = n5;
n3 -> left = n6; n3 -> righ = n7;
n4 -> left = NULL; n4 -> righ = n8;
n5 -> left = NULL; n5 -> righ = NULL;
n6 -> left = NULL; n6 -> righ = NULL;
n7 -> left = NULL; n7 -> righ = NULL;
n8 -> left = n9; n8 -> righ = na;
n9 -> left = NULL; n9 -> righ = nb;
na -> left = NULL; na -> righ = nc;
nb -> left = NULL; nb -> righ = NULL;
nc -> left = NULL; nc -> righ = NULL;
btr = n1;
}
pstack * stc = NULL;
void postorder(btree * root)
{
assert(root != NULL);
node * ptr = root;
pstack_push( & stc, ptr);
short flag;
while (pstack_hasmore(stc)) {
if (ptr == NULL && pstack_hasmore(stc)) {
if (flag == 0 ) { /* a left node is accessed */
ptr = pstack_top(stc);
if (ptr -> righ != NULL) { /* stack right node */
ptr = ptr -> righ;
pstack_push( & stc, ptr);
flag = 1 ; /* made a right move */
}
else {
pstack_pop( & stc); /* no right node */
printf( " %d " , ptr -> data);
if (pstack_isempty(stc)) break ;
node * prt = pstack_top(stc); /* get parent node */
if (prt -> left != ptr) flag = 1 ; /* right node accessed */
ptr = NULL;
}
}
else { /* flag == 1 */
ptr = pstack_pop( & stc);
printf( " %d " , ptr -> data);
if (pstack_isempty(stc)) break ;
node * prt = pstack_top(stc); /* get parent */
if (prt -> left == ptr) flag = 0 ; /* left node accessed */
ptr = NULL;
}
continue ;
}
if (ptr -> left != NULL) {
ptr = ptr -> left;
pstack_push( & stc, ptr);
flag = 0 ; /* made a left move */
continue ;
}
if (ptr -> righ != NULL) {
ptr = ptr -> righ;
pstack_push( & stc, ptr);
flag = 1 ; /* made a right move */
continue ;
}
/* access the leaf node */
pstack_pop( & stc);
printf( " %d " , ptr -> data);
ptr = NULL; /* indicate to access next node */
}
puts( "" );
}
int main()
{
init();
postorder(btr);
pstack_free( & stc);
return 0 ;
}
My stdext.h for pstack implementation
#ifndef _STDEXT_H_
#define _STDEXT_H_
#include < stdbool.h >
#include < assert.h >
/* *
* ****************************************************************************
* By JonsenElizee
* ****************************************************************************
*/
/* *****************************************************************************
* bool
***************************************************************************** */
#undef null
#if defined(__cplusplus)
#define null 0
#else
#define null ((void *)0)
#endif
/* *****************************************************************************
* bool
***************************************************************************** */
// #define bool unsigned
/*
typedef unsigned bool;
#define false 0
#define true 1
*/
/* #include <stdbool.h> */
/* *****************************************************************************
* classic quick sort
***************************************************************************** */
void quicksort_char( char * str, int low, int hig)
{
if (low >= hig) return ;
int i = low, j = hig, key = str[low];
while (i < j)
{
while (str[j] > key) j -- ;
str[i ++ ] = str[j];
while (i <= j && str[i] <= key) i ++ ;
if (i < j) str[j -- ] = str[i];
else str[j] = key;
}
quicksort_char(str, low, j - 1 );
quicksort_char(str, j + 1 , hig);
return ;
}
/* *****************************************************************************
* enhanced quick sort
***************************************************************************** */
void enhanced_quicksort_char( char * str, int low, int hig)
{
if (low >= hig) { return ; }
int k = low, m = low + 1 , i = low + 1 , j = hig;
while (i <= hig && str[i] < str[k]) { i ++ ; m ++ ; }
while (j > low && str[j] >= str[k]) j -- ;
while (i ++ <= j) if (str[i] < str[k]) swap_char(str + m ++ , str + i);
swap_char(str + k, str + m - 1 );
enhanced_quicksort_char(str, low, m - 2 );
enhanced_quicksort_char(str, m, hig);
return ;
}
/* *****************************************************************************
* factorial
***************************************************************************** */
long long factorial( int n)
{
assert(n >= 0 && n <= 20 );
if (n == 0 ) return 1 ;
long long rtv = 1 ;
int i = 1 ;
while (i <= n) rtv *= i ++ ;
return rtv;
}
/* *****************************************************************************
* swap
***************************************************************************** */
/*
* if you use this macro, you can not use ++ or -- in the parameters as
* swap(ptr++, tmp++);
* if you really want to use ++ or -- in swap, please use swap_xxx functions.
*/
#define swap(a, b) if((a) != (b)) { (*(a)) ^= (*(b)); (*(b)) ^= (*(a)); (*(a)) ^= (*(b));}
void swap_char( char * a, char * b) { if (a != b) { * a ^= * b; * b ^= * a; * a ^= * b; }}
void swap_short( short * a, short * b) { if (a != b) { * a ^= * b; * b ^= * a; * a ^= * b; }}
void swap_unsigned(unsigned * a, unsigned * b) { if (a != b) { * a ^= * b; * b ^= * a; * a ^= * b; }}
void swap_int( int * a, int * b) { if (a != b) { * a ^= * b; * b ^= * a; * a ^= * b; }}
void swap_long( long * a, long * b) { if (a != b) { * a ^= * b; * b ^= * a; * a ^= * b; }}
/* *****************************************************************************
* plist
* used for pointers. never use this plist to store char, short, int or other
* nonpointers.
* if you really want store int data into plist, please define a struct as a
* package or a kind of encapsulation. then just store the pointer of struct.
***************************************************************************** */
typedef struct {
struct plist * next;
void * data; // to store the pointer.
} plist;
plist * plist_create() {
return NULL;
}
/*
* append node after last node
*/
bool plist_append(plist ** ptr, const void * data) {
assert(ptr != NULL);
plist * nod = (plist * )malloc( sizeof (plist));
if (nod == NULL) return false ; // failure!
nod -> next = NULL;
nod -> data = data;
if ( * ptr == NULL) * ptr = nod;
else {
plist * bak = * ptr;
while (( * ptr) -> next != NULL) * ptr = ( * ptr) -> next;
( * ptr) -> next = nod;
* ptr = bak;
}
return true ; // success!
}
/*
* insert new node with data at pos. pos starts with zero.
*/
bool plist_insert(plist ** ptr, const void * data, const int pos) {
assert(ptr != NULL && pos >= 0 );
plist * nod = (plist * )malloc( sizeof (plist));
if (nod == NULL) return false ; // failure!
nod -> next = * ptr;
nod -> data = data;
if (pos == 0 ) * ptr = nod;
else {
if ( * ptr == NULL) return false ;
plist * bak = * ptr;
int idx = pos;
while (( * ptr) -> next != NULL && idx -- > 1 ) * ptr = ( * ptr) -> next;
if (idx == 0 ) {
nod -> next = ( * ptr) -> next;
( * ptr) -> next = nod;
}
else {
* ptr = bak;
return false ;
}
* ptr = bak;
}
return true ; // success!
}
/*
* delete first node of list
*/
void * plist_pop(plist ** ptr) {
assert(ptr != NULL);
if ( * ptr == NULL) return NULL;
plist * hed = * ptr;
* ptr = ( * ptr) -> next;
void * rtv = hed -> data;
free(hed);
hed = NULL;
return rtv;
}
/*
* get next offset node
*/
plist * plist_getnode( const plist * ptr, const int offset) {
int idx = offset;
while (ptr -> next != NULL && idx -- > 0 ) ptr = ptr -> next;
if (idx == 0 ) return ptr;
else return NULL;
}
/*
* get data in next offset node
*/
void * plist_getdata( const plist * ptr, const int offset) {
int idx = offset;
while (ptr -> next != NULL && idx -- > 0 ) ptr = ptr -> next;
if (idx == 0 ) return ptr -> data;
else return NULL;
}
bool plist_isempty( const plist * ptr) {
return ptr == NULL ? true : false ;
}
bool plist_hasmore( const plist * ptr) {
return ptr == NULL ? false : true ;
}
size_t plist_size( const plist * ptr) {
size_t rtv = 0 ;
while (ptr != NULL) {
rtv ++ ;
ptr = ptr -> next;
}
return rtv;
}
void plist_free(plist ** ptr)
{
if (ptr == NULL || * ptr == NULL) return ;
plist * nod = * ptr;
plist * nxt = NULL;
while (nod != NULL) {
nxt = nod -> next;
free(nod);
nod = nxt;
}
* ptr = NULL;
}
/* *****************************************************************************
* pstack
* used for pointers. never use this pstack to store char, short, int or other
* nonpointers.
* if you really want store int data into pstack, please define a struct as a
* package or a kind of encapsulation. then just store the pointer of struct.
***************************************************************************** */
typedef struct {
struct pstack * next;
void * data; // to store the pointer.
} pstack;
pstack * pstack_create() {
return NULL;
}
bool pstack_push(pstack ** ptr, const void * data) {
pstack * nod = (pstack * )malloc( sizeof (pstack));
if (nod == NULL) return false ; // failure!
nod -> next = * ptr;
nod -> data = data;
* ptr = nod;
return true ; // success!
}
void * pstack_pop(pstack ** ptr) {
assert(ptr != NULL && * ptr != NULL);
pstack * top = * ptr;
void * rtv = top -> data;
* ptr = ( * ptr) -> next;
free(top);
return rtv;
}
void * pstack_top( const pstack * ptr) {
assert(ptr != NULL);
return ptr -> data;
}
bool pstack_isempty( const pstack * ptr) {
return ptr == NULL ? true : false ;
}
bool pstack_hasmore( const pstack * ptr) {
return ptr == NULL ? false : true ;
}
size_t pstack_size( const pstack * ptr) {
size_t rtv = 0 ;
while (ptr != NULL) {
rtv ++ ;
ptr = ptr -> next;
}
return rtv;
}
void pstack_free(pstack ** ptr)
{
if (ptr == NULL || * ptr == NULL) return ;
pstack * nod = * ptr;
pstack * nxt = NULL;
while (nod != NULL) {
nxt = nod -> next;
free(nod);
nod = nxt;
}
* ptr = NULL;
}
/* **************************************************************************** */
#endif /* _STDEXT_H_ */
#define _STDEXT_H_
#include < stdbool.h >
#include < assert.h >
/* *
* ****************************************************************************
* By JonsenElizee
* ****************************************************************************
*/
/* *****************************************************************************
* bool
***************************************************************************** */
#undef null
#if defined(__cplusplus)
#define null 0
#else
#define null ((void *)0)
#endif
/* *****************************************************************************
* bool
***************************************************************************** */
// #define bool unsigned
/*
typedef unsigned bool;
#define false 0
#define true 1
*/
/* #include <stdbool.h> */
/* *****************************************************************************
* classic quick sort
***************************************************************************** */
void quicksort_char( char * str, int low, int hig)
{
if (low >= hig) return ;
int i = low, j = hig, key = str[low];
while (i < j)
{
while (str[j] > key) j -- ;
str[i ++ ] = str[j];
while (i <= j && str[i] <= key) i ++ ;
if (i < j) str[j -- ] = str[i];
else str[j] = key;
}
quicksort_char(str, low, j - 1 );
quicksort_char(str, j + 1 , hig);
return ;
}
/* *****************************************************************************
* enhanced quick sort
***************************************************************************** */
void enhanced_quicksort_char( char * str, int low, int hig)
{
if (low >= hig) { return ; }
int k = low, m = low + 1 , i = low + 1 , j = hig;
while (i <= hig && str[i] < str[k]) { i ++ ; m ++ ; }
while (j > low && str[j] >= str[k]) j -- ;
while (i ++ <= j) if (str[i] < str[k]) swap_char(str + m ++ , str + i);
swap_char(str + k, str + m - 1 );
enhanced_quicksort_char(str, low, m - 2 );
enhanced_quicksort_char(str, m, hig);
return ;
}
/* *****************************************************************************
* factorial
***************************************************************************** */
long long factorial( int n)
{
assert(n >= 0 && n <= 20 );
if (n == 0 ) return 1 ;
long long rtv = 1 ;
int i = 1 ;
while (i <= n) rtv *= i ++ ;
return rtv;
}
/* *****************************************************************************
* swap
***************************************************************************** */
/*
* if you use this macro, you can not use ++ or -- in the parameters as
* swap(ptr++, tmp++);
* if you really want to use ++ or -- in swap, please use swap_xxx functions.
*/
#define swap(a, b) if((a) != (b)) { (*(a)) ^= (*(b)); (*(b)) ^= (*(a)); (*(a)) ^= (*(b));}
void swap_char( char * a, char * b) { if (a != b) { * a ^= * b; * b ^= * a; * a ^= * b; }}
void swap_short( short * a, short * b) { if (a != b) { * a ^= * b; * b ^= * a; * a ^= * b; }}
void swap_unsigned(unsigned * a, unsigned * b) { if (a != b) { * a ^= * b; * b ^= * a; * a ^= * b; }}
void swap_int( int * a, int * b) { if (a != b) { * a ^= * b; * b ^= * a; * a ^= * b; }}
void swap_long( long * a, long * b) { if (a != b) { * a ^= * b; * b ^= * a; * a ^= * b; }}
/* *****************************************************************************
* plist
* used for pointers. never use this plist to store char, short, int or other
* nonpointers.
* if you really want store int data into plist, please define a struct as a
* package or a kind of encapsulation. then just store the pointer of struct.
***************************************************************************** */
typedef struct {
struct plist * next;
void * data; // to store the pointer.
} plist;
plist * plist_create() {
return NULL;
}
/*
* append node after last node
*/
bool plist_append(plist ** ptr, const void * data) {
assert(ptr != NULL);
plist * nod = (plist * )malloc( sizeof (plist));
if (nod == NULL) return false ; // failure!
nod -> next = NULL;
nod -> data = data;
if ( * ptr == NULL) * ptr = nod;
else {
plist * bak = * ptr;
while (( * ptr) -> next != NULL) * ptr = ( * ptr) -> next;
( * ptr) -> next = nod;
* ptr = bak;
}
return true ; // success!
}
/*
* insert new node with data at pos. pos starts with zero.
*/
bool plist_insert(plist ** ptr, const void * data, const int pos) {
assert(ptr != NULL && pos >= 0 );
plist * nod = (plist * )malloc( sizeof (plist));
if (nod == NULL) return false ; // failure!
nod -> next = * ptr;
nod -> data = data;
if (pos == 0 ) * ptr = nod;
else {
if ( * ptr == NULL) return false ;
plist * bak = * ptr;
int idx = pos;
while (( * ptr) -> next != NULL && idx -- > 1 ) * ptr = ( * ptr) -> next;
if (idx == 0 ) {
nod -> next = ( * ptr) -> next;
( * ptr) -> next = nod;
}
else {
* ptr = bak;
return false ;
}
* ptr = bak;
}
return true ; // success!
}
/*
* delete first node of list
*/
void * plist_pop(plist ** ptr) {
assert(ptr != NULL);
if ( * ptr == NULL) return NULL;
plist * hed = * ptr;
* ptr = ( * ptr) -> next;
void * rtv = hed -> data;
free(hed);
hed = NULL;
return rtv;
}
/*
* get next offset node
*/
plist * plist_getnode( const plist * ptr, const int offset) {
int idx = offset;
while (ptr -> next != NULL && idx -- > 0 ) ptr = ptr -> next;
if (idx == 0 ) return ptr;
else return NULL;
}
/*
* get data in next offset node
*/
void * plist_getdata( const plist * ptr, const int offset) {
int idx = offset;
while (ptr -> next != NULL && idx -- > 0 ) ptr = ptr -> next;
if (idx == 0 ) return ptr -> data;
else return NULL;
}
bool plist_isempty( const plist * ptr) {
return ptr == NULL ? true : false ;
}
bool plist_hasmore( const plist * ptr) {
return ptr == NULL ? false : true ;
}
size_t plist_size( const plist * ptr) {
size_t rtv = 0 ;
while (ptr != NULL) {
rtv ++ ;
ptr = ptr -> next;
}
return rtv;
}
void plist_free(plist ** ptr)
{
if (ptr == NULL || * ptr == NULL) return ;
plist * nod = * ptr;
plist * nxt = NULL;
while (nod != NULL) {
nxt = nod -> next;
free(nod);
nod = nxt;
}
* ptr = NULL;
}
/* *****************************************************************************
* pstack
* used for pointers. never use this pstack to store char, short, int or other
* nonpointers.
* if you really want store int data into pstack, please define a struct as a
* package or a kind of encapsulation. then just store the pointer of struct.
***************************************************************************** */
typedef struct {
struct pstack * next;
void * data; // to store the pointer.
} pstack;
pstack * pstack_create() {
return NULL;
}
bool pstack_push(pstack ** ptr, const void * data) {
pstack * nod = (pstack * )malloc( sizeof (pstack));
if (nod == NULL) return false ; // failure!
nod -> next = * ptr;
nod -> data = data;
* ptr = nod;
return true ; // success!
}
void * pstack_pop(pstack ** ptr) {
assert(ptr != NULL && * ptr != NULL);
pstack * top = * ptr;
void * rtv = top -> data;
* ptr = ( * ptr) -> next;
free(top);
return rtv;
}
void * pstack_top( const pstack * ptr) {
assert(ptr != NULL);
return ptr -> data;
}
bool pstack_isempty( const pstack * ptr) {
return ptr == NULL ? true : false ;
}
bool pstack_hasmore( const pstack * ptr) {
return ptr == NULL ? false : true ;
}
size_t pstack_size( const pstack * ptr) {
size_t rtv = 0 ;
while (ptr != NULL) {
rtv ++ ;
ptr = ptr -> next;
}
return rtv;
}
void pstack_free(pstack ** ptr)
{
if (ptr == NULL || * ptr == NULL) return ;
pstack * nod = * ptr;
pstack * nxt = NULL;
while (nod != NULL) {
nxt = nod -> next;
free(nod);
nod = nxt;
}
* ptr = NULL;
}
/* **************************************************************************** */
#endif /* _STDEXT_H_ */
