Android_高清加载巨图方案 拒绝压缩图片
原文出处:http://blog.csdn.net/lmj623565791/article/details/49300989
一、概述
距离上一篇博客有段时间没更新了,主要是最近有些私事导致的,那么就先来一篇简单一点的博客脉动回来。
对于加载图片,大家都不陌生,一般为了尽可能避免OOM都会按照如下做法:
对于图片显示:根据需要显示图片控件的大小对图片进行压缩显示。
如果图片数量非常多:则会使用LruCache等缓存机制,将所有图片占据的内容维持在一个范围内。
其实对于图片加载还有种情况,就是单个图片非常巨大,并且还不允许压缩。比如显示:世界地图、清明上河图、微博长图等。
那么对于这种需求,该如何做呢?
首先不压缩,按照原图尺寸加载,那么屏幕肯定是不够大的,并且考虑到内存的情况,不可能一次性整图加载到内存中,所以肯定是局部加载,那么就需要用到一个类:
BitmapRegionDecoder
其次,既然屏幕显示不完,那么最起码要添加一个上下左右拖动的手势,让用户可以拖动查看。
那么综上,本篇博文的目的就是去自定义一个显示巨图的View,支持用户去拖动查看,大概的效果图如下:
好吧,这清明上河图太长了,想要观看全图,文末下载,图片在assets目录。当然如果你的图,高度也很大,肯定也是可以上下拖动的。
二、初识BitmapRegionDecoder
BitmapRegionDecoder主要用于显示图片的某一块矩形区域,如果你需要显示某个图片的指定区域,那么这个类非常合适。
对于该类的用法,非常简单,既然是显示图片的某一块区域,那么至少只需要一个方法去设置图片;一个方法传入显示的区域即可;详见:
BitmapRegionDecoder提供了一系列的newInstance方法来构造对象,支持传入文件路径,文件描述符,文件的inputstrem等。
例如:
BitmapRegionDecoder bitmapRegionDecoder = BitmapRegionDecoder.newInstance(inputStream, false);
上述解决了传入我们需要处理的图片,那么接下来就是显示指定的区域。
bitmapRegionDecoder.decodeRegion(rect, options)
参数一很明显是一个rect,参数二是BitmapFactory.Options,你可以控制图片的inSampleSize,inPreferredConfig等。
那么下面看一个超级简单的例子:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
|
package com.zhy.blogcodes.largeImage;
import android.graphics.Bitmap;
import android.graphics.BitmapFactory;
import android.graphics.BitmapRegionDecoder;
import android.graphics.Rect;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.widget.ImageView;
import com.zhy.blogcodes.R;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
public class LargeImageViewActivity extends AppCompatActivity
{
private ImageView mImageView;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState)
{
super
.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_large_image_view);
mImageView = (ImageView) findViewById(R.id.id_imageview);
try
{
InputStream inputStream = getAssets().open(
"tangyan.jpg"
);
//获得图片的宽、高
BitmapFactory.Options tmpOptions =
new
BitmapFactory.Options();
tmpOptions.inJustDecodeBounds =
true
;
BitmapFactory.decodeStream(inputStream,
null
, tmpOptions);
int width = tmpOptions.outWidth;
int height = tmpOptions.outHeight;
//设置显示图片的中心区域
BitmapRegionDecoder bitmapRegionDecoder = BitmapRegionDecoder.newInstance(inputStream,
false
);
BitmapFactory.Options options =
new
BitmapFactory.Options();
options.inPreferredConfig = Bitmap.Config.RGB_565;
Bitmap bitmap = bitmapRegionDecoder.decodeRegion(
new
Rect(width / 2 - 100, height / 2 - 100, width / 2 + 100, height / 2 + 100), options);
mImageView.setImageBitmap(bitmap);
}
catch
(IOException e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
|
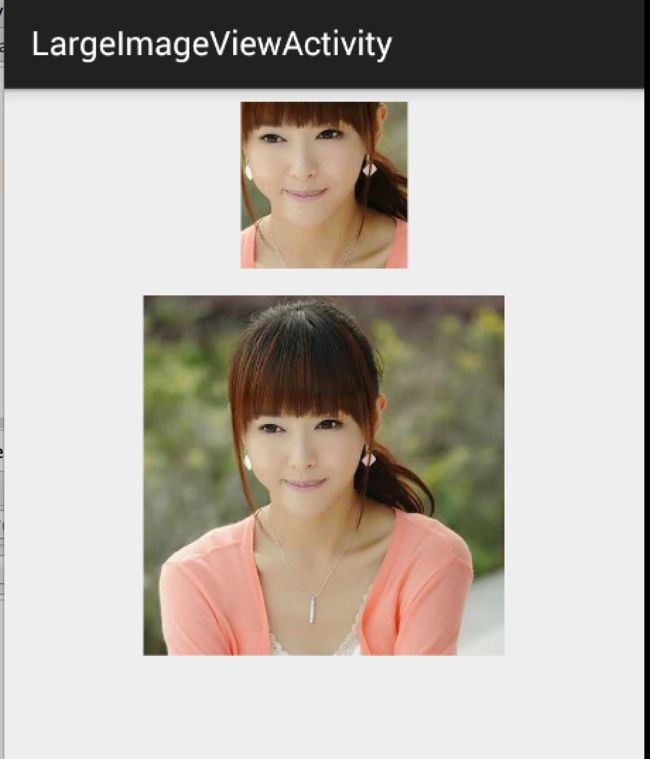
上面的小图显示的即为下面的大图的中间区域。
ok,那么目前我们已经了解了BitmapRegionDecoder的基本用户,那么往外扩散,我们需要自定义一个控件去显示巨图就很简单了,首先Rect的范围就是我们View的大小,然后根据用户的移动手势,不断去更新我们的Rect的参数即可。
三、自定义显示大图控件
根据上面的分析呢,我们这个自定义控件思路就非常清晰了:
提供一个设置图片的入口
重写onTouchEvent,在里面根据用户移动的手势,去更新显示区域的参数
每次更新区域参数后,调用invalidate,onDraw里面去regionDecoder.decodeRegion拿到bitmap,去draw
理清了,发现so easy,下面上代码:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
|
package com.zhy.blogcodes.largeImage.view;
import android.content.Context;
import android.graphics.Bitmap;
import android.graphics.BitmapFactory;
import android.graphics.BitmapRegionDecoder;
import android.graphics.Canvas;
import android.graphics.Rect;
import android.util.AttributeSet;
import android.view.MotionEvent;
import android.view.View;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
/**
* Created by zhy on 15/5/16.
*/
public class LargeImageView extends View
{
private BitmapRegionDecoder mDecoder;
/**
* 图片的宽度和高度
*/
private int mImageWidth, mImageHeight;
/**
* 绘制的区域
*/
private volatile Rect mRect =
new
Rect();
private MoveGestureDetector mDetector;
private static final BitmapFactory.Options options =
new
BitmapFactory.Options();
static
{
options.inPreferredConfig = Bitmap.Config.RGB_565;
}
public void setInputStream(InputStream is)
{
try
{
mDecoder = BitmapRegionDecoder.newInstance(is,
false
);
BitmapFactory.Options tmpOptions =
new
BitmapFactory.Options();
// Grab the bounds for the scene dimensions
tmpOptions.inJustDecodeBounds =
true
;
BitmapFactory.decodeStream(is,
null
, tmpOptions);
mImageWidth = tmpOptions.outWidth;
mImageHeight = tmpOptions.outHeight;
requestLayout();
invalidate();
}
catch
(IOException e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
} finally
{
try
{
if
(is !=
null
) is.close();
}
catch
(Exception e)
{
}
}
}
public void init()
{
mDetector =
new
MoveGestureDetector(getContext(),
new
MoveGestureDetector.SimpleMoveGestureDetector()
{
@Override
public boolean onMove(MoveGestureDetector detector)
{
int moveX = (int) detector.getMoveX();
int moveY = (int) detector.getMoveY();
if
(mImageWidth > getWidth())
{
mRect.offset(-moveX, 0);
checkWidth();
invalidate();
}
if
(mImageHeight > getHeight())
{
mRect.offset(0, -moveY);
checkHeight();
invalidate();
}
return
true
;
}
});
}
private void checkWidth()
{
Rect rect = mRect;
int imageWidth = mImageWidth;
int imageHeight = mImageHeight;
if
(rect.right > imageWidth)
{
rect.right = imageWidth;
rect.left = imageWidth - getWidth();
}
if
(rect.left < 0)
{
rect.left = 0;
rect.right = getWidth();
}
}
private void checkHeight()
{
Rect rect = mRect;
int imageWidth = mImageWidth;
int imageHeight = mImageHeight;
if
(rect.bottom > imageHeight)
{
rect.bottom = imageHeight;
rect.top = imageHeight - getHeight();
}
if
(rect.top < 0)
{
rect.top = 0;
rect.bottom = getHeight();
}
}
public LargeImageView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs)
{
super
(context, attrs);
init();
}
@Override
public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent event)
{
mDetector.onToucEvent(event);
return
true
;
}
@Override
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas)
{
Bitmap bm = mDecoder.decodeRegion(mRect, options);
canvas.drawBitmap(bm, 0, 0,
null
);
}
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec)
{
super
.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
int width = getMeasuredWidth();
int height = getMeasuredHeight();
int imageWidth = mImageWidth;
int imageHeight = mImageHeight;
//默认直接显示图片的中心区域,可以自己去调节
mRect.left = imageWidth / 2 - width / 2;
mRect.top = imageHeight / 2 - height / 2;
mRect.right = mRect.left + width;
mRect.bottom = mRect.top + height;
}
}
|
根据上述源码:
setInputStream里面去获得图片的真实的宽度和高度,以及初始化我们的mDecoder
onMeasure里面为我们的显示区域的rect赋值,大小为view的尺寸
onTouchEvent里面我们监听move的手势,在监听的回调里面去改变rect的参数,以及做边界检查,最后invalidate
在onDraw里面就是根据rect拿到bitmap,然后draw了
ok,上面并不复杂,不过大家有没有注意到,这个监听用户move手势的代码写的有点奇怪,恩,这里模仿了系统的ScaleGestureDetector,编写了MoveGestureDetector,代码如下:
MoveGestureDetector
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
|