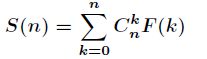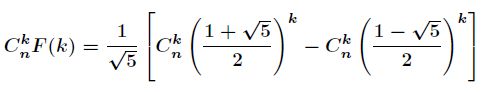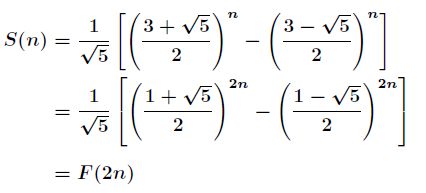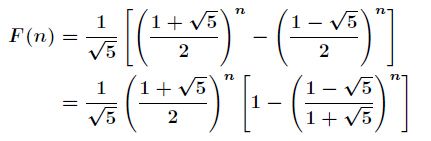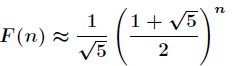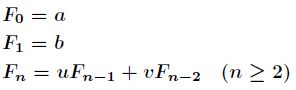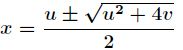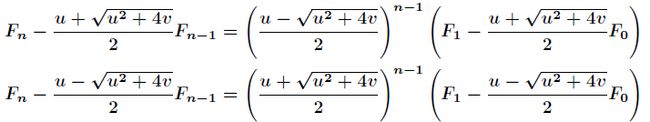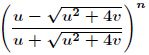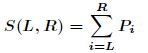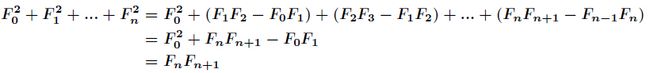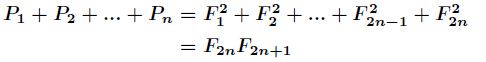斐波那契数列初级版
从今天开始,我会介绍一些关于斐波那契数列在ACM竞赛中的典型题目,以便广大的ACMer能从中受益,能更好地
掌握它,本文名为斐波那契数列初级版,以后还会有斐波那契数列终极版。接下来让我们一起走进斐波那契数列
的世界吧!
题目:http://acm.nefu.edu.cn/JudgeOnline/problemshow.php?problem_id=462
题意:已知![]() 是斐波那契数列,求如下表达式的值。
是斐波那契数列,求如下表达式的值。
分析:我们知道斐波那契数列的公式是
那么得到
进一步有
通过二项式定理,知道
那么最终得到
题目:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=1568
分析:题意是求斐波那契数列的前4位。根据斐波那契数列的公式,可以得到
很明显,当![]() 足够大时,得到
足够大时,得到
代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <math.h>
using namespace std;
const int N = 25;
int fac[N] = {0, 1, 1};
int main()
{
int n;
for(int i=3; i<22; i++)
fac[i] = fac[i-1] + fac[i-2];
while(cin>>n)
{
if(n <= 20)
{
cout<<fac[n]<<endl;
continue;
}
double bit = -0.5 * log10(5.0) + n * log10((sqrt(5.0) + 1) / 2.0);
bit = bit - floor(bit);
bit = pow(10.0, bit);
while(bit < 1000) bit *= 10.0;
printf("%d\n", (int)bit);
}
return 0;
}
题目:http://acm.nefu.edu.cn/JudgeOnline/problemshow.php?problem_id=461
题意:广义斐波那契数列的定义如下
这里![]() 是实数,
是实数,![]() 是正整数,给定
是正整数,给定![]() ,求
,求![]() 的位数。
的位数。
分析:广义斐波那契数列是可以推出公式的,接下来,我将会详细写出公式的推导过程
根据![]() ,知道对应的特征方程为
,知道对应的特征方程为![]() ,解之得
,解之得
然后可以写出
两式联立消去![]() ,得到
,得到
再进一步得到
针对本题来说,在![]() 大于200的情况下
大于200的情况下
近似为零,所以最终得到
接下来就可以根据上述方程求![]() 的位数了。
的位数了。
代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <math.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
int main()
{
LL n, a, b, u, v;
while(cin>>n>>a>>b>>u>>v)
{
double t = sqrt(u * u + 4 * v);
double p = (u + t) / 2.0;
double q = (u - t) / 2.0;
double ans = n * log10(p) + log10(b - q * a) - log10(t);
cout<<(LL)ans + 1<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
题目:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=2814
题意:已知![]() 是斐波那契数列,给定
是斐波那契数列,给定![]() ,求
,求![]() 的值,其中。
的值,其中。
分析:本题由于![]() 比较小,可以直接暴力找循环节,然后再通过指数循环节进行降幂即可。
比较小,可以直接暴力找循环节,然后再通过指数循环节进行降幂即可。
代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdio.h>
using namespace std;
typedef unsigned long long LL;
LL f[5500];
int search(int c)
{
f[0] = 0;
f[1] = 1;
int loop = 0;
for(int i = 2; i < 2005; i++)
{
f[i] = (f[i-1] + f[i-2]) % c;
if(f[i] == 1 && f[i-1] == 0)
{
loop = i;
break;
}
}
return loop - 1;
}
int phi(int n)
{
int rea = n;
for(int i = 2; i * i <= n; i++)
{
if(n % i == 0)
{
rea = rea - rea / i;
while(n % i == 0) n /= i;
}
}
if(n > 1)
rea = rea - rea / n;
return rea;
}
LL multi(LL a, LL b, LL m)
{
LL ans = 0;
while(b)
{
if(b & 1)
{
ans = (ans + a) % m;
b--;
}
b >>= 1;
a = (a + a) % m;
}
return ans;
}
LL quick_mod(LL a, LL b, LL m)
{
LL ans = 1;
a %= m;
while(b)
{
if(b & 1)
{
ans = multi(ans, a, m);
b--;
}
b >>= 1;
a = multi(a, a, m);
}
return ans;
}
int main()
{
int T;
scanf("%d", &T);
for(int i = 1; i <= T; i++)
{
int c;
LL a, b, n;
scanf("%I64u %I64u %I64u %d", &a, &b, &n, &c);
printf("Case %d: ",i);
if(c == 1)
{
puts("0");
continue;
}
int p = phi(c);
int loop1 = search(c);
LL t1 = quick_mod(a, b, loop1);
LL tmp1 = f[t1] % c;
int loop2 = search(p);
LL t2 = quick_mod(a, b, loop2);
LL tmp2 = f[t2] % p;
tmp2 = quick_mod(tmp2, n - 1, p);
tmp2 += p;
tmp1 = quick_mod(tmp1, tmp2, c);
printf("%I64u\n", tmp1);
}
return 0;
}
题目:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=3936
题意:已知![]() 是斐波那契数列,
是斐波那契数列,![]() ,给定
,给定![]() ,求下面表达式的值
,求下面表达式的值
分析:首先我们要认识两个重要的性质
![]()
推导过程如下
因为![]() ,那么
,那么![]() ,依次累加得到
,依次累加得到
![]()
根据上述的两个性质,可以得到
那么最终得到
![]()
到了这里,剩下的仅仅是矩阵快速幂而已。
题目:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=1316
题意:给定两个数![]() 和
和![]() ,其中
,其中![]() ,求在区间
,求在区间![]() 内有多少个斐波数。
内有多少个斐波数。
分析:先预处理出一定范围内的斐波数,然后再做两次比较就可以了。比较简单,代码省略。
题目:http://codeforces.com/contest/318/problem/C
题意:给定一对![]() ,每次可以用
,每次可以用![]() 去替换
去替换![]() 或
或![]() ,使得最后
,使得最后![]() 和
和![]() 中至少有一个大于等于
中至少有一个大于等于![]() ,求最少的替换
,求最少的替换
操作数。
分析:模拟一下,每次用![]() 去替换
去替换![]() 和
和![]() 中最小的那个,会看出与斐波那契数列有关。
中最小的那个,会看出与斐波那契数列有关。
代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdio.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
const int N = 95;
LL dp[N];
void Init()
{
dp[0] = 0;
dp[1] = 1;
for(int i = 2; i < N; i++)
dp[i] = dp[i - 1] + dp[i - 2];
}
LL Find(LL x, LL y, LL m, LL t)
{
LL ans = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < N - 1; i++)
{
if(x * dp[i] + y * dp[i + 1] >= m)
{
ans = i;
break;
}
}
ans += t;
return ans;
}
int main()
{
Init();
LL x, y, m;
while(cin>>x>>y>>m)
{
if(x > y) swap(x, y);
if(x >= m || y >= m)
{
puts("0");
continue;
}
if(x <= 0 && y <= 0)
{
if(y >= m) puts("0");
else puts("-1");
continue;
}
LL t = 0;
if(x < 0)
{
t = -x / y + 1;
x += t * y;
}
LL ans = Find(x, y, m, t);
cout<<ans<<endl;
}
return 0;
}