【SpringMVC框架】注解的处理器映射器和适配器配置
下面我们来探讨注解的处理器映射器和适配器
1.注解的处理器映射器和适配器
在spring3.1之前使用org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.annotation.DefaultAnnotationHandlerMapping注解映射器。
在spring3.1之后使用org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerMapping注解映射器。
在spring3.1之前使用org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.annotation.AnnotationMethodHandlerAdapter注解适配器。
在spring3.1之后使用org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerAdapter注解适配器。
2.配置注解映射器和适配器。
在springmvc.xml中写:
下面的开发可能就与非注解的产生了翻天覆地的变化了
3.开发注解Handler
使用注解的映射器和注解的适配器。(注解的映射器和注解的适配器必须配对使用)
ItemsController3:
这个注解的Handler的好处还有可以在类中在添加其他的方法,如商品添加、商品删除等。
5.3在spring容器中加载Handler
看一下最终的springmvc.xml:
5.4部署调试
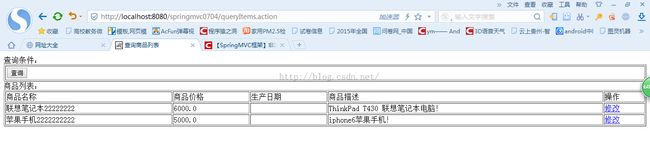
访问:http://localhost:8080/springmvcfirst1208/queryItems.action
1.注解的处理器映射器和适配器
在spring3.1之前使用org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.annotation.DefaultAnnotationHandlerMapping注解映射器。
在spring3.1之后使用org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerMapping注解映射器。
在spring3.1之前使用org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.annotation.AnnotationMethodHandlerAdapter注解适配器。
在spring3.1之后使用org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerAdapter注解适配器。
2.配置注解映射器和适配器。
在springmvc.xml中写:
<!-- 注解映射器 -->
<bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerMapping"/>
<!-- 注解适配器 -->
<bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerAdapter"/>
<!-- 使用mvc:annotation-driven代替上边注解映射器和注解适配器配置
mvc:annotation-driven默认加载很多的参数绑定方法,
比如json转换解析器就默认加载了,如果使用mvc:annotation-driven就不用配置上边的
RequestMappingHandlerMapping和RequestMappingHandlerAdapter
实际开发时使用mvc:annotation-driven-->
<!-- <mvc:annotation-driven></mvc:annotation-driven>-->
下面的开发可能就与非注解的产生了翻天覆地的变化了
3.开发注解Handler
使用注解的映射器和注解的适配器。(注解的映射器和注解的适配器必须配对使用)
ItemsController3:
package cn.edu.hpu.ssm.controller;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.ModelAndView;
import cn.edu.hpu.ssn.po.Items;
//注解的Handler类
//使用@Controller来标识它是一个控制器
@Controller
public class ItemsController3 {
//商品查询列表
//@RequestMapping实现 对queryItems方法和url进行映射,一个方法对应一个url
//一般建议将url和方法写成一样
@RequestMapping("/queryItems")
public ModelAndView queryItems()throws Exception{
//调用Service查找数据库,查询商品列表,这里使用静态数据模拟
List<Items> itemsList=new ArrayList<Items>();
//向List中填充静态数据
Items items_1 = new Items();
items_1.setName("联想笔记本22222222");
items_1.setPrice(6000f);
items_1.setDetail("ThinkPad T430 联想笔记本电脑!");
Items items_2 = new Items();
items_2.setName("苹果手机22222222");
items_2.setPrice(5000f);
items_2.setDetail("iphone6苹果手机!");
itemsList.add(items_1);
itemsList.add(items_2);
//返回ModelAndView
ModelAndView modelAndView=new ModelAndView();
//相当于request的setAttribut,在jsp页面中通过这个来取数据
modelAndView.addObject("itemsList",itemsList);
//指定视图
modelAndView.setViewName("/WEB-INF/jsp/items/itemsList.jsp");
return modelAndView;
}
//定义其它方法
//商品添加
//商品删除
}
这个注解的Handler的好处还有可以在类中在添加其他的方法,如商品添加、商品删除等。
5.3在spring容器中加载Handler
<!-- 对于注解的Handler可以单个配置, 实际开发中建议使用扫描组件,因为一个一个配bean太麻烦 --> <!-- <bean class="cn.edu.hpu.ssm.controller.ItemsController3"></bean>--> <!-- 可以扫描controller、service、... 这里让扫描controller,指定controller的包--> <context:component-scan base-package="cn.edu.hpu.ssm.controller"></context:component-scan>
看一下最终的springmvc.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:mvc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.2.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc
http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc-3.2.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-3.2.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-3.2.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx-3.2.xsd ">
<!-- 对于注解的Handler可以单个配置,
实际开发中建议使用扫描组件,因为一个一个配bean太麻烦 -->
<!-- <bean class="cn.edu.hpu.ssm.controller.ItemsController3"></bean>-->
<!-- 可以扫描controller、service、...
这里让扫描controller,指定controller的包-->
<context:component-scan base-package="cn.edu.hpu.ssm.controller"></context:component-scan>
<!-- 注解映射器 -->
<bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerMapping"/>
<!-- 注解适配器 -->
<bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerAdapter"/>
<!-- 使用mvc:annotation-driven代替上边注解映射器和注解适配器配置
mvc:annotation-driven默认加载很多的参数绑定方法,
比如json转换解析器就默认加载了,如果使用mvc:annotation-driven就不用配置上边的
RequestMappingHandlerMapping和RequestMappingHandlerAdapter
实际开发时使用mvc:annotation-driven-->
<!-- <mvc:annotation-driven></mvc:annotation-driven>-->
<!-- 视图解析器
解析jsp解析,默认使用jstl标签,classpath下的得有jstl的包
-->
<bean
class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver">
</bean>
</beans>
5.4部署调试
访问:http://localhost:8080/springmvcfirst1208/queryItems.action
访问结果如图
下一篇总结我们来分析一下springmvc中一些源码的分析
转载请注明出处:http://blog.csdn.net/acmman/article/details/46980427