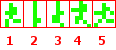Android游戏开发十日通(4)-行走,跳跃,碰撞检测
提要
经过前面的三篇文章,我们已经对libgdx有了一定的了解,并且搭建了一个简单的游戏场景,下面我们就继续在之前场景上添加更多的元素。
今天要实现的是精灵的行走、跳跃动画,还有碰撞检测。
行走
今天要实现的东西都是基于物理和数学的原理,首先我们来分析一下行走。
游戏中的动画都是帧动画,比如对Bob的行走一步的动画分解:
当这个序列连续播放的时候,就有了行走的效果。
之前已经有了移动的效果,所以只要在移动的时候循环播放动画就可以了。
现在需要的是决定帧的持续时间。
假设游戏渲染的是60FPS, 那么一帧的持续时间就是1/60s = 0.016 s。
对于一个成年人,每分钟大约走180步,那么每秒走的步数就是180/60 = 3,需要播放的帧为3×5 = 15.
那么每一帧持续时间就是1/15 = 0.066s.及66毫秒,即人物在运动的时候只要以66ms/帧对速度播放帧序列,就可以产生行走的效果了。
下面是代码实现。
首先是加载贴图。
和上一篇不同,这里用的是一次性加载贴图的方式,算是对游戏的一种优化。
需要和贴图textures.png一起添加到Android工程的asset/image/textures文件下的还有一个textures.pack文件,类似于一个xml,用于读取序列。
textures.png format: RGBA8888 filter: Nearest,Nearest repeat: none block rotate: false xy: 1, 11 size: 48, 48 orig: 48, 48 offset: 0, 0 index: -1 bob-01 rotate: false xy: 51, 31 size: 24, 28 orig: 24, 28 offset: 0, 0 index: -1 /*..omit..*/
接下来需要修改Bob类。
添加一个statetime成员用于记录Bob生存的时间,后面会用它来决定显示帧序列的哪一帧。
package com.me.testgdxgame.model;
import com.badlogic.gdx.math.Rectangle;
import com.badlogic.gdx.math.Vector2;
public class Bob {
public enum State {
IDLE, WALKING, JUMPING, DYING
}
public static final float SPEED = 4f; // unit per second
static final float JUMP_VELOCITY = 1f;
public static final float SIZE = 0.5f; // half a unit
Vector2 position = new Vector2();
Vector2 acceleration = new Vector2();
Vector2 velocity = new Vector2();
Rectangle bounds = new Rectangle();
State state = State.IDLE;
boolean facingLeft = true;
float stateTime = 0;
public Bob(Vector2 position) {
this.position = position;
this.bounds.height = SIZE;
this.bounds.width = SIZE;
}
public boolean isFacingLeft() {
return facingLeft;
}
public void setFacingLeft(boolean facingLeft) {
this.facingLeft = facingLeft;
}
public Vector2 getPosition() {
return position;
}
public Vector2 getAcceleration() {
return acceleration;
}
public Vector2 getVelocity() {
return velocity;
}
public Rectangle getBounds() {
return bounds;
}
public State getState() {
return state;
}
public void setState(State newState) {
this.state = newState;
}
public float getStateTime() {
return stateTime;
}
public void update(float delta) {
stateTime += delta;
position.add(velocity.cpy().mul(delta));
}
}
在libgdx中用于处理这种序列图的工具类是TextureAtlas。
getKeyFrame用于获取动画中的关键帧。
修改WorldRender类。
package com.me.testgdxgame.view;
import com.me.testgdxgame.*;
import com.me.testgdxgame.model.Block;
import com.me.testgdxgame.model.Bob;
import com.me.testgdxgame.model.Bob.State;
import com.me.testgdxgame.model.World;
import com.badlogic.gdx.Gdx;
import com.badlogic.gdx.graphics.Color;
import com.badlogic.gdx.graphics.GL10;
import com.badlogic.gdx.graphics.OrthographicCamera;
import com.badlogic.gdx.graphics.Texture;
import com.badlogic.gdx.graphics.g2d.Animation;
import com.badlogic.gdx.graphics.g2d.SpriteBatch;
import com.badlogic.gdx.graphics.g2d.TextureAtlas;
import com.badlogic.gdx.graphics.g2d.TextureRegion;
import com.badlogic.gdx.graphics.glutils.ShapeRenderer;
import com.badlogic.gdx.graphics.glutils.ShapeRenderer.ShapeType;
import com.badlogic.gdx.math.Rectangle;
public class WorldRenderer {
private World world;
private OrthographicCamera cam;
private static final float RUNNING_FRAME_DURATION = 0.06f;
private SpriteBatch spriteBatch;
private boolean debug=false;
private int width;
private int height;
private float ppuX; // pixels per unit on the X axis
private float ppuY; // pixels per unit on the Y axis
private static final float CAMERA_WIDTH = 10f;
private static final float CAMERA_HEIGHT = 7f;
/** Textures **/
private TextureRegion bobIdleLeft;
private TextureRegion bobIdleRight;
private TextureRegion blockTexture;
private TextureRegion bobFrame;
/** Animations **/
private Animation walkLeftAnimation;
private Animation walkRightAnimation;
/** for debug rendering **/
ShapeRenderer debugRenderer = new ShapeRenderer();
public WorldRenderer(World world) {
this.world = world;
this.cam = new OrthographicCamera(10, 7);
this.cam.position.set(5, 3.5f, 0);
this.cam.update();
spriteBatch=new SpriteBatch();
loadTextures();
}
public void setSize (int w, int h) {
this.width = w;
this.height = h;
ppuX = (float)width / CAMERA_WIDTH;
ppuY = (float)height / CAMERA_HEIGHT;
}
private void loadTextures() {
TextureAtlas atlas = new TextureAtlas(Gdx.files.internal("images/textures/textures.pack"));
bobIdleLeft = atlas.findRegion("bob-01");
bobIdleRight = new TextureRegion(bobIdleLeft);
bobIdleRight.flip(true, false);
blockTexture = atlas.findRegion("block");
TextureRegion[] walkLeftFrames = new TextureRegion[5];
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
walkLeftFrames[i] = atlas.findRegion("bob-0" + (i + 2));
}
walkLeftAnimation = new Animation(RUNNING_FRAME_DURATION, walkLeftFrames);
TextureRegion[] walkRightFrames = new TextureRegion[5];
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
walkRightFrames[i] = new TextureRegion(walkLeftFrames[i]);
walkRightFrames[i].flip(true, false);
}
walkRightAnimation = new Animation(RUNNING_FRAME_DURATION, walkRightFrames);
}
public void render() {
spriteBatch.begin();
drawBlocks();
drawBob();
spriteBatch.end();
if(debug) drawDebug();
}
private void drawBlocks(){
for (Block block : world.getBlocks()) {
spriteBatch.draw(blockTexture, block.getPosition().x * ppuX, block.getPosition().y * ppuY, Block.SIZE * ppuX, Block.SIZE * ppuY);
}
}
private void drawBob(){
Bob bob = world.getBob();
bobFrame = bob.isFacingLeft() ? bobIdleLeft : bobIdleRight;
//spriteBatch.draw(bobIdleLeft, bob.getPosition().x * ppuX, bob.getPosition().y * ppuY, Bob.SIZE * ppuX, Bob.SIZE * ppuY);
if(bob.getState().equals(State.WALKING)){
bobFrame = bob.isFacingLeft() ? walkLeftAnimation.getKeyFrame(bob.getStateTime(),true):walkRightAnimation.getKeyFrame(bob.getStateTime(),true);
}
spriteBatch.draw(bobFrame, bob.getPosition().x * ppuX, bob.getPosition().y * ppuY, Bob.SIZE * ppuX, Bob.SIZE * ppuY);
}
private void drawDebug(){
// render blocks
debugRenderer.setProjectionMatrix(cam.combined);
debugRenderer.begin(ShapeType.Rectangle);
for (Block block : world.getBlocks()) {
Rectangle rect = block.getBounds();
float x1 = block.getPosition().x + rect.x;
float y1 = block.getPosition().y + rect.y;
debugRenderer.setColor(new Color(1, 0, 0, 1));
debugRenderer.rect(x1, y1, rect.width, rect.height);
}
// render Bob
Bob bob = world.getBob();
Rectangle rect = bob.getBounds();
float x1 = bob.getPosition().x + rect.x;
float y1 = bob.getPosition().y + rect.y;
debugRenderer.setColor(new Color(0, 1, 0, 1));
debugRenderer.rect(x1, y1, rect.width, rect.height);
debugRenderer.end();
}
}
跑一下mian.java,键盘左右键就可以控制小人跑了。
跳跃
首先来复习一下初中的牛顿三定律...
第一定律:倘物体处于静止状态,或呈等速直线运动,只要没外力作用,物体将保持静止状态,或呈等速直线运动之状态。这定律又称为惯性定律。
第二定律:物体的加速度,与所受的净外力成正比。加速度的方向与净外力的方向相同。即 ;其中,是加速度, 是净外力, 是质量。
第三定律:两个物体的相互作用力总是大小相等,方向相反,同时出现或消失。强版第三定律还额外要求两支作用力的方向都处于同一直线。
第二定律:物体的加速度,与所受的净外力成正比。加速度的方向与净外力的方向相同。即 ;其中,是加速度, 是净外力, 是质量。
第三定律:两个物体的相互作用力总是大小相等,方向相反,同时出现或消失。强版第三定律还额外要求两支作用力的方向都处于同一直线。
分析一下Bob的状态。
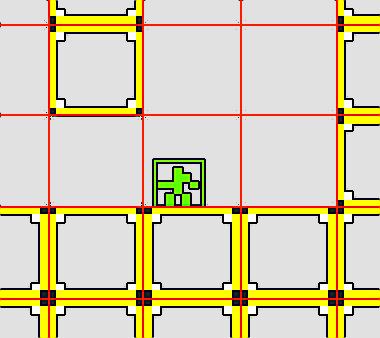
最初始的时候,Bob处于静止状态,受两个力,一个是重力,一个是地面的支持力,二力平衡。
上图左边是Bob处于起跳状态,此时Bob用力蹬地面,地面给的反作用力大于Bob受的重力,Bob离开地面,起跳。
上图右边是Bob处于空中的状态,只受重力影响。
要用到一个速度计算公式:
v=u+at
u为初速度,a为加速度,t为时间。
下面看具体的代码实现。只需要在WorldController中添加对应的按键事件处理就可以了。
添加一些静态变量作为世界的参数。修改inputProcess和update函数。
注意仔细分析跳跃处理的逻辑。
package com.me.testgdxgame.controller;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import com.me.testgdxgame.model.Bob;
import com.me.testgdxgame.model.Bob.State;
import com.me.testgdxgame.model.World;
public class WorldController {
enum Keys{
LEFT,RIGHT,JUMP,FIRE
}
private World world;
private Bob bob;
private long jumpPressedTime;
private boolean jumpingPressed;
static Map<Keys,Boolean> keys = new HashMap<WorldController.Keys,Boolean>();
static {
keys.put(Keys.LEFT, false);
keys.put(Keys.RIGHT, false);
keys.put(Keys.JUMP, false);
keys.put(Keys.FIRE, false);
};
private static final long LONG_JUMP_PRESS = 150l;
private static final float ACCELERATION = 20f;
private static final float GRAVITY = -20f;
private static final float MAX_JUMP_SPEED = 7f;
private static final float DAMP = 0.8f;
private static final float MAX_VEL = 4f;
private static final float WIDTH =10f;
public WorldController(World w){
world=w;
bob=world.getBob();
}
//Key presses and touches
public void leftPressed(){
keys.get(keys.put(Keys.LEFT, true));
}
public void rightPressed() {
keys.get(keys.put(Keys.RIGHT, true));
}
public void jumpPressed() {
keys.get(keys.put(Keys.JUMP, true));
}
public void firePressed() {
keys.get(keys.put(Keys.FIRE, false));
}
public void leftReleased() {
keys.get(keys.put(Keys.LEFT, false));
}
public void rightReleased() {
keys.get(keys.put(Keys.RIGHT, false));
}
public void jumpReleased() {
keys.get(keys.put(Keys.JUMP, false));
jumpingPressed = false;
}
public void fireReleased() {
keys.get(keys.put(Keys.FIRE, false));
}
public void update(float delta){
processInput();
bob.getAcceleration().y = GRAVITY;
bob.getAcceleration().mul(delta);
bob.getVelocity().add(bob.getAcceleration().x, bob.getAcceleration().y);
if (bob.getAcceleration().x == 0) bob.getVelocity().x *= DAMP;
if (bob.getVelocity().x > MAX_VEL) {
bob.getVelocity().x = MAX_VEL;
}
if (bob.getVelocity().x < -MAX_VEL) {
bob.getVelocity().x = -MAX_VEL;
}
bob.update(delta);
//Set Bob's state to State.IDLE when Bob touch edge
if (bob.getPosition().y < 0) {
bob.getPosition().y = 0f;
bob.setPosition(bob.getPosition());
if (bob.getState().equals(State.JUMPING)) {
bob.setState(State.IDLE);
}
}
if (bob.getPosition().x < 0) {
bob.getPosition().x = 0;
bob.setPosition(bob.getPosition());
if (!bob.getState().equals(State.JUMPING)) {
bob.setState(State.IDLE);
}
}
if (bob.getPosition().x > WIDTH - bob.getBounds().width ) {
bob.getPosition().x = WIDTH - bob.getBounds().width;
bob.setPosition(bob.getPosition());
if (!bob.getState().equals(State.JUMPING)) {
bob.setState(State.IDLE);
}
}
}
private boolean processInput(){
if (keys.get(Keys.JUMP)) {
if (!bob.getState().equals(State.JUMPING)) {
jumpingPressed = true;
jumpPressedTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
bob.setState(State.JUMPING);
bob.getVelocity().y = MAX_JUMP_SPEED;
} else {
if (jumpingPressed && ((System.currentTimeMillis() - jumpPressedTime) >= LONG_JUMP_PRESS)) {
jumpingPressed = false;
} else {
if (jumpingPressed) {
bob.getVelocity().y = MAX_JUMP_SPEED;
}
}
}
}
if(keys.get(Keys.LEFT)){
bob.setFacingLeft(true);
if(!bob.getState().equals(State.JUMPING)){
bob.setState(State.WALKING);
}
bob.getVelocity().x=-ACCELERATION;
}else if (keys.get(Keys.RIGHT)) {
// left is pressed
bob.setFacingLeft(false);
if(!bob.getState().equals(State.JUMPING)){
bob.setState(State.WALKING);
}
bob.getVelocity().x=ACCELERATION;
}else {
if(!bob.getState().equals(State.JUMPING)){
bob.setState(State.IDLE);
} ;
// acceleration is 0 on the x
bob.getAcceleration().x = 0;
}
return false;
}
}
在WorldRender中还需要添加与跳跃对应的纹理还有修改drawBob函数。
加载纹理:
private void loadTextures() {
TextureAtlas atlas = new TextureAtlas(Gdx.files.internal("images/textures/textures.pack"));
bobJumpLeft = atlas.findRegion("bob-up");
bobJumpRight = new TextureRegion(bobJumpLeft);
bobJumpRight.flip(true, false);
bobFallLeft=atlas.findRegion("bob-down");
bobFallRight = new TextureRegion(bobFallLeft);
bobFallRight.flip(true, false);
bobIdleLeft = atlas.findRegion("bob-01");
bobIdleRight = new TextureRegion(bobIdleLeft);
bobIdleRight.flip(true, false);
blockTexture = atlas.findRegion("block");
TextureRegion[] walkLeftFrames = new TextureRegion[5];
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
walkLeftFrames[i] = atlas.findRegion("bob-0" + (i + 2));
}
walkLeftAnimation = new Animation(RUNNING_FRAME_DURATION, walkLeftFrames);
TextureRegion[] walkRightFrames = new TextureRegion[5];
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
walkRightFrames[i] = new TextureRegion(walkLeftFrames[i]);
walkRightFrames[i].flip(true, false);
}
walkRightAnimation = new Animation(RUNNING_FRAME_DURATION, walkRightFrames);
}
drawBob函数
private void drawBob(){
Bob bob = world.getBob();
bobFrame = bob.isFacingLeft() ? bobIdleLeft : bobIdleRight;
if(bob.getState().equals(State.WALKING)) {
bobFrame = bob.isFacingLeft() ? walkLeftAnimation.getKeyFrame(bob.getStateTime(), true) : walkRightAnimation.getKeyFrame(bob.getStateTime(), true);
} else if (bob.getState().equals(State.JUMPING)) {
if (bob.getVelocity().y > 0) {
bobFrame = bob.isFacingLeft() ? bobJumpLeft : bobJumpRight;
} else {
bobFrame = bob.isFacingLeft() ? bobFallLeft : bobFallRight;
}
}
spriteBatch.draw(bobFrame, bob.getPosition().x * ppuX, bob.getPosition().y * ppuY, Bob.SIZE * ppuX, Bob.SIZE * ppuY);
}
运行一下:
碰撞检测
现在的demo是可以穿墙的-_-!,这里的碰撞检测指的是Bob与Blocks之间的碰撞,当Bob撞墙的时候,Bob需要停止前进跳跃或是落下。
最简单的方法就是每update一次就检测Bob与每一个Block是否相撞,当然效率会非常低。
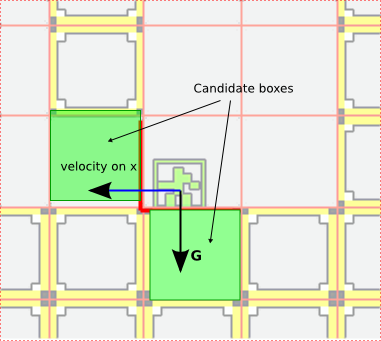
仔细来分析一下:每次与Bob可能发生碰撞的Block只有Bob身边的8块砖,那么在每次Update的时候与检测是否与身边的砖块相碰就可以了。
还可以再简单么?
看下面的图片。
假设Bob正在向右行走,那么在可能与Bob产生碰撞的Block中,只有下面的那个。所以,根据Bob当前的状态进行碰撞检测可以高效地进行碰撞检测。
我们用一个二维数组来保存地形,用于碰撞检测。
首先我们创建一个level,就是关卡,用world来装载,而不是直接在world里面生成。
package com.me.testgdxgame.model;
import com.badlogic.gdx.math.Vector2;
public class Level {
private int width;
private int height;
private Block[][] blocks;
public int getWidth() {
return width;
}
public void setWidth(int width) {
this.width = width;
}
public int getHeight() {
return height;
}
public void setHeight(int height) {
this.height = height;
}
public Block[][] getBlocks() {
return blocks;
}
public void setBlocks(Block[][] blocks) {
this.blocks = blocks;
}
public Level() {
loadDemoLevel();
}
public Block get(int x, int y) {
return blocks[x][y];
}
private void loadDemoLevel() {
width = 10;
height = 7;
blocks = new Block[width][height];
for (int col = 0; col < width; col++) {
for (int row = 0; row < height; row++) {
blocks[col][row] = null;
}
}
for (int col = 0; col < 10; col++) {
blocks[col][0] = new Block(new Vector2(col, 0));
blocks[col][6] = new Block(new Vector2(col, 6));
if (col > 2) {
blocks[col][1] = new Block(new Vector2(col, 1));
}
}
blocks[9][2] = new Block(new Vector2(9, 2));
blocks[9][3] = new Block(new Vector2(9, 3));
blocks[9][4] = new Block(new Vector2(9, 4));
blocks[9][5] = new Block(new Vector2(9, 5));
blocks[6][3] = new Block(new Vector2(6, 3));
blocks[6][4] = new Block(new Vector2(6, 4));
blocks[6][5] = new Block(new Vector2(6, 5));
}
}
World类做对应的修改:
package com.me.testgdxgame.model;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import com.badlogic.gdx.math.Rectangle;
import com.badlogic.gdx.math.Vector2;
import com.badlogic.gdx.utils.Array;
public class World {
/** Our player controlled hero **/
Bob bob;
/** A world has a level through which Bob needs to go through **/
Level level;
/** The collision boxes **/
Array<Rectangle> collisionRects = new Array<Rectangle>();
// Getters -----------
public Array<Rectangle> getCollisionRects() {
return collisionRects;
}
public Bob getBob() {
return bob;
}
public Level getLevel() {
return level;
}
/** Return only the blocks that need to be drawn **/
public List<Block> getDrawableBlocks(int width, int height) {
int x = (int)bob.getPosition().x - width;
int y = (int)bob.getPosition().y - height;
if (x < 0) {
x = 0;
}
if (y < 0) {
y = 0;
}
int x2 = x + 2 * width;
int y2 = y + 2 * height;
if (x2 > level.getWidth()) {
x2 = level.getWidth() - 1;
}
if (y2 > level.getHeight()) {
y2 = level.getHeight() - 1;
}
List<Block> blocks = new ArrayList<Block>();
Block block;
for (int col = x; col <= x2; col++) {
for (int row = y; row <= y2; row++) {
block = level.getBlocks()[col][row];
if (block != null) {
blocks.add(block);
}
}
}
return blocks;
}
// --------------------
public World() {
createDemoWorld();
}
private void createDemoWorld() {
bob = new Bob(new Vector2(7, 2));
level = new Level();
}
}
然后在WorldController中添加一个checkCollisionWithBlocks函数,函数里面首先检测X方向是否有碰撞,再检测Y方向是否有碰撞。
在update函数中,每运行一次就进行一次检测。
完整的WorldController类如下:
package com.me.testgdxgame.controller;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import com.badlogic.gdx.math.Rectangle;
import com.badlogic.gdx.utils.Array;
import com.badlogic.gdx.utils.Pool;
import com.me.testgdxgame.model.Block;
import com.me.testgdxgame.model.Bob;
import com.me.testgdxgame.model.Bob.State;
import com.me.testgdxgame.model.World;
public class WorldController {
enum Keys {
LEFT, RIGHT, JUMP, FIRE
}
private static final long LONG_JUMP_PRESS = 150l;
private static final float ACCELERATION = 20f;
private static final float GRAVITY = -20f;
private static final float MAX_JUMP_SPEED = 7f;
private static final float DAMP = 0.90f;
private static final float MAX_VEL = 4f;
private World world;
private Bob bob;
private long jumpPressedTime;
private boolean jumpingPressed;
private boolean grounded = false;
// This is the rectangle pool used in collision detection
// Good to avoid instantiation each frame
private Pool<Rectangle> rectPool = new Pool<Rectangle>() {
@Override
protected Rectangle newObject() {
return new Rectangle();
}
};
static Map<Keys, Boolean> keys = new HashMap<WorldController.Keys, Boolean>();
static {
keys.put(Keys.LEFT, false);
keys.put(Keys.RIGHT, false);
keys.put(Keys.JUMP, false);
keys.put(Keys.FIRE, false);
};
// Blocks that Bob can collide with any given frame
private Array<Block> collidable = new Array<Block>();
public WorldController(World world) {
this.world = world;
this.bob = world.getBob();
}
// ** Key presses and touches **************** //
public void leftPressed() {
keys.get(keys.put(Keys.LEFT, true));
}
public void rightPressed() {
keys.get(keys.put(Keys.RIGHT, true));
}
public void jumpPressed() {
keys.get(keys.put(Keys.JUMP, true));
}
public void firePressed() {
keys.get(keys.put(Keys.FIRE, false));
}
public void leftReleased() {
keys.get(keys.put(Keys.LEFT, false));
}
public void rightReleased() {
keys.get(keys.put(Keys.RIGHT, false));
}
public void jumpReleased() {
keys.get(keys.put(Keys.JUMP, false));
jumpingPressed = false;
}
public void fireReleased() {
keys.get(keys.put(Keys.FIRE, false));
}
/** The main update method **/
public void update(float delta) {
// Processing the input - setting the states of Bob
processInput();
// If Bob is grounded then reset the state to IDLE
if (grounded && bob.getState().equals(State.JUMPING)) {
bob.setState(State.IDLE);
}
// Setting initial vertical acceleration
bob.getAcceleration().y = GRAVITY;
// Convert acceleration to frame time
bob.getAcceleration().mul(delta);
// apply acceleration to change velocity
bob.getVelocity().add(bob.getAcceleration().x, bob.getAcceleration().y);
// checking collisions with the surrounding blocks depending on Bob's velocity
checkCollisionWithBlocks(delta);
// apply damping to halt Bob nicely
bob.getVelocity().x *= DAMP;
// ensure terminal velocity is not exceeded
if (bob.getVelocity().x > MAX_VEL) {
bob.getVelocity().x = MAX_VEL;
}
if (bob.getVelocity().x < -MAX_VEL) {
bob.getVelocity().x = -MAX_VEL;
}
// simply updates the state time
bob.update(delta);
}
/** Collision checking **/
private void checkCollisionWithBlocks(float delta) {
// scale velocity to frame units
bob.getVelocity().mul(delta);
// Obtain the rectangle from the pool instead of instantiating it
Rectangle bobRect = rectPool.obtain();
// set the rectangle to bob's bounding box
bobRect.set(bob.getBounds().x, bob.getBounds().y, bob.getBounds().width, bob.getBounds().height);
// we first check the movement on the horizontal X axis
int startX, endX;
int startY = (int) bob.getBounds().y;
int endY = (int) (bob.getBounds().y + bob.getBounds().height);
// if Bob is heading left then we check if he collides with the block on his left
// we check the block on his right otherwise
if (bob.getVelocity().x < 0) {
startX = endX = (int) Math.floor(bob.getBounds().x + bob.getVelocity().x);
} else {
startX = endX = (int) Math.floor(bob.getBounds().x + bob.getBounds().width + bob.getVelocity().x);
}
// get the block(s) bob can collide with
populateCollidableBlocks(startX, startY, endX, endY);
// simulate bob's movement on the X
bobRect.x += bob.getVelocity().x;
// clear collision boxes in world
world.getCollisionRects().clear();
// if bob collides, make his horizontal velocity 0
for (Block block : collidable) {
if (block == null) continue;
if (bobRect.overlaps(block.getBounds())) {
bob.getVelocity().x = 0;
world.getCollisionRects().add(block.getBounds());
break;
}
}
// reset the x position of the collision box
bobRect.x = bob.getPosition().x;
// the same thing but on the vertical Y axis
startX = (int) bob.getBounds().x;
endX = (int) (bob.getBounds().x + bob.getBounds().width);
if (bob.getVelocity().y < 0) {
startY = endY = (int) Math.floor(bob.getBounds().y + bob.getVelocity().y);
} else {
startY = endY = (int) Math.floor(bob.getBounds().y + bob.getBounds().height + bob.getVelocity().y);
}
populateCollidableBlocks(startX, startY, endX, endY);
bobRect.y += bob.getVelocity().y;
for (Block block : collidable) {
if (block == null) continue;
if (bobRect.overlaps(block.getBounds())) {
if (bob.getVelocity().y < 0) {
grounded = true;
}
bob.getVelocity().y = 0;
world.getCollisionRects().add(block.getBounds());
break;
}
}
// reset the collision box's position on Y
bobRect.y = bob.getPosition().y;
// update Bob's position
bob.getPosition().add(bob.getVelocity());
bob.getBounds().x = bob.getPosition().x;
bob.getBounds().y = bob.getPosition().y;
// un-scale velocity (not in frame time)
bob.getVelocity().mul(1 / delta);
}
/** populate the collidable array with the blocks found in the enclosing coordinates **/
private void populateCollidableBlocks(int startX, int startY, int endX, int endY) {
collidable.clear();
for (int x = startX; x <= endX; x++) {
for (int y = startY; y <= endY; y++) {
if (x >= 0 && x < world.getLevel().getWidth() && y >=0 && y < world.getLevel().getHeight()) {
collidable.add(world.getLevel().get(x, y));
}
}
}
}
/** Change Bob's state and parameters based on input controls **/
private boolean processInput() {
if (keys.get(Keys.JUMP)) {
if (!bob.getState().equals(State.JUMPING)) {
jumpingPressed = true;
jumpPressedTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
bob.setState(State.JUMPING);
bob.getVelocity().y = MAX_JUMP_SPEED;
grounded = false;
} else {
if (jumpingPressed && ((System.currentTimeMillis() - jumpPressedTime) >= LONG_JUMP_PRESS)) {
jumpingPressed = false;
} else {
if (jumpingPressed) {
bob.getVelocity().y = MAX_JUMP_SPEED;
}
}
}
}
if (keys.get(Keys.LEFT)) {
// left is pressed
bob.setFacingLeft(true);
if (!bob.getState().equals(State.JUMPING)) {
bob.setState(State.WALKING);
}
bob.getAcceleration().x = -ACCELERATION;
} else if (keys.get(Keys.RIGHT)) {
// left is pressed
bob.setFacingLeft(false);
if (!bob.getState().equals(State.JUMPING)) {
bob.setState(State.WALKING);
}
bob.getAcceleration().x = ACCELERATION;
} else {
if (!bob.getState().equals(State.JUMPING)) {
bob.setState(State.IDLE);
}
bob.getAcceleration().x = 0;
}
return false;
}
}
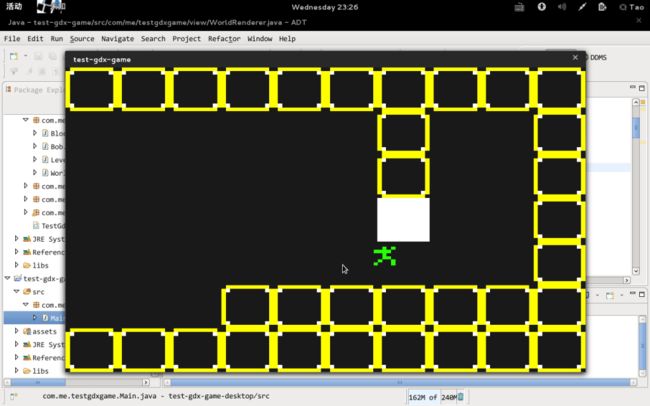
运行截图:
总结
这篇blog的内容有点多,需要多花时间去体会。
特别是碰撞检测,思路一定要缕清晰。
这个游戏也暂时告一段落了,主要原因是国外的那位大牛也没有更新此系列的文章了...
当然,游戏还在继续。
工程下载
参考:Getting Started in Android Game Development with libgdx-http://obviam.net/