Android 网络通讯、通信
网络操作是进行网络通信的安卓程序必不可少的一个重要部分,Android平台有三种网络接口可以使用,他们分别是:java.net.*(标准Java接口)、Org.apache HttpComponents接口和Android.net.*(Android网络接口)。当然还可以使用浏览器webkit来进行网络访问等。其中,前两个接口可以用来进行http、socket通讯,后一个接口主要是用来判断安卓设备网络连接状况的。所以,本节重点说一下前两个接口。
1、java.net.* HttpURLConnection接口
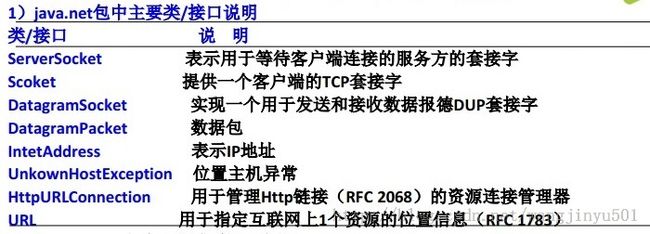
此接口提供与联网有关的类,包括流和数据包套接字、Internet协议、常见HTTP处理。如:创建URL以及URLConnection/HttpURLConnection对象、设置连接参数、连接服务器、向服务器写数据、从服务器读取数据等通信。下例为常见java.net包的Http例子:
HttpURLConnection是继承于URLConnection类,二者都是抽象类。其对象主要通过URL的openConnection方法获得。创建方法如下代码所示:
URL url = new URL("访问的url");
HttpURLConnection conn=(HttpURLConnection)url.openConnection(); 通过以下方法可以对请求的属性进行一些设置,如下所示:
//设置输入和输出流
conn.setDoOutput(true);
conn.setDoInput(true);
//设置请求方式为POST
conn.setRequestMethod("POST");
//POST请求不能使用缓存
urlConn.setUseCaches(false);
conn.connect();建立链接
//关闭连接
conn.disConnection(); HttpURLConnection默认使用GET方式,例如下面代码所示:
HttpURLConnection conn = (HttpURLConnection) url.openConnection(); //使用HttpURLConnection打开连接
int nRC = http.getResponseCode();//得到连接状态
if(nRC == HttpURLConnection.HTTP_OK){
InputStreamReader in = new InputStreamReader(urlConn.getInputStream());//得到读取的内容(流)
// 为输出创建BufferedReader
BufferedReader buffer = new BufferedReader(in);
String inputLine = null;
//使用循环来读取获得的数据
while (((inputLine = buffer.readLine()) != null))
{
//我们在每一行后面加上一个"\n"来换行
resultData += inputLine + "\n";
}
//关闭InputStreamReader
}
in.close();
//关闭http连接
conn.disconnect();
如果需要使用POST方式,则需要setRequestMethod设置。代码如下:
String httpUrl = "访问的url";
//获得的数据
String resultData = "";
URL url = null;
try
{
//构造一个URL对象
url = new URL(httpUrl);
}
catch (MalformedURLException e)
{
Log.e(DEBUG_TAG, "MalformedURLException");
}
if (url != null)
{
try
{
// 使用HttpURLConnection打开连接
HttpURLConnection conn = (HttpURLConnection) url.openConnection();
//因为这个是post请求,设立需要设置为true
conn.setDoOutput(true);
conn.setDoInput(true);
// 设置以POST方式
conn.setRequestMethod("POST");
// Post 请求不能使用缓存
conn.setUseCaches(false);
conn.setInstanceFollowRedirects(true);
// 配置本次连接的Content-type,配置为application/x-www-form-urlencoded的
conn.setRequestProperty("Content-Type","application/x-www-form-urlencoded");
// 连接,从postUrl.openConnection()至此的配置必须要在connect之前完成,
// 要注意的是connection.getOutputStream会隐含的进行connect。
conn.connect();
//DataOutputStream流
DataOutputStream out = new DataOutputStream(urlConn.getOutputStream());
//要上传的参数
String content = "par=" + URLEncoder.encode("ABCDEFG", "gb2312");
//将要上传的内容写入流中
out.writeBytes(content);
//刷新、关闭
out.flush();
out.close();
也可以对其进行通用属性的设定:
// 设置通用的请求属性
conn.setRequestProperty("accept", "*/*");
conn.setRequestProperty("connection", "Keep-Alive");
conn.setRequestProperty("user-agent",
"Mozilla/4.0 (compatible; MSIE 6.0; Windows NT 5.1; SV1)");
// 建立实际的连接
2、Apache Http Client
Apache Http Client是一个开源项目,功能更加完善,为客户端的Http编程提供高效、最新、功能丰富的工具包支持。它包含了get和post两种请求方式,下面分别举例:
get方式:
StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder();
HttpClient client = new DefaultHttpClient();
HttpGet httpGet = new HttpGet(URL);
try {
HttpResponse response = client.execute(httpGet);
StatusLine statusLine = response.getStatusLine();
int statusCode = statusLine.getStatusCode();
if (statusCode == 200) {
HttpEntity entity = response.getEntity();
if(entity!=null){
InputStream content = entity.getContent();
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(
new InputStreamReader(content));
String line;
while ((line = reader.readLine()) != null) {
stringBuilder.append(line);
}
}else{
Log.e("JSON", "Failed to download file");
}
} else {
Log.e("JSON", "Failed to download file");
}
} catch (ClientProtocolException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return stringBuilder.toString();
post方式:使用post方法进行参数传递时,需要使用NameValuePair来保存要传递的参数。另外,还需要设置所使用的字符集。代码如下所示:
String httpUrl = "http://192.168.1.110:8080/httppost";
//HttpPost连接对象
HttpPost httpRequest = new HttpPost(httpUrl);
//使用NameValuePair来保存要传递的Post参数
List<NameValuePair> params = new ArrayList<NameValuePair>();
//添加要传递的参数
params.add(new BasicNameValuePair("par", "HttpClient_android_Post"));
//设置字符集
HttpEntity httpentity = new UrlEncodedFormEntity(params, "gb2312");
//请求httpRequest
httpRequest.setEntity(httpentity);
//取得默认的HttpClient
HttpClient httpclient = new DefaultHttpClient();
//取得HttpResponse
HttpResponse httpResponse = httpclient.execute(httpRequest);
//HttpStatus.SC_OK表示连接成功
if (httpResponse.getStatusLine().getStatusCode() == HttpStatus.SC_OK)
{
String strResult = EntityUtils.toString(httpResponse.getEntity());
mTextView.setText(strResult);
}
else
{
mTextView.setText("请求错误!");
}
} HttpClient实际上是对Java提供方法的一些封装,在HttpURLConnection中的输入输出流操作,在这个接口中被统一封装成了HttpPost(HttpGet)和HttpResponse,这样,就减少了操作的繁琐性。