Android SurfaceFlinger对VSync信号的处理过程分析
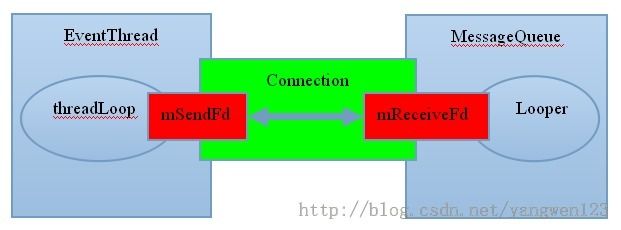
在Android SurfaceFlinger服务的消息循环过程源码分析中分析了SurfaceFlinger的消息循环过程,SurfaceFlinger通过维护一个消息队列来实现消息的异步处理。Android应用程序消息循环源码分析介绍了消息循环定义的Looper对象不仅可以处理Java层和C++层的消息,同时也可以监控用户添加的文件句柄。Android SurfaceFlinger服务的消息循环过程源码分析也介绍了SurfaceFlinger与EventThread线程间的VSync事件连接Connection的创建及注册到EventThread线程过程,同时将Connection中的Socket读端添加到SurfaceFlinger消息循环中监听。在Android VSync事件分发过程源码分析中介绍了EventThread线程负责分发VSync事件给已注册的Connection连接,下图就是SurfaceFlinger与EventThread之间的关系图:
上图显示了EventThread线程是通过Socket方式与SurfaceFlinger的消息循环通信的,EventThread线程是Server,往Socket的发送端写入VSync事件信息,SurfaceFlinger是Client,从Socket的接收端读取到VSync事件信息,从而响应VSync中断信号。在将Socket的接收端添加到SurfaceFlinger的消息循环Looper对象中时,注册了Socket接收端数据读取时的回调函数:
void MessageQueue::setEventThread(const sp<EventThread>& eventThread)
{
mEventThread = eventThread;
mEvents = eventThread->createEventConnection();
mEventTube = mEvents->getDataChannel();
mLooper->addFd(mEventTube->getFd(), 0, ALOOPER_EVENT_INPUT,MessageQueue::cb_eventReceiver, this);
}createEventConnection()用于创建一个事件连接Connection,通过调用Connection的getDataChannel()函数返回一个BitTube对象,这是对Socket通信方式的封装类,描述了VSync事件信息的数据通道。调用BitTube对象的getFd()函数既可得到创建的Socket的发送端句柄,然后调用Looper类提供的addFd()函数将Socket发送端句柄添加到SurfaceFlinger的消息循环Looper对象中监听,同时注册回调函数MessageQueue::cb_eventReceiver。通过Looper添加了一个fd,这实际上就是Socket pair中的一端。然后Looper将这个fd与其callback函数(即MessageQueue::cb_eventReceiver)加入全局的mRequests进行管理。这个Vector会集中所有需要监测的fd,这样当Looper进行pollInner时,只要Socket接收端有数据可以读取时,SurfaceFlinger消息循环自动调用该函数来处理VSync事件,addFd()函数的最后一个参数this指向当前SurfaceFlinger的消息队列MessageQueue对象。
int MessageQueue::cb_eventReceiver(int fd, int events, void* data) {
MessageQueue* queue = reinterpret_cast<MessageQueue *>(data);
return queue->eventReceiver(fd, events);
}参数data即是上面addFd()函数的最后一个参数this指向的SurfaceFlinger的消息队列MessageQueue对象,这里进一步调用MessageQueue的eventReceiver()函数
int MessageQueue::eventReceiver(int fd, int events) {
ssize_t n;
DisplayEventReceiver::Event buffer[8];
while ((n = DisplayEventReceiver::getEvents(mEventTube, buffer, 8)) > 0) {
for (int i=0 ; i<n ; i++) {
if (buffer[i].header.type == DisplayEventReceiver::DISPLAY_EVENT_VSYNC) {
//如果事件类型为DISPLAY_EVENT_VSYNC时,通过指定消息队列对象的mHandler发送刷新消息
mHandler->signalRefresh();
break;
}
}
}
return 1;
}函数通过调用DisplayEventReceiver::getEvents()函数从Socket接收端读取VSync事件信息, Android VSync事件分发过程源码分析中介绍了,EventThread线程可以通过Socket发送端写入多个Event事件信息,在Socket接收端同样可以连续读取多个事件信息,当getEvents()函数从Socket接收端读取到多个事件信息时,接着就遍历这些事件,并且只对事件类型为DisplayEventReceiver::DISPLAY_EVENT_VSYNC的事件即VSync事件做处理,事件处理过程就是通过Handler向SurfaceFlinger的消息队列发送一个消息:
void MessageQueue::Handler::signalRefresh() {
if ((android_atomic_or(eventMaskRefresh, &mEventMask) & eventMaskRefresh) == 0) {
mQueue.mLooper->sendMessage(this, Message(MessageQueue::REFRESH));
}
}这里只是简单地向SurfaceFlinger的消息队列发送一个MessageQueue::REFRESH消息,关于消息的发送过程,请参考 Android应用程序消息循环源码分析。SurfaceFlinger消息循环线程对该消息的处理过程如下:
void MessageQueue::Handler::handleMessage(const Message& message) {
switch (message.what) {
case INVALIDATE:
android_atomic_and(~eventMaskInvalidate, &mEventMask);
mQueue.mFlinger->onMessageReceived(message.what);
break;
case REFRESH:
android_atomic_and(~eventMaskRefresh, &mEventMask);
mQueue.mFlinger->onMessageReceived(message.what);
break;
}
}从上面可以看出,函数调用SurfaceFlinger的onMessageReceived函数来处理MessageQueue::REFRESH消息
void SurfaceFlinger::onMessageReceived(int32_t what)
{
ATRACE_CALL();
switch (what) {
case MessageQueue::REFRESH: {
const uint32_t mask = eTransactionNeeded | eTraversalNeeded;
uint32_t transactionFlags = peekTransactionFlags(mask);
if (CC_UNLIKELY(transactionFlags)) {
handleTransaction(transactionFlags);
}
handlePageFlip();
handleRefresh();
const DisplayHardware& hw(graphicPlane(0).displayHardware());
if (CC_UNLIKELY(mHwWorkListDirty)) {
handleWorkList();
}
if (CC_LIKELY(hw.canDraw())) {
handleRepaint();
hw.compositionComplete();
postFramebuffer();
#if defined(LAYER_DUMP_BMP)
frame_count++;
#endif
} else {
hw.compositionComplete();
}
} break;
}
}
1. handleTransaction
函数handleTransaction处理系统显示屏以及应用程序窗口的属性变化。
frameworks\native\services\surfaceflinger\SurfaceFlinger.cpp
void SurfaceFlinger::handleTransaction(uint32_t transactionFlags)
{
ATRACE_CALL();
// here we keep a copy of the drawing state (that is the state that's
// going to be overwritten by handleTransactionLocked()) outside of
// mStateLock so that the side-effects of the State assignment
// don't happen with mStateLock held (which can cause deadlocks).
State drawingState(mDrawingState);
Mutex::Autolock _l(mStateLock);
const nsecs_t now = systemTime();
mDebugInTransaction = now;
//系统显示屏的属性发生了变化,eTransactionNeeded位就会等于1
//应用程序窗口的属性发生了变化,eTraversalNeeded位就会等于1
const uint32_t mask = eTransactionNeeded | eTraversalNeeded;
//检查系统显示屏或者应用程序窗口的属性是否发生了变化
transactionFlags = getTransactionFlags(mask);
handleTransactionLocked(transactionFlags);
mLastTransactionTime = systemTime() - now;
mDebugInTransaction = 0;
invalidateHwcGeometry();
// here the transaction has been committed
}
函数handleTransaction是通过调用另外一个成员函数handleTransactionLocked来处理系统显示屏以及应用程序窗口的属性变化。
void SurfaceFlinger::handleTransactionLocked(uint32_t transactionFlags)
{
//mCurrentState指向当前状态State对象,State对象的成员变量layersSortedByZ保存了SufaceFlinger服///务当前所需要渲染的应用程序窗口
const LayerVector& currentLayers(mCurrentState.layersSortedByZ);
const size_t count = currentLayers.size();
//应用程序窗口的属性发生了变化
const bool layersNeedTransaction = transactionFlags & eTraversalNeeded;
if (layersNeedTransaction) {
//循环检查每一个应用程序窗口的属性是否发生了变化
for (size_t i=0 ; i<count ; i++) {
const sp<LayerBase>& layer = currentLayers[i];
uint32_t trFlags = layer->getTransactionFlags(eTransactionNeeded);
//应用程序窗口的属性被修改过
if (!trFlags) continue;
//处理应用程序窗口的属性变化
const uint32_t flags = layer->doTransaction(0);
//如果一个应用程序窗口发生的属性变化是可见区域发生了改变
if (flags & Layer::eVisibleRegion)
//要重新计算各个应用程序窗口的可见区域
mVisibleRegionsDirty = true;
}
}
//系统显示屏的属性发生了变化
if (transactionFlags & eTransactionNeeded) {
//mDrawingState用来描述SufaceFlinger服务的上一次渲染状态
//mCurrentState用来描述SufaceFlinger服务当前渲染状态
//判断系统显示屏的旋转方向是否发生变化
if (mCurrentState.orientation != mDrawingState.orientation) {
//重新设置系统显示屏的旋转方向
const int dpy = 0;
const int orientation = mCurrentState.orientation;
// Currently unused: const uint32_t flags = mCurrentState.orientationFlags;
GraphicPlane& plane(graphicPlane(dpy));
plane.setOrientation(orientation);
//同步更新的是mServerCblk中的信息,它是提供给各应用程序查询当前显示属性的,
//包括宽、高、格式、旋转角度、fps、密度等一系列数据。
// update the shared control block
const DisplayHardware& hw(plane.displayHardware());
volatile display_cblk_t* dcblk = mServerCblk->displays + dpy;
dcblk->orientation = orientation;
dcblk->w = plane.getWidth();
dcblk->h = plane.getHeight();
//需要重新计算各个应用程序窗口的可见区域
mVisibleRegionsDirty = true;
//需要重新绘制整个显示屏
mDirtyRegion.set(hw.bounds());
}
//判断是否增加了应用程序窗口
if (currentLayers.size() > mDrawingState.layersSortedByZ.size()) {
//需要重新计算各个应用程序窗口的可见区域
mVisibleRegionsDirty = true;
}
//判断是否移除了某些应用程序窗口
if (mLayersRemoved) {
mLayersRemoved = false;
//一旦图层被移除,意味着被它遮盖的区域就有可能重新显露出来
//所以需要重新计算各个应用程序窗口的可见区域
mVisibleRegionsDirty = true;
const LayerVector& previousLayers(mDrawingState.layersSortedByZ);
const size_t count = previousLayers.size();
//查找已经被移除的应用程序窗口
for (size_t i=0 ; i<count ; i++) {
const sp<LayerBase>& layer(previousLayers[i]);
//在mCurrentState找不到了,就认为被移除了
if (currentLayers.indexOf( layer ) < 0) {
//需要将它所占用的区域增加到mDirtyRegionRemovedLayer所描述的一个区域去
mDirtyRegionRemovedLayer.orSelf(layer->visibleRegionScreen);
}
}
}
}
//系统显示屏以及各个应用程序窗口的属性变化已经处理完毕,把mCurrentState赋给mmDrawingState
commitTransaction();
}
应用程序窗口属性变化处理过程
frameworks\native\services\surfaceflinger\Layer.cpp
frameworks\native\services\surfaceflinger\Layer.cpp
uint32_t Layer::doTransaction(uint32_t flags)
{
ATRACE_CALL();
//每一个应用程序窗口在内部也分别使用两个类型为State的成员变量来描述前后状态
//mDrawingState描述上一次的渲染状态
const Layer::State& front(drawingState());
//mCurrentState描述当前渲染状态
const Layer::State& temp(currentState());
//判断窗口大小是否改变
const bool sizeChanged = (temp.requested.w != front.requested.w) ||
(temp.requested.h != front.requested.h);
//应用程序窗口的大小发生了变化
if (sizeChanged) {
// the size changed, we need to ask our client to request a new buffer
// record the new size, form this point on, when the client request
// a buffer, it'll get the new size.
mSurfaceTexture->setDefaultBufferSize(temp.requested.w, temp.requested.h);
}
//判断是否为固定大小模式
if (!isFixedSize()) {
const bool resizePending = (temp.requested.w != temp.active.w) ||
(temp.requested.h != temp.active.h);
if (resizePending) {
flags |= eDontUpdateGeometryState;
}
}
return LayerBase::doTransaction(flags);
}
frameworks\native\services\surfaceflinger\LayerBase.cpp
uint32_t LayerBase::doTransaction(uint32_t flags)
{
const Layer::State& front(drawingState());
const Layer::State& temp(currentState());
// always set active to requested, unless we're asked not to
// this is used by Layer, which special cases resizes.
if (flags & eDontUpdateGeometryState) {
} else {
Layer::State& editTemp(currentState());
editTemp.active = temp.requested;
}
//窗口激活状态发生变化,需要重新计算可见区域
if (front.active != temp.active) {
// invalidate and recompute the visible regions if needed
flags |= Layer::eVisibleRegion;
}
//sequence用来描述一个应用程序窗口的其它属性是否发生过变化,当Layer的position、zorder、alpha
//matrix、transparent region、flags、crop等一系列属性发生变化,sequence的值就会比原来增加1。
//通过sequence收集属性的变化,而到了VSYNC信号产生时才做统一处理
if (temp.sequence != front.sequence) {
// invalidate and recompute the visible regions if needed
flags |= eVisibleRegion;
this->contentDirty = true;
// we may use linear filtering, if the matrix scales us
const uint8_t type = temp.transform.getType();
mNeedsFiltering = (!temp.transform.preserveRects() ||(type >= Transform::SCALE));
}
//应用程序窗口属性变化已经处理完毕,交换前后状态
commitTransaction();
return flags;
}
首先获得SufaceFlinger服务当前所需要渲染的应用程序窗口,接着通过一个循环来依次检查每一个应用程序窗口的属性是否发生了变化。在SurfaceFlinger这边,应用程序窗口使用一个Layer对象来描述,在LayerBase类中,有一个类型为int32_t的成员变量mTransactionFlags,每当SurfaceFlinger服务修改某一个应用程序窗口的属性时,都会将与其对应的LayerBase的成员变量mTransactionFlags的相应的位设置为1,这样LayerBase类的成员函数getTransactionFlags就可以通过这个成员变量来判断一个应用程序窗口的属性是否发生变化了。如果某一个应用程序窗口的属性被修改,调用这个LayerBase对象的成员函数doTransaction来处理对应的应用程序窗口的属性变化。如果一个应用程序窗口发生的属性变化是可见区域发生了改变,那么函数doTransaction的返回值flags的Layer:eVisibleRegion位就会等于1。在这种情况下,将 SurfaceFlinger类的成员变量mVisibleRegionsDirty的值设置为true,表示后面要重新计算各个应用程序窗口的可见区域。当参数transactionFlags的eTransactionNeeded位等于1,表示系统显示屏的属性发生了变化。此时首先判断系统显示屏的旋转方向是否发生变化,判断方法就是比较mCurrentState对象的成员变量orientation与mDrawingState对象的成员变量orientation的值。如果不相同,就说明系统显示屏的旋转方向发生了变化。此时,就需要将系统显示屏的旋转方向设置为mCurrentState对象的成员变量orientation的值。 SurfaceFlinger服务在启动时,创建了类型为surface_flinger_cblk_t的对象mServerCblk,用来保存系统显示屏的信息,并共享显示屏信息给其他进程访问。因此,当系统显示屏的旋转方向发生了变化时,需要修改mServerCblk中保存的显示屏信息。系统显示屏的方向发生变化意味着需要重新计算各个应用程序窗口的可见区域以及重新绘制整个显示屏,因此,将变量mVisibleRegionsDirty的值设置为true,同时将系统UI的脏区域mDirtyRegion的大小设置为整个显示屏的大小。当mCurrentState的成员变量layersSortedByZ所指向的向量大小大于mDrawingState的成员变量layersSortedByZ所指向的向量大小时,就说明系统新增了应用程序窗口。mLayersRemoved用来描述是否有应用程序窗口被移除了。如果有应用程序窗口被移除的话,就需要查找出被移除的应用程序窗口。如果一个应用程序窗口存在于mDrawingState的成员变量layersSortedByZ所指向的向量中,但是不存在于mCurrentState的成员变量layersSortedByZ所指向的向量中,就说明这个应用程序窗口被移除了,因此需要将被移除的应用程序窗口所占用区域增加到mDirtyRegionRemovedLayer描述的区域中。无论是新增应用程序窗口还是移除应用程序窗口,都需要重新计算各个应用程序窗口的可见区域,因此将变量mVisibleRegionsDirty的值设置为true。