Inserting Sort (插入排序)
Since an array with one element is a sorted array. By insert second element into this one array, we get a sorted array of size 2, Continuing in this way, we obtain a sorted array of size n.
// InsertionSort.cpp : Defines the entry point for the console application.
//
#include "stdafx.h"
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
template <class T>
void PrintfNum(T a[], int n);
template <class T>
void InsertionSort(T a[], int n){
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
T t = a[i];
int j;
for (j = i-1; j >= 0 && t < a[j]; j--)
a[j+1] = a[j];
a[j+1] = t;
PrintfNum(a,4);
}
}
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
int a[4]={4,3,2,1};
cout << "Before sort:" << endl;
PrintfNum(a,4);
cout << "Insertion Sort :" << endl;
InsertionSort(a, 4);
return 0;
}
template <class T>
void PrintfNum(T a[], int n){
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
cout << a[i] << ",";
}
cout << endl;
}
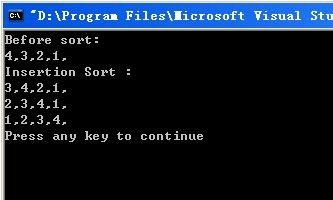
An example , There is a array 4, 3, 2, 1
First element is 4, it is a sorted array of size 1.
The second element 3 is smaller than 4, so set 4 one more position to the right.
So the array changed to 3, 4, 2, 1. The 3, 4 is a sorted array of size 2.
The third element 2 is smaller than 3, so set 3 and 4 one more position to the right.
So the array changed to 2, 3, 4, 1. The 2, 3, 4 is a sorted array of size 3.
The fourth element 1 is smaller than 2, so set2, 3 and 4 one more position to the right.
So the array changed to 1,2, 3, 4, Done.
http://www.waitingfy.com/?p=407