用Java2D画出树的结构_v0.1.0
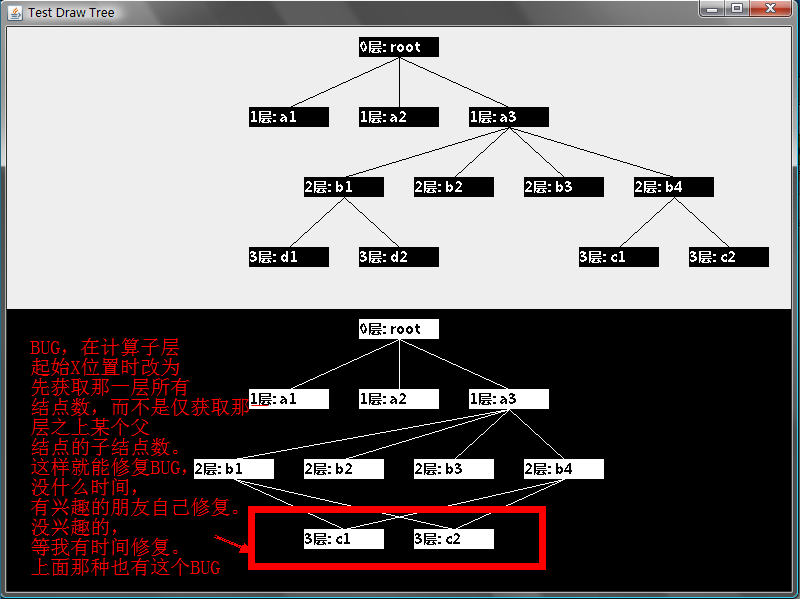
先看效果图:
定义树的数据结构
/** * 2010-11-8 * John */ package tree; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; /** * 树的结构 * @author John * */ public class Node { private String name; //该结点名字 private int layer = 0; //该结点层级 private List<Node> childs = null; //保存该结点的孩子 public Node(String name){ this.name = name; } /** * 增加一个孩子 * @param n 要作为孩子增加的结点 */ public void add(Node n){ if(childs == null) childs = new ArrayList<Node>(); n.setLayer(layer+1); setChildLayout(n); childs.add(n); } /** * 递归设置孩子的层级 * @param n */ private void setChildLayout(Node n){ if(n.hasChild()){ List<Node> c = n.getChilds(); for(Node node : c){ node.setLayer(node.getLayer()+1); setChildLayout(node); } } } /** * 获取结点名 * @return 结点名 */ public String getName() { return name; } /** * 设置结点名 * @param name 结点名 */ public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } /** * 获取该结点的层级 * @return 该结点的层级 */ public int getLayer() { return layer; } /** * 设置该结点的层级 * @param layer 该结点的层级 */ public void setLayer(int layer) { this.layer = layer; } /** * 获取该结点的孩子 * @return 所有孩子结点 */ public List<Node> getChilds() { return childs; } /** * 检查是否存在孩子 * @return 是则返回true,否则返回false */ public boolean hasChild(){ return childs == null ? false : true; } /** * 递归打印所有的结点(包括子结点) * @param n 要打印的根结点 */ public void printAllNode(Node n){ System.out.println(n); if(n.hasChild()){ List<Node> c = n.getChilds(); for(Node node : c){ printAllNode(node); } } } public String getAllNodeName(Node n){ String s = n.toString()+"/n"; if(n.hasChild()){ List<Node> c = n.getChilds(); for(Node node : c){ s+=getAllNodeName(node)+"/n"; } } return s; } public String toString(){ return layer+"层/t: "+name; } }
Node的测试类:
/** * 2010-11-9 * John */ package tree.demo; import tree.Node; /** * @author John * */ public class TestPrintNode { public static void main(String[] args){ Node n = new Node("root"); n.add(new Node("a1")); n.add(new Node("a2")); Node n2 = new Node("a3"); n2.add(new Node("b1")); n2.add(new Node("b2")); n2.add(new Node("b3")); Node n3 = new Node("b4"); n2.add(n3); n3.add(new Node("c1")); n3.add(new Node("c2")); n.add(n2); n.printAllNode(n); //输出树 } }
画树的Panel
/** * 2010-11-9 * John */ package tree; import java.awt.Color; import java.awt.Font; import java.awt.FontMetrics; import java.awt.Graphics; import java.util.List; import javax.swing.JPanel; /** * TODO 同一层结点过多有BUG,应该对每一层的所有结点都进行个数统计,之后才绘制。 * @author John * */ public class TreePanel extends JPanel { private Node tree; //保存整棵树 private int gridWidth = 80; //每个结点的宽度 private int gridHeight = 20; //每个结点的高度 private int vGap = 50; //每2个结点的垂直距离 private int hGap = 30; //每2个结点的水平距离 private int startY = 10; //根结点的Y,默认距离顶部10像素 private int startX = 0; //根结点的X,默认水平居中对齐 private int childAlign; //孩子对齐方式 public static int CHILD_ALIGN_ABSOLUTE = 0; //相对Panel居中 public static int CHILD_ALIGN_RELATIVE = 1; //相对父结点居中 private Font font = new Font("微软雅黑",Font.BOLD,14); //描述结点的字体 private Color gridColor = Color.BLACK; //结点背景颜色 private Color linkLineColor = Color.BLACK; //结点连线颜色 private Color stringColor = Color.WHITE; //结点描述文字的颜色 /** * 默认构造 */ public TreePanel(){ this(null,CHILD_ALIGN_ABSOLUTE); } /** * 根据传入的Node绘制树,以绝对居中的方式绘制 * @param n 要绘制的树 */ public TreePanel(Node n){ this(n,CHILD_ALIGN_ABSOLUTE); } /** * 设置要绘制时候的对齐策略 * @param childAlign 对齐策略 * @see tree.TreePanel#CHILD_ALIGN_RELATIVE * @see tree.TreePanel#CHILD_ALIGN_ABSOLUTE */ public TreePanel(int childAlign){ this(null,childAlign); } /** * 根据孩子对齐策略childAlign绘制的树的根结点n * @param n 要绘制的树的根结点 * @param childAlign 对齐策略 */ public TreePanel(Node n, int childAlign){ super(); setTree(n); this.childAlign = childAlign; } /** * 设置用于绘制的树 * @param n 用于绘制的树的 */ public void setTree(Node n) { tree = n; } //重写而已,调用自己的绘制方法 public void paintComponent(Graphics g){ startX = (getWidth()-gridWidth)/2; super.paintComponent(g); g.setFont(font); drawAllNode(tree, startX, g); } /** * 递归绘制整棵树 * @param n 被绘制的Node * @param xPos 根节点的绘制X位置 * @param g 绘图上下文环境 */ public void drawAllNode(Node n, int x, Graphics g){ int y = n.getLayer()*(vGap+gridHeight)+startY; int fontY = y + gridHeight - 5; //5为测试得出的值,你可以通过FM计算更精确的,但会影响速度 g.setColor(gridColor); g.fillRect(x, y, gridWidth, gridHeight); //画结点的格子 g.setColor(stringColor); g.drawString(n.toString(), x, fontY); //画结点的名字 if(n.hasChild()){ List<Node> c = n.getChilds(); int size = n.getChilds().size(); int tempPosx = childAlign == CHILD_ALIGN_RELATIVE ? x+gridWidth/2 - (size*(gridWidth+hGap)-hGap)/2 : (getWidth() - size*(gridWidth+hGap)+hGap)/2; int i = 0; for(Node node : c){ int newX = tempPosx+(gridWidth+hGap)*i; //孩子结点起始X g.setColor(linkLineColor); g.drawLine(x+gridWidth/2, y+gridHeight, newX+gridWidth/2, y+gridHeight+vGap); //画连接结点的线 drawAllNode(node, newX, g); i++; } } } public Color getGridColor() { return gridColor; } /** * 设置结点背景颜色 * @param gridColor 结点背景颜色 */ public void setGridColor(Color gridColor) { this.gridColor = gridColor; } public Color getLinkLineColor() { return linkLineColor; } /** * 设置结点连接线的颜色 * @param gridLinkLine 结点连接线的颜色 */ public void setLinkLineColor(Color gridLinkLine) { this.linkLineColor = gridLinkLine; } public Color getStringColor() { return stringColor; } /** * 设置结点描述的颜色 * @param stringColor 结点描述的颜色 */ public void setStringColor(Color stringColor) { this.stringColor = stringColor; } public int getStartY() { return startY; } /** * 设置根结点的Y位置 * @param startY 根结点的Y位置 */ public void setStartY(int startY) { this.startY = startY; } public int getStartX() { return startX; } /** * 设置根结点的X位置 * @param startX 根结点的X位置 */ public void setStartX(int startX) { this.startX = startX; } }
测试TreePanel
/** * 2010-11-9 * John */ package tree.demo; import java.awt.BorderLayout; import java.awt.Color; import java.awt.GridLayout; import java.awt.Panel; import javax.swing.JFrame; import javax.swing.JPanel; import javax.swing.JScrollPane; import javax.swing.JTextArea; import tree.Node; import tree.TreePanel; /** * @author John * */ public class TestDrawTree extends JFrame{ public TestDrawTree(){ super("Test Draw Tree"); initComponents(); } public static void main(String[] args){ TestDrawTree frame = new TestDrawTree(); frame.setSize(800, 600); frame.setVisible(true); frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE); } public void initComponents(){ /* * 初始化树的数据 */ Node n = new Node("root"); Node a1 = new Node("a1"); Node a2 = new Node("a2"); n.add(a1); n.add(a2); Node a3 = new Node("a3"); Node b1 = new Node("b1"); Node d1 = new Node("d1"); Node d2 = new Node("d2"); b1.add(d1); b1.add(d2); a3.add(b1); a3.add(new Node("b2")); a3.add(new Node("b3")); Node n3 = new Node("b4"); a3.add(n3); n3.add(new Node("c1")); n3.add(new Node("c2")); n.add(a3); //n.printAllNode(n); //输出树 /* * 创建一个用于绘制树的面板并将树传入,使用相对对齐方式 */ TreePanel panel1 = new TreePanel(TreePanel.CHILD_ALIGN_RELATIVE); panel1.setTree(n); /* * 创建一个用于绘制树的面板并将树传入,使用绝对对齐方式 */ TreePanel panel2 = new TreePanel(TreePanel.CHILD_ALIGN_ABSOLUTE); panel2.setTree(n); panel2.setBackground(Color.BLACK); panel2.setGridColor(Color.WHITE); panel2.setLinkLineColor(Color.WHITE); panel2.setStringColor(Color.BLACK); JPanel contentPane = new JPanel(); contentPane.setLayout(new GridLayout(2,1)); contentPane.add(panel1); contentPane.add(panel2); add(contentPane,BorderLayout.CENTER); } }