spring integration之http-rest例子解析
spring integration例子代码下载地址,以及如何导入eclipse并使用maven构建等请参看上一篇:
Spring Integration实例代码分析之basic--http
先看一下http-rest例子的readme
This sample demonstrates how you can send an HTTP request to a Spring Integration's HTTP service while utilizing Spring Integration's new HTTP Path usage;
This sample also uses Spring Security for HTTP Basic authentication. With HTTP Path facility, the client program can send requests with URL Variables.
It consists of two parts - Client and Server.
The following client program can be used to test the HTTP Path usage.
1. RestHttpClientTest. It uses Spring's RestTemplate to assemble and send HTTP request
Server is Spring Integration's HTTP endpoint configuration.
此示例演示了如何发送一个HTTP请求到一个Spring集成的HTTP服务,同时利用Spring Integration的新的HTTP Path;
此示例还使用了Spring HTTP基本身份验证安全性。 HTTP Path,客户端程序可以发送请求的URL变量。
它由两部分组成 - 客户端和服务器。
客户端程序,可以用来测试使用HTTP path。RestHttpClientTest。它使用Spring的RestTemplate的组装和发送HTTP请求
服务端是Spring集成的HTTP端点配置。
代码结构
仍然先看web.xml
<context-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>
<!-- Spring application context declaration -->
/WEB-INF/config/web-application-config.xml
</param-value>
</context-param>
<!--
Key of the system property that should specify the root directory of this
web app. Applied by WebAppRootListener or Log4jConfigListener.
-->
<context-param>
<param-name>webAppRootKey</param-name>
<param-value>rest-http.root</param-value>
</context-param>
<!--
Location of the Log4J config file, for initialization and refresh checks.
Applied by Log4jConfigListener.
-->
<context-param>
<param-name>log4jConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>/WEB-INF/classes/log4j.properties</param-value>
</context-param>
<listener>
<listener-class>org.springframework.web.util.Log4jConfigListener</listener-class>
</listener>
<!--
- Loads the root application context of this web app at startup,
- by default from "/WEB-INF/applicationContext.xml".
- Note that you need to fall back to Spring's ContextLoaderServlet for
- J2EE servers that do not follow the Servlet 2.4 initialization order.
-
- Use WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(servletContext)
- to access it anywhere in the web application, outside of the framework.
-
- The root context is the parent of all servlet-specific contexts.
- This means that its beans are automatically available in these child contexts,
- both for getBean(name) calls and (external) bean references.
-->
<listener>
<listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class>
</listener>
接着是filter,包含指定字符的,和security的,用于认证。
<filter> <filter-name>charEncodingFilter</filter-name> <filter-class>org.springframework.web.filter.CharacterEncodingFilter</filter-class> <init-param> <param-name>encoding</param-name> <param-value>UTF-8</param-value> </init-param> <init-param> <param-name>forceEncoding</param-name> <param-value>true</param-value> </init-param> </filter> <filter-mapping> <filter-name>charEncodingFilter</filter-name> <url-pattern>/*</url-pattern> </filter-mapping> <filter> <filter-name>springSecurityFilterChain</filter-name> <filter-class>org.springframework.web.filter.DelegatingFilterProxy</filter-class> </filter> <filter-mapping> <filter-name>springSecurityFilterChain</filter-name> <url-pattern>/*</url-pattern> </filter-mapping>
最后才是用于spring mvc的DispatcherServlet,指定配置文件为contextConfigLocation的 /WEB-INF/config/web-application-config.xml
<servlet> <servlet-name>Spring Integration Rest HTTP Path Usage</servlet-name> <servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class> <init-param> <param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name> <param-value></param-value> </init-param> <load-on-startup>2</load-on-startup> </servlet> <servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>Spring Integration Rest HTTP Path Usage</servlet-name> <url-pattern>/*</url-pattern> </servlet-mapping>
Spring 配置
先看:web-application-config.xml
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-3.0.xsd">
<import resource="security-config.xml" />
<import resource="classpath:META-INF/spring/integration/applicationContext-http-int.xml"/>
<context:component-scan base-package="org.springframework.integration.samples.rest"/>
</beans>
我们主要看一下applicationContext-http-int.xml
<int:annotation-config/>inbound gateway's 和 inbound adapter 都需要指定这个,用于其path属性。
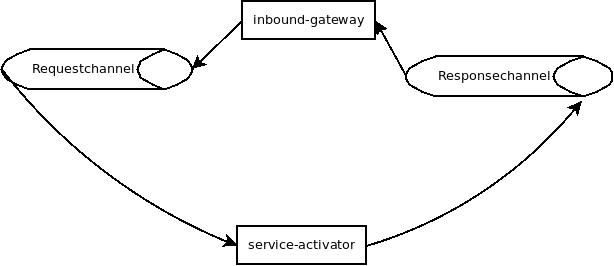
<bean class="org.springframework.integration.http.inbound.UriPathHandlerMapping"/>接着指定两个channel通道,一个用于请求一个用于响应。
<!-- Inbound/Outbound Channels --> <int:channel id="employeeSearchRequest" /> <int:channel id="employeeSearchResponse" />下面就是gateway(能翻译为网关么??)了,使用http inbound-gateway来通过http接受信息,关联上之前的两个通道,指定path路径,通过路径解析出参数id.
<!-- To receive messages over HTTP, you need to use an HTTP Inbound Channel Adapter or Gateway. -->
<int-http:inbound-gateway id="inboundEmployeeSearchRequestGateway"
supported-methods="GET, POST"
request-channel="employeeSearchRequest"
reply-channel="employeeSearchResponse"
mapped-response-headers="Return-Status, Return-Status-Msg, HTTP_RESPONSE_HEADERS"
view-name="/employee"
path="/services/employee/{id}/search"
reply-timeout="50000">
<int-http:header name="employeeId" expression="#pathVariables.id"/>
</int-http:inbound-gateway>
其中用于将对象转为xml的为marshaller,它的contextPath="org.springframework.integration.samples.rest.domain",就是对这个包下的进行转换。
<bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.ContentNegotiatingViewResolver"> <property name="order" value="1" /> <property name="defaultContentType" value="application/xml"/> <property name="favorParameter" value="true"/> <property name="ignoreAcceptHeader" value="true" /> <property name="mediaTypes"> <map> <entry key="json" value="application/json" /> <entry key="xml" value="application/xml" /> </map> </property> <property name="defaultViews"> <list> <bean class="org.springframework.integration.samples.rest.json.view.ExtendedMappingJacksonJsonView" > <property name="objectMapper" ref="jaxbJacksonObjectMapper"/> </bean> <bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.xml.MarshallingView"> <constructor-arg ref="marshaller"/> </bean> </list> </property> </bean> <!-- 将java bean 转换为xml string并利用ContentNegotiatingViewResolver来提供输出 As stated in the introduction, a marshaller serializes an object to XML, and an unmarshaller deserializes XML stream to an object. --> <oxm:jaxb2-marshaller id="marshaller" contextPath="org.springframework.integration.samples.rest.domain" /> <bean id="jaxbJacksonObjectMapper" class="org.springframework.integration.samples.rest.json.JaxbJacksonObjectMapper"/>
但实际返回的却是 {"jsonResult":{"success":true,"msg":"return ok"}}
原因是MappingJacksonJsonView中对返回值的处理未考虑modelMap中只有一个值的情况,直接是按照mapName:{mapResult}的格式来返回数据的。
修改方法如下代码,重载MappingJacksonJsonView类并重写filterModel方法,处理一下map.size为1的情况。
public class ExtendedMappingJacksonJsonView extends MappingJacksonJsonView {
@SuppressWarnings({"rawtypes" })
@Override
protected Object filterModel(Map<String, Object> model){
Object result = super.filterModel(model);
if (!(result instanceof Map)){
return result;
}
Map map = (Map) result;
if (map.size() == 1){
return map.values().toArray()[0];
}
return map;
}
}
<int:service-activator id="employeeServiceActivator" input-channel="employeeSearchRequest" output-channel="employeeSearchResponse" ref="employeeSearchService" method="getEmployee" requires-reply="true" send-timeout="60000"/>
代码解析
@XmlAccessorType(XmlAccessType.FIELD)
@XmlType(name = "", propOrder = {
"employeeId",
"fname",
"lname"
})
@XmlRootElement(name = "Customer")
public class Employee {
private Integer employeeId;
private String fname;
private String lname;
public Employee() {}
public Employee(Integer employeeId, String fname, String lname) {
this.employeeId = employeeId;
this.fname = fname;
this.lname = lname;
}
//get and set ...
}
EmployeeList
@XmlAccessorType(XmlAccessType.FIELD)
@XmlType(name = "", propOrder = {
"employee",
"returnStatus",
"returnStatusMsg"
})
@XmlRootElement(name = "EmployeeList")
public class EmployeeList {
@XmlElement(name = "Employee", required = true)
private List<Employee> employee;
@XmlElement(name = "returnStatus", required = true)
private String returnStatus;
@XmlElement(name = "returnStatusMsg", required = true)
private String returnStatusMsg;
/**
* @return the employee
*/
public List<Employee> getEmployee() {
if (employee == null){
employee = new ArrayList<Employee>();
}
return employee;
}
}
EmployeeSearchService
@Service("employeeSearchService")
public class EmployeeSearchService {
private static Logger logger = Logger.getLogger(EmployeeSearchService.class);
/**
* The API <code>getEmployee()</code> looks up the mapped in coming message header's id param
* and fills the return object with the appropriate employee details. The return
* object is wrapped in Spring Integration Message with response headers filled in.
* This example shows the usage of URL path variables and how the service act on
* those variables.
* @param inMessage
* @return an instance of <code>{@link Message}</code> that wraps <code>{@link EmployeeList}</code>
*/
@Secured("ROLE_REST_HTTP_USER")
public Message<EmployeeList> getEmployee(Message<?> inMessage){
EmployeeList employeeList = new EmployeeList();
Map<String, Object> responseHeaderMap = new HashMap<String, Object>();
try{
MessageHeaders headers = inMessage.getHeaders();
String id = (String)headers.get("employeeId");
boolean isFound;
if (id.equals("1")){
employeeList.getEmployee().add(new Employee(1, "John", "Doe"));
isFound = true;
}else if (id.equals("2")){
employeeList.getEmployee().add(new Employee(2, "Jane", "Doe"));
isFound = true;
}else if (id.equals("0")){
employeeList.getEmployee().add(new Employee(1, "John", "Doe"));
employeeList.getEmployee().add(new Employee(2, "Jane", "Doe"));
isFound = true;
}else{
isFound = false;
}
if (isFound){
setReturnStatusAndMessage("0", "Success", employeeList, responseHeaderMap);
}else{
setReturnStatusAndMessage("2", "Employee Not Found", employeeList, responseHeaderMap);
}
}catch (Throwable e){
setReturnStatusAndMessage("1", "System Error", employeeList, responseHeaderMap);
logger.error("System error occured :"+e);
}
Message<EmployeeList> message = new GenericMessage<EmployeeList>(employeeList, responseHeaderMap);
return message;
}
/**
* The API <code>setReturnStatusAndMessage()</code> sets the return status and return message
* in the return message payload and its header.
* @param status
* @param message
* @param employeeList
* @param responseHeaderMap
*/
private void setReturnStatusAndMessage(String status,
String message,
EmployeeList employeeList,
Map<String, Object> responseHeaderMap){
employeeList.setReturnStatus(status);
employeeList.setReturnStatusMsg(message);
responseHeaderMap.put("Return-Status", status);
responseHeaderMap.put("Return-Status-Msg", message);
}
}这些代码就都很简单,一目了然,不用怎么解释了。
运行
final String fullUrl = "http://localhost:8080/rest-http/services/employee/{id}/search";
EmployeeList employeeList = restTemplate.execute(fullUrl, HttpMethod.GET,
new RequestCallback() {
@Override
public void doWithRequest(ClientHttpRequest request) throws IOException {
HttpHeaders headers = getHttpHeadersWithUserCredentials(request);
headers.add("Accept", "application/xml");
}
}, responseExtractor, employeeSearchMap);
@Test
public void testGetEmployeeAsJson() throws Exception{
Map<String, Object> employeeSearchMap = getEmployeeSearchMap("0");
final String fullUrl = "http://localhost:8080/rest-http/services/employee/{id}/search?format=json";
HttpHeaders headers = getHttpHeadersWithUserCredentials(new HttpHeaders());
headers.add("Accept", "application/json");
HttpEntity<Object> request = new HttpEntity<Object>(headers);
ResponseEntity<?> httpResponse = restTemplate.exchange(fullUrl, HttpMethod.GET, request, EmployeeList.class, employeeSearchMap);
logger.info("Return Status :"+httpResponse.getHeaders().get("X-Return-Status"));
logger.info("Return Status Message :"+httpResponse.getHeaders().get("X-Return-Status-Msg"));
assertTrue(httpResponse.getStatusCode().equals(HttpStatus.OK));
jaxbJacksonObjectMapper.writeValue(System.out, httpResponse.getBody());
}
可以获取到xml内容,也可以得到json内容,上面为测试类的主要代码。