c++ 学习错误列表
这是学习和使用c++语言过程中,出现的错误及解决方法列表,随着学习和实践深入,此列表将不断更新。
No.1:prog4.cpp(8) : error C2440: “初始化”: 无法从“const int”转换为“int &”
转换丢失限定符
#include <iostream>
int main()
{
const int iSize = 1024;
int iCnt = 0;
const int &iRefval = iSize;//ok
int &iRef = iSize;//不允许非const引用绑定到const对象
const int &icRef = iCnt;//const引用可以绑定到右值
std::cout<<"iRefval: "<<iRefval<<std::endl;
std::cout<<"icRef: "<<icRef<<std::endl;
return 0;
}
解决办法: 非const引用绑定到const对象,如果允许的话,那么可以通过非const引用修改const原对象,这个出现一个矛盾,因此c++不允许执行此操作。解决方法就是使用非const引用绑定到同类型的非const对象,使用const引用绑定到不同但相关的类型的对象或者右值。
No.2: prog2.cpp(8) : error C2664: '__thiscall std::list<int,class std::allocator<int> >::std::list<int,class std::allocator<int> >(unsigned int,const int &,
const class std::allocator<int> &)' : cannot convert parameter 1 from 'class std::deque<int,class std::allocator<int> >::iterator' to 'unsigned int'
No user-defined-conversion operator available that can perform this conversion, or the operator cannot be called
//prog2.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <list>
#include <deque>
using namespace std;
void main()
{
//Define a list that holds elements that are deques that hold ints
deque<int> ideque(10,1);
list<int> ilist(ideque.begin(),ideque.end());
for(list<int>::const_iterator itbegin=ilist.begin(),itend=ilist.end();itbegin!=itend;++itbegin)
cout<<*itbegin<<endl;
}
解决方法:vc 6.0对模板库支持不够好,使用vs2010编译通过。
No.3 TextQuery.cpp(63) : warning C4172: returning address of local variable or temporary
//返回单词出现的行号set
const set<int> & TextQuery::RunQuery(string word) const
{
map< string,set<int> >::const_iterator it = m_mapWordLine.find(word);
if(it != m_mapWordLine.end())
return it->second;
else
return set<int>();//emptyset
}
解决方法:愿意是返回set对象的const引用以减轻复制set对象的负担,但是这里返回空的set对象的局部引用是错误的,c++ primer 原文采用的方法是返回set对象,不使用引用,这也是一种解决方法。另外使用std::vector<std::string>::size_type 比int型的set好。
No.4 printchar.cpp(13) : error C2440: 'initializing' : cannot convert from 'char *' to 'const class std::basic_string<char,struct std::char_traits<char>,class std::allocator<char> > *'
Types pointed to are unrelated; conversion requires reinterpret_cast, C-style cast or function-style cast
//输出一行中所有字符
void printchar(string &line)
{
istringstream iss(line);
string word;
while(iss>>word)
for(vector<string>::const_iterator itbegin=word.begin(),itend=word.end();itbegin != itend; ++itbegin)
cout<<*itbegin<<endl;
}
解决方法:标准库string对象可以使用迭代器操作 ,但是其迭代器要正确使用,应该使用string::const_iterator 后者使用下标操作来获取string对象中的字符。
No.5 fatal error "vector iterator + offset out of range" "standard C++ libraries out of range "
代码如下:
#include <iostream>
#include <iterator>//使用back_inserter
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
void main()
{
vector<int> ivec;
try
{
fill_n(ivec.begin(),10,1);//error should use fill_n (back_inserter(ivec), 10, 1);
for(vector<int>::iterator itbegin=ivec.begin(),itend=ivec.end();itbegin!=itend;++itbegin)
cout<<*itbegin<<endl;
}
catch (runtime_error err)
{
cerr << "Error: "<<err.what()<<endl;
}
catch(out_of_range or)
{
cerr << "Error: "<<or.what()<<endl;
}
catch(exception ex)
{
cerr << "Error: "<<ex.what()<<endl;
}
}
解决方法:fill_n()函数将在vector中从头开始,将指定个数的元素设置为给定的值。fill_n函数假定对指定数量的元素做写操作是安全的。初学者常犯的错误的是:在没有元素的空容器上调用 fill_n 函数,因此需要使用back_inserter ,这种插入迭代器。当使用插入迭代器赋值时,则会在容器中添加一个新元素,其值等于赋值运算的右操作数的值。因此需将代码改为:
fill_n (back_inserter(ivec), 10, 1);
No.6 prog7.cpp(8) : error C2780: 'void __cdecl std::sort(_RI,_RI,_Pr)' : expects 3 arguments - 2 provided
C:\Program Files\Microsoft Visual Studio\VC98\include\algorithm(588) : see declaration of 'sort'
prog7.cpp(8) : error C2782: 'void __cdecl std::sort(_RI,_RI)' : template parameter '_RI' is ambiguous
could be 'class std::reverse_iterator<int *,int,int &,int *,int>'
or 'int *'
代码如下:
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
void main()
{
vector<int> ivec1(10,1);
sort(ivec1.begin(), ivec1.rend());//类型不匹配的错误 可以在编译时检查出来
}
解决方法:
sort函数重载有两个版本,所以出现上面的错误提示,无论哪个版本,要求给定一对迭代器范围,而在标准库中,有输入范围的泛型算法要求其两个迭代器类型完全一样,包括const属性。要么都是const,要么都是非const,否则无法通过编译。
上述的begin函数返回是普通迭代器,而rend函数返回的是反向迭代器,因此两个实参类型不匹配,出现了上述错误,解决方法就是正确的传递实参,使用类型完全一样的迭代器标记范围。
No.7 ..\sales_item\sales_item.h(24) :error C2804:binary 'operator +' has too many parameters
代码如下:
// header file Sales_item.h
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
class Sales_item
{
// private members
private:
std::string isbn;
unsigned units_sold;
double revenue;
//public method
public:
..
//Overloaded Operator as member function
Sales_item& operator+=(const Sales_item&);//Compound Assignment Operators
Sales_item operator+(const Sales_item& lhs, const Sales_item& rhs);
};
// implement file Sales_item.cpp
using std::istream;
using std::ostream;
//Overloaded Operator as nonmember functions
inline Sales_item Sales_item::operator+(const Sales_item& lhs, const Sales_item& rhs)
{
Sales_item ret(lhs); // copy lhs into a local object that we'll return
ret += rhs; // add in the contents of rhs
return ret; // return ret by value ,not by reference
}
解决方法:+操作符包括两个操作数,应该重载为普通非成员函数。
注意重载操作符的形参数目(包括成员函数的隐式 this 指针)与操作符的操作数数目相同。对称的操作符,如算术操作符、相等操作符、关系操作符和位操作符,最好定义为普通非成员函数。因此+应该重载为普通非成员函数。这里重载为成员函数时多了一个this形参,故对于+操作符来说,出现参数过多的错误。
即书写为:
// header file
Sales_item operator+(const Sales_item& lhs, const Sales_item& rhs);
//implement file
//Overloaded Operator as nonmember functions
inline Sales_item operator+(const Sales_item& lhs, const Sales_item& rhs)
{
Sales_item ret(lhs); // copy lhs into a local object that we'll return
ret += rhs; // add in the contents of rhs
return ret; // return ret by value ,not by reference
}
No.8 Compiling...main.cppLinking...main.obj :error LNK2001: unresolved external symbol "class std::basic_ostream<char,struct std::char_traits<char> > &__cdecloperator<<(class std::basic_ostream<char,struct std::char_traits<char> > &,class Sales_item const &)"(??6@YAAAV?$basic_ostream@DU$char_traits@D@std@@@std@@AAV01@ABVSales_item@@@Z)
....(省略后续同类错误)
Sales_item.exe - 4 error(s), 0 warning(s)
错误原因之一,在于将inline函数的实现放在了单独的实现文件中了,解决方法:
将inline函数的实现放置在头文件中。具体请参考:《类的内联函数的实现应该放在哪里》一文。
N0.9 conflict.cpp(7) : error C2872: “count”: 不明确的符号
可能是“conflict.cpp(4) : int count”
或 “C:\Program Files\Microsoft Visual Studio 11.0\VC\INCLUDE\xutility(3251) : iterato
r_traits<_Iter>::difference_type std::count(_InIt,_InIt,const _Ty &)”
conflict.cpp(12) : error C2872: “count”: 不明确的符号
可能是“conflict.cpp(4) : int count”
或 “C:\Program Files\Microsoft Visual Studio 11.0\VC\INCLUDE\xutility(3251) : iterato
r_traits<_Iter>::difference_type std::count(_InIt,_InIt,const _Ty &)”
出错代码
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int count = 0;
int increment()
{
return ++count;// error, identifier count is ambiguous
}
int main()
{
increment();
cout<<"count= "<<count<<endl;
return 0;
}
解决办法: 使用命名机制来避免命名冲突,这里count既可以是程序中全局变量count,也可能是
std::count,因此引起歧义,导致出错。解决方法:
1)尽量少用directive方式来引用命名空间:(directive方式即using namespace std;)
#include <iostream>
using std::cout;//使用命名空间一个名字
using std::endl;
int count = 0;
int increment()
{
return ++count;
}
int main()
{
increment();
cout<<"count= "<<count<<endl;
return 0;
}
2)使用命名空间引用变量,在命名空间中定义变量、函数和类。
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
namespace global {
int count = 0;//重新定义一个命名空间
}
int increment()
{
return ++global::count;
}
int main()
{
increment();
cout<<"count= "<<global::count<<endl;
return 0;
}
No.10 error C2664: “find_char”: 不能将参数 1 从“const char [14]”转换为“std::string &
出错代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
using std::string;
//const引用形参举例
//非const引用形参只能与完全同类型的非const对象关联
std::size_t find_char(string &s,char c)
{
string::size_type i = 0;
while(i != s.size() && s[i] != c)
++i;
if(i == s.size())
return string::npos;
else
return i;
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
//字面值常量为const对象,调用出错
if(find_char("Hello, world.",'.') != string::npos)
{
cout<<"a sentence."<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
解决方法: 如果函数不修改相应实参,应该将引用形参定义为const引用,这样字面值常量、const对象也能调用此函数,避免不必要的限制。
No.11 error C2512: “Foo”: 没有合适的默认构造函数可用
错误信息如下:
C:\Program Files\Microsoft Visual Studio 11.0\VC\INCLUDE\xmemory0(601) : error C2512: “Foo”: 没有
合适的默认构造函数可用
C:\Program Files\Microsoft Visual Studio 11.0\VC\INCLUDE\xmemory0(600): 编译类 模板 成员函数
“void std::allocator<_Ty>::construct(_Ty *)”时
with
[
_Ty=Foo
]
C:\Program Files\Microsoft Visual Studio 11.0\VC\INCLUDE\xmemory0(751): 参见对正在编译的函数
模板 实例化“void std::allocator<_Ty>::construct(_Ty *)”的引用
with
[
_Ty=Foo
]
C:\Program Files\Microsoft Visual Studio 11.0\VC\INCLUDE\type_traits(743): 参见对正在编译的
类 模板 实例化“std::allocator<_Ty>”的引用
with
[
_Ty=Foo
]
C:\Program Files\Microsoft Visual Studio 11.0\VC\INCLUDE\vector(655): 参见对正在编译的类 模
板 实例化“std::is_empty<_Ty>”的引用
with
[
_Ty=std::allocator<Foo>
]
prog26.cpp(15): 参见对正在编译的类 模板 实例化“std::vector<_Ty>”的引用
with
[
_Ty=Foo
]
错误代码:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
//顺序容器举例
class Foo
{
public:
Foo(int i):ival(i){}
private:
int ival;
};
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
vector<Foo> empty;
vector<Foo> bad(10);
vector<Foo> ok(10,1);
return 0;
}
解决办法: 实际上根据c++ primer第四版解释构造空的vector时是不调用对象的构造函数的,但是这里用于 x86 的 Microsoft (R) C/C++ 优化编译器 17.00.61030编译显式错误,可能编译器版本不同结果有所不同。
主要看下面的bad(10)这一行,也同样会报错。错误的原因在于类类型对象没有默认的构造函数,因此无法正确初始化,构造vector失败。解决办法,即是为类添加默认的构造函数。
No.12 error C2440: “return”: 无法从“const Screen”转换为“Screen &”
转换丢失限定符
出错代码:例子来自c++ primer 4th
Screen& Screen::display(std::ostream& os) const
{
os << contents << '\n';
return *this;
}
解决办法: c++语言规定,不能从const成员函数返回指向类对象的普通引用,const成员函数只能返回*this作为一个const引用。因此解决办法即是,把成员函数声明为 const Screen& display(std::ostream &os) const;
No.13 error C2662: “Screen::move”: 不能将“this”指针从“const Screen”转换为“ Screen &” 转换丢失限定符
出错代码:
//成员函数定义
Screen& Screen::move(index r,index c)
{
index row = r * width;
cursor = row + c;
return *this;
}
const Screen& Screen::display(std::ostream& os) const
{
os << contents << '\n';
return *this;
}
//main中处理
myScreen.display(cout).move(4,0).set('#').display(cout);
解决办法: 通过返回调用函数的对象的引用,可以将一些操作链接起来简化代码书写。
这里要注意,display函数返回的是const引用,因此在调用move函数中返回非const引用时无法实现转换导致出错。
解决的办法就是通过成员函数是否为const实现函数重载,定义两套函数,分别作为const成员函数和非const成员函数。
代码片段如下:
//通过是否为const成员函数实现重载
Screen& display(std::ostream &os)
{do_display(os);return *this;}
const Screen& display(std::ostream &os) const
{do_display(os);return *this;}
//提取公共函数
void do_display(std::ostream &os) const
{os<<contents;}
//main中处理
int main()
{
Screen myScreen(5,3);
const Screen blank(5,3);
//调用非const版本display
myScreen.display(cout).set('#').display(cout);
cout << endl;
//调用 const版本display
blank.display(cout);
return 0;
}这样非常量myScreen调用非const版本的display
函数,而const的blank对象调用const版本的display函数,从而避免了混淆。
No.14 error C2758: “ConstInit::cival”: 必须在构造函数基/成员初始值设定项列表中初始化
prog28.cpp(12) : 参见“ConstInit::cival”的声明
解决办法:类的成员可以在构造函数体类或者构造函数列表中初始化,但是某些类型,例如默认构造函数的类类型成员、const后者引用类型的成员则必须在构造函数初始化列表中进行初始化。例如:
//const成员初始化
class ConstInit {
public:
ConstInit(int i,int j)
{
ival = i;
cival = j;
rival = ival;
}
private:
int ival;
const int cival;
int &rival;
};
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
ConstInit ci;
}
这里引用类型rival以及const类型cival都没有在初始化列表中初始化,因此报错。解决办法就是在初始化列表中初始化这些特殊的类成员。如下例所示:
//const成员初始化
#include <iostream>
using std::cout;
class ConstInit {
public:
ConstInit(int i=0):ival(i),cival(i),rival(i){}
private:
int ival;
const int cival;
int &rival;
//只要初始化表达式是一个常量,可以再定义体中进行初始化
static const int period = 30;
public:
static const unsigned int ARRAY[3];//静态常量数组
};
const unsigned int ConstInit::ARRAY[3] = {1,3,5};
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
ConstInit ci;
cout<<ConstInit::ARRAY[1];
}
No .15 error C2248: “Foo::Foo”: 无法访问 private 成员(在“Foo”类中声明)
prog29.cpp(12) : 参见“Foo::Foo”的声明
prog29.cpp(7) : 参见“Foo”的声明
出错代码:
#include <iostream>
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
//为了禁止复制,类必须显式声明其复制构造函数为private
//要禁止类的友元和成员复制对象,可以声明但不定义复制构造函数
class Foo
{
public:
Foo(int i=0):ival(i){}
int getVal() const {return ival;}
private:
Foo(const Foo& orig){ival = orig.ival;};//声明为私有
private:
int ival;
};
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
Foo foo1(1);//ok,调用构造函数
cout<<foo1.getVal()<<endl;
Foo foo2;
foo2 = foo1;//ok,使用合成的赋值操作符
cout<<foo2.getVal()<<endl;
Foo foo3(foo1);//error,无法调用复制构造函数
cout<<foo3.getVal()<<endl;
return 0;
}
解决办法: 这里旨在说明三种初始化方式,foo1使用构造函数初始化,foo2使用默认值调用构造函数,而foo3代用私有的复制构造函数因而产生错误。注意,为了禁止复制,类必须显式声明其复制构造函数为private;要禁止类的友元和成员复制对象,可以声明但不定义复制构造函数。遇到这种错误,说明赋值构造函数函数的使用不当。
No.16 与复制构造函数相关的错误.例如:0x77D9FCAA (ntdll.dll) (prog31.exe 中)处有未经处理的异常: 0xC0000374:堆已损坏。 (参数: 0x77DC6668)。
这种错误可能就是与内存有关的释放问题。这里的错误示例代码主要是为了说明复制构造函数,尤其是含有指针类型或者有成员表示在构造函数中分配的其他资源的情况下应该应当被正确处理。
错误示例代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
//复制构造函数举例1
//此例包含指针成员,没有复制构造函数出错
struct Node
{
Node(char *n="",int a = 0)
{
name = strdup(n);
strcpy(name,n);
age = a ;
}
~Node()
{
delete[] name;
}
char *name;
int age;
};
int main()
{
Node node1("Roger",20),node2(node1);
//print Roger 20 Roger 20
cout<<node1.name<<" "<<node1.age<<" "
<<node2.name<<" "<<node2.age<<endl;
strcpy(node2.name,"Wendy");
node2.age = 30;
//print Wendy 20 Wendy 30
cout<<node1.name<<" "<<node1.age<<" "
<<node2.name<<" "<<node2.age<<endl;
}
注意,这里的strdup函数是C语言中函数,它会根据串长用malloc分配内存的,返回分配的内存首地址。
这段程序执行时输出:
Roger 20 Roger 20
Wendy 20 Wendy 30
并产生错误:
0x77D9FCAA (ntdll.dll) (prog31.exe 中)处有未经处理的异常: 0xC0000374: 堆已损坏。 (参数: 0x77DC6668)。
解决办法:包含指针类型或者构造函数中包含资源分配的类,需要定义自己的复制构造函数而不是依赖编译器合成的复制构造函数。
这里依赖编译器合成的复制构造函数,从node1构造node2时,node2.name指针进行简单的重定向,定向到node1.name所指向的字符串,因此二者共享同一份字符串地址,因此再执行strcpy(node2.name,"Wendy");出现了数据不一致行的错误,两者的name全部都是Wendy,而年龄更新却是正确的。同样,由于共享同一份字符串地址,在析构函数中释放同一份内存两次,导致堆已损坏的错误。当然,如果在析构函数中删除name数组空间后,将name指针置为空,不会产生堆损坏错误。但是在析构函数中将指针置为空,将隐藏程序bug,与复制构造函数相关的错误依然存在。
因此解决的办法,就是正确定义Node类如下:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
//复制构造函数举例2
struct Node
{
Node(char *n="",int a = 0)
{
name = strdup(n);
strcpy(name,n);
age = a ;
}
//复制构造函数
Node(const Node& node)
{
name = strdup(node.name);
age = node.age;
}
//赋值操作符
Node& operator=(const Node& n)
{
if(this != &n)
{
if(name != NULL)
delete [] name;//释放先前空间
name = strdup(n.name);//重新分配内存
age = n.age;
}
return *this;
}
//析构函数
~Node()
{
delete[] name;
}
char *name;
int age;
};
int main()
{
Node node1("Roger",20),node2(node1),node3("Tom",22);
//print Roger 20 Roger 20
cout<<node1.name<<" "<<node1.age<<" "
<<node2.name<<" "<<node2.age<<endl;
strcpy(node2.name,"Wendy");
node2.age = 30;
//print Roger 20 Wendy 30
cout<<node1.name<<" "<<node1.age<<" "
<<node2.name<<" "<<node2.age<<endl;
//赋值操作符
node2 = node3;
//print Tom 22 Tom 22
cout<<node2.name<<" "<<node2.age<<" "
<<node3.name<<" "<<node3.age<<endl;
return 0;
}
这里因为可以由三法则(Rule of Three)即一个类如果需要析构函数,则该类几乎也必然需要定义自己的复制构造函数和赋值操作符解释。重新运行程序,即可得到正确结果并避免堆损坏错误。
No.17 error C2664: “std::list<_Ty>::list(const std::allocator<_Ty> &)”: 不能将参数 1 从
“std::vector<_Ty>”转换为“const std::allocator<_Ty> &”
with
[
_Ty=int
]
原因如下: 无法从“std::vector<_Ty>”转换为“const std::allocator<_Ty>”
with
[
_Ty=int
]
没有可用于执行该转换的用户定义的转换运算符,或者无法调用该运算符
prog33.cpp(13) : error C2664: “std::vector<_Ty>::vector(const std::allocator<_Ty> &)”: 不能将参数
1 从“std::vector<_Ty>”转换为“const std::allocator<_Ty> &”
with
[
_Ty=double
]
and
[
_Ty=int
]
and
[
_Ty=double
]
原因如下: 无法从“std::vector<_Ty>”转换为“const std::allocator<_Ty>”
with
[
_Ty=int
]
and
[
_Ty=double
]
没有可用于执行该转换的用户定义的转换运算符,或者无法调用该运算符
错误代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <list>
using std::vector;
using std::list;
using std::cout;
//容器初始化举例
int main()
{
vector<int> ivec;//使用默认构造函数
vector<int> ivec2(ivec);//初始化为同型容器的副本
list<int> ilist(ivec);//错误,容器类型不同
vector<double> dvec(ivec);//错误,容器元素类型不同
return 0;
}解决办法: c++标准库中不允许容器初始化为不同类型或者容器元素类型不同的容器的副本。如果需要从其他容器的元素初始化容器,可以使用一对迭代范围的构造函数初始化。例如:
vector<int> ivec; list<int> ilist(ivec.begin(),ivec.end()); vector<double> dvec(ivec.begin(),ivec.end());
No.18 与迭代器失效相关的错误,例如:0x008D1127 处有未经处理的异常(在 prog34.exe 中): 0xC0000005: 读取位置 0x010AC000 时发生访问冲突。
错误代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using std::vector;
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
//迭代器失效举例-避免存储end操作返回的迭代器
int main()
{
vector<int> ivec;
ivec.push_back(3);
ivec.push_back(5);
ivec.push_back(7);
vector<int>::iterator end = ivec.end();
for(vector<int>::iterator first = ivec.begin();first != end;++first)
cout<<*first<<endl;
ivec.insert(ivec.begin(),1);
//cause fatal error
for(vector<int>::iterator first = ivec.begin();first != end;++first)
cout<<*first<<endl;
return 0;
}
解决办法: 这里保存了end操作返回的迭代器,然后又在容器中执行插入操作,导致迭代器失效,因而第二次的输出操作无法正常结束导致死循环,产生访问冲突。要警惕迭代器失效的操作,c++ primer建议假设迭代器失效是最安全的做法。这里可以在for语句中重新获取迭代器,以避免此类错误。
No.19 ...VC\INCLUDE\iterator(93) : error C2039: “push_front”:
不是“std::vector<_Ty>”的成员
with[
_Ty=int
]
错误代码:
int ia[] = {1,5,3,3,4};
const int array_size = sizeof(ia)/sizeof(*ia);
list<int> ilist(ia,ia+array_size);
vector<int> temp;
copy(ilist.begin(),ilist.end(),
front_inserter(temp));//使用push_front插入,导致错误
解决办法: 迭代器与底层容器之间的操作实际上存在限制关系,也就是说并不是所有的容器都支持诸如push_front之类的操作。这里front_inserter将使用push_front方法来向vector插入元素,但是vector并不支持push_front操作。因此,解决的方法就是使用back_inserter 或者inserter函数返回的插入迭代器来进行操作。
NO.20 类模板使用时 TestDrive.obj : error LNK2019: 无法解析的外部符号 "public: __thiscall LinkedList<int>::~LinkedList<i
nt>(void)" (??1?$LinkedList@H@@QAE@XZ),该符号在函数 _main 中被引用.
错误代码:
LikedList.h
#ifndef _PAIR_H_
#define _PAIR_H_
#include <string>
template <class T>
class Node
{
public:
Node(T dat,Node *n=NULL):data(dat),next(n){}
public:
T data;
Node *next;
};
template <class T>
class LinkedList
{
public:
LinkedList():head(NULL){}
~LinkedList();//free space here
void add(T e);//add element
std::string toString();//print content
public:
Node<T> *head;
};
#endifLinkedList.cpp
#include "LinkedList.h"
//free space
template <class T> LinkedList<T>::~LinkedList()
{
Node<T> * ptr = head;
while(ptr != NULL)
{
Node<T> * tmp = ptr->next;
delete ptr;
ptr = tmp;
}
}
template <class T> void LinkedList<T>::add(T e)
{
Node<T> *node = new Node<T>(e);
node->next = head;
head = node;//update head
}
template <class T> std::string LinkedList<T>::toString()
{
std::string asString("List:[");
for(Node<T>* ptr = head;ptr != NULL;ptr = ptr->next)
asString += std::to_string(ptr->data);
asString += "]";
return asString;
}
TestDrive.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include "LinkedList.h"
int main()
{
LinkedList<int> list;
list.add(1);
list.add(2);
list.add(3);
std::cout<<list.toString()<<std::endl;
return 0;
}
解决办法: 模板类文件编译要采取一些手段。
主要有两种方式,方式一在头文件中包含类的实现,合并成一个文件来编译.
方式二,通过使用export关键字,让编译器知道要记住给定的模板定义。当然要看编译器支持否,我的vs2013编译提示, warning C4237: 目前还不支持“export”关键字,但已保留该关键字供将来使用。因此这里使用方式一,例如代码:
#ifndef _PAIR_H_
#define _PAIR_H_
#include <string>
template <class T>
class Node
{
public:
Node(T dat,Node *n=NULL):data(dat),next(n){}
public:
T data;
Node *next;
};
template <class T>
class LinkedList
{
public:
LinkedList():head(NULL){}
~LinkedList();//free space here
void add(T e);//add element
std::string toString();//print content
public:
Node<T> *head;
};
template <class T> LinkedList<T>::~LinkedList()
{
Node<T> * ptr = head;
while(ptr != NULL)
{
Node<T> * tmp = ptr->next;
delete ptr;
ptr = tmp;
}
}
template <class T> void LinkedList<T>::add(T e)
{
Node<T> *node = new Node<T>(e);
node->next = head;
head = node;//update head
}
template <class T> std::string LinkedList<T>::toString()
{
std::string asString("List:[");
for(Node<T>* ptr = head;ptr != NULL;ptr = ptr->next)
asString += std::to_string(ptr->data);
asString += "]";
return asString;
}
#endif
测试结果:
List:[321].
No 21: 类成员变量和函数重名问题 error C2365: “ArrayStack<T>::top”: 重定义;以前的定义是“成员函数”
这个错误发生纯属意外,但是让人纠结了半天。在c++中类的成员变量和函数是不可以重名的,这与java之中不同。例如使用数组实现一个栈时,ArrayStack类的top指针成员和基类的函数top重名,导致的错误,一开始让人莫名其妙。
错误代码:
Stack基类中声明了函数top:
template<typename T>
class Stack
{
public:
virtual ~Stack(){};
virtual void push(T data)=0;
virtual T pop()=0;
virtual T top()=0;
virtual bool isEmpty()=0;
virtual void clear() = 0;
virtual int getSize()=0;
};
利用数组实现时:
template<typename T = int>
class ArrayStack : public Stack<T>
{
public:
T top()
{
if(top == base)
{
throw std::logic_error("top at empty stack");
}
return *(top-1);
}
//other member function
private:
T *base,*top;
int capacity;
};
因为类使用了指针top,同时实现了函数top,重名错误,因此导致了编译器给出如下错误信息:
d:\ds\stack\ArrayStack.h(79) : error C2365: “ArrayStack<T>::top”: 重定义;以前的定义是“成员函数”
d:\ds\stack\ArrayStack.h(58) : 参见“ArrayStack<T>::top”的声明
d:\ds\stack\ArrayStack.h(81): 参见对正在编译的类 模板 实例化“ArrayStack<T>”的引用
d:\ds\stack\ArrayStack.h(79) : error C2365: “ArrayStack<T>::top”: 重定义;以前的定义是“成员函数”
with
[
T=int
]
d:\ds\stack\ArrayStack.h(58) : 参见“ArrayStack<T>::top”的声明
with
[
T=int
]
StackTest.cpp(6): 参见对正在编译的类 模板 实例化“ArrayStack<T>”的引用
with
[
T=int
]
解决办法,遵照合理的命名规则。
No.22 使用标准库sort等方法却未定义关系操作符 algorithm(3618) : error C2784: “bool std::
operator <(const std::basic_string<_Elem,_Traits,_Alloc> &,const _Elem *)”: 未能从“Person”为“con
st std::basic_string<_Elem,_Traits,_Alloc> &”推导 模板 参数
...(省略)
algorithm(3619) : error C2676: 二进制“<”:“Person”不定义该运算符或到预定义运算符可接收的类型的转换
错误代码示例:
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
class Person
{
public:
// default constructor
Person() : age(0) {}
Person(int age, std::string name) {
this->age = age; this->name = name;
}
int age;
std::string name;
};
int main()
{
std::vector<Person> vecPerson;
vecPerson.push_back(Person(24,"Calvin"));
vecPerson.push_back(Person(30,"Benny"));
vecPerson.push_back(Person(28,"Alison"));
std::sort(vecPerson.begin(),vecPerson.end());
//using c++11
for(const Person& p : vecPerson)
std::cout<<p.age<<", "<<p.name<<std::endl;
return 0;
}
解决办法: 定义STL算法需要的关系操作符。在上例中,sort算法默认使用std::less,而std::less使用类的<操作符,因此可以定义一个全局的
重载<操作符的函数来满足sort算法需求,如下:
inline bool operator<(const Person& a, const Person& b)
{
return a.age < b.age;
}
程序输出:
24, Calvin
28, Alison
30, Benny
No.23 error C2661: “std::less<_Ty>::less”: 没有重载函数接受 2 个参数
Std::less<T>是一个函数对象,错误在于没有正确的使用函数对象。
错误代码示例:
template<typename T,typename Compare=std::less<T> >
class PriorityQueue : public Queue<T>
{
template<typename T,typename Compare>
T PriorityQueue<T,Compare>::dequeue()
{
if(index == 0)
{
std::cerr<<"logic error : dequeue at empty queue. "<<std::endl;
throw std::logic_error("dequeue at empty queue");
}
//pick up one with highest priority
int highIndex = 0;
for(int i = 1;i < index ;i++) // O(n)
{
if( Compare( queue[i],queue[highIndex] ) )
highIndex = i;
}
T result = queue[highIndex];
index--;
queue[highIndex] = queue[index]; //put the last element to the removed position
return result;
}
}
错误的代码出现在: if( Compare( queue[i],queue[highIndex] ) )。
Compare是一个函数对象,函数对象使用方式两种:
第一种,显式构造一个函数对象,然后使用它,例如:
std::less<Key> a; //定义一个函数对象 if(a(x,y)) ...
第二种,在使用时构造,例如:
if(std::less<Key>()(x,y)) ...
对于上述代码中,解决办法:代码更正为:if( Compare()( queue[i],queue[highIndex] ) )。
No.24 自增变量传递参数引起的段错误 (核心已转储)
这里给出我书写一段代码引起的段错误:
#include <iostream>
#include <list>
using namespace std;
void printList(list<int>::iterator itCur,list<int>::iterator end);
int main()
{
list<int> iList;
for(int i = 0;i < 10 ;i++)
iList.push_back(i);
printList(iList.begin(),iList.end());
}
void printList(list<int>::iterator itCur,list<int>::iterator end)
{
if( itCur == end)
{
std::cout<<std::endl;
return;
}
std::cout<<*itCur<<" ";
printList(itCur++,end);
}
这段程序中,利用尾递归输出链表,实际上将进入死循环,导致输出时linux下提示段错误。在传递参数时,利用printList(itCur++,end)却没有达到预期效果,原因是后置自增变量用错了,这个错误很低级,需要引起注意。
解决办法,就是通过++itCur后者*itCur++来传递正确的参数。
No.25 栈使用已经改变的数据引起的不一致问题
这是一个不经留意犯的错误。
错误代码如下:
while(!stack.empty()) {
if(top == stack.top()->left && stack.top()->right != 0) {
stack.push(stack.top()->right);
visit(stack.top()->right);//should visit last top right,not the new top right
break;
}else {
top = stack.top();
stack.pop();
}
}
这里visit的本意是访问当前栈顶的右子树,结果因为与stack.push弄错了顺序,导致访问的是新的栈顶的右子树,从而导致出错。
这里没有意识到,stack.top->right本身已经改变了,使用不一致的数据导致出错。
No.26 segmentation fault
段错误,简而言之,是由于你使用已经释放的内存,写入只读的内存引起的错误。参考自:SO segmentation fault
例子1:解引用空指针
int main()
{
//dereference a null pointer,can cause segmentation fault
int *p = 0;
*p = 1;
return 0;
}
例子2: 写入只读内存
int main()
{
// write to a portion of memory that has marked as read-only
char *str = "Foo";// compiler marks the constant string as read-only
*str = 'b';//which means this is illegal and results in a segfault
return 0;
}
关于segfault更多内容,可以参考: C/C++中的段错误.
No.27 warning: xxx will be initialized after [-Wreorder]
c++使用参数列表进行初始话时,初始化成员变量的顺序和声明的顺序相同,如果在写参数列表时没有按照声明的顺序写,则出现此警告。
这个警告是为了避免在参数列表初始化时,值之间初始化产生依赖的错误。解决方法就是按照声明的顺序书写参数初始化列表。
Class C {
int a;
int b;
C():b(1),a(2){} //warning, should be C():a(2),b(1)
}
或者取消警告: -Wno-reorder.
No.28 error: ‘std::ios_base::ios_base(const std::ios_base&)’ is private
ios_base(const ios_base&);
synthesized method ‘std::basic_ostream<char>::basic_ostream(const std::basic_ostream<char>&)’ first required here
return s;
这个错误的原因大概是std::ios_base类的拷贝构造函数是私有的,从return s语句返回时缺少一个合成的构造拷贝构造函数完成流的复制。
错误代码示例:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
struct Person {
std::string name;
Person(std::string n):name(n){}
};
// should return a reference to std::ostream
std::ostream operator<<(std::ostream& s,const Person &p) {
s << p.name;
return s;
}
int main() {
Person p(std::string("Tom"));
std::cout<<p<<std::endl;
}
重载输出操作符时,由于流对象不能复制,因此如果以值(by value)形式返回时,无法完成从s到std::osream的复制,因此导致上述错误。
解决方法是返回流的引用,即改变函数的返回类型为:std::ostream&即可。
No 29 . passing xxx as 'this' argument of xxx discards qualifiers
这是由于常量对象调用了非常量成员函数引起的错误,错误原因在于常量对象只能调用常量成员函数(因为常量成员函数约定不对非静态成员进行修改).
来自 stackoverflow的例子:
#include <iostream>
#include <set>
using namespace std;
class StudentT {
public:
int id;
string name;
public:
StudentT(int _id, string _name) : id(_id), name(_name) {
}
int getId() { // 应该声明为const成员
return id;
}
string getName() { // 应该声明为const成员
return name;
}
};
inline bool operator< (StudentT s1, StudentT s2) {
return s1.getId() < s2.getId();
}
int main() {
set<StudentT> st;
StudentT s1(0, "Tom");
StudentT s2(1, "Tim");
st.insert(s1);
st.insert(s2);
set<StudentT> :: iterator itr;
for (itr = st.begin(); itr != st.end(); itr++) {
cout << itr->getId() << " " << itr->getName() << endl;
}
return 0;
}
这个例子中,加入set的StudentT对象都变成const对象了,那么调用getId等方法时只能调用其const版本,因为没有定义这个版本,因此编译器提示错误.
解决方法就是将getId和getName方法声明为const成员,即在函数末尾加上const关键字.
No.30 error: cannot dynamic_cast ‘b’ (of type ‘class Base*’) to type ‘class Derived<int>*’ (source type is not polymorphic)
在将父类型转换为子类型时,可以使用static_cast和dynamic_cast.如果使用dynamic_cast,它要求父类必须为多态的,即要求至少有一个虚函数,因此需要仔细检查类定义中有无虚函数,例如可以将析构函数设置为虚函数.
更正后的代码为(来自: c++ - converting a base class pointer to a derived class pointer):
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Base {
public:
Base() {};
virtual ~Base() {}; // make it polymorphic
};
template<class T>
class Derived: public Base {
T _val;
public:
Derived() {}
Derived(T val): _val(val) {}
T raw() {return _val;}
};
int main()
{
Base * b = new Derived<int>(1);
Derived<int> * d = dynamic_cast<Derived<int>* >(b);
cout << d->raw() << endl;
return 0;
}
No.31 error: conversion from ‘SmallInt’ to ‘long double’ is ambiguous
当实参与形参匹配的过程中,如果提供了多个转换操作符,而每个转换操作符都不能与形参类型匹配,需要额外的标准转换时,则没有哪种转换明显优于另一种,则编译器提示这个转换存在二义性,例如(来自c++ primer 4th):
// this example show paramaters matching process
// note SmallInt is a bad design
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class SmallInt {
public:
SmallInt(int x=0):val(x){ cout << "int ctor" << endl; }
SmallInt(double x):val(x){ cout << "double ctor" << endl;}
operator int() const { cout << "int conversion " << endl;return val;}
operator double() const { cout << "double conversion" << endl; return val;}
private:
std::size_t val;
};
void compute(int x){}
void fp_compute(double x){}
void extended_compute(long double x){}
int main() {
SmallInt si;
compute(si); // using SmallInt::operator int() const
fp_compute(si); // using SmallInt::operator double() const
extended_compute(si); // error: ambiguous
return 0;
}
这里的extended_compute函数需要long double类型,而SmallInt两个转换函数,都不能直接转换为long double,必须后接标准转换,因此没有哪种转换优于另一种,导致二义性错误.一般地,对一个类设置两个内置类型之间的转换,是不好的做法,这个例子的设计主要是为了说明这个缺陷.
No.32 /usr/include/c++/4.9/bits/stl_iterator_base_types.h:165:53: error: ‘int’ is not a class, struct, or union type
先看下面的代码(来自: SO):
#include <iostream>
#include <cmath>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
double distance(int a, int b)
{
return fabs(a-b);
}
int main()
{
vector<int> age;
age.push_back(10);
age.push_back(15);
cout << distance(age[0],age[1]);
return 0;
}
这段代码初看起来并无错误,编译时提示上述错误,原因在于使用std命名空间,而std命名空间中已经有了std::distance函数.
原型为:
template<class InputIterator>
typename iterator_traits<InputIterator>::difference_type
distance (InputIterator first, InputIterator last);
这个函数要求两个参数至少都满足InPut Iterator约束,y而age[0]为int类型,不满足这个约束,因此导致上面的错误信息.
这段代码的错误之处,在于std命名空间中的distance屏蔽了本地的distance函数,解决方法即为,显式调用本地方法,例如使用
::distance(age[0],age[1])
或者将distance放在一个命名空间中,例如:
namespace foo
{
double distance(int a, int b)
{
return fabs(a-b);
}
}
int main()
{
foo::distance(x,y); //now you're calling your own distance function.
}
或者不使用命名空间std,显式声明std::vector也可以解决.
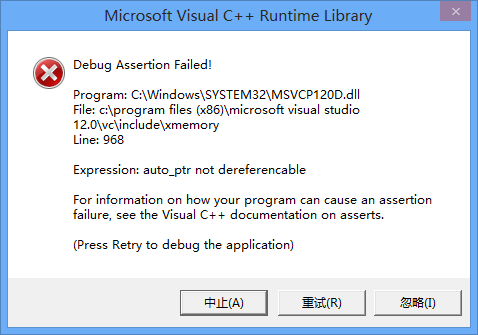
No.33 auto_ptr is not dereferencable
如下图所示:
错误代码示例:
// Example : Transferring ownership from
// one auto_ptr to another
void testAutoPtr6()
{
std::auto_ptr<TC> pt1(new TC);
std::auto_ptr<TC> pt2;
pt1->someFunc(); // OK
pt2 = pt1; // now pt2 owns the pointer, and pt1 does not
std::cout << "Content of pt1 is " << pt1.get() << std::endl;
std::cout << "Content of pt2 is " << pt2.get() << std::endl;
pt2->someFunc(); // OK
pt1->someFunc(); // error! following a null pointer
} // as we go out of scope, pt2's destructor
// deletes the pointer, but pt1's does nothing
auto_ptr在拷贝时会转移内存控制权,例子中pt1赋值给pt2后,将内存管理权转移给pt2, 此时pt1指针为NULL.
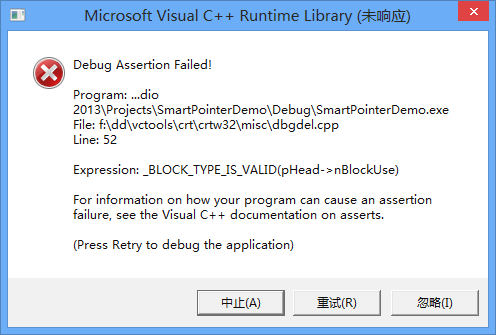
No.34 _block_type_is_valid(phead- nblockuse)
出现这种错误的原因有多个,基本原因有四个, 可以参见:SO。
错误如下:
比较常见的错误时,把多个对象的数组当做一个对象删除了,例如:
void testSharedPtr1()
{
//std::shared_ptr<TC> pt(new TC[5]); // will crash , since default desctrctor using delete
std::shared_ptr<TC> sptr1(new TC[5],
[](TC* p) { delete[] p; });
}
这里std::shared_ptr默认使用delete删除,因此会导致出现上述错误。使用lamda表达式可以解决。
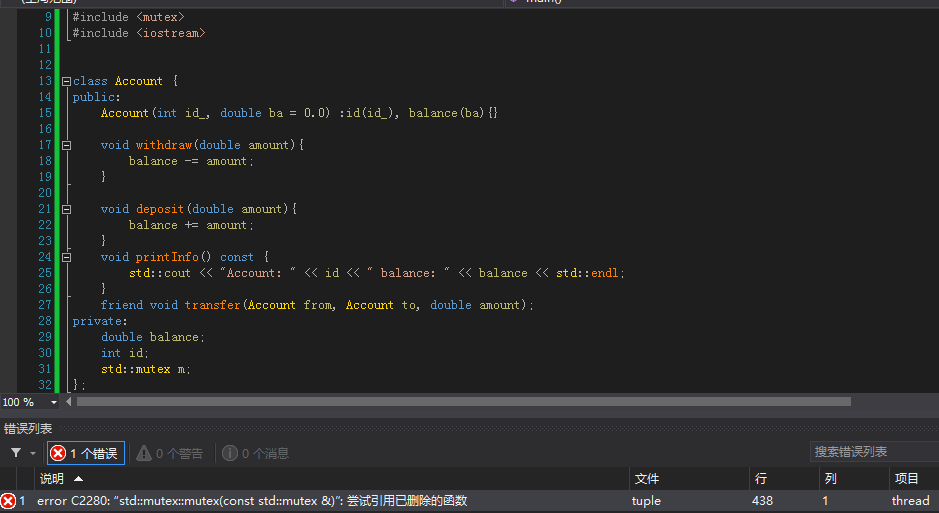
No:35 error C2280: 'std::mutex::mutex(const std::mutex &)' : attempting to reference a deleted function
std::mutex是noncopyable的结构,因此不存在拷贝构造函数,所以这里错误提示引用已经删除的函数。
错误示例代码如下:
解决方法:
将包含std::mutex的类的拷贝构造函数和赋值操作符重载函数,自定义或者标记为delete.
例如:
class Account {
public:
Account(int id_, double ba = 0.0) :id(id_), balance(ba){}
void withdraw(double amount){
balance -= amount;
}
void deposit(double amount){
balance += amount;
}
void printInfo() const {
std::cout << "Account id: " << id << " balance: " << balance << std::endl;
}
Account(const Account& other) = delete;
Account& operator=(const Account& other) = delete;
friend void transfer(Account& from, Account& to, double amount);
private:
double balance;
int id;
std::mutex m;
};