Android建立dialog
自从有了图形化应用程序之后,对话框(Dialog)一直是元老级组件(widget)。Android的组件库考虑了小尺寸的触摸屏,在基本元件的设计上,Android也为使用者做了很体贴的设计。以Android手机应用程序来说,经常使用的组件件已经不能像过去的点击式系统那么多又复杂。以使用性的角度来看,常被使用的元件如下:
-
菜单(Menu)
-
对话框(Dialog)
-
快显信息(Toast)
使用以上三个组件,以及他们的“变化体”,就能组成一个好用的应用程序的界面;再加上Android针对手机操作特性,对其组件库做了很好的使用设计,因此使用很少的组件,也能提供一个舒适友好的操作界面。
对话框的概念就不多介绍了,学过windows图形编程的基本上都是从对话框开始入门的,估计很多人跟我一样看见对话框就有一种似是故人来的感觉。Android提供的对话框对象为android.app.Dialog,实现上继承Dialog的AlertDialog是最基本的对话框。使用AlertDialog,可以增加应用程序的用户交互体验,增加程序的界面友好性。下面是AlertDialog的设计方法:
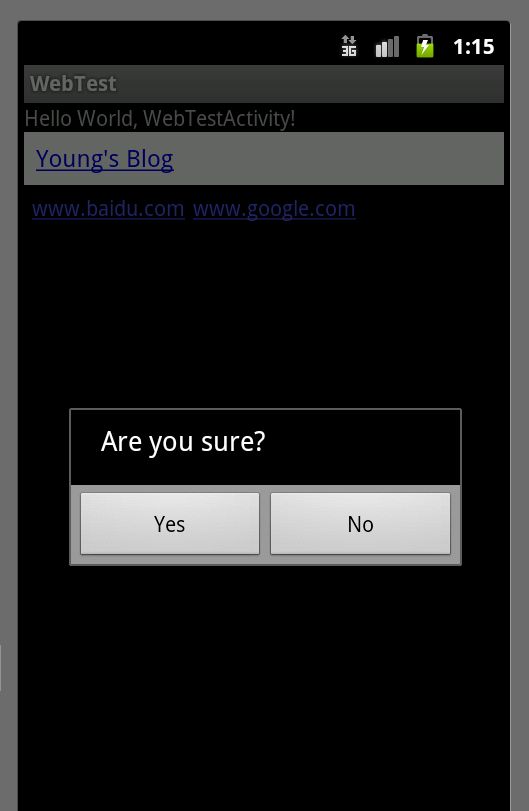
延续WebTest范例,现在加入以下的使用情景:
- 用户按下Menu键
- 用户选择"Play"选项
- 出现对话框、询问用户是否确定"Yes/No"
由以上的使用场景来看,应该在onOptionsItemSelected()里判断到R.id.play项目时,在UI上建立一个对话框。以下是代码:
@Override
public boolean onOptionsItemSelected(MenuItem item) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
int item_id = item.getItemId();
switch (item_id) {
case R.id.play:
AlertDialog.Builder builder = new AlertDialog.Builder(this);
builder.setMessage("Are you sure?");
builder.setCancelable(false);
builder.setPositiveButton("Yes", new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() {
public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int id) {
Intent intent = new Intent(WebTestActivity.this, yypService.class);
startService(intent);
Toast.makeText(WebTestActivity.this,"It's playing music.",Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
}
});
builder.setNegativeButton("No", new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() {
public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int id) {
}
});
AlertDialog alert = builder.create();
alert.show();
break;
case R.id.stop:
this.onStop();
Toast.makeText(this,"music is stopped.",Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
break;
default:
return false;
}
return true;
}
AlertDialog说明:
- 建立AlertDialog.builder对象(dialog builder),这是一个用来建立对话框内容的对象;
- 设定dialog builder的显示信息--builder.setMessage();
- 设定对话框能不能被取消-builder.setCancelable();
- 利用dialog builder在对话框生成两个按钮(Yes/No)--builder.setPositiveButton()与builder.setNegativeButton()
- 使用dialog builder来生创建AlertDialog对象,AlertDialog是真正的对话框对象-builder.create()
- 将AlertDialog显示在UI上-alert.show()
builder.setPositiveButton("Yes", new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() {
public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int id) {
}
});
调用builder.setPositiveButton()方法建立一個「正面(Yes)」的按钮,参数說明如下:
1. 第一個参数:显示在按钮上的文字
2. 第二個参数:指定 click listener