《STL源码剖析》---stl_algobase.h阅读笔记
STL标准中没有区分基本算法或复杂算法,单SGI把常用的一些算法定义在<stl_algobase.h>只中,其他算法定义在<stl_algo.h>中。
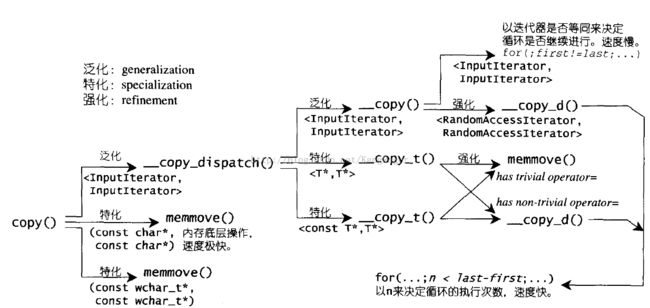
stl_algobase.h中的算法,比较值得学习的是copy(),它“无所不用其极”的改善效率。copy的目的是复制一段元素到指定区间,复制操作最容易想到赋值操作符=,但是有的赋值操作符=是trivial的,可以直接拷贝。关于赋值操作符=是不是trivial的,可以参考“Memberwise copy(深拷贝)与Bitwise copy(浅拷贝)的区别”。
G++ 2.91.57,cygnus\cygwin-b20\include\g++\stl_algobase.h 完整列表
/*
*
* Copyright (c) 1994
* Hewlett-Packard Company
*
* Permission to use, copy, modify, distribute and sell this software
* and its documentation for any purpose is hereby granted without fee,
* provided that the above copyright notice appear in all copies and
* that both that copyright notice and this permission notice appear
* in supporting documentation. Hewlett-Packard Company makes no
* representations about the suitability of this software for any
* purpose. It is provided "as is" without express or implied warranty.
*
*
* Copyright (c) 1996
* Silicon Graphics Computer Systems, Inc.
*
* Permission to use, copy, modify, distribute and sell this software
* and its documentation for any purpose is hereby granted without fee,
* provided that the above copyright notice appear in all copies and
* that both that copyright notice and this permission notice appear
* in supporting documentation. Silicon Graphics makes no
* representations about the suitability of this software for any
* purpose. It is provided "as is" without express or implied warranty.
*/
/* NOTE: This is an internal header file, included by other STL headers.
* You should not attempt to use it directly.
*/
#ifndef __SGI_STL_INTERNAL_ALGOBASE_H
#define __SGI_STL_INTERNAL_ALGOBASE_H
#ifndef __STL_CONFIG_H
#include <stl_config.h>
#endif
#ifndef __SGI_STL_INTERNAL_RELOPS
#include <stl_relops.h>
#endif
#ifndef __SGI_STL_INTERNAL_PAIR_H
#include <stl_pair.h>
#endif
#ifndef __TYPE_TRAITS_H_
#include <type_traits.h>
#endif
#include <string.h>
#include <limits.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stddef.h>
#include <new.h>
#include <iostream.h>
#ifndef __SGI_STL_INTERNAL_ITERATOR_H
#include <stl_iterator.h>
#endif
__STL_BEGIN_NAMESPACE
template <class ForwardIterator1, class ForwardIterator2, class T>
inline void __iter_swap(ForwardIterator1 a, ForwardIterator2 b, T*) {//T是迭代器,T*就是
T tmp = *a; //迭代器指向的类型了
*a = *b;
*b = tmp;
}
//对调两个迭代器指向元素的值
template <class ForwardIterator1, class ForwardIterator2>
inline void iter_swap(ForwardIterator1 a, ForwardIterator2 b) {
// iter_swap() 是「有必要运用迭代器之 value type」的一个好例子。
// 是的,它必须知道迭代器的 value type,才能够据此宣告一个物件,用來
// 暂时放置迭代器所指的物件。
__iter_swap(a, b, value_type(a)); // 注意第三參數的型別!
/*
// 以下定义于 <stl_iterator.h>
template <class Iterator>
inline typename iterator_traits<Iterator>::value_type*
value_type(const Iterator&) {
return static_cast<typename iterator_traits<Iterator>::value_type*>(0);
}
*/
// 侯捷认为(并予实证),不需像上行那样调用,可改用以下写法:
// typename iterator_traits<ForwardIterator1>::value_type tmp = *a;
// *a = *b;
// *b = tmp;
}
template <class T>
inline void swap(T& a, T& b) {
T tmp = a;
a = b;
b = tmp;
}
#ifndef __BORLANDC__
#undef min
#undef max
template <class T>
inline const T& min(const T& a, const T& b) {
return b < a ? b : a;
}
template <class T>
inline const T& max(const T& a, const T& b) {
return a < b ? b : a;
}
#endif /* __BORLANDC__ */
template <class T, class Compare>
inline const T& min(const T& a, const T& b, Compare comp) {
return comp(b, a) ? b : a; // 由 comp 決定「大小比较」标准
}
template <class T, class Compare>
inline const T& max(const T& a, const T& b, Compare comp) {
return comp(a, b) ? b : a; // 由 comp 決定「大小比较」标准
}
template <class InputIterator, class OutputIterator>
inline OutputIterator __copy(InputIterator first, InputIterator last,
OutputIterator result, input_iterator_tag)
{
for ( ; first != last; ++result, ++first)
*result = *first;
return result;
}
template <class RandomAccessIterator, class OutputIterator, class Distance>
inline OutputIterator
__copy_d(RandomAccessIterator first, RandomAccessIterator last,
OutputIterator result, Distance*)
{
for (Distance n = last - first; n > 0; --n, ++result, ++first)
*result = *first;//一个一个赋值
return result;
}
template <class RandomAccessIterator, class OutputIterator>
inline OutputIterator
__copy(RandomAccessIterator first, RandomAccessIterator last,
OutputIterator result, random_access_iterator_tag)
{
return __copy_d(first, last, result, distance_type(first));
}
template <class InputIterator, class OutputIterator>
struct __copy_dispatch
{
OutputIterator operator()(InputIterator first, InputIterator last,
OutputIterator result) {
return __copy(first, last, result, iterator_category(first));
}
};
#ifdef __STL_CLASS_PARTIAL_SPECIALIZATION
//__true_type意味着has trivial operator=。可以直接拷贝
template <class T>
inline T* __copy_t(const T* first, const T* last, T* result, __true_type) {
memmove(result, first, sizeof(T) * (last - first));
return result + (last - first);
}
//__false_type意味着has non-rivial operator=
template <class T>
inline T* __copy_t(const T* first, const T* last, T* result, __false_type) {
return __copy_d(first, last, result, (ptrdiff_t*) 0);
}
template <class T>
struct __copy_dispatch<T*, T*>
{
T* operator()(T* first, T* last, T* result) {
typedef typename __type_traits<T>::has_trivial_assignment_operator t;
return __copy_t(first, last, result, t());
}
};
template <class T>
struct __copy_dispatch<const T*, T*>
{
T* operator()(const T* first, const T* last, T* result) {
//赋值操作符=是否是trivial的
typedef typename __type_traits<T>::has_trivial_assignment_operator t;
return __copy_t(first, last, result, t());
}
};
#endif /* __STL_CLASS_PARTIAL_SPECIALIZATION */
//将[first last)区间元素复制到[result result+(last-first))
// copy 函数运用了 function overloading, type traits, partial
// specialization, 无所不用其极的改善效率。
//下面还有个copy_backward,它是从后向前复制。防止两个区间
//[first last)和[result result+(last-first))可能会有重叠。
//如果一一赋值,会有覆盖,但是用memmove则不会,因为它会先将
//值拷贝下来。
template <class InputIterator, class OutputIterator>
inline OutputIterator copy(InputIterator first, InputIterator last,
OutputIterator result)
{
return __copy_dispatch<InputIterator,OutputIterator>()(first, last, result);
}
inline char* copy(const char* first, const char* last, char* result) {
memmove(result, first, last - first);
return result + (last - first);
}
inline wchar_t* copy(const wchar_t* first, const wchar_t* last,
wchar_t* result) {
memmove(result, first, sizeof(wchar_t) * (last - first));
return result + (last - first);
}
template <class BidirectionalIterator1, class BidirectionalIterator2>
inline BidirectionalIterator2 __copy_backward(BidirectionalIterator1 first,
BidirectionalIterator1 last,
BidirectionalIterator2 result) {
while (first != last) *--result = *--last;
return result;
}
template <class BidirectionalIterator1, class BidirectionalIterator2>
struct __copy_backward_dispatch
{
BidirectionalIterator2 operator()(BidirectionalIterator1 first,
BidirectionalIterator1 last,
BidirectionalIterator2 result) {
return __copy_backward(first, last, result);
}
};
#ifdef __STL_CLASS_PARTIAL_SPECIALIZATION
template <class T>
inline T* __copy_backward_t(const T* first, const T* last, T* result,
__true_type) {
const ptrdiff_t N = last - first;
memmove(result - N, first, sizeof(T) * N);
return result - N;
}
template <class T>
inline T* __copy_backward_t(const T* first, const T* last, T* result,
__false_type) {
return __copy_backward(first, last, result);
}
template <class T>
struct __copy_backward_dispatch<T*, T*>
{
T* operator()(T* first, T* last, T* result) {
typedef typename __type_traits<T>::has_trivial_assignment_operator t;
return __copy_backward_t(first, last, result, t());
}
};
template <class T>
struct __copy_backward_dispatch<const T*, T*>
{
T* operator()(const T* first, const T* last, T* result) {
typedef typename __type_traits<T>::has_trivial_assignment_operator t;
return __copy_backward_t(first, last, result, t());
}
};
#endif /* __STL_CLASS_PARTIAL_SPECIALIZATION */
template <class BidirectionalIterator1, class BidirectionalIterator2>
inline BidirectionalIterator2 copy_backward(BidirectionalIterator1 first,
BidirectionalIterator1 last,
BidirectionalIterator2 result) {
return __copy_backward_dispatch<BidirectionalIterator1,
BidirectionalIterator2>()(first, last,
result);
}
template <class InputIterator, class Size, class OutputIterator>
pair<InputIterator, OutputIterator> __copy_n(InputIterator first, Size count,
OutputIterator result,
input_iterator_tag) {
for ( ; count > 0; --count, ++first, ++result)
*result = *first;
return pair<InputIterator, OutputIterator>(first, result);
}
template <class RandomAccessIterator, class Size, class OutputIterator>
inline pair<RandomAccessIterator, OutputIterator>
__copy_n(RandomAccessIterator first, Size count,
OutputIterator result,
random_access_iterator_tag) {
RandomAccessIterator last = first + count;
return pair<RandomAccessIterator, OutputIterator>(last,
copy(first, last, result));
}
// 以下为 SGI STL 专属,从 first 开始复制 count 个元素到 result 以后的空间。
template <class InputIterator, class Size, class OutputIterator>
inline pair<InputIterator, OutputIterator>
copy_n(InputIterator first, Size count,
OutputIterator result) {
return __copy_n(first, count, result, iterator_category(first));
}
//将[first last)内所有元素改填新值value
template <class ForwardIterator, class T>
void fill(ForwardIterator first, ForwardIterator last, const T& value) {
for ( ; first != last; ++first) // 迭代走过整个范围
*first = value;
}
//注意:n不能超过区间长度
template <class OutputIterator, class Size, class T>
OutputIterator fill_n(OutputIterator first, Size n, const T& value) {
for ( ; n > 0; --n, ++first) // 经过n个元素
*first = value; // 注意,assignment 是覆盖(overwrite)而不是插入(insert)
return first;
}
//用于比较两个区间,指出两者之间的第一个不匹配点。返回一对迭代器,分别
//指出两个区间的不匹配点。如果都匹配,返回的是指向两个区间的last迭代器。
template <class InputIterator1, class InputIterator2>
pair<InputIterator1, InputIterator2> mismatch(InputIterator1 first1,
InputIterator1 last1,
InputIterator2 first2) {
// 以下,如果序列一走完,就结束。
// 以下,如果序列一和序列二的对应元素相等,就结束。
// 显然,区间一的元素个数必须多过序列二的元素个数,否则结果不可预期。
while (first1 != last1 && *first1 == *first2) {
++first1;
++first2;
}
return pair<InputIterator1, InputIterator2>(first1, first2);
}
template <class InputIterator1, class InputIterator2, class BinaryPredicate>
pair<InputIterator1, InputIterator2> mismatch(InputIterator1 first1,
InputIterator1 last1,
InputIterator2 first2,
BinaryPredicate binary_pred) {
while (first1 != last1 && binary_pred(*first1, *first2)) {
++first1;
++first2;
}
return pair<InputIterator1, InputIterator2>(first1, first2);
}
//如果两个区间在[first last)区间相等,返回true。如果第二个区间元素比较多,多出来的
//不予考虑。如果第二个区间元素少,会有不可预测的结果。因此在使用前最好判断区间大小。
template <class InputIterator1, class InputIterator2>
inline bool equal(InputIterator1 first1, InputIterator1 last1,
InputIterator2 first2) {
// 遍历一遍区间的元素
// 如果区间一的元素个数多过区间二的元素个数,就糟糕了。
for ( ; first1 != last1; ++first1, ++first2)
if (*first1 != *first2) // 只要对应元素不相等,
return false; // 就结束并返回 false。
return true; // 至此,全部相等,返回true。
}
template <class InputIterator1, class InputIterator2, class BinaryPredicate>
inline bool equal(InputIterator1 first1, InputIterator1 last1,
InputIterator2 first2, BinaryPredicate binary_pred) {
for ( ; first1 != last1; ++first1, ++first2)
if (!binary_pred(*first1, *first2))
return false;
return true;
}
//以“字典排序方式”对两个区间[first1 last1)和[first2 last2)进行比较
template <class InputIterator1, class InputIterator2>
bool lexicographical_compare(InputIterator1 first1, InputIterator1 last1,
InputIterator2 first2, InputIterator2 last2) {
// 以下,任何一个区间到达尾端,就结束。否则两个区间就相应元素一一进行比对。
for ( ; first1 != last1 && first2 != last2; ++first1, ++first2) {
if (*first1 < *first2) // 第一序列元素值小于第二序列的相应元素值
return true;
if (*first2 < *first1) // 第二序列元素值小于第一序列的相应元素值
return false;
// 如果不符合以上两条件,表示两值相等,那就进行下一组相应元素值的比对。
}
// 运行到这里,如果第一区间到达尾端而第二区间尚有余额,那么第一区间小于第二区间。
return first1 == last1 && first2 != last2;
}
template <class InputIterator1, class InputIterator2, class Compare>
bool lexicographical_compare(InputIterator1 first1, InputIterator1 last1,
InputIterator2 first2, InputIterator2 last2,
Compare comp) {
for ( ; first1 != last1 && first2 != last2; ++first1, ++first2) {
if (comp(*first1, *first2))
return true;
if (comp(*first2, *first1))
return false;
}
return first1 == last1 && first2 != last2;
}
inline bool
lexicographical_compare(const unsigned char* first1,
const unsigned char* last1,
const unsigned char* first2,
const unsigned char* last2)
{
const size_t len1 = last1 - first1; // 第一区间長度
const size_t len2 = last2 - first2; // 第二区间長度
// 先比较相同长度的一截。memcmp() 速度极快。
const int result = memcmp(first1, first2, min(len1, len2));
// 如果不相上下,则长度较长者被视为比较大。
return result != 0 ? result < 0 : len1 < len2;
}
inline bool lexicographical_compare(const char* first1, const char* last1,
const char* first2, const char* last2)
{
#if CHAR_MAX == SCHAR_MAX
// 转换为 const signed char*
return lexicographical_compare((const signed char*) first1,
(const signed char*) last1,
(const signed char*) first2,
(const signed char*) last2);
#else
// 转换为 const unsigned char*
return lexicographical_compare((const unsigned char*) first1,
(const unsigned char*) last1,
(const unsigned char*) first2,
(const unsigned char*) last2);
#endif
}
template <class InputIterator1, class InputIterator2>
int lexicographical_compare_3way(InputIterator1 first1, InputIterator1 last1,
InputIterator2 first2, InputIterator2 last2)
{
while (first1 != last1 && first2 != last2) {
if (*first1 < *first2) return -1;
if (*first2 < *first1) return 1;
++first1; ++first2;
}
if (first2 == last2) {
return !(first1 == last1);
} else {
return -1;
}
}
inline int
lexicographical_compare_3way(const unsigned char* first1,
const unsigned char* last1,
const unsigned char* first2,
const unsigned char* last2)
{
const ptrdiff_t len1 = last1 - first1;
const ptrdiff_t len2 = last2 - first2;
const int result = memcmp(first1, first2, min(len1, len2));
return result != 0 ? result : (len1 == len2 ? 0 : (len1 < len2 ? -1 : 1));
}
inline int lexicographical_compare_3way(const char* first1, const char* last1,
const char* first2, const char* last2)
{
#if CHAR_MAX == SCHAR_MAX
return lexicographical_compare_3way(
(const signed char*) first1,
(const signed char*) last1,
(const signed char*) first2,
(const signed char*) last2);
#else
return lexicographical_compare_3way((const unsigned char*) first1,
(const unsigned char*) last1,
(const unsigned char*) first2,
(const unsigned char*) last2);
#endif
}
__STL_END_NAMESPACE
#endif /* __SGI_STL_INTERNAL_ALGOBASE_H */
// Local Variables:
// mode:C++
// End: