控制你的CPU占用率,读编程之美第一章的一点总结
题目:写一个程序,让用户来决定Windows任务管理器(Task Manager)的CPU占用率。程序越精简越好,计算机语言不限。例如,可以实现下面三种情况:
1. CPU的占用率固定在50%,为一条直线;
2. CPU的占用率为一条直线,但是具体占用率由命令行参数决定(参数范围1~ 100);
3. CPU的占用率状态是一个正弦曲线。
首先,什么是CPU占用率真?《编程之美》写道:“在任务管理器的一个刷新周期内,CPU忙(执行应用程序)的时间和刷新周期总时间的比率,就是CPU的占用率,也就是说,任务管理器中显示的是每个刷新周期内CPU占用率的统计平均值。”
书中提到了多种方法 ,前面几种简单的都是对应单核CPU的。
第一种是通过CPU的主频计算出在一秒种内CPU能运行的空循环次数,再调节忙/闲的时间比(闲时间设为10ms,使接近于系统调度的时间片),此法在双核CPU上运行看不到任何效果。
第二法方法用到了GetTickCount来获取“系统从启动到现在”经历的毫秒值,通过统计的方法来调节时间比。
using System;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading;
namespace _50persentCPU
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int busyTime = 10;
int startTime = Environment.TickCount;
Console.WriteLine(startTime .ToString ());
while (true)
{
startTime = Environment.TickCount;
while (Environment.TickCount - startTime <= busyTime)
{
//Console.WriteLine(Environment.TickCount.ToString());
}
Thread.Sleep(10);
}
}
}
}
程序运行截图1:
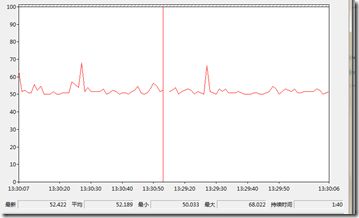
CPU占用率还是一直稳定在50%左右。从上图可看出,程序是单线程运行,但由于是运行在双核上,很难猜到具体的运行情况,燥音也比较大。
下面通过SetThreadAffinityMask函数为线程指定CPU亲和性,让线程只运行在特定的CPU核心上
using System;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading;
using System.Runtime.InteropServices;
namespace _50persentCPU
{
class Program
{
[DllImport("Kernel32.dll", CharSet = CharSet.Auto)]
public static extern int SetThreadAffinityMask(IntPtr hWnd, int nIndex);
static void Main(string[] args)
{
IntPtr nHD = new IntPtr(Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId);
SetThreadAffinityMask(nHD, 0);
int busyTime = 10;
int startTime = Environment.TickCount;
Console.WriteLine(startTime .ToString ());
while (true)
{
startTime = Environment.TickCount;
while (Environment.TickCount - startTime <= busyTime)
{
//Console.WriteLine(Environment.TickCount.ToString());
}
Thread.Sleep(10);
}
}
}
}
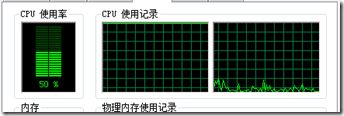
运行截图2:
可以看出,线程只占用0号核心的时间片,cpu占用率很稳定在保持在50%,燥音很弱。
通过PerformanceCounter来采集CPU占用率信息,程序中输出可以输各个实例的CPU占用率。但我运行起来看不到任何效果,在双核上运行真是诡异,还得多了解一些东西才行。
using System;
using System.Diagnostics;
using System.Threading;
namespace _50persentCPU2
{
class Program
{
static void MakeUsage(float level)
{
PerformanceCounter p = new PerformanceCounter("Processor", "% Processor Time","_Total");
while (true)
{
if (p.NextValue ()> level)
{
System.Threading.Thread.Sleep(10);
}
}
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
MakeUsage(50 );
}
}
}
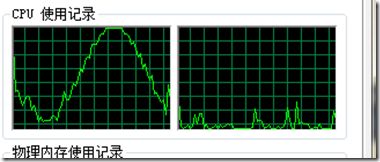
再给出一个C++版的在单核心在运行绘出正弦曲线的例子。
#include "Windows.h"
#include "stdlib.h"
#include "math.h"
#include
#include
const double SPLIT = 0.01;
const int COUNT = 200;
const double PI = 3.14159265;
const int INTERVAL = 300;
int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[])
{
SetProcessAffinityMask(
GetCurrentProcess(),
0x00000001 //cpu mask
);
DWORD busySpan[COUNT]; //array of busy times
DWORD idleSpan[COUNT]; //array of idle times
int half = INTERVAL / 2;
double radian = 0.0;
for(int i = 0; i < COUNT; i++)
{
busySpan[i] = (DWORD)(half + (sin(PI * radian) * half));
idleSpan[i] = INTERVAL - busySpan[i];
radian += SPLIT;
printf("%d/t%d/n",busySpan[i],INTERVAL-busySpan[i]);
}
DWORD startTime = 0;
int j = 0;
while (true)
{
j = j % COUNT;
startTime = GetTickCount();
while ((GetTickCount() - startTime) <= busySpan[j]) ;
Sleep(idleSpan[j]);
j++;
}
return 0;
}
C#版 双线程编程,使用两个核心的cpu占用率都是正弦曲线。
class1.cs
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading;
namespace CPU
{
public class Sin1ThreadParam
{
public int AffinityMask = 0x00000000;
public Sin1ThreadParam(int AffinityMask)
{
this.AffinityMask = AffinityMask;
}
}
class Sin1
{
public void DoWork(object o)
{
Sin1ThreadParam param = o as Sin1ThreadParam;
if (param != null)
{
// 设置线程CPU亲和性
IntPtr nHD = new IntPtr(Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId);
Win32.SetThreadAffinityMask(nHD, param.AffinityMask);
// 采样率
const double SPLIT = 0.01;
// 采样总数
const int COUNT = 200;
const double PI = 3.14159265;
// 扫描速度,控制曲线波长
const int INTERVAL = 300;
// 忙循环时间长度
int[] busySpan = new int[COUNT];
// 闲循环时间长度
int[] idleSpan = new int[COUNT];
int half = INTERVAL / 2;
// X
double radian = 0.0;
// 构成一个具有COUNT个采样点的忙、闲循环
for (int i = 0; i < COUNT; i++)
{
busySpan[i] = (int)((half + (Math.Sin(PI * radian) * half)));
idleSpan[i] = INTERVAL - busySpan[i];
radian += SPLIT;
}
int startTime = 0;
int j = 0;
// 按照忙闲循环比率跑死循环和Sleep
while (true)
{
j = j % COUNT;
startTime = Environment.TickCount;
while ((Environment.TickCount - startTime) <= busySpan[j])
{
}
Thread.Sleep(idleSpan[j]);
j++;
}
}
}
}
}
program.cs
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading;
using System.Diagnostics;
using System.Runtime.InteropServices;
namespace CPU
{
class Win32
{
[DllImport("Kernel32.dll", CharSet = CharSet.Auto)]
public static extern int SetThreadAffinityMask(IntPtr hWnd, int nIndex);
}
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Sin1 sin11 = new Sin1();
Thread t1 = new Thread(new ParameterizedThreadStart(sin11.DoWork));
Sin1ThreadParam p1 = new Sin1ThreadParam(0);
Thread t2 = new Thread(new ParameterizedThreadStart(sin11.DoWork));
Sin1ThreadParam p2 = new Sin1ThreadParam(1);
t1.Start(p1);
t2.Start(p2);
}
}
}