HTTP协议
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hypertext_Transfer_Protocol
Request methods [edit]
HTTP defines methods (sometimes referred to as verbs) to indicate the desired action to be performed on the identified resource. What this resource represents, whether pre-existing data or data that is generated dynamically, depends on the implementation of the server. Often, the resource corresponds to a file or the output of an executable residing on the server.
The HTTP/1.0 specification[10]:section 8 defined the GET, POST and HEAD methods and the HTTP/1.1 specification[1]:section 9 added 5 new methods: OPTIONS, PUT, DELETE, TRACE and CONNECT. By being specified in these documents their semantics are well known and can be depended upon. Any client can use any method and the server can be configured to support any combination of methods. If a method is unknown to an intermediate it will be treated as an unsafe and non-idempotent method. There is no limit to the number of methods that can be defined and this allows for future methods to be specified without breaking existing infrastructure. For example WebDAV defined 7 new methods and RFC5789 specified the PATCH method.
- GET
- Requests a representation of the specified resource. Requests using GET should only retrieve data and should have no other effect. (This is also true of some other HTTP methods.) [1] The W3C has published guidance principles on this distinction, saying, " Web application design should be informed by the above principles, but also by the relevant limitations." [11] See safe methods below.
- HEAD
- Asks for the response identical to the one that would correspond to a GET request, but without the response body. This is useful for retrieving meta-information written in response headers, without having to transport the entire content.
- POST
- Requests that the server accept the entity enclosed in the request as a new subordinate of the web resource identified by the URI. The data POSTed might be, as examples, an annotation for existing resources; a message for a bulletin board, newsgroup, mailing list, or comment thread; a block of data that is the result of submitting a web form to a data-handling process; or an item to add to a database. [12]
- PUT
- Requests that the enclosed entity be stored under the supplied URI. If the URI refers to an already existing resource, it is modified; if the URI does not point to an existing resource, then the server can create the resource with that URI. [13]
- DELETE
- Deletes the specified resource.
- TRACE
- Echoes back the received request so that a client can see what (if any) changes or additions have been made by intermediate servers.
- OPTIONS
- Returns the HTTP methods that the server supports for specified URL. This can be used to check the functionality of a web server by requesting '*' instead of a specific resource.
- CONNECT
- Converts the request connection to a transparent TCP/IP tunnel, usually to facilitate SSL-encrypted communication ( HTTPS) through an unencrypted HTTP proxy. [14] [15]
- PATCH
- Is used to apply partial modifications to a resource. [16]
HTTP servers are required to implement at least the GET and HEAD methods[17] and, whenever possible, also the OPTIONS method.[citation needed]
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_HTTP_header_fields
Requests [edit]
| Field name | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Accept | Content-Types that are acceptable for the response | Accept: text/plain |
| Accept-Charset | Character sets that are acceptable | Accept-Charset: utf-8 |
| Accept-Encoding | Acceptable encodings. See HTTP compression. | Accept-Encoding: gzip, deflate |
| Accept-Language | Acceptable human languages for response | Accept-Language: en-US |
| Accept-Datetime | Acceptable version in time | Accept-Datetime: Thu, 31 May 2007 20:35:00 GMT |
| Authorization | Authentication credentials for HTTP authentication | Authorization: Basic QWxhZGRpbjpvcGVuIHNlc2FtZQ== |
| Cache-Control | Used to specify directives that MUST be obeyed by all caching mechanisms along the request/response chain | Cache-Control: no-cache |
| Connection | What type of connection the user-agent would prefer | Connection: keep-alive |
| Cookie | an HTTP cookie previously sent by the server with Set-Cookie (below) | Cookie: $Version=1; Skin=new; |
| Content-Length | The length of the request body in octets (8-bit bytes) | Content-Length: 348 |
| Content-MD5 | A Base64-encoded binary MD5 sum of the content of the request body | Content-MD5: Q2hlY2sgSW50ZWdyaXR5IQ== |
| Content-Type | The MIME type of the body of the request (used with POST and PUT requests) | Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded |
| Date | The date and time that the message was sent | Date: Tue, 15 Nov 1994 08:12:31 GMT |
| Expect | Indicates that particular server behaviors are required by the client | Expect: 100-continue |
| From | The email address of the user making the request | From: [email protected] |
| Host | The domain name of the server (for virtual hosting), and the TCP port number on which the server is listening. The port number may be omitted if the port is the standard port for the service requested.[5] Mandatory since HTTP/1.1. Although domain name are specified as case-insensitive,[6][7]it is not specified whether the contents of the Host field should be interpreted in a case-insensitive manner[8] and in practice some implementations of virtual hosting interpret the contents of the Host field in a case-sensitive manner.[citation needed] | Host: en.wikipedia.org:80
|
| If-Match | Only perform the action if the client supplied entity matches the same entity on the server. This is mainly for methods like PUT to only update a resource if it has not been modified since the user last updated it. | If-Match: "737060cd8c284d8af7ad3082f209582d" |
| If-Modified-Since | Allows a 304 Not Modified to be returned if content is unchanged | If-Modified-Since: Sat, 29 Oct 1994 19:43:31 GMT |
| If-None-Match | Allows a 304 Not Modified to be returned if content is unchanged, see HTTP ETag | If-None-Match: "737060cd8c284d8af7ad3082f209582d" |
| If-Range | If the entity is unchanged, send me the part(s) that I am missing; otherwise, send me the entire new entity | If-Range: "737060cd8c284d8af7ad3082f209582d" |
| If-Unmodified-Since | Only send the response if the entity has not been modified since a specific time. | If-Unmodified-Since: Sat, 29 Oct 1994 19:43:31 GMT |
| Max-Forwards | Limit the number of times the message can be forwarded through proxies or gateways. | Max-Forwards: 10 |
| Origin | Initiates a request for cross-origin resource sharing (asks server for an 'Access-Control-Allow-Origin' response header) . | Origin: http://www.example-social-network.com |
| Pragma | Implementation-specific headers that may have various effects anywhere along the request-response chain. | Pragma: no-cache |
| Proxy-Authorization | Authorization credentials for connecting to a proxy. | Proxy-Authorization: Basic QWxhZGRpbjpvcGVuIHNlc2FtZQ== |
| Range | Request only part of an entity. Bytes are numbered from 0. | Range: bytes=500-999 |
| Referer[sic] | This is the address of the previous web page from which a link to the currently requested page was followed. (The word “referrer” is misspelled in the RFC as well as in most implementations.) | Referer: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Main_Page |
| TE | The transfer encodings the user agent is willing to accept: the same values as for the response header Transfer-Encoding can be used, plus the "trailers" value (related to the "chunked" transfer method) to notify the server it expects to receive additional headers (the trailers) after the last, zero-sized, chunk. | TE: trailers, deflate |
| Upgrade | Ask the server to upgrade to another protocol. | Upgrade: HTTP/2.0, SHTTP/1.3, IRC/6.9, RTA/x11 |
| User-Agent | The user agent string of the user agent | User-Agent: Mozilla/5.0 (X11; Linux x86_64; rv:12.0) Gecko/20100101 Firefox/12.0 |
| Via | Informs the server of proxies through which the request was sent. | Via: 1.0 fred, 1.1 example.com (Apache/1.1) |
| Warning | A general warning about possible problems with the entity body. | Warning: 199 Miscellaneous warning |
Common non-standard request headers [edit]
Non-standard header fields were conventionally marked by prefixing the field name with X- .[9] However, this convention became deprecated in June 2012 due to the inconveniences it caused when non-standard headers then became standard.[10] For example, X-Gzip and Gzip are now both supported headers for compressed HTTP requests and responses.
| Field name | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| X-Requested-With | mainly used to identify Ajax requests. Most JavaScript frameworks send this header with value ofXMLHttpRequest |
X-Requested-With: XMLHttpRequest |
| DNT[11] | Requests a web application to disable their tracking of a user. This is Mozilla's version of the X-Do-Not-Track header (since Firefox 4.0 Beta 11). Safari and IE9 also have support for this header.[12] On March 7, 2011, a draft proposal was submitted to IETF.[13] The W3C Tracking Protection Working Group is producing a specification.[14] | DNT: 1 (Do Not Track Enabled)
|
| X-Forwarded-For[15] | a de facto standard for identifying the originating IP address of a client connecting to a web server through an HTTP proxy or load balancer | X-Forwarded-For: client1, proxy1, proxy2
|
| X-Forwarded-Proto[16] | a de facto standard for identifying the originating protocol of an HTTP request, since a reverse proxy (load balancer) may communicate with a web server using HTTP even if the request to the reverse proxy is HTTPS | X-Forwarded-Proto: https |
| Front-End-Https[17] | Non-standard header used by Microsoft applications and load-balancers | Front-End-Https: on |
| X-ATT-DeviceId[18] | Allows easier parsing of the MakeModel/Firmware that is usually found in the User-Agent String of AT&T Devices | x-att-deviceid: MakeModel/Firmware |
| X-Wap-Profile[19] | Links to an XML file on the Internet with a full description and details about the device currently connecting. In the example to the right is an XML file for an AT&T Samsung Galaxy S2. | x-wap-profile:http://wap.samsungmobile.com/uaprof/SGH-I777.xml |
| Proxy-Connection[20] | Implemented as a misunderstanding of the HTTP specifications. Common because of mistakes in implementations of early HTTP versions. Has exactly the same functionality as standard Connection header. | Proxy-Connection: keep-alive |
Responses [edit]
| Field name | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Access-Control-Allow-Origin | Specifying which web sites can participate in cross-origin resource sharing | Access-Control-Allow-Origin: * |
| Accept-Ranges | What partial content range types this server supports | Accept-Ranges: bytes |
| Age | The age the object has been in a proxy cache in seconds | Age: 12 |
| Allow | Valid actions for a specified resource. To be used for a 405 Method not allowed | Allow: GET, HEAD |
| Cache-Control | Tells all caching mechanisms from server to client whether they may cache this object. It is measured in seconds | Cache-Control: max-age=3600 |
| Connection | Options that are desired for the connection[21] | Connection: close |
| Content-Encoding | The type of encoding used on the data. See HTTP compression. | Content-Encoding: gzip |
| Content-Language | The language the content is in | Content-Language: da |
| Content-Length | The length of the response body in octets (8-bit bytes) | Content-Length: 348 |
| Content-Location | An alternate location for the returned data | Content-Location: /index.htm |
| Content-MD5 | A Base64-encoded binary MD5 sum of the content of the response | Content-MD5: Q2hlY2sgSW50ZWdyaXR5IQ== |
| Content-Disposition[22][23][24] | An opportunity to raise a "File Download" dialogue box for a known MIME type with binary format or suggest a filename for dynamic content. Quotes are necessary with special characters. | Content-Disposition: attachment; filename="fname.ext" |
| Content-Range | Where in a full body message this partial message belongs | Content-Range: bytes 21010-47021/47022 |
| Content-Type | The MIME type of this content | Content-Type: text/html; charset=utf-8 |
| Date | The date and time that the message was sent | Date: Tue, 15 Nov 1994 08:12:31 GMT |
| ETag | An identifier for a specific version of a resource, often a message digest | ETag: "737060cd8c284d8af7ad3082f209582d" |
| Expires | Gives the date/time after which the response is considered stale | Expires: Thu, 01 Dec 1994 16:00:00 GMT |
| Last-Modified | The last modified date for the requested object, in RFC 2822 format | Last-Modified: Tue, 15 Nov 1994 12:45:26 GMT |
| Link | Used to express a typed relationship with another resource, where the relation type is defined by RFC 5988 | Link: </feed>; rel="alternate"[25] |
| Location | Used in redirection, or when a new resource has been created. | Location: http://www.w3.org/pub/WWW/People.html |
| P3P | This header is supposed to set P3P policy, in the form ofP3P:CP="your_compact_policy". However, P3P did not take off,[26] most browsers have never fully implemented it, a lot of websites set this header with fake policy text, that was enough to fool browsers the existence of P3P policy and grant permissions for third party cookies. |
P3P: CP="This is not a P3P policy! See http://www.google.com/support/accounts/bin/answer.py?hl=en&answer=151657 for more info." |
| Pragma | Implementation-specific headers that may have various effects anywhere along the request-response chain. | Pragma: no-cache |
| Proxy-Authenticate | Request authentication to access the proxy. | Proxy-Authenticate: Basic |
| Refresh | Used in redirection, or when a new resource has been created. This refresh redirects after 5 seconds. This is a proprietary, non-standard header extension introduced by Netscape and supported by most web browsers. | Refresh: 5; url=http://www.w3.org/pub/WWW/People.html |
| Retry-After | If an entity is temporarily unavailable, this instructs the client to try again after a specified period of time (seconds). | Retry-After: 120 |
| Server | A name for the server | Server: Apache/2.4.1 (Unix) |
| Set-Cookie | An HTTP cookie | Set-Cookie: UserID=JohnDoe; Max-Age=3600; Version=1 |
| Status | The HTTP status of the response | Status: 200 OK |
| Strict-Transport-Security | A HSTS Policy informing the HTTP client how long to cache the HTTPS only policy and whether this applies to subdomains. | Strict-Transport-Security: max-age=16070400; includeSubDomains |
| Trailer | The Trailer general field value indicates that the given set of header fields is present in the trailer of a message encoded with chunked transfer-coding. | Trailer: Max-Forwards |
| Transfer-Encoding | The form of encoding used to safely transfer the entity to the user. Currently defined methods are: chunked, compress, deflate, gzip, identity. | Transfer-Encoding: chunked |
| Vary | Tells downstream proxies how to match future request headers to decide whether the cached response can be used rather than requesting a fresh one from the origin server. | Vary: * |
| Via | Informs the client of proxies through which the response was sent. | Via: 1.0 fred, 1.1 example.com (Apache/1.1) |
| Warning | A general warning about possible problems with the entity body. | Warning: 199 Miscellaneous warning |
| WWW-Authenticate | Indicates the authentication scheme that should be used to access the requested entity. | WWW-Authenticate: Basic |
Common non-standard response headers [edit]
Non-standard header fields are conventionally marked by prefixing the field name with X- .
| Field name | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| X-Frame-Options[27] | Clickjacking protection: "deny" - no rendering within a frame, "sameorigin" - no rendering if origin mismatch | X-Frame-Options: deny |
| X-XSS-Protection[28] | Cross-site scripting (XSS) filter | X-XSS-Protection: 1; mode=block |
| Content-Security-Policy, X-Content-Security-Policy, X-WebKit-CSP[29] | Content Security Policy definition. | X-WebKit-CSP: default-src 'self' |
| X-Content-Type-Options[30] | The only defined value, "nosniff", prevents Internet Explorer from MIME-sniffing a response away from the declared content-type. This also applies to Google Chrome, when downloading extensions.[31] | X-Content-Type-Options: nosniff |
| X-Powered-By[32] | specifies the technology (e.g. ASP.NET, PHP, JBoss) supporting the web application (version details are often in X-Runtime, X-Version, or X-AspNet-Version) |
X-Powered-By: PHP/5.4.0 |
| X-UA-Compatible[33] | Recommends the preferred rendering engine (often a backward-compatibility mode) to use to display the content. Also used to activate Chrome Frame in Internet Explorer. | X-UA-Compatible: IE=EmulateIE7X-UA-Compatible: IE=edgeX-UA-Compatible: Chrome=1 |
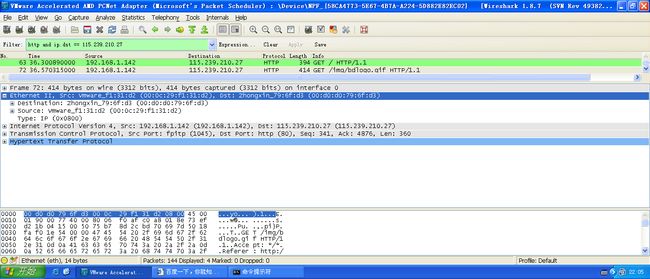
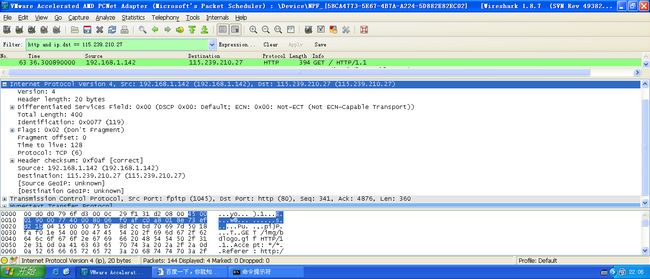
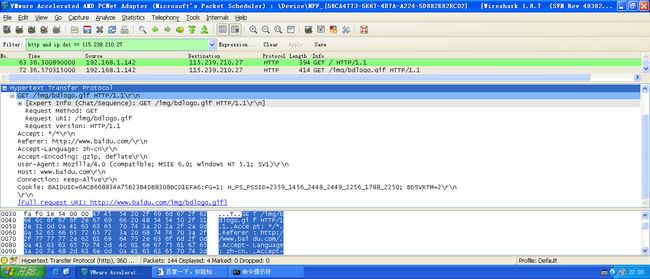
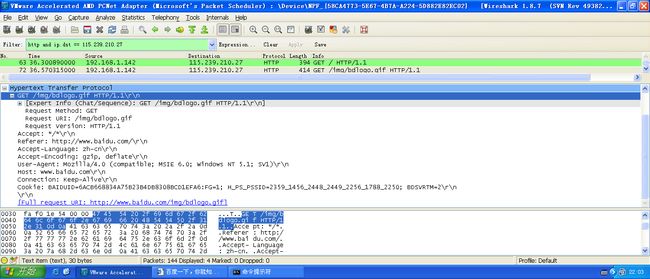
用Wireshark抓包: