ExFAT boot sector checksum简单介绍
在测试各种卡插拔测试的时候,遇到这样的一个error:
ExFAT: Invalid boot sector checksum. Was 0x12345678, should be 0x87654321.这个error会导致系统弹出提示框
“You need to format the disk in driver J: before you can use it. Do you want to format it?”
于是很好奇什么是boot sector checksum,是否真的是boot sector checksum错误导致这样的error。
这里我们只看Classical Generic的版本,参考下图:
| Address | Description | Size (bytes) |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hex | Dec | |||
| +000h | +0 | Bootstrap code area | 446 | |
| +1BEh | +446 | Partition entry #1 | Partition table (for primary partitions) |
16 |
| +1CEh | +462 | Partition entry #2 | 16 | |
| +1DEh | +478 | Partition entry #3 | 16 | |
| +1EEh | +494 | Partition entry #4 | 16 | |
| +1FEh | +510 | 55h | Boot signature[a] | 2 |
| +1FFh | +511 | AAh | ||
| Total size: 446 + 4×16 + 2 | 512 | |||
| Offset (bytes) |
Field length |
Description | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| +0h | 1 byte | status / physical drive (bit 7 set: active / bootable, old MBRs only accept 80h), 00h: inactive,01h–7Fh: invalid)[a] | ||||||||||||||||||
| +1h | 3 bytes | CHS address of first absolute sector in partition.[b] The format is described by 3 bytes, see the next 3 rows. | ||||||||||||||||||
| +1h | 1 byte |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| +2h | 1 byte |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| +3h | 1 byte |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| +4h | 1 byte | Partition type[14] | ||||||||||||||||||
| +5h | 3 byte | CHS address of last absolute sector in partition.[b] The format is described by 3 bytes, see the next 3 rows. | ||||||||||||||||||
| +5h | 1 byte |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| +6h | 1 byte |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| +7h | 1 byte |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| +8h | 4 bytes | LBA of first absolute sector in the partition[d] | ||||||||||||||||||
| +Ch | 4 bytes | Number of sectors in partition[d] | ||||||||||||||||||
| Notes: ^ a Originally, status values other than 00h and80h were invalid, but modern MBRs treat bit 7 as active flag and use this entry to store the physical boot unit (see below). ^ b Starting Sector fields are limited to 1023+1 cylinders, 255+1 heads, and 63 sectors; Ending Sector fields have the same limitations. ^ c The range for sector is 1 through 63; the range for cylinder is 0 through 1023; the range for head is 0 through 255 inclusive.[15] ^ d Used by OSes in certain circumstances; in such cases the CHS addresses are ignored.[16] |
||||||||||||||||||||
从中可以获取这张卡只有一个partition,他开始的绝对地址是0x2000 sector。接下来就是要从0x2000 sector来解析ExFAT的boot sector了。
ExFat是从FAT12、FAT16、FAT32演变而来,主要增加了一下改进:
支持更大的文件、更大的卷
原生支持unicode文件名
更大的boot空间,支持更多的boot code
更好的速度、性能
对时区的支持
对OEM参数的支持
接下来我们的重点还是首先了解一下ExFAT boot sector的组成,可以参考:http://www.ntfs.com/exfat-volume-layout.htm
Volume Layout
| Offset, sectors |
Size, sectors |
Block |
Comments |
|---|---|---|---|
| Main Boot Region | |||
| 0 |
1 |
Boot Sector |
|
| 1 |
8 |
Extended Boot Sectors |
|
| 9 |
1 |
OEM Parameters |
|
| 10 |
1 |
Reserved |
|
| 11 |
1 |
Boot Checksum |
|
| Backup Boot Region | |||
| 12 |
1 |
Boot Sector |
|
| 13 |
8 |
Extended Boot Sectors |
|
| 21 |
1 |
OEM Parameters |
|
| 22 |
1 |
Reserved |
|
| 23 |
1 |
Boot Checksum |
|
| FAT Region | |||
| 24 |
FatOffset - 24 |
FAT Alignment |
Boot Sectors contain FatOffset |
| FatOffset |
FatLength |
First FAT |
Boot Sectors contain FatOffset and FatLength |
| FatOffset + FatLength |
FatLength |
Second FAT |
For TexFAT only |
| Data Region | |||
| FatOffset + FatLength * NumberOfFats |
ClusterHeapOffset – (FatOffset + FatLength * NumberOfFats) |
Cluster Heap Alignment |
|
| ClusterHeapOffset |
ClusterCount * 2^SectorsPerClusterShift |
Cluster Heap |
|
| ClusterHeapOffset + ClusterCount * 2^SectorsPerClusterShift |
VolumeLength – (ClusterHeapOffset + ClusterCount * 2^SectorsPerClusterShift) |
Excess Space |
|
从这个表中可以看到我们所需要找的 boot sector checksum 位于第12个sector,它是对前11个sector所做的checksum。我们可以从上面的链接中找到boot sector checksum的计算方法,参考下面:
exFAT Boot Checksum
This sector contains a repeating 32-bit checksum of the previous 11 sectors. The checksum calculation excludes VolumeFlags and PercentInUse fields in Boot Sector (bytes 106, 107, 112). The checksum is repeated until the end of the sector. The number of repetitions depends on the size of the sector.
UNIT32 BootChecksum(constunsignedchardata[], intbytes) { UINT32 checksum = 0; for (inti = 0; i < bytes; i++) { if (i == 106 || i == 107 || i == 112) continue; checksum = (checksum<<31) | (checksum>> 1) + data[i]; } returnchecksum;
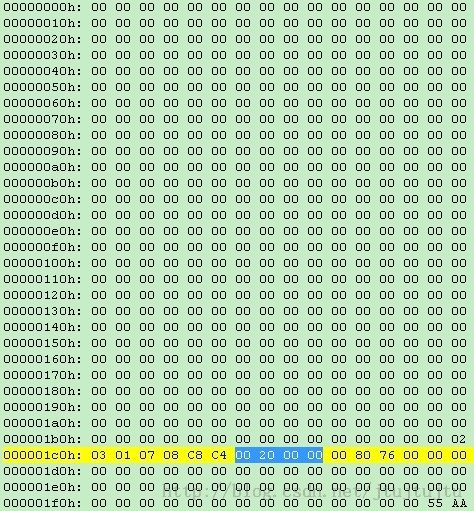
有了上面的partition开始地址、boot sector checksum计算方法,我们就可以读取并check boot sector checksum是否正确。checksum这个sector以4个字节为计算结果,一直重复这个计算结果。例如:
...
第12个sector开始地址是 11*512 = 5632 = 0x1600
上述的boot sector checksum为 0x8B165B51
通过手动将这个数字改变,并重新写入相同的位置,重新认卡,会发现弹出上述的对话框,提示卡需要format,同时在debug log中显示boot sector checksum error。
以上就是对ExFAT boot sector checksum error所做的实验。
ExFAT对比FAT32可以参考上述链接,主要区别如下:
exFAT vs. FAT32 Comparison
| Feature |
FAT32 |
exFAT |
|---|---|---|
| Maximum Volume Size |
8 TB* |
128 PB |
| Maximum File Size |
4 GB |
16 EB |
| Maximum Cluster Size |
32 KB ** |
32 MB |
| Maximum Cluster Count |
228 |
232 |
| Maximum File Name Length |
255 |
255 |
| Date/Time resolution |
2 s |
10 ms |
| MBR Partition Type Identifier |
0x0B, 0x0C |
0x07 |
* Windows cannot format FAT32 volumes bigger than 32GB, though itsupports larger volumes created by third party implementations; 16 TB is the maximum volume size if formatted with 64KB cluster
** According to Microsoft KB184006 clusters cannot be 64KB or larger, though some third party implementations support up to 64KB.