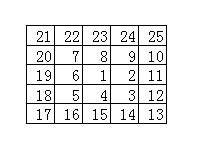
螺旋矩阵
参考:
http://www.cnblogs.com/drizzlecrj/archive/2007/04/10/706784.html
http://www.cnblogs.com/eshizhan/archive/2010/06/01/1749013.html
http://blog.csdn.net/dennis101/article/details/3053739
从里到外螺旋:
21 22................
20 7 8 9 10
19 6 1 2 11
18 5 4 3 12
17 16 15 14 13
的矩阵。
问题有两个:
1. 编程实现输出这个矩阵
2. 设1点的坐标是(0,0),x方向向右为正,y方向向下为正.例如:7的坐标为(-1,-1) ,2的坐标为(0,1),3的坐标为(1,1).编程实现输入任意一点坐标(x,y),输出所对应的数字。
1. 第一个问题我是采用模拟进行构造的,可以看到从1开始的方向变化始终是 right->down->left->up,
所持续走的长度为1->1->2->2->3->3->...,发现了这个规律不难写出代码了!注意下面我把1的位置设置
在((n-1)/2, (n-1)/2)的位置。
2. 第二个问题我也是先找出规律,然后进行模拟。
首先,不难看出n*n的螺旋矩阵的右下角的坐标一定是(m, m),这里m=n-1
通过观察,可以看出 n=1的时候,右下角(0,0)的值为1,当n=2的时候,右下角(1,1)的坐标值为(3,3),当n=3的时候,右下角(2,2)的坐标值为13.直觉告诉我,这个值是关于n的二次函数,设f(n) = a*n^2 + b*n + c
联立方程组,可以求得a,b,c。 最终算出来的f(n) = 4*n^2 - 2*n + 1
下面再根据(x,y)和右下角(n-1,n-1)之间的关系,计算出值即可。这里要注意当x的值与n-1相同时,应优先考虑y与-m是否有联系。这就要求在函数中要注意x,y的判断先后顺序了。
代码如下:
我的实现:
const int n = 10;
int a[n][n];
int main() {
int x = (n - 1) / 2;
int y = x;
int num = 2;
int sum = n * n;
a[x][y] = 1;
int i = 0;
int step = 1;
while (num <= sum) {
for (int j = 0 ;num <=sum && j <step ;++j) {
switch (i) {
case 0:
++y;
break;
case 1:
++x;
break;
case 2:
--y;
break;
case 3:
--x;
break;
}
a[x][y] = num ++;
}
if (i % 2 ==1)
++step;
i = (i + 1) %4;
}
for (int i = 0; i< n; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j)
printf("%8d",a[i][j]);
cout<<endl;
}
}
int GetValue(int n, int i, int j)//这也是个不错的思路
{
assert(n>0 && i<n && j<n);
int x = n/2;
int y = n/2;
if (n%2 == 0)
x--;
if (x == i && y == j) return 1;
bool bXDec = false;
bool bYDec = true;
int nSteps = 1;
int nRet = 1;
while (nSteps <= n && nRet <= n*n)
{
//calculate each step
int nLeftX = nSteps;
int nLeftY = nSteps;
while (0 != nLeftY)
{
bYDec ? y-- : y++;
nRet++;
if (i == x && j == y) return nRet;
nLeftY--;
}
while (0 != nLeftX)
{
bXDec ? x-- : x++;
nRet++;
if (i == x && j == y) return nRet;
nLeftX--;
}
nSteps++;
bXDec = !bXDec;
bYDec = !bYDec;
}
return -1;
}
也可以这样做:
这个螺旋矩阵有几类,我当时拿到的题是从中间往外顺时针旋转,如下所示:
7 8 9
6 1 2
5 4 3
这个太小不好分析规律,来个大的:
看出规律没?找张草稿纸研究研究。
我当时是这么想的:
红线方程y=x,绿线方程y=-x+4,4为矩形边长。
两条直线将区域分为四个部分,划分好每个区域的边界值,每个区域的坐标变化规律有四种,x++,y++,x--,y--,接下来仔细分析就能得到算法:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
|
void
SpiralArray(
int
size,
int
** ar)
{
int
a=size/2*2+1;
//保证边长为奇数
int
y=a/2,x=a/2;
//从中心点开始
for
(
int
i=1;i<=size*size;i++)
//(int i=size*size;i>=1;i--)
{
if
(x<=a-y-1&&x>=y)
{
ar[y][x]=i;
x++;
}
else
if
(x>a-y-1&&x>y)
{
ar[y][x]=i;
y++;
}
else
if
(x>a-y-1&&x<=y)
{
ar[y][x]=i;
x--;
}
else
if
(x<=a-y-1&&x<y)
{
ar[y][x]=i;
y--;
}
}
}
|
2. 从外向内螺旋矩阵:
1 按顺时针方向构建一个m * n的螺旋矩阵(或按顺时针方向螺旋访问一个m * n的矩阵):
2 在不构造螺旋矩阵的情况下,给定坐标i、j值求其对应的值f(i, j)。
比如对11 * 7矩阵, f(6, 0) = 27 f(6, 1) = 52 f(6, 3) = 76 f(6, 4) = 63
构建螺旋矩阵
对m * n 矩阵,最先访问最外层的m * n的矩形上的元素,接着再访问里面一层的 (m - 2) * (n - 2) 矩形上的元素…… 最后可能会剩下一些元素,组成一个点或一条线(见图1)。
对第i个矩形(i=0, 1, 2 …),4个顶点的坐标为:
(i, i) ----------------------------------------- (i, n–1-i)
| |
| |
| |
(m-1-i, i) ----------------------------------------- (m-1-i, n-1-i)
要访问该矩形上的所有元素,只须用4个for循环,每个循环访问一个点和一边条边上的元素即可(见图1)。另外,要注意对最终可能剩下的1 * k 或 k * 1矩阵再做个特殊处理。
代码:
inline void act(int t) { printf("%3d ", t); }
const int small = col < row ? col : row;
const int count = small / 2;
for (int i = 0; i < count; ++i) {
const int C = col - 1 - i;
const int R = row - 1 - i;
for (int j = i; j < C; ++j) act(arr[i][j]);
for (int j = i; j < R; ++j) act(arr[j][C]);
for (int j = C; j > i; --j) act(arr[R][j]);
for (int j = R; j > i; --j) act(arr[j][i]);
}
if (small & 1) {
const int i = count;
if (row <= col) for (int j = i; j < col - i; ++j) act(arr[i][j]);
else for (int j = i; j < row - i; ++j) act(arr[j][i]);
}
如果只是构建螺旋矩阵的话,稍微修改可以实现4个for循环独立:
const int small = col < row ? col : row;
const int count = small / 2;
for (int i = 0; i < count; ++i) {
const int C = col - 1 - i;
const int R = row - 1 - i;
const int cc = C - i;
const int rr = R - i;
const int s = 2 * i * (row + col - 2 * i) + 1;
for (int j = i, k = s; j < C; ++j) arr[i][j] = k++;
for (int j = i, k = s + cc; j < R; ++j) arr[j][C] = k++;
for (int j = C, k = s + cc + rr; j > i; --j) arr[R][j] = k++;
for (int j = R, k = s + cc * 2 + rr; j > i; --j) arr[j][i] = k++;
}
if (small & 1) {
const int i = count;
int k = 2 * i * (row + col - 2 * i) + 1;
if (row <= col) for (int j = i; j < col - i; ++j) arr[i][j] = k++;
else for (int j = i; j < row - i; ++j) arr[j][i] = k++;
}
关于s的初始值取 2 * i * (row + col - 2 * i) + 1请参考下一节。
由于C++的二维数组是通过一维数组实现的。二维数组的实现一般有下面三种:
静态分配足够大的数组;
动态分配一个长为m*n的一维数组;
动态分配m个长为n的一维数组,并将它们的指针存在一个长为m的一维数组。
二维数组的不同实现方法,对函数接口有很大影响。
给定坐标直接求值f(x, y)
如前面所述,对第i个矩形(i=0, 1, 2 …),4个顶点的坐标为:
(i, i) ----------------------------------------- (i, n–1-i)
| |
| |
| |
(m-1-i, i) ----------------------------------------- (m-1-i, n-1-i)
对给定的坐标(x,y),如果它落在某个这类矩形上,显然其所在的矩形编号为:
k = min{x, y, m-1-x, n-1-y}
m*n矩阵删除访问第k个矩形前所访问的所有元素后,可得到(m-2*k)*(n-2*k)矩阵,因此已访问的元素个数为:m*n-(m-2*k)*(n-2*k)=2*k*(m+n-2*k),因而 (k,k)对应的值为:
T(k) = 2*k*(m+n-2*k)+ 1
对某个矩形,设点(x, y)到起始点(k,k)的距离d = x-k + y-k = x+y-2*k
① 向右和向下都只是横坐标或纵坐标增加1,这两条边上的点满足f(x, y) = T(k) + d
② 向左和向下都只是横坐标或纵坐标减少1,这两条边上的点满足f(x, y) = T(k+1) - d
如果给定坐标的点(x, y),不在任何矩形上,则它在一条线上,仍满足f(x, y) = T(k) + d
int getv(int row, int col, int max_row, int max_col) // row < max_row, col < max_col
{
int level = min(min(row, max_row - 1 - row), min(col, max_col - 1 - col));
int distance = row + col - level * 2;
int start_value = 2 * level * (max_row + max_col - 2 * level) + 1;
if (row == level || col == max_col - 1 - level ||
(max_col < max_row && level * 2 + 1 == max_col))
return start_value + distance;
int next_value = start_value + (max_row + max_col - 4 * level - 2) * 2;
return next_value - distance;
}
特别说明
上面的讨论都是基于m*n矩阵的,对于特例n*n矩阵,可以做更多的优化。比如构建螺旋矩阵,如果n为奇数,则矩阵可以拆分为几个矩形加上一个点。前面的条件判断可以优化为:
if (small & 1) act[count][count];
甚至可以调整4个for循环的遍历元素个数(前面代码,每个for循环遍历n-1-2*i个元素,可以调整为:n-2*i,n-1-2*i, n-1-2*i,n-2-2*i)从而达到省略if判断。
3. 双螺旋矩阵
这是有道的一道笔试题,题目描述如下:
双螺旋矩阵的定义如下,矩阵的最中心是1,往上是2,右拐3,向下4,然后依次5、6,7...构成一条顺序增大的螺旋线,此外,如果从中心往下走的话,也是一条对称的螺旋线。题目是给定一个矩阵维度N,将其打印出来,示例如下。要求在纸上把代码写完整,时间半小时左右。
25 14 15 16 17 18 19
24 13 6 7 8 9 20
23 12 5 2 3 10 21
22 11 4 1 4 11 22
21 10 3 2 5 12 23
20 9 8 7 6 13 24
19 18 17 16 15 14 25
前面有一篇螺旋矩阵的日志,那里面用的方法都是分析坐标,用公式去计算当前位置的值。现在发现其实模拟可以更简单,只要从(0,0)开始,一圈一圈往里走就行了,再根据对称,把另一半也算出来。代码如下,
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int dx[4] = {1,0,-1,0};
int dy[4] = {0,1,0,-1};
int M[101][101];
int main()
{
int n;
cout << "input an odd integer: ";
cin >> n;
int start = (n * n + 1) / 2;
int x = 0, y = 0, side = n - 1, dir = 0, cnt = 0;
int temp = side;
while(start > 0)
{
M[x][y] = M[n-1-x][n-1-y] = start;
x += dx[dir];
y += dy[dir];
cnt++;
start--;
if(cnt == side)
{
if(dir % 2 == 0)
{
if(side == temp)
side--;
else
side -= 2 ;
}
dir = (dir + 1) % 4;
cnt = 0;
}
}
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
for(int j = 0; j < n; j++)
cout << M[i][j] << "\t";
cout << endl;
}
}
和第一题类似