Java中String类方法说明
一、构造函数
1.String(byte[ ]bytes):通过byte数组构造字符串对象。
2.String(char[ ]value):通过char数组构造字符串对象。
3.String(Stingoriginal):构造一个original的副本。即:拷贝一个original。
4.String(StringBufferbuffer):通过StringBuffer数组构造字符串对象。
二、String类方法
说明:
①、所有方法均为public。
②、书写格式: [修饰符] <返回类型><方法名([参数列表])>
例如:static intparseInt(String s)
表示此方法(parseInt)为类方法(static),返回类型为(int),方法所需要为String类型。
1. char charAt(int index) :
取字符串中的某一个字符,其中的参数index指的是字符串中序数。字符串的序数从0开始到length()-1 。
例如:
String s = new String("abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz");
System.out.println("s.charAt(5): " + s.charAt(5) );
结果为:s.charAt(5): f
2. int compareTo(String anotherString):
当前String对象与anotherString比较。相等关系返回0;不相等时,从两个字符串第0个字符开始比较,返回第一个不相等的字符差,另一种情况,较长字符串的前面部分恰巧是较短的字符串,返回它们的长度差。
3. int compareTo(Object o) :如果o是String对象,和2的功能一样;否则抛出ClassCastException异常。
例如:
String s1 = new String("abcdefghijklmn");
String s2 = newString("abcdefghij");
String s3 = newString("abcdefghijalmn");
String s4 = new String("abcdefghijalmn");
System.out.println("s1.compareTo(s2):" + s1.compareTo(s2) ); //返回长度差
System.out.println("s1.compareTo(s3): " + s1.compareTo(s3) ); //返回'k'-'a'的差
System.out.println("s4.compareTo(s3): " + s4.compareTo(s3)); //返回0
结果为:s1.compareTo(s2):4
s1.compareTo(s3):10
s4.compareTo(s3): 0
4. Stringconcat(String str) :将该String对象与str连接在一起。’
System.out.println("s1.concat(s2): " + s1.concat(s2));
结果为:s1.concat(s2):abcdefghijklmnabcdefghij
5. boolean contentEquals(StringBuffersb) :将该String对象与StringBuffer对象sb进行比较。
System.out.println("s1.contentEquals(sb_buf): "+s1.contentEquals(sb_buf));
结果为:s1.contentEquals(sb_buf): false
6. static StringcopyValueOf(char[] data):
7. static StringcopyValueOf(char[] data, int offset, int count) :这两个方法将char数组转换成String,与其中一个构造函数类似。
System.out.println("s1.copyValueOf(c): "+s1.copyValueOf(c) );
结果为:s1.copyValueOf(c): 0123456789
8. booleanendsWith(String suffix) :该String对象是否以suffix结尾。
例如:
String s1 = new String("abcdefghij");
String s2 = newString("ghij");
System.out.println("s1.endsWith(s2): " + s1.endsWith(s2) );
结果为:s1.endsWith(s2):true
9. boolean equals(Object anObject):当anObject不为空并且与当前String对象一样,返回true;否则,返回false。
10. byte[] getBytes() :将该String对象转换成byte数组。
System.out.println("s1.getBytes(): "+s1.getBytes() );
结果为:s1.getBytes(): [B@110003
11. void getChars(intsrcBegin, int srcEnd, char[] dst, int dstBegin) :
该方法将字符串拷贝到字符数组中。其中,srcBegin为拷贝的起始位置、srcEnd为拷贝的结束位置、字符串数值dst为目标字符数组、dstBegin为目标字符数组的拷贝起始位置。
例如:
char[] s1 = {'I',' ','l','o','v','e',' ','h','e','r','!'};//s1=Ilove her!
String s2 = newString("you!");
s2.getChars(0,3,s1,7); //s1=I love you!
System.out.println( s1 );
结果为:I loveyou!
12. int hashCode():返回当前字符的哈希表码。
System.out.println("s1.hashCode(): "+s1.hashCode());
结果为:s1.hashCode(): 2093908199
13. int indexOf(int ch) :只找第一个匹配字符位置。
System.out.println("s1.indexOf('b'): "+s1.indexOf('b'));
结果为:s1.indexOf('b'): 1
14. int indexOf(int ch,intfromIndex) :从fromIndex开始找第一个匹配字符位置。
15. int indexOf(Stringstr) :只找第一个匹配字符串位置。
16. int indexOf(String str, intfromIndex) :从fromIndex开始找第一个匹配字符串位置。
例如:
String s = new String("write once, run anywhere!");
String ss = new String("run");
System.out.println("s.indexOf('r'): " + s.indexOf('r') );
System.out.println("s.indexOf('r',2): " + s.indexOf('r',2) );
System.out.println("s.indexOf(ss): " + s.indexOf(ss) );
结果为:s.indexOf('r'):1
s.indexOf('r',2): 12
s.indexOf(ss): 12
17. int lastIndexOf(intch)
18. int lastIndexOf(intch, int fromIndex)
19. intlastIndexOf(String str)
20. intlastIndexOf(String str, int fromIndex) 以上四个方法与13、14、15、16类似,不同的是:找最后一个匹配的内容。
String s1 = new String("acbdebfg");
System.out.println(s1.lastIndexOf((int)'b',7));
结果为:5
(其中fromIndex的参数为7,是从字符串acbdebfg的最后一个字符g开始往前数的位数。既是从字符c开始匹配,寻找最后一个匹配b的位置。所以结果为5)
21. int length():返回当前字符串长度。
22. String replace(char oldChar, charnewChar) :将字符号串中第一个oldChar替换成newChar。
23. boolean startsWith(String prefix):该String对象是否以prefix开始。
24. boolean startsWith(String prefix, inttoffset) :该String对象从toffset位置算起,是否以prefix开始。
例如:
String s = new String("write once, run anywhere!");
Stringss = new String("write");
Stringsss = new String("once");
System.out.println("s.startsWith(ss): " + s.startsWith(ss) );
System.out.println("s.startsWith(sss,6): " + s.startsWith(sss,6) );
结果为:s.startsWith(ss):true
s.startsWith(sss,6): true
25. Stringsubstring(int beginIndex):取从beginIndex位置开始到结束的子字符串。
26. String substring(int beginIndex, intendIndex) :取从beginIndex位置开始到endIndex位置的子字符串。
27. char[ ] toCharArray():将该String对象转换成char数组。
28. String toLowerCase() :将字符串转换成小写。
29. String toUpperCase() :将字符串转换成大写。
例如:
String s = new String("java.lang.Class String");
System.out.println("s.toUpperCase(): " + s.toUpperCase() );
System.out.println("s.toLowerCase(): " + s.toLowerCase() );
结果为:s.toUpperCase():JAVA.LANG.CLASS STRING
s.toLowerCase(): java.lang.class string
30. static StringvalueOf(boolean b)
31. static StringvalueOf(char c)
32. static StringvalueOf(char[] data)
33. static StringvalueOf(char[] data, int offset, int count)
34. static StringvalueOf(double d)
35. static StringvalueOf(float f)
36. static StringvalueOf(int i)
37. static StringvalueOf(long l)
38. static StringvalueOf(Object obj)
以上方法用于将各种不同类型转换成Java字符型。这些都是类方法。
三、常用方法
public charcharAt(int index)
返回字符串中第index个字符;
public int compareTo(Stringstr)/ public int compareToIgnoreCase(String str)
返回与字符串str比较的结果int,第二个比较时忽略大小写;
public int length()
返回字符串的长度;
public String concat(Stringstr)
返回连接str后的字符串;
public int indexOf(String str)
返回字符串中第一次出现str的位置;
public int indexOf(String str,intfromIndex)
返回字符串从fromIndex开始第一次出现str的位置;
public booleanequalsIgnoreCase(String another)
比较字符串与another是否一样(忽略大小写);
public String replace(charoldchar,char newChar)
在字符串中用newChar字符替换oldChar字符
public StringreplaceAll/replaceFirst(String oldStr,String newStr)
在字符串中用串newStr代替原串中所有/第一次出现的子串oldStr,返回新串
public boolean startsWith(Stringprefix)
判断字符串是否以prefix字符串开头;
public boolean endsWith(Stringsuffix)
判断一个字符串是否以suffix字符串结尾;
public String toUpperCase()
返回一个字符串为该字符串的大写形式;
public String toLowerCase()
返回一个字符串为该字符串的小写形式
public String substring(intbeginIndex)
返回该字符串从beginIndex开始到结尾的子字符串;
public String substring(intbeginIndex,int endIndex)
返回该字符串从beginIndex开始到endsIndex结尾的子字符串
public String trim()
返回该字符串去掉开头和结尾空格后的字符串,但是不去中间的空格
public String[] split(String regex)
将一个字符串按照指定的分隔符分隔,返回分隔后的字符串数组
四、源码结果
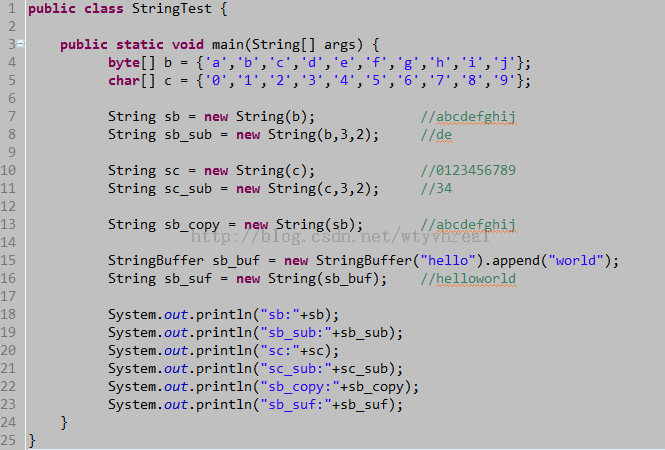
public class StringTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
byte[] b = {'a','b','c','d','e','f','g','h','i','j'};
char[] c = {'0','1','2','3','4','5','6','7','8','9'};
String sb = new String(b); //abcdefghij
String sb_sub = new String(b,3,2); //de
String sc = new String(c); //0123456789
String sc_sub = new String(c,3,2); //34
String sb_copy = new String(sb); //abcdefghij
StringBuffer sb_buf = new StringBuffer("hello").append("world");
String sb_suf = new String(sb_buf); //helloworld
System.out.println("sb:"+sb);
System.out.println("sb_sub:"+sb_sub);
System.out.println("sc:"+sc);
System.out.println("sc_sub:"+sc_sub);
System.out.println("sb_copy:"+sb_copy);
System.out.println("sb_suf:"+sb_suf);
String s1 = new String("abcdefghijklmn");
String s2 = new String("abcdefghij");
String s3 = new String("abcdefghijalmn");
String s4 = new String("abcdefghijalmn");
String s5 = new String(" a bc d ");
System.out.println("s1.compareTo(s2): " + s1.compareTo(s2) ); //返回长度差
System.out.println("s1.compareTo(s3): " + s1.compareTo(s3) ); //返回'k'-'a'的差
System.out.println("s4.compareTo(s3): " + s4.compareTo(s3) ); //返回0
System.out.println("s1.concat(s2): "+s1.concat(s2));
System.out.println("s1.contentEquals(sb_buf): "+s1.contentEquals(sb_buf));
System.out.println("s1.copyValueOf(c): "+s1.copyValueOf(c) );
System.out.println("s1.getBytes(): "+s1.getBytes() );
System.out.println("s1.hashCode(): "+s1.hashCode());
System.out.println("s1.indexOf('b'): "+s1.indexOf('b'));
System.out.println("s1.indexOf('i', 1): "+s1.indexOf('i', 1));
System.out.println("s5.trim(): "+s5.trim());//去掉开始和结尾的空格
String date = "2008/09/10";
String[ ] dateAfterSplit= new String[3];
dateAfterSplit=date.split("/"); //以“/”作为分隔符来分割date字符串,并把结果放入3个字符串中。
for(int i=0;i<dateAfterSplit.length;i++)
System.out.print(dateAfterSplit[i]+" ");
System.out.println();
//介绍一个简单的应用,判断一个自然数是几位数字的逻辑代码如下:
int n = 12345;
String strTest = String.valueOf(n);
System.out.println(strTest.length());
}
}
sb:abcdefghij
sb_sub:de
sc:0123456789
sc_sub:34
sb_copy:abcdefghij
sb_suf:helloworld
s1.compareTo(s2): 4
s1.compareTo(s3): 10
s4.compareTo(s3): 0
s1.concat(s2): abcdefghijklmnabcdefghij
s1.contentEquals(sb_buf): false
s1.copyValueOf(c): 0123456789
s1.getBytes(): [B@c62c8
s1.hashCode(): 2093908199
s1.indexOf('b'): 1
s1.indexOf('i', 1): 8
s5.trim(): a bc d
2008 09 10
5
五、引用参考
http://www.cnblogs.com/springcsc/archive/2009/12/03/1616326.html
http://www.cnblogs.com/YSO1983/archive/2009/12/07/1618564.html