leveldb源代码分析4:SkipList
skiplist思想可以具体参考这:
Skip list
View more documents from xuqianghitsoft
或者是参考我的这篇博文:http://www.cnblogs.com/xuqiang/archive/2011/05/22/2053516.html, leveldb中的实现方式基本上和我的那篇博文中的实现方式类似。SkipList在db/skiplist.h中声明,向外界暴漏接口非常简单,如下:
// Create a new SkipList object that will use "cmp" for comparing keys, // and will allocate memory using "*arena". Objects allocated in the arena // must remain allocated for the lifetime of the skiplist object. explicit SkipList(Comparator cmp, Arena* arena); // Insert key into the list. // REQUIRES: nothing that compares equal to key is currently in the list. void Insert(const Key& key); // Returns true iff an entry that compares equal to key is in the list. bool Contains(const Key& key) const;
private成员变量:
// 最大的level
enum { kMaxHeight = 12 };
// Immutable after construction
Comparator const compare_;
// 内存分配器
Arena* const arena_; // Arena used for allocations of nodes
// 指向第一个节点,构造函数中初始化
Node* const head_;
// Modified only by Insert(). Read racily by readers, but stale
// values are ok.
port::AtomicPointer max_height_; // Height of the entire list我们下面来首先分析初始化操作,如下:
// 初始化:
// 1. 初始化compare_
// 2. 初始化arena_
// 3. 初始化head_,指向指针数组
// 4. 初始化max_height_
// 5. 初始化rnd_随机数的seed
// 6. 初始化head_指向的数组
template<typename Key, class Comparator>
SkipList<Key,Comparator>::SkipList(Comparator cmp, Arena* arena)
: compare_(cmp),
arena_(arena),
head_(NewNode(0 /* any key will do */, kMaxHeight)),
max_height_(reinterpret_cast<void*>(1)),
rnd_(0xdeadbeef) {
// 初始化head_指向的数组
for (int i = 0; i < kMaxHeight; i++) {
head_->SetNext(i, NULL);
}
}
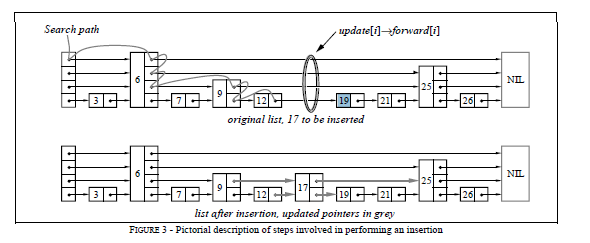
下面是一个插入操作的示意图:
leveldb中实现的插入代码就是按照上面的思路实现,首先查找到合适的位置,并记录查找过程中经过的路径,之后新生成一个节点,修改指针。
// 插入操作
// 这里的key其实已经是经过处理的key,包含了用户指定的key和value
template<typename Key, class Comparator>
void SkipList<Key,Comparator>::Insert(const Key& key) {
// TODO(opt): We can use a barrier-free variant of FindGreaterOrEqual()
// here since Insert() is externally synchronized.
// prev记录的是查询路径,下面需要使用prev来修改新生成
// 节点的指针
Node* prev[kMaxHeight];
Node* x = FindGreaterOrEqual(key, prev);
// Our data structure does not allow duplicate insertion
// 不允许插入重复的值
assert(x == NULL || !Equal(key, x->key));
// 随即生成节点高度
int height = RandomHeight();
// 对prev数组中未赋值的元素进行赋值
if (height > GetMaxHeight()) {
for (int i = GetMaxHeight(); i < height; i++) {
prev[i] = head_;
}
// It is ok to mutate max_height_ without any synchronization
// with concurrent readers. A concurrent reader that observes
// the new value of max_height_ will see either the old value of
// new level pointers from head_ (NULL), or a new value set in
// the loop below. In the former case the reader will
// immediately drop to the next level since NULL sorts after all
// keys. In the latter case the reader will use the new node.
// 设置max_height变量
max_height_.NoBarrier_Store(reinterpret_cast<void*>(height));
}
// 新生成一个节点,之后插入数据
x = NewNode(key, height);
for (int i = 0; i < height; i++) {
// NoBarrier_SetNext() suffices since we will add a barrier when
// we publish a pointer to "x" in prev[i].
// 修改两部分的指针,一部分是需要执行新插入节点的指针
// 另外的一部分是x节点的指针
x->NoBarrier_SetNext(i, prev[i]->NoBarrier_Next(i));
prev[i]->SetNext(i, x);
}
}
函数FindGreaterOrEqual中完成查询操作,就是向下(level控制)和向右(x控制)移动过程,并不断经经过路径保存到参数prev中。
template<typename Key, class Comparator>
typename SkipList<Key,Comparator>::Node*
SkipList<Key,Comparator>::FindGreaterOrEqual(const Key& key,
Node** prev)
const {
// 从最高层开始查找
Node* x = head_;
int level = GetMaxHeight() - 1;
while (true) {
Node* next = x->Next(level);
if (KeyIsAfterNode(key, next)) { // 向右移动
// Keep searching in this list
x = next;
}
else // 向下移动
{
// 记录查找路径
if (prev != NULL)
prev[level] = x;
if (level == 0) {
return next;
} else {
// Switch to next list下一层寻找
level--;
}
}
}
}
查找操作基本上就是调用函数上面的函数FindGreaterOrEqual实现:
// 查询操作
template<typename Key, class Comparator>
bool SkipList<Key,Comparator>::Contains(const Key& key) const {
Node* x = FindGreaterOrEqual(key, NULL);
if (x != NULL && Equal(key, x->key)) {
return true;
} else {
return false;
}
}
上面基本上就是skiplist在leveldb中实现,leveldb中没有使用复杂的红黑树等机制去保证数据的有序性,而是使用了轻快的skiplist实现。最后需要注意skiplist中每个节点存储key是用户传递keyvalue经过变幻(变幻方法参考http://blog.csdn.net/xuqianghit/article/details/6948164)得到的。