druid简单教程
java程序很大一部分要操作数据库,为了提高性能操作数据库的时候,有不得不使用数据库连接池。数据库连接池有很多选择,c3p、dhcp、proxool等,druid作为一名后起之秀,凭借其出色的性能,也逐渐印入了大家的眼帘。接下来本教程就说一下druid的简单使用。
首先从http://repo1.maven.org/maven2/com/alibaba/druid/ 下载最新的jar包。如果想使用最新的源码编译,可以从https://github.com/alibaba/druid 下载源码,然后使用maven命令行,或者导入到eclipse中进行编译。
1 配置
和dbcp类似,druid的常用配置项如下
| 配置 | 缺省值 | 说明 |
| name | 配置这个属性的意义在于,如果存在多个数据源,监控的时候 可以通过名字来区分开来。如果没有配置,将会生成一个名字, 格式是:"DataSource-" + System.identityHashCode(this) |
|
| jdbcUrl | 连接数据库的url,不同数据库不一样。例如: mysql : jdbc:mysql://10.20.153.104:3306/druid2 oracle : jdbc:oracle:thin:@10.20.149.85:1521:ocnauto |
|
| username | 连接数据库的用户名 | |
| password | 连接数据库的密码。如果你不希望密码直接写在配置文件中, 可以使用ConfigFilter。详细看这里: https://github.com/alibaba/druid/wiki/%E4%BD%BF%E7%94%A8ConfigFilter |
|
| driverClassName | 根据url自动识别 | 这一项可配可不配,如果不配置druid会根据url自动识别dbType, 然后选择相应的driverClassName |
| initialSize | 0 | 初始化时建立物理连接的个数。初始化发生在显示调用init方法, 或者第一次getConnection时 |
| maxActive | 8 | 最大连接池数量 |
| maxIdle | 8 | 已经不再使用,配置了也没效果 |
| minIdle | 最小连接池数量 | |
| maxWait | 获取连接时最大等待时间,单位毫秒。配置了maxWait之后, 缺省启用公平锁,并发效率会有所下降, 如果需要可以通过配置useUnfairLock属性为true使用非公平锁。 |
|
| poolPreparedStatements | false | 是否缓存preparedStatement,也就是PSCache。 PSCache对支持游标的数据库性能提升巨大,比如说oracle。 在mysql5.5以下的版本中没有PSCache功能,建议关闭掉。 5.5及以上版本有PSCache,建议开启。 |
| maxOpenPreparedStatements | -1 | 要启用PSCache,必须配置大于0,当大于0时, poolPreparedStatements自动触发修改为true。 在Druid中,不会存在Oracle下PSCache占用内存过多的问题, 可以把这个数值配置大一些,比如说100 |
| validationQuery | 用来检测连接是否有效的sql,要求是一个查询语句。 如果validationQuery为null,testOnBorrow、testOnReturn、 testWhileIdle都不会其作用。在mysql中通常为select 'x',在oracle中通常为 select 1 from dual |
|
| testOnBorrow | true | 申请连接时执行validationQuery检测连接是否有效, 做了这个配置会降低性能。 |
| testOnReturn | false | 归还连接时执行validationQuery检测连接是否有效, 做了这个配置会降低性能 |
| testWhileIdle | false | 建议配置为true,不影响性能,并且保证安全性。 申请连接的时候检测,如果空闲时间大于 timeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis, 执行validationQuery检测连接是否有效。 |
| timeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis | 有两个含义: 1) Destroy线程会检测连接的间隔时间 2) testWhileIdle的判断依据,详细看testWhileIdle属性的说明 |
|
| numTestsPerEvictionRun | 不再使用,一个DruidDataSource只支持一个EvictionRun | |
| minEvictableIdleTimeMillis | Destory线程中如果检测到当前连接的最后活跃时间和当前时间的差值大于 minEvictableIdleTimeMillis,则关闭当前连接。 |
|
| connectionInitSqls | 物理连接初始化的时候执行的sql | |
| exceptionSorter | 根据dbType自动识别 | 当数据库抛出一些不可恢复的异常时,抛弃连接 |
| filters | 属性类型是字符串,通过别名的方式配置扩展插件, 常用的插件有: 监控统计用的filter:stat 日志用的filter:log4j 防御sql注入的filter:wall |
|
| proxyFilters | 类型是List<com.alibaba.druid.filter.Filter>, 如果同时配置了filters和proxyFilters, 是组合关系,并非替换关系 |
|
| removeAbandoned | 对于建立时间超过removeAbandonedTimeout的连接强制关闭 | |
| removeAbandonedTimeout | 指定连接建立多长时间就需要被强制关闭 | |
| logAbandoned | 指定发生removeabandoned的时候,是否记录当前线程的堆栈信息到日志中 |
表1.1 配置属性
表1.1仅仅列出了常用配置属性,完整的属性列表可以参考代码类DruidDataSourceFactory 的ALL_PROPERTIES属性,根据常用的配置属性,首先给出一个如下的配置文件,放置于src目录下。
url:jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/dragoon_v25_masterdb
driverClassName:com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
username:root
password:aaaaaaaa
filters:stat
maxActive:20
initialSize:1
maxWait:60000
minIdle:10
#maxIdle:15
timeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis:60000
minEvictableIdleTimeMillis:300000
validationQuery:SELECT 'x'
testWhileIdle:true
testOnBorrow:false
testOnReturn:false
#poolPreparedStatements:true
maxOpenPreparedStatements:20
#禁用对于长时间不使用的连接强制关闭的功能
removeAbandoned:false
#超过30分钟开始关闭空闲连接,由于removeAbandoned为false,这个设置项不再起作用
removeAbandonedTimeout:1800
#将当前关闭动作记录到日志,由于removeAbandoned为false,这个设置项不再起作用
logAbandoned:true
配置文件1.1
配置项中指定了各个参数后,在连接池内部是这么使用这些参数的。数据库连接池在初始化的时候会创建initialSize个连接,当有数据库操作时,会从池中取出一个连接。如果当前池中正在使用的连接数等于maxActive,则会等待一段时间,等待其他操作释放掉某一个连接,如果这个等待时间超过了maxWait,则会报错;如果当前正在使用的连接数没有达到maxActive,则判断当前是否空闲连接,如果有则直接使用空闲连接,如果没有则新建立一个连接。在连接使用完毕后,不是将其物理连接关闭,而是将其放入池中等待其他操作复用。
同时连接池内部有机制判断,如果当前的总的连接数少于miniIdle,则会建立新的空闲连接,以保证连接数得到miniIdle。如果当前连接池中某个连接在空闲了timeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis时间后任然没有使用,则被物理性的关闭掉。有些数据库连接的时候有超时限制(mysql连接在8小时后断开),或者由于网络中断等原因,连接池的连接会出现失效的情况,这时候可以设置一个testWhileIdle参数为true,注意这里的“while”这个单词应该翻译成“如果”,换句话说testWhileIdle写为testIfIdle更好理解些,其含义为连接在获取连接的时候,如果检测到当前连接不活跃的时间超过了timeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis,则去手动检测一下当前连接的有效性,在保证确实有效后才加以使用。在检测活跃性时,如果当前的活跃时间大于minEvictableIdleTimeMillis,则认为需要关闭当前连接。当然,为了保证绝对的可用性,你也可以使用testOnBorrow为true(即在每次获取Connection对象时都检测其可用性),不过这样会影响性能。
最后说一下removeAbandoned参数,其实druid是不能检测到当前使用的连接是否发生了连接泄露,所以在代码内部就假定如果一个连接建立连接的时间很长,则将其认定为泄露,继而强制将其关闭掉。这个参数在druid中默认是不开启的,github上给出的wiki中也对其没有丝毫提及。其实在代码中设置testWhileIdle就能在一定程序上消灭掉泄露的连接,因为如果发生了泄露,那么他的不活跃时间肯定会在某个时间点大于timeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis,继而被回收掉。
2 代码编写
2.1 使用spring
首先给出spring配置文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc-3.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-3.0.xsd">
<!-- 给web使用的spring文件 -->
<bean id="propertyConfigurer"
class="org.springframework.beans.factory.config.PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer">
<property name="locations">
<list>
<value>/WEB-INF/classes/dbconfig.properties</value>
</list>
</property>
</bean>
<bean id="dataSource" class="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource"
destroy-method="close">
<property name="url" value="${url}" />
<property name="username" value="${username}" />
<property name="password" value="${password}" />
<property name="driverClassName" value="${driverClassName}" />
<property name="filters" value="${filters}" />
<property name="maxActive" value="${maxActive}" />
<property name="initialSize" value="${initialSize}" />
<property name="maxWait" value="${maxWait}" />
<property name="minIdle" value="${minIdle}" />
<property name="timeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis" value="${timeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis}" />
<property name="minEvictableIdleTimeMillis" value="${minEvictableIdleTimeMillis}" />
<property name="validationQuery" value="${validationQuery}" />
<property name="testWhileIdle" value="${testWhileIdle}" />
<property name="testOnBorrow" value="${testOnBorrow}" />
<property name="testOnReturn" value="${testOnReturn}" />
<property name="maxOpenPreparedStatements"
value="${maxOpenPreparedStatements}" />
<property name="removeAbandoned" value="${removeAbandoned}" /> <!-- 打开removeAbandoned功能 -->
<property name="removeAbandonedTimeout" value="${removeAbandonedTimeout}" /> <!-- 1800秒,也就是30分钟 -->
<property name="logAbandoned" value="${logAbandoned}" /> <!-- 关闭abanded连接时输出错误日志 -->
</bean>
<bean id="dataSourceDbcp" class="org.apache.commons.dbcp.BasicDataSource"
destroy-method="close">
<property name="driverClassName" value="${driverClassName}" />
<property name="url" value="${url}" />
<property name="username" value="${username}" />
<property name="password" value="${password}" />
<property name="maxActive" value="${maxActive}" />
<property name="minIdle" value="${minIdle}" />
<property name="maxWait" value="${maxWait}" />
<property name="defaultAutoCommit" value="true" />
<property name="timeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis" value="${timeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis}" />
<property name="minEvictableIdleTimeMillis" value="${minEvictableIdleTimeMillis}" />
<property name="validationQuery" value="${validationQuery}" />
<property name="testWhileIdle" value="${testWhileIdle}" />
<property name="testOnBorrow" value="${testOnBorrow}" />
<property name="testOnReturn" value="${testOnReturn}" />
<property name="maxOpenPreparedStatements"
value="${maxOpenPreparedStatements}" />
<property name="removeAbandoned" value="${removeAbandoned}" />
<property name="removeAbandonedTimeout" value="${removeAbandonedTimeout}" />
<property name="logAbandoned" value="${logAbandoned}" />
</bean>
<!-- jdbcTemplate -->
<bean id="jdbc" class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate">
<property name="dataSource">
<ref bean="dataSource" />
</property>
</bean>
<bean id="SpringTableOperatorBean" class="com.whyun.druid.model.TableOperator"
scope="prototype">
<property name="dataSource">
<ref bean="dataSource" />
</property>
</bean>
</beans>
配置文件2.1
其中第一个bean中给出的配置文件/WEB-INF/classes/dbconfig.properties就是第1节中给出的配置文件。我这里还特地给出dbcp的spring配置项,目的就是将两者进行对比,方便大家进行迁移。这里没有使用JdbcTemplate,所以jdbc那个bean没有使用到。下面给出com.whyun.druid.model.TableOperator类的代码。
package com.whyun.druid.model;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.Statement;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
public class TableOperator {
private DataSource dataSource;
public void setDataSource(DataSource dataSource) {
this.dataSource = dataSource;
}
private static final int COUNT = 800;
public TableOperator() {
}
public void tearDown() throws Exception {
try {
dropTable();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public void insert() throws Exception {
StringBuffer ddl = new StringBuffer();
ddl.append("INSERT INTO t_big (");
for (int i = 0; i < COUNT; ++i) {
if (i != 0) {
ddl.append(", ");
}
ddl.append("F" + i);
}
ddl.append(") VALUES (");
for (int i = 0; i < COUNT; ++i) {
if (i != 0) {
ddl.append(", ");
}
ddl.append("?");
}
ddl.append(")");
Connection conn = dataSource.getConnection();
// System.out.println(ddl.toString());
PreparedStatement stmt = conn.prepareStatement(ddl.toString());
for (int i = 0; i < COUNT; ++i) {
stmt.setInt(i + 1, i);
}
stmt.execute();
stmt.close();
conn.close();
}
private void dropTable() throws SQLException {
Connection conn = dataSource.getConnection();
Statement stmt = conn.createStatement();
stmt.execute("DROP TABLE t_big");
stmt.close();
conn.close();
}
public void createTable() throws SQLException {
StringBuffer ddl = new StringBuffer();
ddl.append("CREATE TABLE t_big (FID INT AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY ");
for (int i = 0; i < COUNT; ++i) {
ddl.append(", ");
ddl.append("F" + i);
ddl.append(" BIGINT NULL");
}
ddl.append(")");
Connection conn = dataSource.getConnection();
Statement stmt = conn.createStatement();
stmt.execute(ddl.toString());
stmt.close();
conn.close();
}
}
代码片段2.1
注意:在使用的时候,通过获取完Connection对象,在使用完之后,要将其close掉,这样其实是将用完的连接放入到连接池中,如果你不close的话,会造成连接泄露。
然后我们写一个servlet来测试他.package com.whyun.druid.servelt;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import javax.servlet.ServletContext;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import org.springframework.web.context.WebApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.web.context.support.WebApplicationContextUtils;
import com.whyun.druid.model.TableOperator;
public class TestServlet extends HttpServlet {
private TableOperator operator;
@Override
public void init() throws ServletException {
super.init();
ServletContext servletContext = this.getServletContext();
WebApplicationContext ctx
= WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(servletContext);
operator = (TableOperator)ctx.getBean("SpringTableOperatorBean");
}
/**
* The doGet method of the servlet. <br>
*
* This method is called when a form has its tag value method equals to get.
*
* @param request the request send by the client to the server
* @param response the response send by the server to the client
* @throws ServletException if an error occurred
* @throws IOException if an error occurred
*/
public void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
response.setContentType("text/html");
PrintWriter out = response.getWriter();
boolean createResult = false;
boolean insertResult = false;
boolean dropResult = false;
try {
operator.createTable();
createResult = true;
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
if (createResult) {
try {
operator.insert();
insertResult = true;
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
operator.tearDown();
dropResult = true;
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
out.println("{'createResult':"+createResult+",'insertResult':"
+insertResult+",'dropResult':"+dropResult+"}");
out.flush();
out.close();
}
}
代码片段2.2
这里没有用到struts2或者springmvc,虽然大部分开发者用的是这两种框架。
2.2 不使用spring
类似于dbcp,druid也提供了原生态的支持。这里仅仅列出来了如何获取一个DataSource对象,实际使用中要将获取DataSource的过程封装到一个单体模式类中。先看下面这段代码:
package com.whyun.util.db;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import org.apache.commons.dbcp.BasicDataSourceFactory;
import com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSourceFactory;
import com.whyun.util.config.MySqlConfigProperty;
import com.whyun.util.config.MySqlConfigProperty2;
import com.whyun.util.db.source.AbstractDataSource;
import com.whyun.util.db.source.impl.DbcpSourceMysql;
import com.whyun.util.db.source.impl.DruidSourceMysql;
import com.whyun.util.db.source.impl.DruidSourceMysql2;
// TODO: Auto-generated Javadoc
/**
* The Class DataSourceUtil.
*/
public class DataSourceUtil {
/** 使用配置文件dbconfig.properties构建Druid数据源. */
public static final int DRUID_MYSQL_SOURCE = 0;
/** The duird mysql source. */
private static DataSource duirdMysqlSource;
/** 使用配置文件dbconfig2.properties构建Druid数据源. */
public static final int DRUID_MYSQL_SOURCE2 = 1;
/** The druid mysql source2. */
private static DataSource druidMysqlSource2;
/** 使用配置文件dbconfig.properties构建Dbcp数据源. */
public static final int DBCP_SOURCE = 4;
/** The dbcp source. */
private static DataSource dbcpSource;
/**
* 根据类型获取数据源.
*
* @param sourceType 数据源类型
* @return druid或者dbcp数据源
* @throws Exception the exception
* @NotThreadSafe
*/
public static final DataSource getDataSource(int sourceType)
throws Exception {
DataSource dataSource = null;
switch(sourceType) {
case DRUID_MYSQL_SOURCE:
if (duirdMysqlSource == null) {
duirdMysqlSource = DruidDataSourceFactory.createDataSource(
MySqlConfigProperty.getInstance().getProperties());
}
dataSource = duirdMysqlSource;
break;
case DRUID_MYSQL_SOURCE2:
if (druidMysqlSource2 == null) {
druidMysqlSource2 = DruidDataSourceFactory.createDataSource(
MySqlConfigProperty2.getInstance().getProperties());
}
dataSource = druidMysqlSource2;
break;
case DBCP_SOURCE:
if (dbcpSource == null) {
dbcpSource = BasicDataSourceFactory.createDataSource(
MySqlConfigProperty.getInstance().getProperties());
}
dataSource = dbcpSource;
break;
}
return dataSource;
}
/**
* 根据数据库类型标示获取DataSource对象,跟{@link com.whyun.util.db.DataSourceUtil#getDataSource(int)}
* 不同的是,这里DataSource获取的时候使用了单体模式
*
* @param sourceType 数据源类型
* @return 获取到的DataSource对象
* @throws Exception the exception
*/
public static final DataSource getDataSource2(int sourceType) throws Exception {
AbstractDataSource abstractDataSource = null;
switch(sourceType) {
case DRUID_MYSQL_SOURCE:
abstractDataSource = DruidSourceMysql.getInstance();
break;
case DRUID_MYSQL_SOURCE2:
abstractDataSource = DruidSourceMysql2.getInstance();
break;
case DBCP_SOURCE:
abstractDataSource = DbcpSourceMysql.getInstance();
break;
}
return abstractDataSource == null ?
null :
abstractDataSource.getDataSource();
}
}
代码片段2.3 手动读取配置文件初始化连接池
第37行中调用了类com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSourceFactory中createDataSource方法来初始化一个连接池。对比dbcp的使用方法,两者很相似。
下面给出一个多线程的测试程序。运行后可以比较druid和dbcp的性能差别。
package com.whyun.druid.test;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.concurrent.Callable;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import java.util.concurrent.Future;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
import com.whyun.druid.model.TableOperator;
import com.whyun.util.db.DataSourceUtil;
public class MutilThreadTest {
public static void test(int dbType, int times)
throws Exception {
int numOfThreads =Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors()*2;
ExecutorService executor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(numOfThreads);
final TableOperator test = new TableOperator();
// int dbType = DataSourceUtil.DRUID_MYSQL_SOURCE;
// dbType = DataSourceUtil.DBCP_SOURCE;
test.setDataSource(DataSourceUtil.getDataSource(dbType));
boolean createResult = false;
try {
test.createTable();
createResult = true;
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
if (createResult) {
List<Future<Long>> results = new ArrayList<Future<Long>>();
for (int i = 0; i < times; i++) {
results.add(executor.submit(new Callable<Long>() {
@Override
public Long call() throws Exception {
long begin = System.currentTimeMillis();
try {
test.insert();
//insertResult = true;
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
return end - begin;
}
}));
}
executor.shutdown();
while(!executor.awaitTermination(Long.MAX_VALUE, TimeUnit.DAYS));
long sum = 0;
for (Future<Long> result : results) {
sum += result.get();
}
System.out.println("---------------db type "+dbType+"------------------");
System.out.println("number of threads :" + numOfThreads + " times:" + times);
System.out.println("running time: " + sum + "ms");
System.out.println("TPS: " + (double)(100000 * 1000) / (double)(sum));
System.out.println();
try {
test.tearDown();
//dropResult = true;
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
} else {
System.out.println("初始化数据库失败");
}
}
public static void main (String argc[])
throws Exception {
test(DataSourceUtil.DBCP_SOURCE,50);
test(DataSourceUtil.DRUID_MYSQL_SOURCE,50);
}
}
代码片段2.4 连接池多线程测试程序
3 监控
3.1 web监控
druid提供了sql语句查询时间等信息的监控功能。为了让数据库查询一直运行,下面特地写了一个ajax进行轮询。同时,还要保证在web.xml中配置如下信息
<servlet> <servlet-name>DruidStatView</servlet-name> <servlet-class>com.alibaba.druid.support.http.StatViewServlet</servlet-class> </servlet> <servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>DruidStatView</servlet-name> <url-pattern>/druid/*</url-pattern> </servlet-mapping>配置文件3.1 在web.xml中添加druid监控
同时将ajax代码提供如下
function showTime() {
var myDate = new Date();
var timeStr = '';
timeStr += myDate.getFullYear()+'-'; //获取完整的年份(4位,1970-????)
timeStr += myDate.getMonth()+'-'; //获取当前月份(0-11,0代表1月)
timeStr += myDate.getDate() + ' '; //获取当前日(1-31)
timeStr += myDate.getHours()+':'; //获取当前小时数(0-23)
timeStr += myDate.getMinutes()+':'; //获取当前分钟数(0-59)
timeStr += myDate.getSeconds(); //获取当前秒数(0-59)
return timeStr
}
$(document).ready(function() {
function loadDBTestMessage() {
$.get('servlet/MysqlTestServlet',function(data) {
if (typeof(data) != 'object') {
data = eval('(' + data + ')');
}
var html = '['+showTime()+']';
html += '创建:' + data['createResult'];
html += '插入:' + data['insertResult'];
html += '销毁:' + data['dropResult'];
html +=
$('#message').html(html);
});
}
setInterval(function() {
loadDBTestMessage();
}, 10000);
});
代码片段3.1 ajax轮询
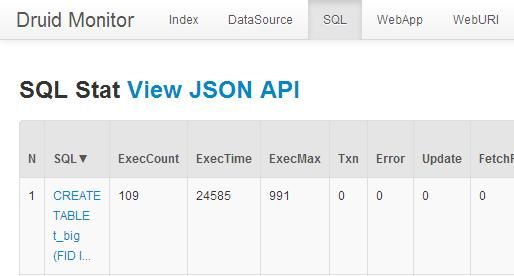
这时打开http://localhost/druid-web/druid/ 地址,会看到监控界面,点击其中的sql标签。
图3.1 监控界面查看sql查询时间
注意:在写配置文件1.1时,要保证filter配置项中含有stat属性,否则这个地方看不到sql语句的监控数据。
从0.2.23开始监控界面支持中英文语言,所以这里就不翻译表格中的英文字段了。
老版本的druid的jar包中不支持通过web界面进行远程监控,从0.2.14开始可以通过配置jmx地址来获取远程运行druid的服务器的监控信息。具体配置方法如下:
<servlet> <servlet-name>DruidStatView</servlet-name> <servlet-class>com.alibaba.druid.support.http.StatViewServlet</servlet-class> <init-param> <param-name>jmxUrl</param-name> <param-value>service:jmx:rmi:///jndi/rmi://localhost:9004/jmxrmi</param-value> </init-param> </servlet> <servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>DruidStatView</servlet-name> <url-pattern>/druid/*</url-pattern> </servlet-mapping>配置文件3.2 远程监控web
这里连接的配置参数中多了一个jmxUrl,里面配置一个jmx连接地址,如果配置了这个init-param后,那么当前web监控界面监控的就不是本机的druid的使用情况,而是jmxUrl中指定的ip的远程机器的druid使用情况。jmx连接中也可以指定用户名、密码,在上面的servlet中添加两个init-param,其param-name分别为jmxUsername和jmxPassword,分别对应连接jmx的用户名和密码。对于jmx在服务器端的配置,可以参考3.2节中的介绍。
3.2 jconsole监控
同时druid提供了jconsole监控的功能,因为界面做的不是很好,所以官方中没有对其的相关介绍。如果是纯java程序的话,可以简单的使用jconsole,也可以使用3.1中提到的通过配置init-param来访问远程druid。下面依然使用的是刚才用的web项目来模拟druid所在的远程机器。
现在假设有两台机器,一台是运行druid的A机器,一台是要查看druid运行信息的B机器。
首先在这台远程机器A的catalina.bat(或者catalina.sh)中加入java的启动选项,放置于if "%OS%" == "Windows_NT" setlocal这句之后。
set JAVA_OPTS=%JAVA_OPTS% -Dcom.sun.management.jmxremote -Dcom.sun.management.jmxremote.port="9004" -Dcom.sun.management.jmxremote.authenticate="false" -Dcom.sun.management.jmxremote.ssl="false"
保存完之后,启动startup.bat(或者startup.sh)来运行tomcat(上面设置java启动项的配置,按理来说在eclipse中也能适用,但是笔者在其下没有试验成功)。然后在要查看监控信息的某台电脑B的命令行中运行如下命令
jconsole -pluginpath E:\kuaipan\workspace6\druid-web\WebRoot\WEB-INF\lib\druid-0.2.11.jar
这里的最后一个参数就是你的druid的jar包的路径。
图3.2 jconsole连接界面
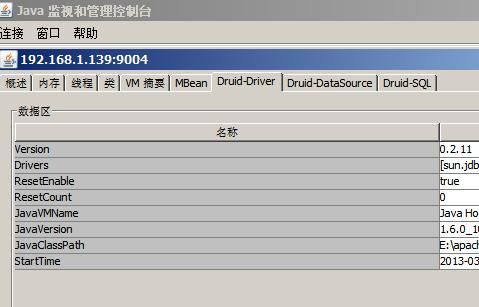
在远程进程的输入框里面输入ip:端口号,然后点击连接(上面的配置中没有指定用户名、密码,所以这里不用填写)。打开的界面如下:
图3.3 jconsole 连接成功界面
可以看到和web监控界面类似的数据了。推荐直接使用web界面配置jmx地址方式来访问远程机器的druid使用情况,因为这种方式查看到的数据信息更全面些。